Professional Documents
Culture Documents
WORKSHEET - Charging Processes
WORKSHEET - Charging Processes
Uploaded by
Mike Piche0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageOriginal Title
WORKSHEET_Charging Processes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageWORKSHEET - Charging Processes
WORKSHEET - Charging Processes
Uploaded by
Mike PicheCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
WORKSHEET_CHARGING PROCESSES WORKSHEET_CHARGING PROCESSES
MIKE Z. PICHE, LPT MIKE Z. PICHE, LPT
NAME: NAME:
SECTION: SECTION:
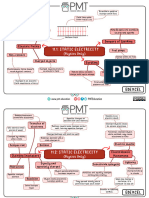
Charging Definition Description Real-life Charging Definition Description Real-life
Process Example Process Example
Rubbing objects When objects rub against each Rubbing a Rubbing objects When objects rub against each Rubbing a
Triboelectric together to create other, electrons can jump from balloon on Triboelectric together to create other, electrons can jump from balloon on
Charging static electricity. one object to the other, creating hair Charging static electricity. one object to the other, creating hair
a charge. a charge.
Charging an object Bringing a charged object close Bringing a Charging an object Bringing a charged object close Bringing a
without direct to another object can cause the charged without direct to another object can cause the charged
Charging by Charging by
contact, by bringing a charges in the second object to balloon near contact, by bringing a charges in the second object to balloon
Induction Induction
charged object rearrange. paper charged object rearrange. near paper
nearby. nearby.
Charging through When a charged object touches Touching a Charging through When a charged object touches Touching a
Charging by direct contact another object, electrons move metal spoon direct contact another object, electrons move metal
Charging by
Conduction between two objects. between them, equalizing the to a charged between two objects. between them, equalizing the spoon to a
Conduction
charge. balloon charge. charged
Removing or adding Connecting a charged object to Lightning balloon
excess charge the ground allows excess charge striking a Removing or adding Connecting a charged object to Lightning
Charging by
from/to an object by to flow away, leaving the object lightning rod excess charge the ground allows excess charge striking a
Grounding Charging by
connecting it to the neutral. from/to an object by to flow away, leaving the object lightning
Grounding
ground. connecting it to the neutral. rod
ground.
I. Study each scenario carefully and determine which type of charging process (Triboelectric Charging,
Charging by Induction, Charging by Conduction, or Charging by Grounding) is depicted in each situation. I. Study each scenario carefully and determine which type of charging process (Triboelectric Charging,
1. Maria rubs a plastic ruler with a piece of wool and then brings it close to small pieces of paper, causing Charging by Induction, Charging by Conduction, or Charging by Grounding) is depicted in each situation.
them to be attracted to the ruler. 1. Maria rubs a plastic ruler with a piece of wool and then brings it close to small pieces of paper, causing
2. Alex touches a metal doorknob after walking across a carpeted floor and feels a small shock. them to be attracted to the ruler.
3. Emily brings a charged balloon near a neutral plastic ruler, causing the ruler to be attracted to the 2. Alex touches a metal doorknob after walking across a carpeted floor and feels a small shock.
balloon. 3. Emily brings a charged balloon near a neutral plastic ruler, causing the ruler to be attracted to the
4. James uses a metal spoon to transfer excess charge from a charged balloon to a neutral metal object. balloon.
5. Lily rubs a glass rod with a silk cloth and then brings it close to a small piece of paper, causing the paper 4. James uses a metal spoon to transfer excess charge from a charged balloon to a neutral metal object.
to be repelled. 5. Lily rubs a glass rod with a silk cloth and then brings it close to a small piece of paper, causing the paper
6. Ethan rubs his feet on the carpet and then touches a metal doorknob, experiencing a small shock. to be repelled.
7. Sophia connects a charged metal rod to a metal pipe in the ground using a wire, causing the excess 6. Ethan rubs his feet on the carpet and then touches a metal doorknob, experiencing a small shock.
charge to flow away. 7. Sophia connects a charged metal rod to a metal pipe in the ground using a wire, causing the excess
8. Nathan rubs a plastic comb with his hair and then brings it close to small pieces of paper, causing them charge to flow away.
to be attracted to the comb. 8. Nathan rubs a plastic comb with his hair and then brings it close to small pieces of paper, causing them
9. Olivia brings a charged plastic ruler near a neutral metal key, causing the key to be attracted to the to be attracted to the comb.
ruler. 9. Olivia brings a charged plastic ruler near a neutral metal key, causing the key to be attracted to the
10. Max touches a neutral metal spoon to a charged metal rod, causing the excess charge to spread ruler.
throughout the spoon. 10. Max touches a neutral metal spoon to a charged metal rod, causing the excess charge to spread
11. Emma rubs a balloon with fur and then brings it close to a neutral plastic ruler, causing the ruler to be throughout the spoon.
repelled. 11. Emma rubs a balloon with fur and then brings it close to a neutral plastic ruler, causing the ruler to be
12. Jacob connects a charged metal sphere to a metal wire, allowing the excess charge to flow into the repe 12. Jacob connects a charged metal sphere to a metal wire, allowing the excess charge to flow into the
ground. groun 13. Isabella rubs a glass rod with a piece of silk and then brings it close to a neutral plastic ruler, causing
13. Isabella rubs a glass rod with a piece of silk and then brings it close to a neutral plastic ruler, causing the ruler to be attracted to the rod.
the ruler to be attracted to the rod. 14. Liam uses a metal spoon to transfer excess charge from a charged balloon to a neutral plastic object.
14. Liam uses a metal spoon to transfer excess charge from a charged balloon to a neutral plastic object. 15. Mia rubs her shoes on the carpet and then touches a metal doorknob, experiencing a small shock.
15. Mia rubs her shoes on the carpet and then touches a metal doorknob, experiencing a small shock.
You might also like
- Science Notebook Ch20section2Document7 pagesScience Notebook Ch20section2coleNo ratings yet
- Pipe Sizing ASHRAEDocument2 pagesPipe Sizing ASHRAESabir Mohamed Abdelhalim100% (2)
- Sci7 Ep7Document4 pagesSci7 Ep7Edsel BelbarNo ratings yet
- Las 7 Q3 Week 7Document2 pagesLas 7 Q3 Week 7Darven CinchezNo ratings yet
- Nayre Q3-Module 1 ActivityDocument2 pagesNayre Q3-Module 1 ActivityJhamie Marie NayreNo ratings yet
- Q3 GenPhys 2 Week 1-2Document14 pagesQ3 GenPhys 2 Week 1-2R Jay GubatangaNo ratings yet
- Interactions BeTYPE OF CHARGING PROCESSDocument20 pagesInteractions BeTYPE OF CHARGING PROCESSRolly Ann RedondaNo ratings yet
- Charging Processes-G7Document20 pagesCharging Processes-G7hmoncatar.bulNo ratings yet
- Gen. Physics 2 Intro To Electric ChargeDocument32 pagesGen. Physics 2 Intro To Electric ChargeYutaNo ratings yet
- Name: - Grade and Section: - Date: - GenderDocument2 pagesName: - Grade and Section: - Date: - Genderfitz zamoraNo ratings yet
- Hesc 112Document15 pagesHesc 112C. Kesav ReddyNo ratings yet
- Types of Charging ProcessesDocument1 pageTypes of Charging ProcessesGiselle QuimpoNo ratings yet
- Mind MapsDocument2 pagesMind MapsSwra GhelaniNo ratings yet
- Quarter 3: Physics Reviewer G12Document8 pagesQuarter 3: Physics Reviewer G12AzefNo ratings yet
- Hesc 112Document15 pagesHesc 112Be HappyNo ratings yet
- Unit Plan B.Ed Mumbai UniversityDocument6 pagesUnit Plan B.Ed Mumbai UniversityPoojaManghirmalaniMishraNo ratings yet
- This PDF Is The Sample PDF Taken From Our Comprehensive Study Material For IIT-JEE Main & AdvancedDocument14 pagesThis PDF Is The Sample PDF Taken From Our Comprehensive Study Material For IIT-JEE Main & AdvancedArchna PareekNo ratings yet
- UNIT 13 Electric Fields IDocument9 pagesUNIT 13 Electric Fields IUlung Gondo Kusumo KhoeNo ratings yet
- LECTURES B5 2nd SEMESTER - Romy GasparDocument48 pagesLECTURES B5 2nd SEMESTER - Romy GasparRomeo GasparNo ratings yet
- UNIDAD8 ElectricityDocument7 pagesUNIDAD8 ElectricityPedro MIRANDA FERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- Aurora Borealis Is Another Name For Northern LightsDocument45 pagesAurora Borealis Is Another Name For Northern LightsNoroña S.R.No ratings yet
- The Nature and Origin of ChargeDocument3 pagesThe Nature and Origin of ChargeFrancesca GenerNo ratings yet
- 1ST Quarter 2ND Sem Week 1-4Document39 pages1ST Quarter 2ND Sem Week 1-4Ma. Alleli ChuaNo ratings yet
- Exp SC 8 - Chapter 15Document18 pagesExp SC 8 - Chapter 15megamind publicationNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Some Natural PhenomenaDocument17 pagesClass 8 Some Natural PhenomenaChirag ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Electricity Lecture Notes Summary (School)Document32 pagesUnit 2 Electricity Lecture Notes Summary (School)itzsanninNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges FieldsDocument52 pagesElectric Charges Fieldsdevesh saiNo ratings yet
- LeaP-Science-G7-Week 8-Q3Document4 pagesLeaP-Science-G7-Week 8-Q3CriselAlamagNo ratings yet
- Electricity 1Document22 pagesElectricity 1Fatima Abacan ReyesNo ratings yet
- Module 7: Be in Charge! Be Electrifying!Document49 pagesModule 7: Be in Charge! Be Electrifying!Camaddu GelaicaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21 - 10th. Edition - (2022-1) ADocument20 pagesChapter 21 - 10th. Edition - (2022-1) Anouf AldosareNo ratings yet
- Static ElectricityDocument15 pagesStatic ElectricityAkaNayep ApNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 - Group 6 PDFDocument4 pagesExperiment 1 - Group 6 PDFRONICA LILIANo ratings yet
- Chapter Note 11185 7-11-2023 104453 Lightning & Charging by RubbingDocument34 pagesChapter Note 11185 7-11-2023 104453 Lightning & Charging by RubbinggowrinihakbNo ratings yet
- Extra-Credit Assignment 2 Electric ChargeDocument3 pagesExtra-Credit Assignment 2 Electric ChargeAriel Humberto Velasquez GodoyNo ratings yet
- Physics FinalDocument3 pagesPhysics FinalMike_Nguyen_2522No ratings yet
- Static ElectricityDocument19 pagesStatic ElectricityYeshadi EkanayakaNo ratings yet
- Definition: Origin of ChargesDocument5 pagesDefinition: Origin of ChargesDavies MasumbaNo ratings yet
- ForcesDocument4 pagesForcesAayan AhmadNo ratings yet
- LAS 1 Week 1 2nd Sem 1 QDocument6 pagesLAS 1 Week 1 2nd Sem 1 QKrizia InjilNo ratings yet
- ES 15 Module 4Document46 pagesES 15 Module 4Verenice FuentesNo ratings yet
- Group 4 Physics1Document50 pagesGroup 4 Physics1cloud kumoishNo ratings yet
- OME Atural HenomenaDocument15 pagesOME Atural HenomenaJohnNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics JEE NotesDocument80 pagesElectrostatics JEE NotesgetsugoshimuraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Electricity UnitDocument72 pagesChapter 11 Electricity Unitt.tremblayNo ratings yet
- LighningDocument12 pagesLighningMaoNo ratings yet
- Process of Charging Technology of The Future.Document8 pagesProcess of Charging Technology of The Future.Kent Ivan ApiladoNo ratings yet
- Creative Technology 10: Pre - TestDocument4 pagesCreative Technology 10: Pre - TestAliyah RuizNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics (Theory) PDFDocument43 pagesElectrostatics (Theory) PDFKisna guptaNo ratings yet
- Charging by InductionDocument10 pagesCharging by Inductionjuvy な.No ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document22 pagesChapter 13hussainmurtajiz75No ratings yet
- Electrostatic InductionDocument1 pageElectrostatic InductionArpit AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic TheoryDocument15 pagesElectrostatic TheoryShambhaviNo ratings yet
- Ansit Angel Bsce1-D Group 4 Individual Written ReportDocument3 pagesAnsit Angel Bsce1-D Group 4 Individual Written Reportcrizel in nameNo ratings yet
- Conduction and InductionDocument29 pagesConduction and Inductionalkinani.faithNo ratings yet
- LAS 9-LET'S VOLT IN Calara Jhior GR 7-4Document3 pagesLAS 9-LET'S VOLT IN Calara Jhior GR 7-4Paul Jhior CalaraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 GP2Document40 pagesLesson 1 GP2lovlegin diongNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Charging ProcessesDocument23 pagesDifferent Types of Charging ProcessesRiah VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- X 15 U5 Eg W0 V SQDV Zie JXYDocument14 pagesX 15 U5 Eg W0 V SQDV Zie JXYrudrakumbhar2005No ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between Static Charging andDocument5 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between Static Charging andkemcanaboNo ratings yet
- Research Report: Electricity and Gravity, Tornadoes and Hurricanes, Other PhenomenaFrom EverandResearch Report: Electricity and Gravity, Tornadoes and Hurricanes, Other PhenomenaNo ratings yet
- 5-PS1-1 Assessment - Onion-Proof GooglesDocument4 pages5-PS1-1 Assessment - Onion-Proof GooglesMike PicheNo ratings yet
- Cell City AnalogyDocument1 pageCell City AnalogyMike PicheNo ratings yet
- FinalsDocument6 pagesFinalsMike PicheNo ratings yet
- QUIZ - Earth and LIfe - Relative Dating and AbsoluteDocument1 pageQUIZ - Earth and LIfe - Relative Dating and AbsoluteMike PicheNo ratings yet
- Mirror RayDocument1 pageMirror RayMike PicheNo ratings yet
- Incident Report - AlisosoDocument3 pagesIncident Report - AlisosoMike PicheNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology - ACT1Document4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology - ACT1Mike PicheNo ratings yet
- Move It Like A NewtonDocument6 pagesMove It Like A NewtonMike PicheNo ratings yet
- Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0060779 A1Document5 pagesPatent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0060779 A1ferhat aydoganNo ratings yet
- Beam CalculationsDocument17 pagesBeam CalculationsFellaa Supazaein100% (1)
- Failure Analysis of A Damaged Diesel Motor Crankshaft (2019)Document6 pagesFailure Analysis of A Damaged Diesel Motor Crankshaft (2019)Dzaky ArizsaNo ratings yet
- Ce140 PS 1 PDFDocument1 pageCe140 PS 1 PDFsoontobengineerNo ratings yet
- Investigation of Bearing Capacity and Settlement of Strip Footing On Clay Reinforced With Stone ColumnsDocument11 pagesInvestigation of Bearing Capacity and Settlement of Strip Footing On Clay Reinforced With Stone ColumnsHimShikhar NischalNo ratings yet
- SEM Workshop Presentation 3Document28 pagesSEM Workshop Presentation 3felixkern1991No ratings yet
- Photonic Crystal For Gas Sensing - XuDocument12 pagesPhotonic Crystal For Gas Sensing - XuArfatNo ratings yet
- Non-Ferrous Metals and AlloysDocument58 pagesNon-Ferrous Metals and AlloysPradeep Kumar BagadiNo ratings yet
- Some Characteristics of Epoxidized Natural Rubber and The Wood Coated by ItDocument8 pagesSome Characteristics of Epoxidized Natural Rubber and The Wood Coated by ItHa CAO HONGNo ratings yet
- Unsteady Aerodynamics Flutter AnalysisDocument17 pagesUnsteady Aerodynamics Flutter AnalysisAravindNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Design and Development of A Metal Matrix Composite For Aeronautical ApplicationsDocument13 pagesCase Study On Design and Development of A Metal Matrix Composite For Aeronautical ApplicationsAruna MNo ratings yet
- Reinforced and Prestressed ConcreteDocument11 pagesReinforced and Prestressed ConcreteFiel Ericson SolaresNo ratings yet
- Spur Gear Problems PDFDocument79 pagesSpur Gear Problems PDFSharmila Shetty100% (1)
- Physics Porject AnujDocument23 pagesPhysics Porject Anujvinayak mittalNo ratings yet
- Suzuki Garphyttan SWOSC VDocument9 pagesSuzuki Garphyttan SWOSC VPrasadNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials Basics and Equations - Mechanics of Materials - Engineers EdgeDocument6 pagesStrength of Materials Basics and Equations - Mechanics of Materials - Engineers EdgeansarNo ratings yet
- Foundation-Engineering-week-6 PDFDocument6 pagesFoundation-Engineering-week-6 PDFBosz' AceNo ratings yet
- Degradation of Natural Fiber Reinforced Polymer Matrix CompositesDocument55 pagesDegradation of Natural Fiber Reinforced Polymer Matrix CompositesChakma SHIMULNo ratings yet
- Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering: Jianping Zuo, Huihai Liu, Hongtao LiDocument6 pagesJournal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering: Jianping Zuo, Huihai Liu, Hongtao LiCarlos AyamamaniNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 NotesDocument18 pagesUnit 2 NotesSAJITH NFNo ratings yet
- Challenges and Opportunities in Graphene Coatings - DR Lisa ScullionDocument9 pagesChallenges and Opportunities in Graphene Coatings - DR Lisa ScullionLance HernandezNo ratings yet
- Mixer DesignDocument15 pagesMixer DesignMuhammad UsamaNo ratings yet
- Fiber - Evidence - Worksheet SolvedDocument3 pagesFiber - Evidence - Worksheet SolvedYasmeen AlnajjarNo ratings yet
- Results in PhysicsDocument11 pagesResults in PhysicsTesfaneh DebeleNo ratings yet
- Operation Manual: M-RPR2 - Rev.02 - EDocument20 pagesOperation Manual: M-RPR2 - Rev.02 - EJorge Mauricio Sepulveda CabreraNo ratings yet
- Effective Net AreaDocument3 pagesEffective Net AreaAscyiff Traya GravadorNo ratings yet
- High Pressure Vessel Thickness Calculations PDFDocument11 pagesHigh Pressure Vessel Thickness Calculations PDFShriyash Deshpande100% (2)
- Hard Chrome PlatingDocument1 pageHard Chrome PlatingKishora BhatNo ratings yet