Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BIC 101 - Q.B. 25 - Agri Junction
BIC 101 - Q.B. 25 - Agri Junction
Uploaded by
sitharaanairCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Multiple Choice Questions in Biochemistry: Digital Edition © RC GuptaDocument16 pagesMultiple Choice Questions in Biochemistry: Digital Edition © RC Guptatekalignpawulose09No ratings yet
- (Chemistry Research and Applications) Fitzgerald, Adrienne - Emulsifiers - Properties, Functions, and Applications-Nova Science Publishers (2015) PDFDocument116 pages(Chemistry Research and Applications) Fitzgerald, Adrienne - Emulsifiers - Properties, Functions, and Applications-Nova Science Publishers (2015) PDFStefania DavidNo ratings yet
- Igcse Biology - Transport in AnimalsDocument67 pagesIgcse Biology - Transport in AnimalsYoshitaNo ratings yet
- Quiz On Disaccharide and PolysaccharideDocument4 pagesQuiz On Disaccharide and PolysaccharideJEAN I MAGLAQUENo ratings yet
- Unit I CarbohydratesDocument4 pagesUnit I CarbohydratesOVIYA M JNo ratings yet
- BIC Model Mid Sem 2008Document3 pagesBIC Model Mid Sem 2008charusrirajkumar27No ratings yet
- FDocument146 pagesFOla GomaaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry QuizDocument6 pagesBiochemistry QuizPatrick Ngo'nga Chifwema100% (1)
- Quiz CarbDocument7 pagesQuiz CarbKeith AquinoNo ratings yet
- Org Chem II Guiding QuestionsDocument10 pagesOrg Chem II Guiding QuestionsMesfen MeleseNo ratings yet
- MCQsDocument34 pagesMCQsmanin18040% (1)
- ASM2018 Mod 2 & 3 Booklet Part 1Document136 pagesASM2018 Mod 2 & 3 Booklet Part 1Ibrahim JamaluddinNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates MCQsDocument9 pagesCarbohydrates MCQsAyesha BatoolNo ratings yet
- MCQsDocument15 pagesMCQsmanin1804No ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 14 BiomoleculesDocument13 pagesChemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 14 Biomoleculesrathi rupaNo ratings yet
- Dược liệuDocument48 pagesDược liệutrinhthungoct66No ratings yet
- Biochem Questions 1Document4 pagesBiochem Questions 1Swapna ChavanNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Chemistry MCQDocument7 pagesCarbohydrate Chemistry MCQSohaila GodaNo ratings yet
- M3 - Assessment - FinalDocument3 pagesM3 - Assessment - FinalrickyNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument7 pagesCarbohydratesjamila abdirahmanNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Stage Exam Main PaperDocument21 pagesBiochemistry Stage Exam Main PaperDkt Pius KpchirchirNo ratings yet
- Name: Bibek Biswakarma Date: 6Document6 pagesName: Bibek Biswakarma Date: 6Bibek GajmerNo ratings yet
- Chemicals Found in Plants and They Promote Health (Act As Antioxidants)Document3 pagesChemicals Found in Plants and They Promote Health (Act As Antioxidants)AbduladheemNo ratings yet
- TBQDocument7 pagesTBQWilker GoulartNo ratings yet
- Final Biochemistry MCQDocument29 pagesFinal Biochemistry MCQsaraNo ratings yet
- bch-mcqs-43 DPHDocument6 pagesbch-mcqs-43 DPHpharmamylife2No ratings yet
- DownloadDocument115 pagesDownloadvisha rathodNo ratings yet
- FeasgsDocument14 pagesFeasgsjan2072650No ratings yet
- Carbs HW Worksheet 2Document2 pagesCarbs HW Worksheet 2Benay ÇakaloğluNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry 6Th Edition Garrett Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument33 pagesBiochemistry 6Th Edition Garrett Test Bank Full Chapter PDFsean.broom305100% (21)
- BCH 202 First LectureDocument9 pagesBCH 202 First Lecturemetasynthronos748No ratings yet
- AnswersDocument3 pagesAnswersmodyz7raNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates ExercisesDocument5 pagesCarbohydrates Exercisesreemmasri877No ratings yet
- Iloilo Doctors College Quiz (Carbohydrates)Document5 pagesIloilo Doctors College Quiz (Carbohydrates)Kimberly SalarzaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 7 Carbohydrates and The Glyconjugates of Cell SurfaceDocument14 pagesCHAPTER 7 Carbohydrates and The Glyconjugates of Cell Surface楊畯凱No ratings yet
- Lipid Revision WorksheetDocument7 pagesLipid Revision Worksheetnoorayg.jNo ratings yet
- Short EssayDocument13 pagesShort EssayYazhiniNo ratings yet
- BSN Biochemistry MDocument11 pagesBSN Biochemistry MKhubaib KhanNo ratings yet
- Organic Compounds WorksheetDocument3 pagesOrganic Compounds Worksheetz4g4v7gkzjNo ratings yet
- MCQDocument3 pagesMCQea4184386No ratings yet
- 405 Method Not AllowedDocument5 pages405 Method Not AllowedNaji Mohamed AlfatihNo ratings yet
- Hidratos de Carbono TallerDocument10 pagesHidratos de Carbono TallerLeidyNo ratings yet
- 2Document1 page2Vishal SinghNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 14 - Biomolecules Important Questions 2022-23Document22 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 14 - Biomolecules Important Questions 2022-23Archanaa PadmavathiNo ratings yet
- Carbhdrts 1Document10 pagesCarbhdrts 1IshnNo ratings yet
- CarbohydrateDocument4 pagesCarbohydrateLinh Bui Thi ThaiNo ratings yet
- AnswerDocument7 pagesAnswerloginhani40No ratings yet
- Biochemistry 1st Semester BSN Mcqs For Practice AD, Educational Platform-1Document6 pagesBiochemistry 1st Semester BSN Mcqs For Practice AD, Educational Platform-1Prince Masroor Ali Abro100% (2)
- BIOCHEMISTRYDocument4 pagesBIOCHEMISTRYkristilyn nudqueNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry 20 MCQs-1Document6 pagesBiochemistry 20 MCQs-1Muhammadsiddique khanNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules ImpDocument22 pagesBiomolecules ImpmrdaddydaddaNo ratings yet
- BBC1 K14 K15 KarbohidratDocument31 pagesBBC1 K14 K15 Karbohidratbrigita charvioNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates and LipidsDocument18 pagesCarbohydrates and LipidsJasmin RIshel Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules 231224 101920Document10 pagesBiomolecules 231224 101920Mariam HussainiNo ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULES imp quesDocument2 pagesBIOMOLECULES imp quesbhaktikhanijo16No ratings yet
- ChoDocument10 pagesChoLohith HanumNo ratings yet
- Biology SL 2025 Uniform & Function - Carbohydrates and LipidsDocument35 pagesBiology SL 2025 Uniform & Function - Carbohydrates and LipidsAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- The Best Best Best MCQS For Carbohydrates ChapterDocument22 pagesThe Best Best Best MCQS For Carbohydrates Chapterhappy9874648No ratings yet
- Biology Class: 11 Unit: 1Document8 pagesBiology Class: 11 Unit: 1samiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: Carbohydrates: 6.1. General Information About CarbohydratesDocument12 pagesChapter 6: Carbohydrates: 6.1. General Information About CarbohydratesMD. SAJID GHUFRANNo ratings yet
- Bionanocomposites: Integrating Biological Processes for Bioinspired NanotechnologiesFrom EverandBionanocomposites: Integrating Biological Processes for Bioinspired NanotechnologiesCarole AiméNo ratings yet
- Year 9 ENZYMES WSDocument3 pagesYear 9 ENZYMES WSShazeeq Official ChannelNo ratings yet
- Honey Composition - National Honey BoardDocument8 pagesHoney Composition - National Honey BoardBala GangadharNo ratings yet
- KVPY SA StreamDocument100 pagesKVPY SA StreamResonance Dlpd72% (46)
- Carbohydrates - FactRecallDocument5 pagesCarbohydrates - FactRecallRawan Al-tahanNo ratings yet
- 2012 DSE Bio 1BDocument12 pages2012 DSE Bio 1BLeung Man ChunNo ratings yet
- Primary 6Document17 pagesPrimary 6Architecte UrbanisteNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 CarbohydratesDocument5 pagesTutorial 1 CarbohydratesEngNo ratings yet
- NCM 105 LectureDocument17 pagesNCM 105 LectureAaron De DiosNo ratings yet
- Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirement For: A Chemistry Investigatory Project OnDocument18 pagesSubmitted in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirement For: A Chemistry Investigatory Project Onvasu thakurNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document16 pagesChapter 1Mursaleen KhanNo ratings yet
- Why Do Human Cells Rely Far More On Glucose and Fat For The Energy Than On ProteinDocument4 pagesWhy Do Human Cells Rely Far More On Glucose and Fat For The Energy Than On ProteinHamda HassanNo ratings yet
- Fructose - TDSDocument2 pagesFructose - TDSDoly DoolNo ratings yet
- Belay TefferaDocument89 pagesBelay TefferafanusNo ratings yet
- 8 L 5 1 RRR Practice QuestionsDocument8 pages8 L 5 1 RRR Practice QuestionsEliana FeingoldNo ratings yet
- BLS The Hidden Barrier To Effective Eating ExercisingDocument16 pagesBLS The Hidden Barrier To Effective Eating ExercisingParul DhallaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition 1Document15 pagesNutrition 1Bada MubarakNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument41 pagesRespirationChristi Lorraine LayogNo ratings yet
- Application NoteDocument7 pagesApplication NoteIngrid Eliana Fernandez CampoNo ratings yet
- Tacfit Warrior 4 Day Diet Book HiresDocument17 pagesTacfit Warrior 4 Day Diet Book HiresSelena Smith100% (1)
- SCI 220 SCI220 Sci 220 Sci220 Sci 220 Sci220Document49 pagesSCI 220 SCI220 Sci 220 Sci220 Sci 220 Sci220220sci2200% (3)
- Biology Notes For IGCSEDocument54 pagesBiology Notes For IGCSErajeshn186% (37)
- MDS Postal Coaching Synopsis Sample MaterialsDocument232 pagesMDS Postal Coaching Synopsis Sample Materialsbrihaspathiacademy100% (1)
- JCP Moisture Requirement 17Document3 pagesJCP Moisture Requirement 17Huyen HoangNo ratings yet
- Break Thru Nutrition PlanDocument26 pagesBreak Thru Nutrition PlanharbansalNo ratings yet
- Method: Determination of Dextrose EquivalentDocument3 pagesMethod: Determination of Dextrose EquivalentEnamul hasanNo ratings yet
- T&L MaltodextrinesDocument12 pagesT&L MaltodextrinesMurali Krishna IndanaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 CarbohydratesDocument99 pagesUnit 1 CarbohydratesRameshbabuNo ratings yet
- HomevistingDocument17 pagesHomevistingFrank LineNo ratings yet
BIC 101 - Q.B. 25 - Agri Junction
BIC 101 - Q.B. 25 - Agri Junction
Uploaded by
sitharaanairCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BIC 101 - Q.B. 25 - Agri Junction
BIC 101 - Q.B. 25 - Agri Junction
Uploaded by
sitharaanairCopyright:
Available Formats
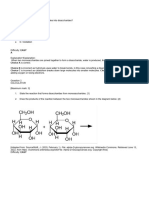
UNIT I - CARBOHYDRATES
A. Choose the best answer:
1. The number of asymmetric carbon atoms in glucose
a. 4 b. 3 c. 5 d. 6
2. The possible optical isomers for glucose
a. 14 b. 16 c. 12 d. 8
3. Which is an aldopentose?
a. Ribulose b. Ribose c. Erythrose d. Xylulose
4. Identify the non reducing sugar from the following
a. Lactose b. Maltose c. Sucrose d. Galactose
5. The epimer of glucose is
a. Galactose b. Fructose c. Ribose d. Erythrose
6. Lactose consists of
a. Glucose and fructose b. Glucose and Galactose c. Glucose and Mannose
d. Mannose and Galactose
7. The pyranose and furanose ring structures of sugars was proposed by
a. Fisher b. Haworth c. Sanger d. Edman
8. The glycosidic linkage present in cellulose is
a. 1- 6 b. 1- 4 c. 1- 4 d. 1- 4 & 1- 4
9. The isomers which differ in configuration around carbonyl carbon are
a. Anomers b. Epimers c. Stereoisomer d. Diastereoisomer
10. Which one of the following is not a homopolysaccharide?
a. Cellulose b. Starch c. Hemicellulose d. Chitin
11. The constituent monosaccharide unit of Chitin is
a. N- Acetyl Galactose b. N- Acetyl Glucosamine c. N- Acetyl Galactosamine
d. N- Acetyl mannosamine
12. A triose is made up of three
a. monosaccharides b. carbon atoms c. sugar atoms d. aldehyde groups
13. An example of heteropolysaccharide is
a. Amylose b. Hemicellulose c. Cellulose d. Amylopectin
14. Acid catalysed dehydrated product of sugars is
a. Uronic acid b. Aldaric acid c. Aldonic acid d. Furfurals
15. Identify the aldohexose from the following
a. Ribose b. Ribulose c. Glucose d. Xylose
16. Identify the linkages present in amylopectin
a. b. c. d.
Which one of the following is not a reducing disaccharide?
a. Lactose b. Maltose c. Cellobiose d. Sucrose
18. The principal storage polysaccharide is
a. Cellulose b. Starch c. Chitin d. Hemicellulose
19. Which one of the following pair are epimers?
a. Glucose and fructose b. Glucose and Galactose c. Mannose and Galactose
d. Fructose and mannose
20. Which of the following pair are diastereoisomers?
a. D- Galactose and D- Glucose b. D- Glucose and D- Fructose
c. D- Glucose and L- Glucose d. D- Fructose and L- Fructose
21. The enantiomer of D- glucose is
a. D- Galactose b. L- Glucose c. L- Galactose d. D- Fructose
22. The epimer of glucose is
a. Fructose b. Mannose c. Ribose d. Cellulose
23. Which one of the following sugar is not dextro rotatory?
a. Glucose b. Mannose c. Sucrose d. Fructose
24. Which one of the following sugar does not exhibit mutaraotation?
a. Lactose b. Maltose c. Sucrose d Glucose
25. Which is the most common microfibrillar polysaccharide found in the plant
kingdom ?
a. Cellulose b. Starch c. Chitin d. Inulin
26. Amylase hydrolyse --------- linkages in starch
a. b. c. d.
The stereoisomers which have mirror image relationship are referred as
a. Enantiomers b. Diastreoisomer c. Epimer d. Anomer
28. Carbon atom which is attached to four different groups is referred as --------
a. Asymmetric b. Reducing c. Anomeric d. Symmetric
29. Which is the dextrosugar that on hydrolysis yields the laevorotatory products
a. Glucose b. Mannose c. Sucrose d. Fructose
30. Which is a branched component of starch.
a. Amylose b. Amylopectin c. Dextrin d. Cellobiose
B. Say True or False
1. Sucrose is a reducing disaccharide.F
2. Dihydroxy acetone is an optically inactive sugar. T
3. Anomers are isomers that arise due to difference in position of groups around
carbonyl carbon. T
4. Fructose is a dextrosugar. F
5. Glucose contains three asymmetric carbon atoms.F
6. Starch is a Glucan. T
7. Cellulose is a storage polysaccharide F
8. Glucose on oxidation forms sorbitol F
9. Sucrose can exist in forms. F
10. Starch is a structural polysaccharide.F
11. All monosacchrides are reducing sugars.T
12. Glucose is a ketohexose. F
13. Glucose and mannose are epimers. T
14. Amylopectin is a branched component of starch T
15. Oxidation of glucose with H2O2 gives Gluconic acid. T
16. Pentose sugars are constituent of nucleic acids. T
17. Invert sugar is sweeter than sucrose. T
18. Sorbitol is oxidized product of glucose. F
19. Glucose is a dextrosugar T
20. Amylose contains 1-4 and 1-6 linkages F
21. Sugars on reduction forms Alditol. T
22. Sucrose is a non-reducing sugar T
23. Presence of asymmetric carbon is a criteria for compound to be optically active T
24. Maltose contains two galactose units. F
25. Invert sugar is mixture of sucrose hydrolysates T
26. Molisch’s test is a test specific for Keto sugars. F
27. The change in optical rotation is referred as Mutarotation. T
28. Sucrose give positive results with Benedict’s Reagent F
29. HFCS refers to High Fructose Corn Syrup. T
30. Carbohydrates are polyhydric alcohols with aldehyde or ketone as functional
groups T
Short Answers:
1. Define : Mutarotation
2. Why Sucrose is a non reducing sugar?
3. Give the structure of β- D- Ribofuranose.
4. What is the monomeric unit present in the following sugars and the nature of
linkages
a. Starch b. Cellulose c. Chitin d. Sucrose e. Maltose f. Lactose
5. Define : Anomers
6. Explain the reaction of sugar with acids
7. Explain the reactions of Sugars with dilute alkali
8. What do you mean by a reducing sugar?
9. Define: Epimers
10. Define: Stereoisomer
11. Differentiate : Starch and Cellulose
12. Differentiate : Amylose and Amyl pectin
13. Differentiate : Storage Polysaccharide and Structural Polysaccharide
14. Differentiate: Homopolysaccharide and Hetero polysaccharide
15. Differentiate: α anomer and β anomer
16. Differentiate : Dextro and Levo sugar
17. Differentiate : Enantiomer and Diastereo isomer
18. Differentiate : D and L Sugars
19. Explain the basis for colour reactions of Carbohydrates
20. What is a Chiral / asymmetric Carbon ?
21. What do you mean by invert sugar?
22. Give the Haworth ring structure of α – D Gluco Pyranose and β- D Fructofuranose
23. How are the hemiacetal ring structures of Glucose formed?
24. Give the classification of Polysaccharides based on their function
25. Why cellulose is not digested by Human beings?
Essay Questions:
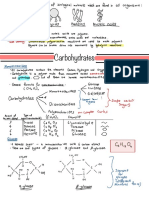
1. Classification of Carbohydrates
2. Explain the structure of Starch
3. Explain the structure of Cellulose
4. Explain the structure of Disaccharides
5. Detailed account on properties of Carbohydrates – Stereoisomerism, Optical activity,
Reducing Property & Mutarotation
6. Explain the industrial uses of Carbohydrates
You might also like
- Multiple Choice Questions in Biochemistry: Digital Edition © RC GuptaDocument16 pagesMultiple Choice Questions in Biochemistry: Digital Edition © RC Guptatekalignpawulose09No ratings yet
- (Chemistry Research and Applications) Fitzgerald, Adrienne - Emulsifiers - Properties, Functions, and Applications-Nova Science Publishers (2015) PDFDocument116 pages(Chemistry Research and Applications) Fitzgerald, Adrienne - Emulsifiers - Properties, Functions, and Applications-Nova Science Publishers (2015) PDFStefania DavidNo ratings yet
- Igcse Biology - Transport in AnimalsDocument67 pagesIgcse Biology - Transport in AnimalsYoshitaNo ratings yet
- Quiz On Disaccharide and PolysaccharideDocument4 pagesQuiz On Disaccharide and PolysaccharideJEAN I MAGLAQUENo ratings yet
- Unit I CarbohydratesDocument4 pagesUnit I CarbohydratesOVIYA M JNo ratings yet
- BIC Model Mid Sem 2008Document3 pagesBIC Model Mid Sem 2008charusrirajkumar27No ratings yet
- FDocument146 pagesFOla GomaaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry QuizDocument6 pagesBiochemistry QuizPatrick Ngo'nga Chifwema100% (1)
- Quiz CarbDocument7 pagesQuiz CarbKeith AquinoNo ratings yet
- Org Chem II Guiding QuestionsDocument10 pagesOrg Chem II Guiding QuestionsMesfen MeleseNo ratings yet
- MCQsDocument34 pagesMCQsmanin18040% (1)
- ASM2018 Mod 2 & 3 Booklet Part 1Document136 pagesASM2018 Mod 2 & 3 Booklet Part 1Ibrahim JamaluddinNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates MCQsDocument9 pagesCarbohydrates MCQsAyesha BatoolNo ratings yet
- MCQsDocument15 pagesMCQsmanin1804No ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 14 BiomoleculesDocument13 pagesChemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 14 Biomoleculesrathi rupaNo ratings yet
- Dược liệuDocument48 pagesDược liệutrinhthungoct66No ratings yet
- Biochem Questions 1Document4 pagesBiochem Questions 1Swapna ChavanNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Chemistry MCQDocument7 pagesCarbohydrate Chemistry MCQSohaila GodaNo ratings yet
- M3 - Assessment - FinalDocument3 pagesM3 - Assessment - FinalrickyNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument7 pagesCarbohydratesjamila abdirahmanNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Stage Exam Main PaperDocument21 pagesBiochemistry Stage Exam Main PaperDkt Pius KpchirchirNo ratings yet
- Name: Bibek Biswakarma Date: 6Document6 pagesName: Bibek Biswakarma Date: 6Bibek GajmerNo ratings yet
- Chemicals Found in Plants and They Promote Health (Act As Antioxidants)Document3 pagesChemicals Found in Plants and They Promote Health (Act As Antioxidants)AbduladheemNo ratings yet
- TBQDocument7 pagesTBQWilker GoulartNo ratings yet
- Final Biochemistry MCQDocument29 pagesFinal Biochemistry MCQsaraNo ratings yet
- bch-mcqs-43 DPHDocument6 pagesbch-mcqs-43 DPHpharmamylife2No ratings yet
- DownloadDocument115 pagesDownloadvisha rathodNo ratings yet
- FeasgsDocument14 pagesFeasgsjan2072650No ratings yet
- Carbs HW Worksheet 2Document2 pagesCarbs HW Worksheet 2Benay ÇakaloğluNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry 6Th Edition Garrett Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument33 pagesBiochemistry 6Th Edition Garrett Test Bank Full Chapter PDFsean.broom305100% (21)
- BCH 202 First LectureDocument9 pagesBCH 202 First Lecturemetasynthronos748No ratings yet
- AnswersDocument3 pagesAnswersmodyz7raNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates ExercisesDocument5 pagesCarbohydrates Exercisesreemmasri877No ratings yet
- Iloilo Doctors College Quiz (Carbohydrates)Document5 pagesIloilo Doctors College Quiz (Carbohydrates)Kimberly SalarzaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 7 Carbohydrates and The Glyconjugates of Cell SurfaceDocument14 pagesCHAPTER 7 Carbohydrates and The Glyconjugates of Cell Surface楊畯凱No ratings yet
- Lipid Revision WorksheetDocument7 pagesLipid Revision Worksheetnoorayg.jNo ratings yet
- Short EssayDocument13 pagesShort EssayYazhiniNo ratings yet
- BSN Biochemistry MDocument11 pagesBSN Biochemistry MKhubaib KhanNo ratings yet
- Organic Compounds WorksheetDocument3 pagesOrganic Compounds Worksheetz4g4v7gkzjNo ratings yet
- MCQDocument3 pagesMCQea4184386No ratings yet
- 405 Method Not AllowedDocument5 pages405 Method Not AllowedNaji Mohamed AlfatihNo ratings yet
- Hidratos de Carbono TallerDocument10 pagesHidratos de Carbono TallerLeidyNo ratings yet
- 2Document1 page2Vishal SinghNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 14 - Biomolecules Important Questions 2022-23Document22 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 14 - Biomolecules Important Questions 2022-23Archanaa PadmavathiNo ratings yet
- Carbhdrts 1Document10 pagesCarbhdrts 1IshnNo ratings yet
- CarbohydrateDocument4 pagesCarbohydrateLinh Bui Thi ThaiNo ratings yet
- AnswerDocument7 pagesAnswerloginhani40No ratings yet
- Biochemistry 1st Semester BSN Mcqs For Practice AD, Educational Platform-1Document6 pagesBiochemistry 1st Semester BSN Mcqs For Practice AD, Educational Platform-1Prince Masroor Ali Abro100% (2)
- BIOCHEMISTRYDocument4 pagesBIOCHEMISTRYkristilyn nudqueNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry 20 MCQs-1Document6 pagesBiochemistry 20 MCQs-1Muhammadsiddique khanNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules ImpDocument22 pagesBiomolecules ImpmrdaddydaddaNo ratings yet
- BBC1 K14 K15 KarbohidratDocument31 pagesBBC1 K14 K15 Karbohidratbrigita charvioNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates and LipidsDocument18 pagesCarbohydrates and LipidsJasmin RIshel Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules 231224 101920Document10 pagesBiomolecules 231224 101920Mariam HussainiNo ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULES imp quesDocument2 pagesBIOMOLECULES imp quesbhaktikhanijo16No ratings yet
- ChoDocument10 pagesChoLohith HanumNo ratings yet
- Biology SL 2025 Uniform & Function - Carbohydrates and LipidsDocument35 pagesBiology SL 2025 Uniform & Function - Carbohydrates and LipidsAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- The Best Best Best MCQS For Carbohydrates ChapterDocument22 pagesThe Best Best Best MCQS For Carbohydrates Chapterhappy9874648No ratings yet
- Biology Class: 11 Unit: 1Document8 pagesBiology Class: 11 Unit: 1samiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: Carbohydrates: 6.1. General Information About CarbohydratesDocument12 pagesChapter 6: Carbohydrates: 6.1. General Information About CarbohydratesMD. SAJID GHUFRANNo ratings yet
- Bionanocomposites: Integrating Biological Processes for Bioinspired NanotechnologiesFrom EverandBionanocomposites: Integrating Biological Processes for Bioinspired NanotechnologiesCarole AiméNo ratings yet
- Year 9 ENZYMES WSDocument3 pagesYear 9 ENZYMES WSShazeeq Official ChannelNo ratings yet
- Honey Composition - National Honey BoardDocument8 pagesHoney Composition - National Honey BoardBala GangadharNo ratings yet
- KVPY SA StreamDocument100 pagesKVPY SA StreamResonance Dlpd72% (46)
- Carbohydrates - FactRecallDocument5 pagesCarbohydrates - FactRecallRawan Al-tahanNo ratings yet
- 2012 DSE Bio 1BDocument12 pages2012 DSE Bio 1BLeung Man ChunNo ratings yet
- Primary 6Document17 pagesPrimary 6Architecte UrbanisteNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 CarbohydratesDocument5 pagesTutorial 1 CarbohydratesEngNo ratings yet
- NCM 105 LectureDocument17 pagesNCM 105 LectureAaron De DiosNo ratings yet
- Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirement For: A Chemistry Investigatory Project OnDocument18 pagesSubmitted in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirement For: A Chemistry Investigatory Project Onvasu thakurNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document16 pagesChapter 1Mursaleen KhanNo ratings yet
- Why Do Human Cells Rely Far More On Glucose and Fat For The Energy Than On ProteinDocument4 pagesWhy Do Human Cells Rely Far More On Glucose and Fat For The Energy Than On ProteinHamda HassanNo ratings yet
- Fructose - TDSDocument2 pagesFructose - TDSDoly DoolNo ratings yet
- Belay TefferaDocument89 pagesBelay TefferafanusNo ratings yet
- 8 L 5 1 RRR Practice QuestionsDocument8 pages8 L 5 1 RRR Practice QuestionsEliana FeingoldNo ratings yet
- BLS The Hidden Barrier To Effective Eating ExercisingDocument16 pagesBLS The Hidden Barrier To Effective Eating ExercisingParul DhallaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition 1Document15 pagesNutrition 1Bada MubarakNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument41 pagesRespirationChristi Lorraine LayogNo ratings yet
- Application NoteDocument7 pagesApplication NoteIngrid Eliana Fernandez CampoNo ratings yet
- Tacfit Warrior 4 Day Diet Book HiresDocument17 pagesTacfit Warrior 4 Day Diet Book HiresSelena Smith100% (1)
- SCI 220 SCI220 Sci 220 Sci220 Sci 220 Sci220Document49 pagesSCI 220 SCI220 Sci 220 Sci220 Sci 220 Sci220220sci2200% (3)
- Biology Notes For IGCSEDocument54 pagesBiology Notes For IGCSErajeshn186% (37)
- MDS Postal Coaching Synopsis Sample MaterialsDocument232 pagesMDS Postal Coaching Synopsis Sample Materialsbrihaspathiacademy100% (1)
- JCP Moisture Requirement 17Document3 pagesJCP Moisture Requirement 17Huyen HoangNo ratings yet
- Break Thru Nutrition PlanDocument26 pagesBreak Thru Nutrition PlanharbansalNo ratings yet
- Method: Determination of Dextrose EquivalentDocument3 pagesMethod: Determination of Dextrose EquivalentEnamul hasanNo ratings yet
- T&L MaltodextrinesDocument12 pagesT&L MaltodextrinesMurali Krishna IndanaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 CarbohydratesDocument99 pagesUnit 1 CarbohydratesRameshbabuNo ratings yet
- HomevistingDocument17 pagesHomevistingFrank LineNo ratings yet