Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Multip Physics
Multip Physics
Uploaded by
AbhinawCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- 1 s2.0 S0377042720301631 MainDocument14 pages1 s2.0 S0377042720301631 Mainmat20d002No ratings yet
- Multivariable Calculus - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument4 pagesMultivariable Calculus - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediad_richard_dNo ratings yet
- C CC C C CDocument6 pagesC CC C C Canushka56No ratings yet
- Jeas 1006 17Document10 pagesJeas 1006 17Oscar AdrianNo ratings yet
- Tutorial: Topic: Finite Element Model Updating Speaker: Wen-Wei LinDocument8 pagesTutorial: Topic: Finite Element Model Updating Speaker: Wen-Wei LinlawfulNo ratings yet
- A Fitted Mesh Method For Partial Differential Equations With A Time LagDocument12 pagesA Fitted Mesh Method For Partial Differential Equations With A Time LagIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Finite Element-1508.02138Document20 pagesFinite Element-1508.02138GrantHermanNo ratings yet
- A Comparitive Study of FVM and FDMDocument7 pagesA Comparitive Study of FVM and FDMHassan AbdelmoamenNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Traffic FlowDocument7 pagesAnalysis of Traffic FlowmansNo ratings yet
- SPE-173200-MS Algebraic Multiscale Solver For Flow in Heterogeneous Fractured Porous MediaDocument14 pagesSPE-173200-MS Algebraic Multiscale Solver For Flow in Heterogeneous Fractured Porous MediaDavid MontoyaNo ratings yet
- Efg 1Document41 pagesEfg 1malenenivamsiNo ratings yet
- Finite Elements in Analysis and Design: Manuel Garcia, Jorge Gutierrez, Nestor RuedaDocument7 pagesFinite Elements in Analysis and Design: Manuel Garcia, Jorge Gutierrez, Nestor RuedachrissbansNo ratings yet
- Solution Techniques For The Vorticity-Streamfunction Formulation O F Two-Dimensional Unsteady Incompressible FlowsDocument25 pagesSolution Techniques For The Vorticity-Streamfunction Formulation O F Two-Dimensional Unsteady Incompressible FlowsIshwar SinghNo ratings yet
- c34 ECM MBI PDFDocument55 pagesc34 ECM MBI PDFThangadurai Senthil Ram PrabhuNo ratings yet
- UNIT NO 1: Finite Difference SchemesDocument9 pagesUNIT NO 1: Finite Difference SchemesAbhishek SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Saurel 2001Document23 pagesSaurel 2001Djamila BENYOUCEFNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 PDFDocument14 pagesAssignment 2 PDFChinmay GosaviNo ratings yet
- A Finite Volume Method On NURBS Geometries and Its Application in Isogeometric Fluid-Structure InteractionDocument22 pagesA Finite Volume Method On NURBS Geometries and Its Application in Isogeometric Fluid-Structure InteractionbradjenoNo ratings yet
- 2016 CMAME Ms Flux Basis SDDocument34 pages2016 CMAME Ms Flux Basis SDDanail VassilevNo ratings yet
- Newrobustandefficient Global Iterations For Large Deformation Finite Element Analysis of Beams and Shells With Material NonlinearityDocument28 pagesNewrobustandefficient Global Iterations For Large Deformation Finite Element Analysis of Beams and Shells With Material NonlinearityRey NCNo ratings yet
- A Finite Difference Method and Effective Modification of Gradient Descent Optimization Algorithm For MHD Fluid Flow Over A Linearly Stretching SurfaceDocument21 pagesA Finite Difference Method and Effective Modification of Gradient Descent Optimization Algorithm For MHD Fluid Flow Over A Linearly Stretching Surfaceyasir.nawaz.mathsNo ratings yet
- JP FernandezDocument251 pagesJP FernandezDiiana WhiteleyNo ratings yet
- A Cartesian Grid Method For Solving The Two-Dimensional Streamfunction-Vorticity Equations in Irregular RegionsDocument45 pagesA Cartesian Grid Method For Solving The Two-Dimensional Streamfunction-Vorticity Equations in Irregular RegionsHamid MojiryNo ratings yet
- An Eulerian Lagrangian Scheme For Solving Large Deformation Fluid Structure Interaction ProblemsDocument31 pagesAn Eulerian Lagrangian Scheme For Solving Large Deformation Fluid Structure Interaction ProblemsUmair QaziNo ratings yet
- Spe 79709 Pa P PDFDocument9 pagesSpe 79709 Pa P PDFtomk2220No ratings yet
- Finite Volume MethodDocument4 pagesFinite Volume MethodpoliskarmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Literature SurveyDocument12 pagesChapter Two Literature Surveymasyuki1979No ratings yet
- A Brief Description of These MethodsDocument6 pagesA Brief Description of These MethodsQi PanNo ratings yet
- MECH3780 Fluid Mechanics 2 and CFDDocument14 pagesMECH3780 Fluid Mechanics 2 and CFDninibearNo ratings yet
- Preprint - Multiscale VEM For The Biot Consolidation Analysis - of Complex and Highly Heterogeneous Domains-MinDocument78 pagesPreprint - Multiscale VEM For The Biot Consolidation Analysis - of Complex and Highly Heterogeneous Domains-MinAbhilash SreekumarNo ratings yet
- Método de Volumen Finito de Alta Orden para Resolver Fluidos ViscoelásticosDocument14 pagesMétodo de Volumen Finito de Alta Orden para Resolver Fluidos ViscoelásticosAaron Arango AyalaNo ratings yet
- Local Discontinuous Galerkin Methods For High-Order Time-Dependent Partial Differential EquationsDocument57 pagesLocal Discontinuous Galerkin Methods For High-Order Time-Dependent Partial Differential EquationsAman JalanNo ratings yet
- Heaviside's Operators and Contour IntegralsDocument28 pagesHeaviside's Operators and Contour IntegralsalpcruzNo ratings yet
- Multi Scale Mixed Finite Element Modeling of Coupled Wellbore Near-Well FlowDocument9 pagesMulti Scale Mixed Finite Element Modeling of Coupled Wellbore Near-Well Flowpetar_damyanovNo ratings yet
- CFDDocument18 pagesCFDPriya PatankarNo ratings yet
- Jac M 189861710880200Document14 pagesJac M 189861710880200Ahmed El KhalfiNo ratings yet
- Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH) : An Overview and Recent DevelopmentsDocument52 pagesSmoothed Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH) : An Overview and Recent DevelopmentsPac Agathe100% (1)
- TMMV08 A1 2024Document9 pagesTMMV08 A1 2024adityaNo ratings yet
- ATOMIZAÇÃO phd8Document9 pagesATOMIZAÇÃO phd8eustaccoNo ratings yet
- A Fully Coupled Finite Volume Solver For The Solution of Incompressible Flows On Locally Refined Non-Matching Block-Structured GridsDocument12 pagesA Fully Coupled Finite Volume Solver For The Solution of Incompressible Flows On Locally Refined Non-Matching Block-Structured GridsErnesto Delfino AguirreNo ratings yet
- Meshless Methods1Document4 pagesMeshless Methods1herevenkatNo ratings yet
- Mathematics With CoverDocument22 pagesMathematics With CoverVaradharajan RNo ratings yet
- Eotvos NumberDocument13 pagesEotvos NumberFoamboom SatjaritanunNo ratings yet
- Module 1: Introduction To Finite Element Analysis Lecture 1: IntroductionDocument6 pagesModule 1: Introduction To Finite Element Analysis Lecture 1: IntroductionMuhammad DaniyalNo ratings yet
- Euclid - Jam.1350488796 GoodDocument14 pagesEuclid - Jam.1350488796 GoodWei GaoNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods in Fluids - 2020 - Traverso - Efficient Stochastic Finite Element Methods For Flow in HeterogeneousDocument27 pagesNumerical Methods in Fluids - 2020 - Traverso - Efficient Stochastic Finite Element Methods For Flow in HeterogeneousGonzalo BustosNo ratings yet
- Lattice Boltzmann MethodDocument11 pagesLattice Boltzmann MethodNishant KumarNo ratings yet
- Basic Sens Analysis Review PDFDocument26 pagesBasic Sens Analysis Review PDFPratik D UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Mirzajani Et AlDocument30 pagesMirzajani Et AlkhodakaramiNo ratings yet
- HenningDocument43 pagesHenningtinaanaNo ratings yet
- Journal of Computational Physics: Armando Coco, Giovanni RussoDocument38 pagesJournal of Computational Physics: Armando Coco, Giovanni RussoAnonymous tIwg2AyNo ratings yet
- Method of Successive Weighted Averages MSWA and SeDocument20 pagesMethod of Successive Weighted Averages MSWA and SeAnonymous Y2ibaULes1No ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Science: Paul W.C. Northrop, P.A. Ramachandran, William E. Schiesser, Venkat R. SubramanianDocument8 pagesChemical Engineering Science: Paul W.C. Northrop, P.A. Ramachandran, William E. Schiesser, Venkat R. SubramanianAbraham SilesNo ratings yet
- Third-And Fifth-Order Finite Volume Schemes For Advection-Diffusion Equation With Variable Coefficients in Semi-Infinite Domain: Finite Volume Schemes For Advection-Diffusion Equa..Document11 pagesThird-And Fifth-Order Finite Volume Schemes For Advection-Diffusion Equation With Variable Coefficients in Semi-Infinite Domain: Finite Volume Schemes For Advection-Diffusion Equa..shiyu xiaNo ratings yet
- Homogeneization Periodic Guy Bonnet IJSS 2016Document47 pagesHomogeneization Periodic Guy Bonnet IJSS 2016auslenderNo ratings yet
- J-HXfer Meshless ConjugateDocument13 pagesJ-HXfer Meshless Conjugatebardock277No ratings yet
- Comparison of Various Fluid-Structure Interaction Methods For Deformable BodiesDocument32 pagesComparison of Various Fluid-Structure Interaction Methods For Deformable BodiesVincent IrawanNo ratings yet
- A Roe Type Scheme - Two Phase Flow (Pelanti and Mangney)Document35 pagesA Roe Type Scheme - Two Phase Flow (Pelanti and Mangney)Avinash SajwanNo ratings yet
- Variational Methods for Boundary Value Problems for Systems of Elliptic EquationsFrom EverandVariational Methods for Boundary Value Problems for Systems of Elliptic EquationsNo ratings yet
- Pressure PointsDocument3 pagesPressure PointsAbhinawNo ratings yet
- Create PathDocument8 pagesCreate PathAbhinawNo ratings yet
- Corporate Rules DoneDocument2 pagesCorporate Rules DoneAbhinawNo ratings yet
- Gone RouteDocument2 pagesGone RouteAbhinawNo ratings yet
- AbstractDocument1 pageAbstractAbhinawNo ratings yet
- Systematic ThiteringDocument2 pagesSystematic ThiteringAbhinawNo ratings yet
- Historical EvidancesDocument4 pagesHistorical EvidancesAbhinawNo ratings yet
Multip Physics
Multip Physics
Uploaded by
AbhinawCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Multip Physics
Multip Physics
Uploaded by
AbhinawCopyright:
Available Formats
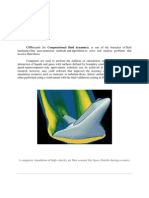
This work presents an overview of techniques that enable the construction of collocated finite volume
method for complex multi-physics models in multiple domains. Each domain is characterized by the
properties of heterogeneous media and features a distinctive multi-physics model. Coupling together
systems of equations, corresponding to multiple unknowns, results in a vector flux. The finite volume
method requires continuity of intradomain and interdomain vector fluxes. The continuous flux is
derived using an extension of the harmonic averaging point concept. Often, the collocated coupling of
the equations results in a saddle-point problem subject to inf-sup stability issues. These issues are
addressed by the eigen-splitting of indefinite matrix coefficients encountered in the flux expression.
The application of the techniques implemented within INMOST platform to hydraulic fracturing
problem is demonstrated.
For elliptic boundary value problems (the diffusion equation and elasticity theory ones) with highly
varying coefficients, there are proposed iterative methods with the number of iterations independent of
the coefficient jumps. In the differential case these methods take solving the boundary value problem
for the Poisson equation at each step of iterations while in the finite difference (finite element)
approximation it is possible to use another operator as a preconditioner.
You might also like
- 1 s2.0 S0377042720301631 MainDocument14 pages1 s2.0 S0377042720301631 Mainmat20d002No ratings yet
- Multivariable Calculus - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument4 pagesMultivariable Calculus - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediad_richard_dNo ratings yet
- C CC C C CDocument6 pagesC CC C C Canushka56No ratings yet
- Jeas 1006 17Document10 pagesJeas 1006 17Oscar AdrianNo ratings yet
- Tutorial: Topic: Finite Element Model Updating Speaker: Wen-Wei LinDocument8 pagesTutorial: Topic: Finite Element Model Updating Speaker: Wen-Wei LinlawfulNo ratings yet
- A Fitted Mesh Method For Partial Differential Equations With A Time LagDocument12 pagesA Fitted Mesh Method For Partial Differential Equations With A Time LagIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Finite Element-1508.02138Document20 pagesFinite Element-1508.02138GrantHermanNo ratings yet
- A Comparitive Study of FVM and FDMDocument7 pagesA Comparitive Study of FVM and FDMHassan AbdelmoamenNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Traffic FlowDocument7 pagesAnalysis of Traffic FlowmansNo ratings yet
- SPE-173200-MS Algebraic Multiscale Solver For Flow in Heterogeneous Fractured Porous MediaDocument14 pagesSPE-173200-MS Algebraic Multiscale Solver For Flow in Heterogeneous Fractured Porous MediaDavid MontoyaNo ratings yet
- Efg 1Document41 pagesEfg 1malenenivamsiNo ratings yet
- Finite Elements in Analysis and Design: Manuel Garcia, Jorge Gutierrez, Nestor RuedaDocument7 pagesFinite Elements in Analysis and Design: Manuel Garcia, Jorge Gutierrez, Nestor RuedachrissbansNo ratings yet
- Solution Techniques For The Vorticity-Streamfunction Formulation O F Two-Dimensional Unsteady Incompressible FlowsDocument25 pagesSolution Techniques For The Vorticity-Streamfunction Formulation O F Two-Dimensional Unsteady Incompressible FlowsIshwar SinghNo ratings yet
- c34 ECM MBI PDFDocument55 pagesc34 ECM MBI PDFThangadurai Senthil Ram PrabhuNo ratings yet
- UNIT NO 1: Finite Difference SchemesDocument9 pagesUNIT NO 1: Finite Difference SchemesAbhishek SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Saurel 2001Document23 pagesSaurel 2001Djamila BENYOUCEFNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 PDFDocument14 pagesAssignment 2 PDFChinmay GosaviNo ratings yet
- A Finite Volume Method On NURBS Geometries and Its Application in Isogeometric Fluid-Structure InteractionDocument22 pagesA Finite Volume Method On NURBS Geometries and Its Application in Isogeometric Fluid-Structure InteractionbradjenoNo ratings yet
- 2016 CMAME Ms Flux Basis SDDocument34 pages2016 CMAME Ms Flux Basis SDDanail VassilevNo ratings yet
- Newrobustandefficient Global Iterations For Large Deformation Finite Element Analysis of Beams and Shells With Material NonlinearityDocument28 pagesNewrobustandefficient Global Iterations For Large Deformation Finite Element Analysis of Beams and Shells With Material NonlinearityRey NCNo ratings yet
- A Finite Difference Method and Effective Modification of Gradient Descent Optimization Algorithm For MHD Fluid Flow Over A Linearly Stretching SurfaceDocument21 pagesA Finite Difference Method and Effective Modification of Gradient Descent Optimization Algorithm For MHD Fluid Flow Over A Linearly Stretching Surfaceyasir.nawaz.mathsNo ratings yet
- JP FernandezDocument251 pagesJP FernandezDiiana WhiteleyNo ratings yet
- A Cartesian Grid Method For Solving The Two-Dimensional Streamfunction-Vorticity Equations in Irregular RegionsDocument45 pagesA Cartesian Grid Method For Solving The Two-Dimensional Streamfunction-Vorticity Equations in Irregular RegionsHamid MojiryNo ratings yet
- An Eulerian Lagrangian Scheme For Solving Large Deformation Fluid Structure Interaction ProblemsDocument31 pagesAn Eulerian Lagrangian Scheme For Solving Large Deformation Fluid Structure Interaction ProblemsUmair QaziNo ratings yet
- Spe 79709 Pa P PDFDocument9 pagesSpe 79709 Pa P PDFtomk2220No ratings yet
- Finite Volume MethodDocument4 pagesFinite Volume MethodpoliskarmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Literature SurveyDocument12 pagesChapter Two Literature Surveymasyuki1979No ratings yet
- A Brief Description of These MethodsDocument6 pagesA Brief Description of These MethodsQi PanNo ratings yet
- MECH3780 Fluid Mechanics 2 and CFDDocument14 pagesMECH3780 Fluid Mechanics 2 and CFDninibearNo ratings yet
- Preprint - Multiscale VEM For The Biot Consolidation Analysis - of Complex and Highly Heterogeneous Domains-MinDocument78 pagesPreprint - Multiscale VEM For The Biot Consolidation Analysis - of Complex and Highly Heterogeneous Domains-MinAbhilash SreekumarNo ratings yet
- Método de Volumen Finito de Alta Orden para Resolver Fluidos ViscoelásticosDocument14 pagesMétodo de Volumen Finito de Alta Orden para Resolver Fluidos ViscoelásticosAaron Arango AyalaNo ratings yet
- Local Discontinuous Galerkin Methods For High-Order Time-Dependent Partial Differential EquationsDocument57 pagesLocal Discontinuous Galerkin Methods For High-Order Time-Dependent Partial Differential EquationsAman JalanNo ratings yet
- Heaviside's Operators and Contour IntegralsDocument28 pagesHeaviside's Operators and Contour IntegralsalpcruzNo ratings yet
- Multi Scale Mixed Finite Element Modeling of Coupled Wellbore Near-Well FlowDocument9 pagesMulti Scale Mixed Finite Element Modeling of Coupled Wellbore Near-Well Flowpetar_damyanovNo ratings yet
- CFDDocument18 pagesCFDPriya PatankarNo ratings yet
- Jac M 189861710880200Document14 pagesJac M 189861710880200Ahmed El KhalfiNo ratings yet
- Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH) : An Overview and Recent DevelopmentsDocument52 pagesSmoothed Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH) : An Overview and Recent DevelopmentsPac Agathe100% (1)
- TMMV08 A1 2024Document9 pagesTMMV08 A1 2024adityaNo ratings yet
- ATOMIZAÇÃO phd8Document9 pagesATOMIZAÇÃO phd8eustaccoNo ratings yet
- A Fully Coupled Finite Volume Solver For The Solution of Incompressible Flows On Locally Refined Non-Matching Block-Structured GridsDocument12 pagesA Fully Coupled Finite Volume Solver For The Solution of Incompressible Flows On Locally Refined Non-Matching Block-Structured GridsErnesto Delfino AguirreNo ratings yet
- Meshless Methods1Document4 pagesMeshless Methods1herevenkatNo ratings yet
- Mathematics With CoverDocument22 pagesMathematics With CoverVaradharajan RNo ratings yet
- Eotvos NumberDocument13 pagesEotvos NumberFoamboom SatjaritanunNo ratings yet
- Module 1: Introduction To Finite Element Analysis Lecture 1: IntroductionDocument6 pagesModule 1: Introduction To Finite Element Analysis Lecture 1: IntroductionMuhammad DaniyalNo ratings yet
- Euclid - Jam.1350488796 GoodDocument14 pagesEuclid - Jam.1350488796 GoodWei GaoNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods in Fluids - 2020 - Traverso - Efficient Stochastic Finite Element Methods For Flow in HeterogeneousDocument27 pagesNumerical Methods in Fluids - 2020 - Traverso - Efficient Stochastic Finite Element Methods For Flow in HeterogeneousGonzalo BustosNo ratings yet
- Lattice Boltzmann MethodDocument11 pagesLattice Boltzmann MethodNishant KumarNo ratings yet
- Basic Sens Analysis Review PDFDocument26 pagesBasic Sens Analysis Review PDFPratik D UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Mirzajani Et AlDocument30 pagesMirzajani Et AlkhodakaramiNo ratings yet
- HenningDocument43 pagesHenningtinaanaNo ratings yet
- Journal of Computational Physics: Armando Coco, Giovanni RussoDocument38 pagesJournal of Computational Physics: Armando Coco, Giovanni RussoAnonymous tIwg2AyNo ratings yet
- Method of Successive Weighted Averages MSWA and SeDocument20 pagesMethod of Successive Weighted Averages MSWA and SeAnonymous Y2ibaULes1No ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Science: Paul W.C. Northrop, P.A. Ramachandran, William E. Schiesser, Venkat R. SubramanianDocument8 pagesChemical Engineering Science: Paul W.C. Northrop, P.A. Ramachandran, William E. Schiesser, Venkat R. SubramanianAbraham SilesNo ratings yet
- Third-And Fifth-Order Finite Volume Schemes For Advection-Diffusion Equation With Variable Coefficients in Semi-Infinite Domain: Finite Volume Schemes For Advection-Diffusion Equa..Document11 pagesThird-And Fifth-Order Finite Volume Schemes For Advection-Diffusion Equation With Variable Coefficients in Semi-Infinite Domain: Finite Volume Schemes For Advection-Diffusion Equa..shiyu xiaNo ratings yet
- Homogeneization Periodic Guy Bonnet IJSS 2016Document47 pagesHomogeneization Periodic Guy Bonnet IJSS 2016auslenderNo ratings yet
- J-HXfer Meshless ConjugateDocument13 pagesJ-HXfer Meshless Conjugatebardock277No ratings yet
- Comparison of Various Fluid-Structure Interaction Methods For Deformable BodiesDocument32 pagesComparison of Various Fluid-Structure Interaction Methods For Deformable BodiesVincent IrawanNo ratings yet
- A Roe Type Scheme - Two Phase Flow (Pelanti and Mangney)Document35 pagesA Roe Type Scheme - Two Phase Flow (Pelanti and Mangney)Avinash SajwanNo ratings yet
- Variational Methods for Boundary Value Problems for Systems of Elliptic EquationsFrom EverandVariational Methods for Boundary Value Problems for Systems of Elliptic EquationsNo ratings yet
- Pressure PointsDocument3 pagesPressure PointsAbhinawNo ratings yet
- Create PathDocument8 pagesCreate PathAbhinawNo ratings yet
- Corporate Rules DoneDocument2 pagesCorporate Rules DoneAbhinawNo ratings yet
- Gone RouteDocument2 pagesGone RouteAbhinawNo ratings yet
- AbstractDocument1 pageAbstractAbhinawNo ratings yet
- Systematic ThiteringDocument2 pagesSystematic ThiteringAbhinawNo ratings yet
- Historical EvidancesDocument4 pagesHistorical EvidancesAbhinawNo ratings yet