Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ionic Bonding Notes
Ionic Bonding Notes
Uploaded by
evango210 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageOriginal Title
ionic bonding notes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageIonic Bonding Notes
Ionic Bonding Notes
Uploaded by
evango21Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
Ions are electrically charged particles formed when atoms lose or gain electrons
Positive (cations) are when atoms lose electrons
Negative (anions) are when atoms gain electrons
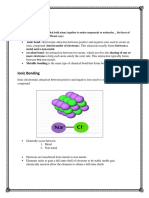
Definition of an ionic bond:
“ The ionic bond is the electrostatic force of attraction of a positively charged metal ion and
a negatively charged non metal ion.”
Ionic compounds have a high melting and boiling point because of the strong electrostatic
forces of attraction holding the lattice together. This requires a lot of energy to break apart
the strong electrostatic forces of attraction between oppositely charged ions in the great
lattice structure.
- Ionic compounds are mostly crystalline
- Ionic compounds tend to be brittle. This is because any small distortion of a crystal
will bring ions of the same charge alongside each other.
Like charges repel, so the crystal splits itself apart.
- Ionic compounds are soluble in water
- Ionic compounds are insoluble in organic solvents
- Ionic compounds conduct electricity when molten (when melted) or aqueous
(dissolved in water). The ions are free to move and they are not in a fixed position.
Compounds with ionic bonding always have a giant ionic structure.
The ions are held in a closely packed 3d lattice arrangement, by the attraction of strong
electrostatic forces of attraction between oppositely charged ions.
The electrostatic force of attraction between oppositely charged ions is very strong.
The structure of an ionic bond is described as a “giant ionic structure”.
You might also like
- 3-Ionic Bonding PDFDocument2 pages3-Ionic Bonding PDFTahmeed AhmedNo ratings yet
- Atoms CombiningDocument12 pagesAtoms Combiningshehryar khanNo ratings yet
- Ionic Bonding and StructureDocument20 pagesIonic Bonding and StructureKaren OrlanskiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonds and StructureDocument17 pagesChemical Bonds and StructureEddie EvansNo ratings yet
- 7.1 7.2Document2 pages7.1 7.2noora.rami48No ratings yet
- CH 3, ChemDocument6 pagesCH 3, ChemAbdullah SalmanNo ratings yet
- Bonding A Level NotesDocument5 pagesBonding A Level NotesWashington NyakaviNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Sodium Chloride Giant Ionic BondDocument12 pagesChemistry Sodium Chloride Giant Ionic BondtsteadmanNo ratings yet
- Forces of AttractionDocument21 pagesForces of AttractionDoveNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document2 pagesChapter 2Muhammad Waheed IqbalNo ratings yet
- Interatomic Forces: What Kind of Force Holds The Atoms Together in A Solid?Document25 pagesInteratomic Forces: What Kind of Force Holds The Atoms Together in A Solid?Anonymous BW2VsFifi9No ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument40 pagesChemical BondingabuhurairabscNo ratings yet
- Ionic Solids: Cations AnionsDocument2 pagesIonic Solids: Cations AnionsMyrna Getuaban SidonNo ratings yet
- Ions and Ionic BondDocument21 pagesIons and Ionic Bondchickuwa pawawawaNo ratings yet
- 06 ANSWERS SummaryDocument1 page06 ANSWERS SummaryJean AlmiraNo ratings yet
- Chemistry-Ch 3 - Chemical BondingDocument8 pagesChemistry-Ch 3 - Chemical BondingHassan RiazNo ratings yet
- Article (Bonding&Structure)Document3 pagesArticle (Bonding&Structure)Fawzan Fahad MDNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding/s2 Kimia UnpDocument36 pagesChemical Bonding/s2 Kimia UnpIda HidayatiNo ratings yet
- Interatomic Forces: What Kind of Force Holds The Atoms Together in A Solid?Document25 pagesInteratomic Forces: What Kind of Force Holds The Atoms Together in A Solid?lianghoo94No ratings yet
- Summary of Bonding, Structure and Properties of SubstancesDocument3 pagesSummary of Bonding, Structure and Properties of SubstancesAnonymous L7ZuSkR100% (1)
- Chemical Bond Notes by TouhidDocument23 pagesChemical Bond Notes by Touhidnabilnakib0077No ratings yet
- Interatomic Forces: What Kind of Force Holds The Atoms Together in A Solid?Document25 pagesInteratomic Forces: What Kind of Force Holds The Atoms Together in A Solid?rahulinder1234No ratings yet
- Bonding in Solids Definition: Solid State ChemistryDocument9 pagesBonding in Solids Definition: Solid State Chemistryhaimanot yibeltalNo ratings yet
- Bonding and Properties of SubstancesDocument3 pagesBonding and Properties of Substancesdan964No ratings yet
- Edexcel Topic 4 Bonding and StructureDocument7 pagesEdexcel Topic 4 Bonding and Structurekmoiz427No ratings yet
- Interatomic Forces: What Kind of Force Holds The Atoms Together in A Solid?Document36 pagesInteratomic Forces: What Kind of Force Holds The Atoms Together in A Solid?aditya_2013No ratings yet
- IB SL Chemistry NotesDocument5 pagesIB SL Chemistry NotesArsh SheikhNo ratings yet
- Describe The Electron Bond Structures For Solid MaterialsDocument4 pagesDescribe The Electron Bond Structures For Solid MaterialsCamilla OvillaNo ratings yet
- Bonding and Naming CompoundsDocument10 pagesBonding and Naming CompoundsDaniel BerryNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding NotesDocument5 pagesChemical Bonding NotesShaswat PattnayakNo ratings yet
- 4 14 Chemical Bonding 1 Ionic Metallic Bonding JL EditedDocument23 pages4 14 Chemical Bonding 1 Ionic Metallic Bonding JL EditedFN5052023 PRAMITA MAHENDRANNo ratings yet
- Bonding and StructureDocument20 pagesBonding and StructureYusma KhanNo ratings yet
- Bonding Revision GuidesDocument1 pageBonding Revision Guidesapi-255623302No ratings yet
- L I L I: Chemical BondingDocument3 pagesL I L I: Chemical BondingMark IanNo ratings yet
- Lesson3 - Chemical Bonding PDFDocument6 pagesLesson3 - Chemical Bonding PDFMia ChanNo ratings yet
- There Are Only Two Known Species ofDocument7 pagesThere Are Only Two Known Species ofmuhammad aslamNo ratings yet
- CSEC Chemistry - Structure and BondingDocument10 pagesCSEC Chemistry - Structure and BondingCornflakes ToastedNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Board NotesDocument19 pagesChemical Bonding Board NotesEmaan KhanNo ratings yet
- BondingDocument25 pagesBondingnya72505No ratings yet
- Chemistry Chemical BondingDocument4 pagesChemistry Chemical Bondinghamarirasoi0803No ratings yet
- 3.0 Chemical BondingDocument50 pages3.0 Chemical Bondingparkinsondilys7No ratings yet
- Lecture1 BondingDocument24 pagesLecture1 BondingChantelle KingNo ratings yet
- Bonding Summary NotesDocument17 pagesBonding Summary NotesaleenNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument5 pagesChemical BondingSANDEEP SINGHNo ratings yet
- SGC Chemical BondingDocument22 pagesSGC Chemical Bondingcassandraolmido18No ratings yet
- Csec Chemistry Notes 5Document3 pagesCsec Chemistry Notes 5debestieNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument8 pagesChemical BondingAhmed AbdelghanyNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledManureet SinghNo ratings yet
- Bonding and Structure: Chemistry Notes GCE Study BuddyDocument17 pagesBonding and Structure: Chemistry Notes GCE Study BuddyKhemou DjvickzNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond 1105Document51 pagesChemical Bond 1105Abid HasanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding (1) AS1C6Document29 pagesChemical Bonding (1) AS1C6tzeina578No ratings yet
- Atomic Bonding in SolidsDocument3 pagesAtomic Bonding in Solidsazmatshahzad786786No ratings yet
- G2 NSE1 ReviewerDocument3 pagesG2 NSE1 ReviewerjohnmilesvillaranteNo ratings yet
- Ionic CompoundsDocument2 pagesIonic CompoundsShenneth De CastroNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument22 pagesChemical BondingJr CarpelaNo ratings yet
- Answers To NCERT/CBSE Chemistry (Class XII) TextbookDocument1 pageAnswers To NCERT/CBSE Chemistry (Class XII) TextbookRohit GrewalNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond Physics and Chemistry ESODocument6 pagesChemical Bond Physics and Chemistry ESOurgazuNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bonds vs. Ionic Bonds: Comparison ChartDocument2 pagesCovalent Bonds vs. Ionic Bonds: Comparison ChartArcelie Alberca EscasinasNo ratings yet
- Ionic Bonding Vs Metallic BondingDocument2 pagesIonic Bonding Vs Metallic BondingsakuraleeshaoranNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.From EverandChemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.No ratings yet
- Physics Lesson: 6:2:2021 :)Document2 pagesPhysics Lesson: 6:2:2021 :)evango21No ratings yet
- BALCom IMC Without IdentificationDocument1 pageBALCom IMC Without Identificationevango21No ratings yet
- Chemistry 2015 Paper1Document17 pagesChemistry 2015 Paper1evango21No ratings yet
- 10 Minutes Main ExtractDocument1 page10 Minutes Main Extractevango21No ratings yet
- IB Periodic Table Notes HLDocument22 pagesIB Periodic Table Notes HLevango21No ratings yet