Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1.1 Materials in Our World
1.1 Materials in Our World
Uploaded by
Ralph Rezin Moore0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesOriginal Title
1.1 Materials in our world (3)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pages1.1 Materials in Our World
1.1 Materials in Our World
Uploaded by
Ralph Rezin MooreCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Learning Describe the characteristic of the classification of substances and mixtures
goals giving examples
Distinguish between pure substances (elements and compounds),
homogeneous mixtures and heterogeneous mixtures
Distinguish between physical and chemical properties and give examples
Recognise properties of mixtures are dependent on the identity and relative
amounts of the substances that make up the mixture
Material in our world
Key Notes to Key Questions
concepts
How does structure of material affect its properties, therefore its uses?
Material Substances used to make objects – wood, nylon, paper used to make houses,
books, clothes;
o carbon dioxide, hydrochloric acid is NOT material
may be pure substance or mixtures
Pure Fixed, well defined physical and chemical properties
Substances Elements
o made of only one type of atom or one type of molecule
o Composed of one type of atom. Cannot be further decomposed
o Au/C/Hg/O2
Compounds
Chemical combination has 2 or more different atoms in fixed proportions. Can
be decomposed by chemical reaction
Ionic: metal x non-metal, eg NaCl
Covalent (MOLECULE): non-metals only. Can also be covalent network eg
diamond
o SiO2
Not able to be separated by physical means
Needs a formula
Mixtures physical combination of 2 or more substances, each of which retains its own
properties
Homogenous: having uniform appearance throughout
o Eg salt dissolved in water -- looks just like water! But is a mixture
o Solution (solute and solvent)
Heterogeneous: having non-uniform appearance. Components can be
distinguished, possibly more than one phase (solid/liquid/gas)
o Colloid (particles do not settle though time. Very thick and sticky)
o Good way to distinguish -- if you took gravel from two different countries
would they still look the same? No? is hetero
Uses of Determined by materials’ physical and chemical properties.
material Measurable properties:
Physical Properties Chemical Properties
A quality that are seen or measured A characteristic observed when
without changing the composition of substance participates in a chemical
the material reaction
Hardness Reactivity with other chemicals
Colour flammability
Density
Conductivity
Melting/boiling points
Ductility
Malleability
Viscosity
Mixing Properties of mixture is dependent on how much of each component in mixture
substances 3 types of material mixture:
(mixture) Alloys: 2 or more metals or metal + non-metals
produces Polymers: many repeating smaller units bonded together eg plastics, nylon
new Ceramics: inorganic (does not contain C) non-metal solid eg kaolinite (porcelain –
material natural)
with
different Composites: 2 or more distinct material with significant different properties eg
properties concrete matrix- concrete with steel bars
Summary
You might also like
- AML Gold - Precious Metal Sector Case StudiesDocument5 pagesAML Gold - Precious Metal Sector Case Studiesjabir pkNo ratings yet
- Methods OT Lee Textbook NOT COMPRESSED (HIGHER QUALITY)Document265 pagesMethods OT Lee Textbook NOT COMPRESSED (HIGHER QUALITY)Ralph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- 1.1 The Components of MatterDocument33 pages1.1 The Components of MatterwisyahazmanNo ratings yet
- Contract of Loan: WitnessethDocument2 pagesContract of Loan: WitnessethJameson UyNo ratings yet
- (CHEM) UNIT 1. Lesson 2. Properties & Characteristics of MatterDocument7 pages(CHEM) UNIT 1. Lesson 2. Properties & Characteristics of MatterTrishia Mae Gregorio BelenNo ratings yet
- 04 Unit 2. Matter and EnergyDocument29 pages04 Unit 2. Matter and EnergyKevin Mark IlaganNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 - Matter-and-EnergyDocument26 pagesChapter-2 - Matter-and-EnergyJam BermejoNo ratings yet
- Matter and Its PropertiesDocument45 pagesMatter and Its PropertiesLu NaNo ratings yet
- (Chem30) Trans Unit 1Document4 pages(Chem30) Trans Unit 1katey perryNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1 - Week 1: Mr. Daryl Vince D. Romerosa - SST1Document41 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 - Week 1: Mr. Daryl Vince D. Romerosa - SST1Abcd Reyes100% (1)
- Week - q1 State of MatterDocument21 pagesWeek - q1 State of Matterjustine alinaNo ratings yet
- 01 Ib Chemistry (SL+HL) - S1.1 Introduction To The Particulate Nature of MatterDocument58 pages01 Ib Chemistry (SL+HL) - S1.1 Introduction To The Particulate Nature of MatterricardochavezrNo ratings yet
- 1 Matter and Its Properties ...Document65 pages1 Matter and Its Properties ...Akira SatoūNo ratings yet
- CLASSIFICATION - OF - MATTER-week 2-pptshwDocument31 pagesCLASSIFICATION - OF - MATTER-week 2-pptshwAlyssa Crizel CalotesNo ratings yet
- Matter and It's Properties PDFDocument55 pagesMatter and It's Properties PDFLemuel Glenn BautistaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Matter and Its PropertiesDocument13 pagesLesson 1: Matter and Its Propertiesricky100% (1)
- Chemistry NotesDocument60 pagesChemistry Noteshcv7cptvs6No ratings yet
- Ach 101-Chemistry For AgricultureDocument262 pagesAch 101-Chemistry For AgricultureTega AgboneNo ratings yet
- L1 Introduction of Gen Chem 1Document5 pagesL1 Introduction of Gen Chem 1John Mark Clouie PlacaNo ratings yet
- Content in Science ChemistryDocument6 pagesContent in Science ChemistryChloe EisenheartNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem Chapt.1Document45 pagesGen Chem Chapt.1Dave Cercado BugadorNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry: Bachelor of Science in Pharmacy Alyn Tapleras, MSPH - RPHDocument26 pagesInorganic Chemistry: Bachelor of Science in Pharmacy Alyn Tapleras, MSPH - RPHNur-aine HajijulNo ratings yet
- HTTPSBMC - unideb.hupublicdocuments2022!09!132BMCI Lecture Week2 Compounds Mixtures PDFDocument82 pagesHTTPSBMC - unideb.hupublicdocuments2022!09!132BMCI Lecture Week2 Compounds Mixtures PDFayoubNo ratings yet
- Intro To Inorg ChemDocument40 pagesIntro To Inorg Chemelizabethabraham310No ratings yet
- Chemistry - Week 1 - 09 09 2022Document2 pagesChemistry - Week 1 - 09 09 2022api-645968894No ratings yet
- Module 1 Lesson 1Document60 pagesModule 1 Lesson 107 JAVIER LLYOD GENELSON B.No ratings yet
- Ch.2 Matter and Change Power PointDocument36 pagesCh.2 Matter and Change Power PointConnor GallagherNo ratings yet
- Classification of MatterDocument41 pagesClassification of MatterRicardo Jr. Uy100% (1)
- MatterDocument38 pagesMattergabbie dumpNo ratings yet
- Qca 1bDocument48 pagesQca 1bAlfredo Salamanca :No ratings yet
- My Chemistry NotesDocument6 pagesMy Chemistry Notess2023100462No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Classification of MatterDocument7 pagesChapter 2 Classification of MatterPatrice Francisco100% (1)
- Matter and Its Properties Properties of MatterDocument4 pagesMatter and Its Properties Properties of MattermiahNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1Document56 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1Liezel Brillantes100% (1)
- MatterDocument34 pagesMatterJimarie CarilNo ratings yet
- MATTERDocument3 pagesMATTERkatherine regioNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Basic Concepts in ScienceDocument51 pagesModule 3 Basic Concepts in Sciencehs4fptm82gNo ratings yet
- Gen Chemistry 1-Task 1Document4 pagesGen Chemistry 1-Task 1khlneNo ratings yet
- CHM012 - Module 1Document9 pagesCHM012 - Module 1haibaalisa00No ratings yet
- CHEM HANDOUT W1 and W2Document4 pagesCHEM HANDOUT W1 and W2Alexander DolinNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer A. Phase Change in MatterDocument6 pagesScience Reviewer A. Phase Change in MatterNicole VictorinoNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument1 pageCHEMISTRYwella wellaNo ratings yet
- Pure Substance and Mixtures Study GuideDocument2 pagesPure Substance and Mixtures Study GuideAlexiandria MaggayNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer MATTERDocument3 pagesScience Reviewer MATTERRACHELL SATSATINNo ratings yet
- MatterDocument29 pagesMatterJeNo ratings yet
- GENCHEM 1 Revised 2020Document43 pagesGENCHEM 1 Revised 2020Mai SasaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Matter Reading MaterialDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Matter Reading MaterialJohann Carlo C. AldecoaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry First SemDocument8 pagesChemistry First SemceeNo ratings yet
- Ros Unit 2 Matter and EnergyDocument18 pagesRos Unit 2 Matter and EnergyNina GanapaoNo ratings yet
- Hapter Atter and Hange: Chemistry 1-2 Mr. ChumbleyDocument33 pagesHapter Atter and Hange: Chemistry 1-2 Mr. Chumbleyshahad mohammadNo ratings yet
- CHE 1-2 Chapter 1 NotesDocument33 pagesCHE 1-2 Chapter 1 NotesCherifa AbdallahNo ratings yet
- Structure 1 Models of Particulate Nature of Matter NotesDocument18 pagesStructure 1 Models of Particulate Nature of Matter Notesphooi.sheng-ernNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Summative ReviewerDocument7 pagesChemistry Summative ReviewerYestine DyNo ratings yet
- Spec I Task 4 Classification of MatterDocument11 pagesSpec I Task 4 Classification of MatterJERIEL MARTIREZNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Gen Chem 1 1Document3 pagesWeek 1 Gen Chem 1 1Cedrick GonzalesNo ratings yet
- LG 1.2 Properties and Classification of MatterDocument10 pagesLG 1.2 Properties and Classification of Matternejomi_lash2003No ratings yet
- I. Matter Matter - Anything That Has Mass and Takes Up Mass - Amount of Matter The Object Contains A. Physical States of Matter - Conditions ofDocument15 pagesI. Matter Matter - Anything That Has Mass and Takes Up Mass - Amount of Matter The Object Contains A. Physical States of Matter - Conditions ofBhoxs Joey CelesparaNo ratings yet
- Matter and Its PropertiesDocument48 pagesMatter and Its PropertiesEji AlcorezaNo ratings yet
- Revision Final Bio ChemDocument21 pagesRevision Final Bio ChemWormaggedonNo ratings yet
- Basic ChemistryDocument3 pagesBasic ChemistryAngelou HernandezNo ratings yet
- Self-Instructed Module in Science 6Document21 pagesSelf-Instructed Module in Science 6NikkiBoy Reyes BernabeNo ratings yet
- Inorganic and Organic Chemistry Prelims ReviewerDocument33 pagesInorganic and Organic Chemistry Prelims ReviewerMary Ann C RecañaNo ratings yet
- What You Need to Know About Beautiful Nails: A Better Understanding of Nail ChemistryFrom EverandWhat You Need to Know About Beautiful Nails: A Better Understanding of Nail ChemistryNo ratings yet
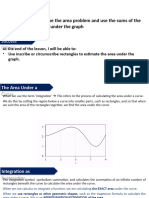
- 26 Ex 6A Area Under A GraphDocument20 pages26 Ex 6A Area Under A GraphRalph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- 04 RedoxDocument31 pages04 RedoxRalph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- 28 - Ex 6C Other AntiderivativesDocument18 pages28 - Ex 6C Other AntiderivativesRalph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- 25 Ex 5I Families of FunctionDocument10 pages25 Ex 5I Families of FunctionRalph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Sample ProportionsDocument23 pagesChapter 6 Sample ProportionsRalph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- 2 Ex 2B - The Exponential FunctionDocument11 pages2 Ex 2B - The Exponential FunctionRalph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- 37 - Ex 8C Discrete Random VariablesDocument16 pages37 - Ex 8C Discrete Random VariablesRalph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Calculus of Trig FNCDocument34 pagesChapter 7 Calculus of Trig FNCRalph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- 65 - Ex 12D Confidence IntervalsDocument23 pages65 - Ex 12D Confidence IntervalsRalph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- 27 - Ex 6B Review of AntiderivativeDocument23 pages27 - Ex 6B Review of AntiderivativeRalph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- Biology Unit 2 Notes LucyDocument39 pagesBiology Unit 2 Notes LucyRalph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- 2019 Human Biology Unit 1Document41 pages2019 Human Biology Unit 1Ralph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- 62 - Ex 12A Populations and SamplesDocument30 pages62 - Ex 12A Populations and SamplesRalph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- Pathogens and Their DiseasesDocument29 pagesPathogens and Their DiseasesRalph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- 18 Ex 5B Rates of ChangeDocument16 pages18 Ex 5B Rates of ChangeRalph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- Toaz - Info Davies The Trompowsky 2nd Edition PRDocument145 pagesToaz - Info Davies The Trompowsky 2nd Edition PRRalph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- Biology Y11 ATAR Syllabus MSCDocument27 pagesBiology Y11 ATAR Syllabus MSCRalph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- Methods OT Lee Revision Series SOLUTIONSDocument114 pagesMethods OT Lee Revision Series SOLUTIONSRalph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Do Well in Human BiologyDocument10 pagesA Guide To Do Well in Human BiologyRalph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- Biology WA ATAR Units 3 & 4 Student Book With 1 X 26 Month NelsonNetBook Access CodeDocument547 pagesBiology WA ATAR Units 3 & 4 Student Book With 1 X 26 Month NelsonNetBook Access CodeRalph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document17 pagesChapter 7Ralph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- 2.physical - Properties of MatterDocument17 pages2.physical - Properties of MatterRalph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- 2017 Exam SolnsDocument30 pages2017 Exam SolnsRalph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- 23 Ex 5G Absolute Maximum and MinimumDocument8 pages23 Ex 5G Absolute Maximum and MinimumRalph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document26 pagesChapter 12Ralph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document26 pagesChapter 10Ralph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document17 pagesChapter 1Ralph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- 8 Ex 4C Differentiating X N When N Is NegativeDocument12 pages8 Ex 4C Differentiating X N When N Is NegativeRalph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- 6 Ex 4A - The Derivative ReviewDocument7 pages6 Ex 4A - The Derivative ReviewRalph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- Provinha 2Document6 pagesProvinha 2Anonymous M0OUUjsF2No ratings yet
- Chinese Trade in 11 Century: What Is Filipino Food?Document6 pagesChinese Trade in 11 Century: What Is Filipino Food?Christine Daine BaccayNo ratings yet
- 26 Rules To Becoming A Successful SpeakerDocument46 pages26 Rules To Becoming A Successful SpeakerSpeakerMatch100% (23)
- Minutes of The Session: Presiding OfficerDocument3 pagesMinutes of The Session: Presiding OfficerCecille SaymoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 AccountingDocument12 pagesChapter 2 Accountingmoon loverNo ratings yet
- Sample Bar Exam QuestionsDocument3 pagesSample Bar Exam QuestionsslydogchuckNo ratings yet
- Social WorkDocument4 pagesSocial WorkoaiatavavaNo ratings yet
- All Software Categories: Operating Systems 3D Cad Graphic Design Multimedia Development Antivirus Education TutorialsDocument10 pagesAll Software Categories: Operating Systems 3D Cad Graphic Design Multimedia Development Antivirus Education TutorialsElla CelineNo ratings yet
- Business PlanDocument25 pagesBusiness PlanJay PatelNo ratings yet
- 114 Layout Secrets For Your Framing Square PDFDocument2 pages114 Layout Secrets For Your Framing Square PDFHomerSimsonnakis100% (1)
- CSS Physics Past Papers 2014-2023Document27 pagesCSS Physics Past Papers 2014-2023Ubaid khokhar100% (1)
- 1-To-8 4K HDMI Distribution Amplifier: HD-DA8-4K-EDocument3 pages1-To-8 4K HDMI Distribution Amplifier: HD-DA8-4K-EthomvalensiNo ratings yet
- Important Plasma Properties: 3.1 Debye ShieldingDocument9 pagesImportant Plasma Properties: 3.1 Debye Shieldingحنين حسن شعبان100% (1)
- Media Penetration and Cultural Identity Among Young Adults in MalaysiaDocument9 pagesMedia Penetration and Cultural Identity Among Young Adults in MalaysiaYavuz SelimNo ratings yet
- Comentary On Nostra AetateDocument11 pagesComentary On Nostra AetateJude nnawuiheNo ratings yet
- Graphic Era Hill University, Dehradun: Presentation & Format of The ProjectDocument5 pagesGraphic Era Hill University, Dehradun: Presentation & Format of The ProjectAjay SinghNo ratings yet
- 57 - Aberca v. Fabian-Ver - DigestDocument1 page57 - Aberca v. Fabian-Ver - DigestloschudentNo ratings yet
- Diaz Sc21 Assessment Scenarios 1Document2 pagesDiaz Sc21 Assessment Scenarios 1John Rafael Obera DiazNo ratings yet
- Poranek (Peer Gynt)Document21 pagesPoranek (Peer Gynt)Katarzyna ChronowskaNo ratings yet
- Let Go, Let Go (D) Embracing The New Normal Among The Youth: ProgramDocument2 pagesLet Go, Let Go (D) Embracing The New Normal Among The Youth: Programmary graceNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Deed of Absolute SaleDocument3 pagesUnderstanding The Deed of Absolute SaleVirgilio VolosoNo ratings yet
- Kusama Artist Presentation 1Document9 pagesKusama Artist Presentation 1api-592346261No ratings yet
- Barud Ahmed Mohamed @Document10 pagesBarud Ahmed Mohamed @Abdirazaq AhmedNo ratings yet
- 3728 8979 1 SM PDFDocument26 pages3728 8979 1 SM PDFJs PonselNo ratings yet
- ABH-072018-BLAB201 Re: R vs. Boisjoli 2018 ABQB 410 (CanLII)Document2 pagesABH-072018-BLAB201 Re: R vs. Boisjoli 2018 ABQB 410 (CanLII)Allen-nelson of the Boisjoli familyNo ratings yet
- Action Report - TamilNadu - Shallots, PerambalurDocument6 pagesAction Report - TamilNadu - Shallots, PerambalurKajal YadavNo ratings yet
- Classification of FolkdanceDocument2 pagesClassification of FolkdanceMica CasimeroNo ratings yet
- Basic ECG Interpretation Practice Test: DIRECTIONS: The Following Test Consists of 20 QuestionsDocument10 pagesBasic ECG Interpretation Practice Test: DIRECTIONS: The Following Test Consists of 20 Questionsmihaela_bondocNo ratings yet