Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Phy 4.2
Phy 4.2
Uploaded by
farahOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Phy 4.2
Phy 4.2
Uploaded by
farahCopyright:
Available Formats
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Revision Notes savemyexams.co.
uk
YOUR NOTES
5.2 Forces: Equilibrium, Density & Pressure ⬇
CONTENTS
5.2.1 Equilibrium of Forces
5.2.2 Density
5.2.3 Pressure
5.2.4 Derivation of ∆p = ρg∆h
5.2.1 EQUILIBRIUM OF FORCES
The Principle of Moments
The principle of moments states: For a system to be balanced (in equilibrium), the sum of
clockwise moments about a point must be equal to the sum of anticlockwise moments
(about the same point)
Diagram showing the moments acting on a balanced beam
© 2015-2021 Save My Exams Ltd
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Resources Page 1
REVISION NOTES TOPIC QUESTIONS PAST PAPERS
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Revision Notes savemyexams.co.uk
YOUR NOTES
5.2 Forces: Equilibrium, Density & Pressure ⬇
In the above diagram:
Force F2 is supplying a clockwise moment;
Forces F1 and F3 are supplying anticlockwise moments
Hence: F2 × d2 = F1 × d1 + F3 × d3
Worked Example
A uniform beam of weight 40 N is 5 m long and is supported by a pivot situated 2 m from one end.
When a load of weight W is hung from that end, the beam is in equilibrium as shown in the
diagram.
What is the value of W?
A 10 N B 50 N C 25 N D 30 N
© 2015-2021 Save My Exams Ltd
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Resources Page 2
REVISION NOTES TOPIC QUESTIONS PAST PAPERS
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Revision Notes savemyexams.co.uk
YOUR NOTES
5.2 Forces: Equilibrium, Density & Pressure ⬇
© 2015-2021 Save My Exams Ltd
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Resources Page 3
REVISION NOTES TOPIC QUESTIONS PAST PAPERS
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Revision Notes savemyexams.co.uk
YOUR NOTES
5.2 Forces: Equilibrium, Density & Pressure ⬇
Exam Tip
Make sure that all the distances are in the same units and you’re considering the correct forces
as clockwise or anticlockwise, as seen in the diagram below
Equilibrium
A system is in equilibrium when all the forces are balanced. This means:
There is no resultant force
There is no resultant torque
An object in equilibrium will therefore remain at rest, or at a constant velocity, and not rotate
The system is in an equilibrium state when applying the principle of moments. See “The
Principle of Moments” for more notes on this
© 2015-2021 Save My Exams Ltd
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Resources Page 4
REVISION NOTES TOPIC QUESTIONS PAST PAPERS
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Revision Notes savemyexams.co.uk
YOUR NOTES
5.2 Forces: Equilibrium, Density & Pressure ⬇
Worked Example
Four beams of the same length each have three forces acting on them.
Which beam has both zero resultant force and zero resultant torque acting?
© 2015-2021 Save My Exams Ltd
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Resources Page 5
REVISION NOTES TOPIC QUESTIONS PAST PAPERS
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Revision Notes savemyexams.co.uk
YOUR NOTES
5.2 Forces: Equilibrium, Density & Pressure ⬇
© 2015-2021 Save My Exams Ltd
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Resources Page 6
REVISION NOTES TOPIC QUESTIONS PAST PAPERS
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Revision Notes savemyexams.co.uk
YOUR NOTES
5.2 Forces: Equilibrium, Density & Pressure ⬇
Coplanar Forces in Equilibrium
Coplanar forces can be represented by vector triangles
In equilibrium, these are closed vector triangles. The vectors, when joined together, form a
closed path
The most common forces on objects are
Weight
Normal reaction force
Tension (from cords and strings)
Friction
The forces on a body in equilibrium are demonstrated below:
Three forces on an object in equilibrium form a closed vector triangle
© 2015-2021 Save My Exams Ltd
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Resources Page 7
REVISION NOTES TOPIC QUESTIONS PAST PAPERS
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Revision Notes savemyexams.co.uk
YOUR NOTES
5.2 Forces: Equilibrium, Density & Pressure ⬇
Worked Example
A weight hangs in equilibrium from a cable at point X. The tensions in the cables are T1 and T2 as
shown.
Which diagram correctly represents the forces acting at point X?
© 2015-2021 Save My Exams Ltd
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Resources Page 8
REVISION NOTES TOPIC QUESTIONS PAST PAPERS
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Revision Notes savemyexams.co.uk
YOUR NOTES
5.2 Forces: Equilibrium, Density & Pressure ⬇
Exam Tip
The diagrams in exam questions about this topic tend to be drawn to scale, so make sure
you have a ruler handy!
© 2015-2021 Save My Exams Ltd
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Resources Page 9
REVISION NOTES TOPIC QUESTIONS PAST PAPERS
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Revision Notes savemyexams.co.uk
YOUR NOTES
5.2 Forces: Equilibrium, Density & Pressure ⬇
5.2.2 DENSITY
Density
Density is the mass per unit volume of an object
Objects made from low-density materials typically have a lower mass
For example, a balloon is less dense than a small bar of lead despite occupying a
larger volume
The units of density depend on the units used for mass and volume:
If the mass is measured in g and volume in cm3, then the density will be in g / cm3
If the mass is measured in kg and volume in m3, then the density will be in kg / m3
Gases are less dense than a solid
© 2015-2021 Save My Exams Ltd
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Resources Page 10
REVISION NOTES TOPIC QUESTIONS PAST PAPERS
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Revision Notes savemyexams.co.uk
YOUR NOTES
5.2 Forces: Equilibrium, Density & Pressure ⬇
The volume of an object may not always be given directly, but can be calculated with the
appropriate equation depending on the object’s shape
Volumes of common 3D shapes
© 2015-2021 Save My Exams Ltd
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Resources Page 11
REVISION NOTES TOPIC QUESTIONS PAST PAPERS
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Revision Notes savemyexams.co.uk
YOUR NOTES
5.2 Forces: Equilibrium, Density & Pressure ⬇
Worked Example
A paving slab has a mass of 73 kg and dimensions 40 mm × 500 mm × 850 mm.
Calculate the density, in kg m-3 of the material from which the paving slab is made.
© 2015-2021 Save My Exams Ltd
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Resources Page 12
REVISION NOTES TOPIC QUESTIONS PAST PAPERS
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Revision Notes savemyexams.co.uk
YOUR NOTES
5.2 Forces: Equilibrium, Density & Pressure ⬇
Exam Tip
• When converting a larger unit to a smaller one, you multiply (×)
⚬ E.g. 125 m = 125 × 100 = 12 500 cm
• When you convert a smaller unit to a larger one, you divide (÷)
⚬ E.g. 5 g = 5 / 1000 = 0.005 or 5 × 10-3 kg
• When dealing with squared or cubic conversions, cube or square the conversion factor too
⚬ E.g. 1 mm3 = 1 / (1000)3 = 1 × 10-9 m3
⚬ E.g. 1 cm3 = 1 / (100)3 = 1 × 10-6 m3
© 2015-2021 Save My Exams Ltd
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Resources Page 13
REVISION NOTES TOPIC QUESTIONS PAST PAPERS
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Revision Notes savemyexams.co.uk
YOUR NOTES
5.2 Forces: Equilibrium, Density & Pressure ⬇
5.2.3 PRESSURE
Pressure
Pressure tells us how concentrated a force is, it is defined as the force per unit area
Pressure is equal to the force per unit area
This equation tells us
If a force is spread over a large area it will result in a small pressure
If it is spread over a small area it will result in a large pressure
© 2015-2021 Save My Exams Ltd
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Resources Page 14
REVISION NOTES TOPIC QUESTIONS PAST PAPERS
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Revision Notes savemyexams.co.uk
YOUR NOTES
5.2 Forces: Equilibrium, Density & Pressure ⬇
Different pressure is exerted for the same force on different areas
The units of pressure depend on the units of area:
If the area is measured in cm2 (and the force in N), then the pressure will be in N/cm2
If the area is measured in m2 (and the force in N), then the pressure will be in N/m2
Pressure can also be measured in pascals, Pa where 1 Pa is the same as 1 N/m2
Pressure, unlike force, is a scalar. Therefore pressure does not have a specific direction
© 2015-2021 Save My Exams Ltd
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Resources Page 15
REVISION NOTES TOPIC QUESTIONS PAST PAPERS
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Revision Notes savemyexams.co.uk
YOUR NOTES
5.2 Forces: Equilibrium, Density & Pressure ⬇
U-tube manometer
A manometer is an instrument to measure pressure and density of two liquids
In Figure 1: The level of liquid is equal because the atmospheric pressure (Patm) is the same
In Figure 2: If the pressure on one side rises, the liquid will be forced down making the liquid
in the other limb rise. The difference between the two levels gives the pressure difference
between the two ends of the tube
In Figure 3: The U-tube now has two different liquids. The density of the blue one is larger
than that of the orange one. The pressure at each point is due to the atmospheric pressure
plus the weight of the liquid above it
© 2015-2021 Save My Exams Ltd
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Resources Page 16
REVISION NOTES TOPIC QUESTIONS PAST PAPERS
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Revision Notes savemyexams.co.uk
YOUR NOTES
5.2 Forces: Equilibrium, Density & Pressure ⬇
Worked Example
A cylinder is placed on a horizontal surface as shown below
The mass of the cylinder is 4.7 kg and the diameter is 8.4 cm. Calculate the pressure produced by
the cylinder on the surface in Pa.
© 2015-2021 Save My Exams Ltd
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Resources Page 17
REVISION NOTES TOPIC QUESTIONS PAST PAPERS
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Revision Notes savemyexams.co.uk
YOUR NOTES
5.2 Forces: Equilibrium, Density & Pressure ⬇
Exam Tip
The area referred to is the ‘cross-sectional’ area of a 3D object. This is the area of the base
that the force is applied on. For a cylinder, this will be a circle.
© 2015-2021 Save My Exams Ltd
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Resources Page 18
REVISION NOTES TOPIC QUESTIONS PAST PAPERS
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Revision Notes savemyexams.co.uk
YOUR NOTES
5.2 Forces: Equilibrium, Density & Pressure ⬇
5.2.4 DERIVATION OF ∆P = ΡG∆H
Derivation of ∆p = ρg∆h
Hydrostatic pressure is the pressure that is exerted by a fluid at equilibrium at a given
point within the fluid, due to the force of gravity
The derivation for this equation is shown below:
© 2015-2021 Save My Exams Ltd
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Resources Page 19
REVISION NOTES TOPIC QUESTIONS PAST PAPERS
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Revision Notes savemyexams.co.uk
YOUR NOTES
5.2 Forces: Equilibrium, Density & Pressure ⬇
Hydrostatic pressure derivation
Exam Tip
You will be expected to remember all the steps for this derivation for an exam question. If
any equations which look unfamiliar, have a look at the notes for “Density” and “Pressure”.
© 2015-2021 Save My Exams Ltd
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Resources Page 20
REVISION NOTES TOPIC QUESTIONS PAST PAPERS
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Revision Notes savemyexams.co.uk
YOUR NOTES
5.2 Forces: Equilibrium, Density & Pressure ⬇
Using the Equation for Hydrostatic Pressure
Hydrostatic pressure is the pressure that is exerted by a fluid at equilibrium at a given
point within the fluid, due to the force of gravity
This is when an object is immersed in a liquid, the liquid will exert a pressure, squeezing the
object
The size of this pressure depends upon the density (ρ) of the liquid, the depth (h) of the
object and the gravitational field strength (g):
When asked about the total pressure remember to also add the atmospheric pressure
Total pressure = Hydrostatic pressure + Atmospheric pressure
Atmospheric pressure (also known as barometric pressure) is 101 325 Pa
Worked Example
Atmospheric pressure at sea level has a value of 100 kPa. The density of sea water is 1020
kg m-3.
At what depth in the sea would the total pressure be 250 kPa?
A. 20 m B. 9.5 m C. 18 m D. 15 m
© 2015-2021 Save My Exams Ltd
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Resources Page 21
REVISION NOTES TOPIC QUESTIONS PAST PAPERS
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Revision Notes savemyexams.co.uk
YOUR NOTES
5.2 Forces: Equilibrium, Density & Pressure ⬇
Exam Tip
These pressures can vary widely and depend on metric prefixes such as kPa or MPa. When
you’re doing calculations make sure all the pressures are in the same units (otherwise you
may be out by a factor of 1000!). To be on the safe side, you can convert them all to
Pascals.
Exam Question: Easy
© 2015-2021 Save My Exams Ltd
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Resources Page 22
REVISION NOTES TOPIC QUESTIONS PAST PAPERS
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Revision Notes savemyexams.co.uk
YOUR NOTES
5.2 Forces: Equilibrium, Density & Pressure ⬇
Exam Question: Medium
© 2015-2021 Save My Exams Ltd
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Resources Page 23
REVISION NOTES TOPIC QUESTIONS PAST PAPERS
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Revision Notes savemyexams.co.uk
YOUR NOTES
5.2 Forces: Equilibrium, Density & Pressure ⬇
Exam Question: Hard
> CHECK YOUR ANSWERS AT SAVEMYEXAMS.CO.UK
© 2015-2021 Save My Exams Ltd
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Resources Page 24
REVISION NOTES TOPIC QUESTIONS PAST PAPERS
You might also like
- CFD PPT Unit 1..Document34 pagesCFD PPT Unit 1..Tejal IkharNo ratings yet
- Siemens J Press Sidebar Filter Press PDFDocument12 pagesSiemens J Press Sidebar Filter Press PDFTrần Khánh Duy100% (1)
- Phy 4.1Document23 pagesPhy 4.1farahNo ratings yet
- Phy 3.2Document14 pagesPhy 3.2farahNo ratings yet
- Physical Quantities & UnitsDocument20 pagesPhysical Quantities & UnitsfarahNo ratings yet
- Phy 1-2Document30 pagesPhy 1-2farahNo ratings yet
- Measurements & ErrorsDocument25 pagesMeasurements & ErrorsfarahNo ratings yet
- 12-Motion in A CircleDocument17 pages12-Motion in A CircleScarlettNo ratings yet
- Mas 42b Cost Behavior With Regression AnalysisDocument7 pagesMas 42b Cost Behavior With Regression AnalysisMary Joyce SiyNo ratings yet
- A Level Physics CIE: 5. Work, Energy & PowerDocument25 pagesA Level Physics CIE: 5. Work, Energy & PowerKazi Tasfia RodoshiNo ratings yet
- 1.2 SI UnitsDocument7 pages1.2 SI Units1227751212No ratings yet
- ME216 MOM - CHPT 1Document60 pagesME216 MOM - CHPT 1Sergio Contreras PancorboNo ratings yet
- HUp FYp 9 CLK HQ 2 GK PDocument7 pagesHUp FYp 9 CLK HQ 2 GK ParnnevagarwaalNo ratings yet
- Geometry m1 Mid Module AssessmentDocument16 pagesGeometry m1 Mid Module AssessmentAmmar TawfiqNo ratings yet
- AP Physics 2 Unit Guides 2020Document153 pagesAP Physics 2 Unit Guides 2020begenovmadiyarNo ratings yet
- Mech BNL 14.0 L04-PlasticityDocument30 pagesMech BNL 14.0 L04-PlasticitycrisNo ratings yet
- Test Report of TEST - 01 Engineering Mechanics (EM01) - GATE (CE)Document9 pagesTest Report of TEST - 01 Engineering Mechanics (EM01) - GATE (CE)Srikar AvrNo ratings yet
- Cie Physics NotesDocument25 pagesCie Physics Notesasmitaritu05No ratings yet
- xYcbajRDXeMn-P1LDocument21 pagesxYcbajRDXeMn-P1LAYMAN HASANNo ratings yet
- Leone MukundaneDocument5 pagesLeone MukundanesherleenNo ratings yet
- Statics: Engineering MechanicsDocument31 pagesStatics: Engineering MechanicsFrensey JynethNo ratings yet
- Homogeneity of Physical Equations (1.1.3) CIE ADocument1 pageHomogeneity of Physical Equations (1.1.3) CIE Amarumura.onwardNo ratings yet
- 12.2 RespirationDocument32 pages12.2 Respirationmptneuro2024No ratings yet
- Physics HL p2Document415 pagesPhysics HL p22025snehithNo ratings yet
- Revision Summary of Unit 1,2,3,4Document106 pagesRevision Summary of Unit 1,2,3,4Reaktivic gaishnikovicNo ratings yet
- Science WA1 NotesDocument4 pagesScience WA1 NotesKrishnaNo ratings yet
- Mech BSN 2019R3 EN LE05Document44 pagesMech BSN 2019R3 EN LE05cananbudak540No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Physical Quantities and UnitsDocument28 pagesChapter 1 Physical Quantities and Unitsshresthaprayan137No ratings yet
- Chap 28Document41 pagesChap 28miacrandall0No ratings yet
- Lesson 05.0Document7 pagesLesson 05.0Patrick Jamiel TorresNo ratings yet
- BCTcwLhtQiMzcbFkDocument11 pagesBCTcwLhtQiMzcbFkAYMAN HASANNo ratings yet
- B217 CulEd210Document5 pagesB217 CulEd210Angel Marie RomiscalNo ratings yet
- Lectures 5.3-5.4Document20 pagesLectures 5.3-5.4Mithun KanishkaNo ratings yet
- 5.work, Energy &powerDocument25 pages5.work, Energy &powerzzrnwdzpsmhs951003No ratings yet
- Lecture 8-Shearing Forces and Bending Moments in Beams (DELIVERED)Document30 pagesLecture 8-Shearing Forces and Bending Moments in Beams (DELIVERED)Naledi KetlogetsweNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3-Vectors-3 - TaggedDocument60 pagesChapter 3-Vectors-3 - TaggedZainabNo ratings yet
- MOD1 WK3 Lesson1Document41 pagesMOD1 WK3 Lesson1AJ BellaNo ratings yet
- AE 191: Competency Appraisal: VisionDocument7 pagesAE 191: Competency Appraisal: VisionMichael Christian TolentinoNo ratings yet
- KZN ATP Physical Science GRADE 12 2024Document7 pagesKZN ATP Physical Science GRADE 12 2024lebomorena12No ratings yet
- Test Report of TEST - 14 Steel Structures (SS02) - GATE (CE) : BookmarkDocument9 pagesTest Report of TEST - 14 Steel Structures (SS02) - GATE (CE) : BookmarkhimanshiNo ratings yet
- Fatigue FailureDocument17 pagesFatigue Failureaiman.mohammadNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-11-28 at 1.47.22 PMDocument1 pageScreenshot 2023-11-28 at 1.47.22 PMAshish KumarNo ratings yet
- 01 HME 712 Week 1 Assoc Agree Kappa StatisticDocument5 pages01 HME 712 Week 1 Assoc Agree Kappa Statisticjackbane69No ratings yet
- General PhysicsDocument100 pagesGeneral Physicscarrisanicole2No ratings yet
- Properties of MaterialsDocument17 pagesProperties of MaterialssabaNo ratings yet
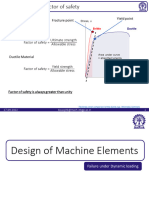
- Mechanical Design Principles Mechanical Design PrinciplesDocument65 pagesMechanical Design Principles Mechanical Design PrinciplesIvan AvramovNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document25 pagesChapter 5Ekaksha SinghNo ratings yet
- 2022 June - Unit 2 Mark SchemeDocument21 pages2022 June - Unit 2 Mark SchemeMohammedNo ratings yet
- IB Diploma Physics HL P1 2017-22-SampleDocument7 pagesIB Diploma Physics HL P1 2017-22-SampleNOTINFINITYNo ratings yet
- 1.physical Quantities and UnitsDocument28 pages1.physical Quantities and UnitssifatclashgamingNo ratings yet
- Stressconcentration 160213175854 PDFDocument10 pagesStressconcentration 160213175854 PDFSyed Haider Abbas AbidiNo ratings yet
- Forces and Newton - S LawsDocument62 pagesForces and Newton - S LawsSayeef MahdiNo ratings yet
- 2 CE 517 - F21 - StressesDocument14 pages2 CE 517 - F21 - StressesMohamed Imbarek EsekbiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4b STATICSDocument17 pagesChapter 4b STATICSIRDINA ZAKIRAH IZUDINNo ratings yet
- Lab 4Document10 pagesLab 4Randy Albaladejo Jr.No ratings yet
- Ap Physics 1 Course at A GlanceDocument4 pagesAp Physics 1 Course at A GlanceAbhinav GargNo ratings yet
- 45905128e8e0b-1 Gs Pre Abhyaas Test 4359 e 2024 LetterDocument22 pages45905128e8e0b-1 Gs Pre Abhyaas Test 4359 e 2024 Lettermp9699532644No ratings yet
- AP Physics C Mech Test-04 SolutionDocument9 pagesAP Physics C Mech Test-04 SolutionOm PrakashNo ratings yet
- BCS RulesDocument40 pagesBCS RulesHKF1971No ratings yet
- Shoeb ResumeDocument4 pagesShoeb ResumeM-Shoeb ShaykNo ratings yet
- BibliographyDocument14 pagesBibliographyhsNo ratings yet
- Session-10 Assignment Name: Dharmi Javiya Enroll No: 92100133058Document3 pagesSession-10 Assignment Name: Dharmi Javiya Enroll No: 92100133058Dharmi JaviyaNo ratings yet
- Copy of Pharmacognosy-and-Plant-ChemistryDocument25 pagesCopy of Pharmacognosy-and-Plant-ChemistryDecemae FuentesNo ratings yet
- Discharge Summary: General FormatDocument6 pagesDischarge Summary: General Formatf archiveNo ratings yet
- PPC DrainDocument6 pagesPPC Drainherysyam1980No ratings yet
- Mass Transfer DR AurobaDocument192 pagesMass Transfer DR Aurobaahmed ubeedNo ratings yet
- Recognized Ho So ListDocument36 pagesRecognized Ho So Listpavan0% (1)
- Hydrochemical Characteristic of Surface Water and Ground Water in The Area Between Dar El-Salam and Akhmim, Eastern Fringes - Sohag Governorate, EgyptDocument20 pagesHydrochemical Characteristic of Surface Water and Ground Water in The Area Between Dar El-Salam and Akhmim, Eastern Fringes - Sohag Governorate, Egyptyoussof2008No ratings yet
- APT NS Grout DatasheetDocument3 pagesAPT NS Grout DatasheetChit San Maung100% (1)
- En - mb997 F407VGT6 E01 SchematicDocument9 pagesEn - mb997 F407VGT6 E01 SchematicBharath Kumar Reddy MNo ratings yet
- E Waste RecyclingDocument49 pagesE Waste RecyclingaskmeeNo ratings yet
- Servo Gear HPDocument2 pagesServo Gear HPsanket puranikNo ratings yet
- Important Seqs of Biochemistry For 1st Year Mbbs StudentsDocument7 pagesImportant Seqs of Biochemistry For 1st Year Mbbs Studentsdr saadia anjum0% (1)
- Baydoun Willett (2000) Islamic Corporate Reports PDFDocument20 pagesBaydoun Willett (2000) Islamic Corporate Reports PDFAqilahAzmiNo ratings yet
- EHS Learnshare Database V1Document53 pagesEHS Learnshare Database V1Rajeev VarmaNo ratings yet
- Bruma Lake - More Than An Environmental Upgrade FinalDocument5 pagesBruma Lake - More Than An Environmental Upgrade FinalElishaNo ratings yet
- Solution A3 NPTEL Control Engg Jan April 2020Document12 pagesSolution A3 NPTEL Control Engg Jan April 2020Akhil Nameirakpam100% (1)
- Book Review-Teach Like A Champion-Hussein Haj AhmadDocument2 pagesBook Review-Teach Like A Champion-Hussein Haj Ahmadapi-286467538No ratings yet
- Summarised Maths Notes (Neilab Osman)Document37 pagesSummarised Maths Notes (Neilab Osman)dubravko_akmacicNo ratings yet
- June 2021 PaperDocument10 pagesJune 2021 PaperAthula Dias NagahawatteNo ratings yet
- Bletchley & District Allotment Association - Autumn News 2010Document3 pagesBletchley & District Allotment Association - Autumn News 2010ArchenfieldNo ratings yet
- Advanced Java Programming (17625) : Event HandlingDocument40 pagesAdvanced Java Programming (17625) : Event HandlingAarti BagojikopNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Heineken BeerDocument13 pagesPresentation On Heineken BeerΣόλα ΚαρίμοβαNo ratings yet
- A Short Introduction To Shortwave Infrared (SWIR) Imaging: Technology White PaperDocument5 pagesA Short Introduction To Shortwave Infrared (SWIR) Imaging: Technology White PapertaikiNo ratings yet
- HSCode Master BPSDocument1,262 pagesHSCode Master BPSsumber jayaNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Age of Empires III Trial Readme File: September 2005Document4 pagesMicrosoft Age of Empires III Trial Readme File: September 2005Yoga RajNo ratings yet
- Big Apple Indoor Schedule 2010Document3 pagesBig Apple Indoor Schedule 2010bigapplehockeyNo ratings yet