Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A4 Serbian Pronouns Chart
A4 Serbian Pronouns Chart
Uploaded by
Никола УзуноскиOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
A4 Serbian Pronouns Chart
A4 Serbian Pronouns Chart
Uploaded by
Никола УзуноскиCopyright:
Available Formats
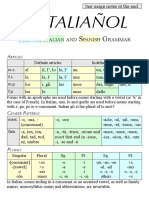
PERSONAL PRONOUNS DEMONSTRATIVE PRONOUNS 5
SUBJECTS OBJECTS POSSESSIVE5,6 M.9 N.9 F.
Nominative Accusative, Locative, Instrumental
this ovaj ovo ova
that
singular
Genitive Dative taj to ta
self 1 sebe, se sebi, si sobom own1 svoj7 that onaj ono ona
over there
I ja me mene, me meni, mi mnom my moj7
M. N. F.
you ti you tebe, te tebi, ti tobom your tvoj7
these ovi ova ove
singular
he on him his njegov
it ono it njega, ga njemu, mu njim its those ti ta te
plural
A nju, je, ju2 those oni ona one
she ona her njoj, joj njom her njen over there
G nje, je
Use neuter singular form for “<this, those, etc.> <is, are, was, will be, etc.> …”.
we mi us nas nama, nam our naš Ex: Ovo su moji roditelji.
Ex: To nisu moje sestre.
plural
you vi you vas vama, vam your vaš But change the gender and plurality to match the noun when using
“<this, those, etc.> <noun, one(s)> …”.
they oni M
M. them njih, ih njima, im their njihov Ex: Taj pas nije moj.
ona N
N.
See footnote 3 for when to use long vs short4 forms.
Ex: Da li su ovi psi tvoji?
one FF. Ex: Ovaj je najbolji. (This one is the best.) “One” is implied by the declension.
1. Reflexively refers back to the subject. Ex: myself, itself, themselves; my own,
• Though not shown above, ti and vi (only) have vocative
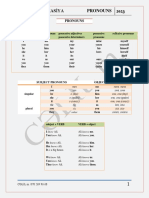
WHOSE, WHO, WHAT?
its own, their own.
2. Use ju with third person singular past tense (ju je <verb>, not je je <verb>). forms, which are the same as nominative (ti and vi).
• Vi forms are used for both plural you and formal-singular Whose5
3. Use long form: ① at the beginning of a sentence ② for emphasis or contrast
③ after prepositions ④ after i, a, or comma. Otherwise, use short form. you. Capitalize Vi, etc. for formal-singular. M. N. F.
4. Short forms of personal pronouns are “second position” words that must • Instrumental singular pronouns mnom, njim, and njom
appear together in a specific order: li ➜ short verb ➜ short pronoun (dative can be used as mnome, njime, and njome when there is singular čije čija
➜ accusative/genitive) ➜ se/je. Ex: Dao si mi ga. (You gave me it.) Here, the no preceding preposition. čiji
second position cluster si mi ga is: verb ➜ dative pronoun ➜ accus. pronoun. • Most adjectives can be used as pronouns in Serbian. plural čija čije
5. Shown in nominative form (for possessive: nominative, masculine, singular). Ex: Žuti odlazi. (The yellow one is leaving.)
Change using adjective declension rules for case, gender, and plurality. Who What
6. Serbian uses the same words for the possessive adjectives my, your, his, etc. 9. This/that in masculine and neuter singular forms have
and the possessive pronouns mine, yours, his, etc. alternative, optional case declensions. nominative ko šta
7. When using svoj, moj, or tvoj to describe masculine or neuter singular nouns,
Accusative8, Locative, Instrumental
special, short declensions are more Genitive Dative
accusative (za) koga (za) šta
commonly used for several cases. Accusative 8
, Locative,
8. For accusative case, this declension Genitive Dative ova j ovog(a ) ovom(e) ovi m(e) genitive od koga od čega
is used with living, masculine s voj s vog s vom ta j tog(a ) tom(e) ti m(e)
nouns only. locative, dative o* kome o* čemu
moj mog mom ona j onog(a) onom(e) oni m(e)
tvoj tvog tvom instrumental s(a) kim čim(e)
Change with case (as shown), but not gender or plurality.
© 2023 Steven Levithan * The o preposition is only/always used with locative.
SERBIAN PRONOUNS CHART v2.3 More charts: slev.life/serbian-charts CC BY 4.0 License
You might also like
- Basics of Biblical Greek - Workbook Answer KeyDocument123 pagesBasics of Biblical Greek - Workbook Answer KeyJackson Trace88% (8)
- Formulario Básico de InglésDocument12 pagesFormulario Básico de InglésPaola Chambe0% (1)
- French Italian Spanish Grammar PDFDocument9 pagesFrench Italian Spanish Grammar PDFSanto Parsons0% (1)
- Grammar - 8 Troublesome ModifiersDocument4 pagesGrammar - 8 Troublesome ModifiersMa Ka Yan100% (1)
- Pearson - Risorse Inglese SSPG Mappe Di SintesiDocument11 pagesPearson - Risorse Inglese SSPG Mappe Di SintesiLeonardoNo ratings yet
- BLS Serbian Personal Pronouns Serbian CasesDocument1 pageBLS Serbian Personal Pronouns Serbian CasesAntibiotikum ZzeroNo ratings yet
- Miq/Sertifikasiya Pronouns 2023Document9 pagesMiq/Sertifikasiya Pronouns 2023Ayshen BedelovaNo ratings yet
- 02.2 Parts of Speech - Types of PronounsDocument2 pages02.2 Parts of Speech - Types of PronounsGadielNo ratings yet
- Possessive Pronouns and Adjectives ExerciseDocument2 pagesPossessive Pronouns and Adjectives ExerciseMariana Valencia MosqueraNo ratings yet
- Plataforma For Basic VIIDocument12 pagesPlataforma For Basic VIIjerson sarmiento lunaNo ratings yet
- Object Pronouns: Subject Pronoun Object PronounDocument2 pagesObject Pronouns: Subject Pronoun Object PronounDaniel VelasquezNo ratings yet
- Pronoun Chart - Backup NDocument2 pagesPronoun Chart - Backup NNada GarelnabiNo ratings yet
- T TP 1662038562 Pronouns Poster - Ver - 1Document1 pageT TP 1662038562 Pronouns Poster - Ver - 1Natalie DorohavtsevaNo ratings yet
- بيسان 1 النهائيةDocument101 pagesبيسان 1 النهائيةkhalednelaNo ratings yet
- Pronoun ChartDocument1 pagePronoun ChartMiss HelensNo ratings yet
- Grammar PracticeDocument11 pagesGrammar PracticeCamila CelaNo ratings yet
- Pronouns and AdjectivesDocument1 pagePronouns and Adjectiveselectra1986No ratings yet
- Grammar Pronouns WorksheetDocument13 pagesGrammar Pronouns WorksheetMoncef ComputerNo ratings yet
- 1c Hello Flash CardsDocument1 page1c Hello Flash CardsGlen CNo ratings yet
- Subject Object Possessive PronounsDocument17 pagesSubject Object Possessive PronounsLarisaNo ratings yet
- Pronouns ExerciseDocument4 pagesPronouns ExerciseFELIZA DHIYA SUSILONo ratings yet
- Pronouns - TableDocument1 pagePronouns - TableDManeraNo ratings yet
- Bai Tap Day Them o NhaDocument1 pageBai Tap Day Them o NhaMelody NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Activity 09Document2 pagesActivity 09dominique1710No ratings yet
- 3.4 Language HW PronounsDocument1 page3.4 Language HW PronounsJosé MejíaNo ratings yet
- To Be Verb 2Document70 pagesTo Be Verb 2Chisco80No ratings yet
- German Grammar: Ig, Ich, Ing Ling En, El Er Ig Ich Ing Ling en El ErDocument9 pagesGerman Grammar: Ig, Ich, Ing Ling En, El Er Ig Ich Ing Ling en El ErDeepa BalwallyNo ratings yet
- Exercícios de Inglês - IniciantesDocument1 pageExercícios de Inglês - Iniciantesisa RibeiroNo ratings yet
- Repaso InglésDocument7 pagesRepaso InglésharavenaNo ratings yet
- Past (прошлое) Present (настоящее) Future (будущее) : Active voiceDocument2 pagesPast (прошлое) Present (настоящее) Future (будущее) : Active voiceАннаNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Grammar For IELTSDocument272 pagesCambridge Grammar For IELTSweonjami0810No ratings yet
- اللغة الانكليزية تحليلات 2Document88 pagesاللغة الانكليزية تحليلات 2ss0857003No ratings yet
- (Prep Sưu Tầm) Giải Thích Ngữ Pháp Tiếng Anh Mai Lan HươngDocument416 pages(Prep Sưu Tầm) Giải Thích Ngữ Pháp Tiếng Anh Mai Lan HươngnguyenphuongkdydsNo ratings yet
- Ingles 1Document1 pageIngles 1Valdir VillalobosNo ratings yet
- 10 Sentences Using The Vocabulary of The Unit 5: Subject Pronouns Object PronounsDocument1 page10 Sentences Using The Vocabulary of The Unit 5: Subject Pronouns Object Pronounseliezer_15141No ratings yet
- Class MettingDocument1 pageClass MettingIjal SyamsurizalNo ratings yet
- Grammar Task I4Document5 pagesGrammar Task I4fioreveralone.faNo ratings yet
- Grade1-English-Verb To Be WS#9Document3 pagesGrade1-English-Verb To Be WS#9How ?No ratings yet
- Captura de Tela 2023-05-10 À(s) 06.57.08Document16 pagesCaptura de Tela 2023-05-10 À(s) 06.57.08raissaalncr09No ratings yet
- Kinds of Pronouns - E9Document4 pagesKinds of Pronouns - E929camziiNo ratings yet
- Final Revision Prep 2 First TermDocument96 pagesFinal Revision Prep 2 First Termkhaled samirNo ratings yet
- JacoboDocument16 pagesJacobozct4nkn4jdNo ratings yet
- A4 Serbian Cases ChartDocument1 pageA4 Serbian Cases ChartAnatoliy KiguradzeNo ratings yet
- Stage 1 5 Possessives Possessive Adjectives 1Document1 pageStage 1 5 Possessives Possessive Adjectives 1soniaca27No ratings yet
- Semestre 8 Parcial 1Document25 pagesSemestre 8 Parcial 1zm9bgq2mg8No ratings yet
- Singular (Is) Plural (Are) Near (Cerca) This TheseDocument1 pageSingular (Is) Plural (Are) Near (Cerca) This TheseRafael A. Aguilar FerroNo ratings yet
- Personal PronounsDocument1 pagePersonal PronounsSonia AgustínNo ratings yet
- PronounsDocument1 pagePronounsEridani OlmosNo ratings yet
- Mto 509Document2 pagesMto 509Edward KITANDWENo ratings yet
- This/jednina/ I These/mnozina/ - Pokazuje Na Stvari Koje Su Blize U Prostoru Ili Vremenu That/jednina/ I Those /mnozina/ - Koji Su DaljeDocument1 pageThis/jednina/ I These/mnozina/ - Pokazuje Na Stvari Koje Su Blize U Prostoru Ili Vremenu That/jednina/ I Those /mnozina/ - Koji Su DaljeBex TasicNo ratings yet
- The Uses of Verb To BeDocument3 pagesThe Uses of Verb To BeInés SolorzanoNo ratings yet
- Gramatica 7mo - Lesson 2Document2 pagesGramatica 7mo - Lesson 2Maggy AguileraNo ratings yet
- Actividad NounsDocument7 pagesActividad NounsLuisa Fernanda Pinzon MarinNo ratings yet
- English - Present SimpleDocument1 pageEnglish - Present Simplerembodi21No ratings yet
- Pronoun RuLESDocument5 pagesPronoun RuLESSheril PatelNo ratings yet
- Lerne Deutch ??Document18 pagesLerne Deutch ??KristinaooNo ratings yet
- 01. 345 그래머 2 - 그래머 차트Document4 pages01. 345 그래머 2 - 그래머 차트rachel ohNo ratings yet
- Error Spotting ArticlesDocument5 pagesError Spotting ArticlesSameer SharmaNo ratings yet
- Relative Clauses - EFLDocument3 pagesRelative Clauses - EFLRenan DiasNo ratings yet
- PronounsDocument10 pagesPronounsCerlin PajilaNo ratings yet
- BCC101 Functional English AssignmentDocument5 pagesBCC101 Functional English AssignmentPriyank GharoteNo ratings yet
- Total English Online Activities Unit 1 VocabularyDocument4 pagesTotal English Online Activities Unit 1 VocabularynewjanerNo ratings yet
- Rules For Infinitives and GerundsDocument2 pagesRules For Infinitives and GerundsPaulina MoyaNo ratings yet
- Gramática Neerlandês ResumidoDocument139 pagesGramática Neerlandês Resumidobianca_carvalho_91No ratings yet
- Comma Sutra (Luarie Rozakis)Document268 pagesComma Sutra (Luarie Rozakis)BrettMinorNo ratings yet
- Grammar 1: VERB-TO-BE: I. Verb "To Be" Indicates Progressive Tense (Continuous Tense) - Thus We HaveDocument13 pagesGrammar 1: VERB-TO-BE: I. Verb "To Be" Indicates Progressive Tense (Continuous Tense) - Thus We HaveSharanya MurugesuNo ratings yet
- PoetryDocument9 pagesPoetry007dcpNo ratings yet
- Compound Noun: Prepared by Mr. Meyphalla OudomDocument8 pagesCompound Noun: Prepared by Mr. Meyphalla Oudomphalla oudomNo ratings yet
- Ufcd 0386 - Plural Nouns Generalizations CompoundsDocument26 pagesUfcd 0386 - Plural Nouns Generalizations Compoundscajoca1No ratings yet
- Canonical Word Order in TagalogDocument55 pagesCanonical Word Order in Tagalogsevilla.laurenceNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary Builder Cahhya HerwantoDocument5 pagesVocabulary Builder Cahhya HerwantoGefft0% (1)
- Chapter I-3 BabDocument93 pagesChapter I-3 BabDbs Abdul HadiNo ratings yet
- Dragon LanguageDocument7 pagesDragon LanguageChristopher100% (1)
- Nama: Lovita Salsabila Balkis NIM: P27820119022 Kelas: Tingkat I Reguler ADocument2 pagesNama: Lovita Salsabila Balkis NIM: P27820119022 Kelas: Tingkat I Reguler ALovita Salsabila BalqisNo ratings yet
- To Be Past Tense PDFDocument2 pagesTo Be Past Tense PDFGuerrero AgeNo ratings yet
- 5-Minute Japanese Class by Hitomi Hirayama: (Frequently Used in Daily Life)Document1 page5-Minute Japanese Class by Hitomi Hirayama: (Frequently Used in Daily Life)Lu Caro LopezNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentences With If Clauses Possible Future SituationDocument5 pagesConditional Sentences With If Clauses Possible Future SituationronaldoNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Duality of Definiteness and Indefiniteness in Arabic On Arabic Sentence Structure With Reference To EnglishDocument30 pagesThe Impact of Duality of Definiteness and Indefiniteness in Arabic On Arabic Sentence Structure With Reference To Englishali mohammedNo ratings yet
- Adjective ClausesDocument4 pagesAdjective ClausesOmar A. RincónNo ratings yet
- Sentence CorrectionDocument10 pagesSentence CorrectionsanjivsingNo ratings yet
- Anglès Selectivitat 2018: IES Duc de MontblancDocument18 pagesAnglès Selectivitat 2018: IES Duc de MontblancMarina BallesterNo ratings yet
- Language Features of Narrative Text:: Name: ClassDocument4 pagesLanguage Features of Narrative Text:: Name: ClassAcib ChusnulNo ratings yet
- Transitive and Intransitive VerbsDocument5 pagesTransitive and Intransitive VerbsPradumna Singh KanhpuriyaNo ratings yet
- Comparatives and Superlatives: Unit 3Document12 pagesComparatives and Superlatives: Unit 3LILIAN DEL CARMEN RAMIREZ RIVASNo ratings yet
- Review of Related LiteratureDocument4 pagesReview of Related LiteratureManny Young50% (2)