Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CH 6 Rational Expressions Notes With Answers
CH 6 Rational Expressions Notes With Answers
Uploaded by
EnglishNotes PPSC,FPSCOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CH 6 Rational Expressions Notes With Answers
CH 6 Rational Expressions Notes With Answers
Uploaded by
EnglishNotes PPSC,FPSCCopyright:
Available Formats
Pre-Calculus 11
Chapter 6 – Rational Expressions
First Name: ________________________ Last Name: ________________________ Block: ______
Ch. 6 – Rational Expressions Notes
6.1 – RATIONAL EXPRESSIONS 2
Ch. 6. 1 HW: p. 317 # 1 – 6 odd letters, 8, 9, 20, 25. 3
6.1 – EXTRA PRACTICE 4
6.2 – MULTIPLYING AND DIVIDING RATIONAL EXPRESSIONS 6
Ch. 6.2 HW: p. 326 # 1 – 4 odd letters, 5 – 7 all, 8, 15, 16, 18 8
6.3 – ADDING AND SUBTRACTING RATIONAL EXPRESSIONS 9
Ch. 6.3 HW: p. 336 # 1 – 11 (odd letters), 12, 15, 18 11
6.4 – RATIONAL EQUATIONS 12
Ch. 6.4 HW: p. 349 # 1 – 13, 14 17
CH. 6 ‐ REVIEW 17
Ch. 6 Review HW: p. 352 All #s, odd letters, p. 355 # 1 – 9 19
Created by Ms. Lee 1 of 19
Reference: McGraw-Hill Ryerson Pre-Calculus 11
Pre-Calculus 11
Chapter 6 – Rational Expressions
6.1 – Rational Expressions
Definition:
Rational Expression is an algebraic fraction with a numerator and a denominator that are polynomials.
Non-Permissible Values: Given a rational expression, non-permissible values are all values of a
variable that make the denominator zero.
Examples: Determine Non-permissible values given a rational expression.
Rational Expressions Non-permissible Value(s)
2x 1
x
2
x5
3x
2x 3
3x
x(2 x 5)
x 1
( x 2)( x 3)
2 p 1
2
p p 12
Created by Ms. Lee 2 of 19
Reference: McGraw-Hill Ryerson Pre-Calculus 11
Pre-Calculus 11
Chapter 6 – Rational Expressions
Examples: Simplify Rational Expressions and determine non-permissible values
Rational Expression Simplified Expression Non-permissible Values
3x 6
2 x 2 x 10
1 t
t 2 1
2 y 2 y 10
y 2 3 y 10
6 2m
m2 9
Examples: Rational Expression in two variables
16 x 2 9 y 2
Simplify .
8x 6 y
a) How can you express non-permissible values for x in terms of y?
b) How can you express non-permissible values for y in terms of x?
Ch. 6. 1 HW: p. 317 # 1 – 6 odd letters, 8, 9, 20, 25.
Created by Ms. Lee 3 of 19
Reference: McGraw-Hill Ryerson Pre-Calculus 11
Pre-Calculus 11
Chapter 6 – Rational Expressions
6.1 – Extra Practice
Created by Mr. Ko
Please use a separate sheet of paper for this worksheet. SHOW ALL WORK!
1) State weather each expression is a rational expression. If the expression is not rational, explain
why.
x a 8 x
a) b) c) d)
4 3 m x
x4 x x 4
e) f) x 2 x 6 g) h)
2x 3 x 1
3
3 a 1 x y
i) j)
a 5b 3x
2) Evaluate each rational expression for x 2 and y 3 .
x2 3x 2 y x3 1 x2 2x 1
a) b) c) d)
3y 1 xy y 3 x2 1
3) For which value(s) of x is each expression not defined?
2 2x 1 x2 x2 1
a) b) c) d)
x 1 5 2x 7 x3 8
3x 4 6x 5 3 x 2 81
e) f) g) h)
x2 9 2x x 4 x3 x3 8
4) Reduce to lowest terms.
36x 5x2 6a 2 c 9m 2 n
a) b) c) d)
4 y 15 x 8ab m5
5) Reduce to lowest terms.
a 9b x 5 16 4 a 7 x 14
a) b) c) d)
3a 27b 10 2 x 32 8a 5 x 10
6) Simplify each expression. Identify the nonpermissible value(s) of x.
2x2 6x 2 x 2 10 x 4 x 2 12 x 3x2 6 x
a) b) c) d)
5x 4 x 20 x3 14 7 x
Created by Ms. Lee 4 of 19
Reference: McGraw-Hill Ryerson Pre-Calculus 11
Pre-Calculus 11
Chapter 6 – Rational Expressions
7) Simplify.
cd 3xy 18 y 2 10 xy 15 x 2 y 60 a 2b 2 24 ab
a) b) c) d)
d c 12 y 2 2xy 6x2 4x 16 ab 40 a 2b 2
8) Simplify each expression, if possible. Identify any nonpermissible value(s) for each variable.
a 2 5a 14 x 3 r2 9 x4
a) b) c) d) 2
a 6a 8
2
x 3x 18
2
r 6r 9
2
x 16
9) Simplify.
9 a 2 16b 2 a 2 ab 6b 2 8t 2 32 c 2 5cd 24 d 2
a) b) c) d)
6 a 2 8ab a 2 2 ab 2t 2 12t 16 c 2 7 cd 12 d 2
e)
a 2 10 ab 24b 2
f)
x 2
36 x 2 25
a 2 36b 2 x 2 x 30
10) Simplify.
32 2 a 2 2 x 3 28 x 2 102 x
a) b)
4 a 2 44 a 112 18 x 2 x 3
3a 2 33a 90 x4 y 4
x2 y2 x2 5xy 4 y2
c) d)
6 a 2 6 a 120
Answers
1) a) Not rational, b) Rational, c) Rational, d) Not rational, e) Rational, f) Rational, g) Not rational ,
h) Rational, i) Not rational, j) Rational
3 1
2) a) 0, b) –2, c) , d) c
2 3
7
3) a) –1, b) Expression is defined for all values of x , c) , d) 2, e) 3 , f) 0, –4, g) 0
2
h) Expression is defined for all values of x
9 x x 3ac 9n 1 1 1 7
4) a) , b) , c) , d) 3 5) a) , b) , c) , d)
y 3 4b m 3 2 2 5
2x 6
6) a) , all real values of x , nonpermissible value: x 0
5
x
b) , all real values of x , nonpermissible value: x 5
2
c) 4x , all real values of x , nonpermissible value: x 3
3x
d) , all real values of x , nonpermissible value: x 2
7
3 5 y 3
7) a) –1, b) , c) , d)
2 2 2
a7 1 r 3 1
8) a) , a 4, 2 , b) , x 6, 3 , c) , r 3 , d) , x 4, 4
a4 x6 r 3 x4
3a 4b a 3b 4t 8 c 8d a 4b
9) a) , b) , c) , d) , e) , f) x 6 x 5
2a a t4 c 4d a 6b
a4 x 17 a6 x y
10) a) , b) , c) , d)
14 2a 3 x 2a 8 x 4y
Created by Ms. Lee 5 of 19
Reference: McGraw-Hill Ryerson Pre-Calculus 11
Pre-Calculus 11
Chapter 6 – Rational Expressions
6.2 – Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions
Recap:
Multiply. Write the answer in simplest form.
5 16
1)
18 15
14 18
2)
6 21
4 x 2 y 2
3)
3 xy 8 x
2x3 15 xy 3
4)
5y2 x 2 y
Divide. Write the answer in simplest form.
16 12
1)
25 15
3 15
2)
100 10
6 x 2 y 3x 2 y 2
3)
4x 2y
3x 5 y 15 x
4)
10 xy 20 x 2 y
Similarly:
Multiply. Write the answer in simplest form. Identify all non-permissible values.
d 2rh
1)
2r d 2
x 3 2x 6
2)
3 x 3x 9
Created by Ms. Lee 6 of 19
Reference: McGraw-Hill Ryerson Pre-Calculus 11
Pre-Calculus 11
Chapter 6 – Rational Expressions
y 2 9 r 2 r
3)
r 3 r y 3
x 1 x2
4)
x 2 5x 6 x 2 5x 4
Divide. Write the answer in simplest form. State the non-permissible values.
2x 4
1) x 2
8
x3 x
2)
x 3 4 x 12
x 7 x 2 2 x 15
3)
x 4 x 2 x 20
Created by Ms. Lee 7 of 19
Reference: McGraw-Hill Ryerson Pre-Calculus 11
Pre-Calculus 11
Chapter 6 – Rational Expressions
8y2 2y 3 2 y2 3y 2 3 4 y
4)
y2 1 2y 2 y 1
Apply:
A sphere is contained in a rectangular box such that the sides of the sphere are touching the sides of the
box. What fraction of the volume of the box does the sphere occupy? Model the situation using a
quotient of rational expression (in simplest form). Then write this value as a percent.
4r 3
Note: Vcube length 3 Vsphere
3
Ch. 6.2 HW: p. 326 # 1 – 4 odd letters, 5 – 7 all, 8, 15, 16, 18
Created by Ms. Lee 8 of 19
Reference: McGraw-Hill Ryerson Pre-Calculus 11
Pre-Calculus 11
Chapter 6 – Rational Expressions
6.3 – Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions
Recap: Reduce first if possible, get a common denominator and add/subtract.
Add. Write the answer in simplest/reduced form.
2
1) 2
3
3 1
2)
4 3
2 4
3)
3 5
Subtract. Write the answer in simplest/reduced form.
2 3
1)
5 15
5 2
2)
2 3
3 3
3)
4 16
3
4) 3
7
Similarly:
Add/Subtract. Write the answer in simplest form. Identify all non-permissible values.
1 3
1)
x 2
1 2
2)
2a 3a 2
3y 3
3) 1
2 xy
2 xy
Created by Ms. Lee 9 of 19
Reference: McGraw-Hill Ryerson Pre-Calculus 11
Pre-Calculus 11
Chapter 6 – Rational Expressions
Add/Subtract. Write the answer in simplest form. Identify all non-permissible values.
m m 1
1)
n n
10 1 8 2m
2)
4m 3 4m 3
5x 2 x 3 6x 4x 2 6x 5
3)
( x 3)( x 1) ( x 3)( x 1) ( x 3)( x 1)
Add/Subtract. Write the answer in simplest form. Identify all non-permissible values.
4 3
5)
p 1 p 1
2
x 1 x2
6)
x2 x 6 x 2 4x 3
Created by Ms. Lee 10 of 19
Reference: McGraw-Hill Ryerson Pre-Calculus 11
Pre-Calculus 11
Chapter 6 – Rational Expressions
4
2
y
7)
4
y
y
1 1
8) x4 x4
x 1
x 16 x 4
2
Ch. 6.3 HW: p. 336 # 1 – 11 (odd letters), 12, 15, 18
Created by Ms. Lee 11 of 19
Reference: McGraw-Hill Ryerson Pre-Calculus 11
Pre-Calculus 11
Chapter 6 – Rational Expressions
6.4 – Rational Equations
Definition:
Rational Equation: An equation containing at least one rational expression.
Example: Solve each rational equation. State any non-permissible values.
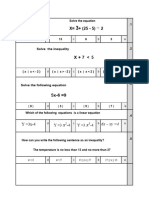
x 7
1) 3
4 x
2 10 1
2)
2
x 4 6 x 12 x 2
Created by Ms. Lee 12 of 19
Reference: McGraw-Hill Ryerson Pre-Calculus 11
Pre-Calculus 11
Chapter 6 – Rational Expressions
9 4 18
3)
y 3 y 6 y 9 y 18
2
3x 5 25
4)
x 2 x 3 x2 x 6
Created by Ms. Lee 13 of 19
Reference: McGraw-Hill Ryerson Pre-Calculus 11
Pre-Calculus 11
Chapter 6 – Rational Expressions
4k 1 k 1 k 2 4k 24
5)
k 2 k 2 k2 4
6) Two friends share a paper route. Sheena can deliver the papers in 40 min. Jeff can cover the same
route in 50 min. How long, to the nearest minute, does the paper route take if they work together?
Fraction of papers delivered by Sheena in Fraction of papers delivered by Jeff in
1 minute: 1 minute:
2 minutes: 2 minute:
3 minutes: 3 minutes:
… …
x minutes: x minutes:
Created by Ms. Lee 14 of 19
Reference: McGraw-Hill Ryerson Pre-Calculus 11
Pre-Calculus 11
Chapter 6 – Rational Expressions
7) Stella takes 4 h to paint a room. It takes Jose 3 h to paint the same area. How long will the paint
job take if they work together?
8) Kyra mows a lawn in 40 min. When Mark and Kyra work together, they can mow the lawn in 24
min. How long would it take Mark to mow the lawn on his own?
Created by Ms. Lee 15 of 19
Reference: McGraw-Hill Ryerson Pre-Calculus 11
Pre-Calculus 11
Chapter 6 – Rational Expressions
9) Given two consecutive numbers, 5 is added to the first number (smaller #) and two is subtracted
from the second number (bigger #). The quotient of the new numbers (first divided by second) is
7
. Determine the numbers algebraically.
4
10)
Created by Ms. Lee 16 of 19
Reference: McGraw-Hill Ryerson Pre-Calculus 11
Pre-Calculus 11
Chapter 6 – Rational Expressions
A boat travels 4 km upstream in the same time that it takes the boat to travel 12 km downstream.
The average speed of the current is 3km/h. What is the average speed of the boat in still water?
Let speed of the boat in still water = s
What would be the speed of the boat going uphill if the current, with the speed of 3 km/h, is against
the boat’s direction?
What would be the speed of the boat going downhill if the current, with the speed of 3km/h is in
the same direction as the boat?
Ch. 6.4 HW: p. 349 # 1 – 13, 14
Ch. 6 - Review
1. Simplify the rational expression:
3x 2 y 3
2x 2 y 3
2
6x3 y 3x 2 y 3
Created by Ms. Lee 17 of 19
Reference: McGraw-Hill Ryerson Pre-Calculus 11
Pre-Calculus 11
Chapter 6 – Rational Expressions
2. Simplify. Identify any non-permissible values.
x 2 3x 2 x3 1
2
x 4 2
x 3x x2
3. Simplify. Identify any non-permissible values.
2x x 1
4 x 2 9 2 x 2 5x 3 2 x 3
Created by Ms. Lee 18 of 19
Reference: McGraw-Hill Ryerson Pre-Calculus 11
Pre-Calculus 11
Chapter 6 – Rational Expressions
4. Solve. Identify all non-permissible values.
5 x3
2
x x6 x2
2
5. True or False
x( x 2)( x 1)
a) ________ x
( x 1)(2 x)
x( x 2)( x 1)
b) ________ x , x 1, 2
( x 1)(2 x)
Ch. 6 Review HW: p. 352 All #s, odd letters, p. 355 # 1 – 9
Created by Ms. Lee 19 of 19
Reference: McGraw-Hill Ryerson Pre-Calculus 11
You might also like
- TSI (Placement Test) College Level Math Assessment TestDocument17 pagesTSI (Placement Test) College Level Math Assessment TestMohammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- Course Review: Chapter 1 Polynomial FunctionsDocument5 pagesCourse Review: Chapter 1 Polynomial FunctionsKnoll711100% (1)
- Updated PDSDocument4 pagesUpdated PDSGloria Obra BarrogaNo ratings yet
- Rational Expressions - Assignment BookletDocument44 pagesRational Expressions - Assignment BookletRand AhmadNo ratings yet
- Sem 2 Review For Final (Virtual)Document12 pagesSem 2 Review For Final (Virtual)soNo ratings yet
- Section 6.3 Extra Practice: Wherever Applicable, State The Non-Permissible Values For The VariablesDocument1 pageSection 6.3 Extra Practice: Wherever Applicable, State The Non-Permissible Values For The VariablesMohammad AlamNo ratings yet
- Rational ExpressionsDocument2 pagesRational ExpressionsRazzler DazzlerNo ratings yet
- ch3 Worksheets EngDocument14 pagesch3 Worksheets EngDarwing LiNo ratings yet
- G-7 3rd Periodic Test MathematicsDocument4 pagesG-7 3rd Periodic Test MathematicsLhot Bilds Siapno0% (1)
- Intermediate Algebra Review Questions For Computer Enhanced ExamDocument8 pagesIntermediate Algebra Review Questions For Computer Enhanced ExamApril Diana CruzNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Excercise 1Document2 pagesFinal Exam Excercise 1Esther LiongNo ratings yet
- Mhfexamreview 2Document4 pagesMhfexamreview 2Oksana MandrykNo ratings yet
- 1) C1 Algebra and FunctionsDocument30 pages1) C1 Algebra and Functionssaud ahmedNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of MathematicsDocument2 pagesFundamental of MathematicsDee-vhine Gee Raposas-RabutNo ratings yet
- G8-Diagnostic TestDocument4 pagesG8-Diagnostic TestJolette StevensNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Chapter 5indices - and - LogarithmDocument14 pagesForm 4 Chapter 5indices - and - LogarithmyokekeannNo ratings yet
- 10 Arts CH # 2 TestDocument2 pages10 Arts CH # 2 TestAli ButtNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Inequalities and Absolute ValuesDocument4 pagesChapter 2: Inequalities and Absolute Valueszan2812No ratings yet
- Model Ukpm 1 Set 1 The Question Paper Consists of 30 QuestionsDocument12 pagesModel Ukpm 1 Set 1 The Question Paper Consists of 30 QuestionsWAN NUR ALEEYA TASNIM BINTI WAN MOHAMED HAZMAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Basic AlgebraDocument11 pagesChapter 2 - Basic AlgebraF1001 NUR SHUHADA AHMADNo ratings yet
- All Exam ReviewDocument8 pagesAll Exam Reviewnubbynubgames3No ratings yet
- Math80reviewCh 5Document3 pagesMath80reviewCh 5besufekadmaregu981No ratings yet
- Practice Exam S2 14-15Document13 pagesPractice Exam S2 14-15David MartinNo ratings yet
- Garde 8 FinalDocument9 pagesGarde 8 FinalPaul MeratzisNo ratings yet
- 5.8 Practice TestDocument2 pages5.8 Practice TestRiasat AzimNo ratings yet
- Onlayn TestDocument2 pagesOnlayn Testiskandarbuyuk9999No ratings yet
- نموذج الاختبار المحاكي الثاني للصف الثالث المتوسطDocument3 pagesنموذج الاختبار المحاكي الثاني للصف الثالث المتوسطakamel7712No ratings yet
- Basic Worksheet Social1Document7 pagesBasic Worksheet Social1Belsty Wale KibretNo ratings yet
- First Montly Add Math f4Document2 pagesFirst Montly Add Math f4Nato Abdul RahimNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 8-Marigold/ Sampaguita MULTIPLE CHOCE: Choose The Letter of The Correct Answer and Write It On The SpaceDocument4 pagesMathematics 8-Marigold/ Sampaguita MULTIPLE CHOCE: Choose The Letter of The Correct Answer and Write It On The SpaceIvy Jane MalacastaNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarterly Test in Mathematics StudentsDocument7 pages1st Quarterly Test in Mathematics StudentsIrish Rhea FamodulanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 PolynomialsDocument29 pagesChapter 6 PolynomialsJihah ZanuddinNo ratings yet
- Math 8 1st Exam 2Document2 pagesMath 8 1st Exam 2isipMath Tutorial100% (2)
- 2A02 Supp Sol 01eDocument4 pages2A02 Supp Sol 01ewncfpnqzxkNo ratings yet
- Mathematic PracticeDocument3 pagesMathematic PracticekirengaremezokellyNo ratings yet
- Beginning Algebra 9Th Edition Baratto Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesBeginning Algebra 9Th Edition Baratto Test Bank Full Chapter PDFmarnie.faber139100% (19)
- Algebra 1 Final Exam ReviewDocument3 pagesAlgebra 1 Final Exam ReviewblakeNo ratings yet
- QM 016 Question PolyDocument3 pagesQM 016 Question PolyamerNo ratings yet
- Summer Packet For BC CalcDocument8 pagesSummer Packet For BC CalcteachopensourceNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Mat093 Sep 2013 N Nov 2013Document8 pagesFinal Exam Mat093 Sep 2013 N Nov 2013Syahir HamidonNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 6 ASM0404 (Function - Limit)Document6 pagesTutorial 6 ASM0404 (Function - Limit)hadassahhadidNo ratings yet
- Mcf3m - Chapter 3 AllDocument18 pagesMcf3m - Chapter 3 AllKiệt Mai AnhNo ratings yet
- Basic Algebra Lecture Notes - Chapter 1Document10 pagesBasic Algebra Lecture Notes - Chapter 1Jálólíddín Rústámóv100% (1)
- Mcf3m - Chapter 2 AllDocument17 pagesMcf3m - Chapter 2 AllKiệt Mai AnhNo ratings yet
- Practica 1Document16 pagesPractica 1Charin HerreraNo ratings yet
- 5 Simplifying Radical ExpressionsDocument53 pages5 Simplifying Radical ExpressionsMark Anthony B. IsraelNo ratings yet
- Nota Chapter 6Document11 pagesNota Chapter 6jujujue.03No ratings yet
- Test Question 12-05-23Document5 pagesTest Question 12-05-23Sheena Tabaog GabuyoNo ratings yet
- Algebra 2 Final Practice TestDocument17 pagesAlgebra 2 Final Practice TestSUNGMIN CHOINo ratings yet
- 24 Ext 8Document2 pages24 Ext 8api-3706821No ratings yet
- MHF4U - Final Review P4 PDFDocument7 pagesMHF4U - Final Review P4 PDFBảo TrânNo ratings yet
- 06rational Expressions PDFDocument2 pages06rational Expressions PDFangelique poNo ratings yet
- Mathematics-8 - Monthly Test-1Document6 pagesMathematics-8 - Monthly Test-1Rafael CaitomNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Maths Mock ExamDocument26 pagesForm 2 Maths Mock ExammahinkamNo ratings yet
- Cycle 3 Review CYUDocument8 pagesCycle 3 Review CYUvNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic - Test All PDFDocument6 pagesDiagnostic - Test All PDFberna goNo ratings yet
- PT 1 Limits and ContinuityDocument2 pagesPT 1 Limits and ContinuityChristine EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Maths 10Document2 pagesMaths 10Fawad Khan WardagNo ratings yet
- Inequalities ExercisesDocument6 pagesInequalities ExercisesHelen GaleanoNo ratings yet
- Dividing Polynomial (Remainder Theorem) MR - Bayoumy BookDocument5 pagesDividing Polynomial (Remainder Theorem) MR - Bayoumy BookAhmed fatahNo ratings yet
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)From EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)No ratings yet
- m3f15 wrksht6Document4 pagesm3f15 wrksht6EnglishNotes PPSC,FPSCNo ratings yet
- Min Max Quadratics HandoutDocument3 pagesMin Max Quadratics HandoutEnglishNotes PPSC,FPSCNo ratings yet
- Factoring Polynomials Part 2Document2 pagesFactoring Polynomials Part 2EnglishNotes PPSC,FPSCNo ratings yet
- Implicit Differentiation SolutionsDocument6 pagesImplicit Differentiation SolutionsEnglishNotes PPSC,FPSCNo ratings yet
- 03 - Power Constant and Sum RulesDocument4 pages03 - Power Constant and Sum RulesEnglishNotes PPSC,FPSCNo ratings yet
- U1D2 Homework SolutionsDocument5 pagesU1D2 Homework SolutionsEnglishNotes PPSC,FPSCNo ratings yet
- Usborne Little Childrens Space Activity BookDocument70 pagesUsborne Little Childrens Space Activity BookEnglishNotes PPSC,FPSCNo ratings yet
- Usborne Little Childrens Zoo Activity Book 2Document62 pagesUsborne Little Childrens Zoo Activity Book 2EnglishNotes PPSC,FPSCNo ratings yet
- The Old Woman Who Swallowed A Fly Horne Sarah Usborne First Reading L3Document25 pagesThe Old Woman Who Swallowed A Fly Horne Sarah Usborne First Reading L3EnglishNotes PPSC,FPSCNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Analysis: Dianna May C. MacapulayDocument19 pagesQuantitative Analysis: Dianna May C. MacapulayDianna May Combate MacapulayNo ratings yet
- Fort Worth ISDDocument224 pagesFort Worth ISDSteveNo ratings yet
- Archmere To Implement Tech "Refresh" of 1:1 Laptop Program For Next FallDocument2 pagesArchmere To Implement Tech "Refresh" of 1:1 Laptop Program For Next FallJoseph MarinelliNo ratings yet
- Narrative Report 4th Week JaysonDocument3 pagesNarrative Report 4th Week Jaysonapi-297926402No ratings yet
- Music As Fine Art: Satisfaction, and Enjoyment of Doing So. He Does Not Gaze at This Beauty in Order To Ensure HisDocument12 pagesMusic As Fine Art: Satisfaction, and Enjoyment of Doing So. He Does Not Gaze at This Beauty in Order To Ensure Hisaugustine abellanaNo ratings yet
- Part of Speech: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleDocument24 pagesPart of Speech: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleSiti RahimahNo ratings yet
- Inadequate Self-Care Behaviors Among Malaysian DiaDocument5 pagesInadequate Self-Care Behaviors Among Malaysian DiatikaNo ratings yet
- Destiny Livers - ResumeDocument1 pageDestiny Livers - Resumeapi-319147745No ratings yet
- MosabIbrahim PDFDocument1 pageMosabIbrahim PDFMosab IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Subject: General Chemistry Test,: Date: May 2015Document7 pagesSubject: General Chemistry Test,: Date: May 2015PHƯƠNG ĐẶNG YẾNNo ratings yet
- The One and Only Ivan Novel Study PreviewDocument12 pagesThe One and Only Ivan Novel Study Previewsuchi ravalia33% (3)
- Group 1 Subjects Ca Inter - Google SearchDocument1 pageGroup 1 Subjects Ca Inter - Google Searchy7frhdvm5fNo ratings yet
- Course Concept Extraction in MOOCs Via Embedding-Based Graph PropagationDocument10 pagesCourse Concept Extraction in MOOCs Via Embedding-Based Graph PropagationPhinodaNo ratings yet
- CHEM F110 Chemistry Laboratory I Sem 2022-23HODocument2 pagesCHEM F110 Chemistry Laboratory I Sem 2022-23HOjohn doeNo ratings yet
- Meghan Mallon: ObjectiveDocument2 pagesMeghan Mallon: Objectiveapi-363313299No ratings yet
- Classcraft - Class CodeDocument13 pagesClasscraft - Class Codepesonalaguna12No ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Human Resource Management Mba Fall 2014Document8 pagesChapter 7 Human Resource Management Mba Fall 2014Amir Al HusseinNo ratings yet
- Arts8 - q1 - Mod5 - Southeast Asian Artifacts in One - S Creation - FINAL08032020 PDFDocument26 pagesArts8 - q1 - Mod5 - Southeast Asian Artifacts in One - S Creation - FINAL08032020 PDFilyn dutado67% (3)
- Ethnicity EssayDocument3 pagesEthnicity EssayGh0ssTNo ratings yet
- LibDocument93 pagesLibsamknight2009No ratings yet
- QA Manager CVDocument2 pagesQA Manager CVSetiyanto HeriNo ratings yet
- Abhpa Baby BookDocument32 pagesAbhpa Baby BookAnca BiancaNo ratings yet
- Associate Membership Candidate GuideDocument20 pagesAssociate Membership Candidate GuideKanagha Raj K100% (1)
- IMJ E - Journal May - August 2017 Vol - IV No.2Document58 pagesIMJ E - Journal May - August 2017 Vol - IV No.2Confidence FoundationNo ratings yet
- Anurag CVDocument3 pagesAnurag CV杨鹏No ratings yet
- G123 - CBSE LO. Chapter Wise.Document30 pagesG123 - CBSE LO. Chapter Wise.FREDNo ratings yet
- Dissertation Statement of EthicsDocument5 pagesDissertation Statement of EthicsSomeoneWriteMyPaperSingapore100% (1)
- 03 幼童華語讀本3 (英文版) PDFDocument48 pages03 幼童華語讀本3 (英文版) PDFDonna Chiang TouatiNo ratings yet
- Eapp Q1-L1Document9 pagesEapp Q1-L1Jeanica Delacosta CesponNo ratings yet