Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Emm 302 Solid and Structural Mechanics 1
Emm 302 Solid and Structural Mechanics 1
Uploaded by
anniemusyimiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Emm 302 Solid and Structural Mechanics 1
Emm 302 Solid and Structural Mechanics 1
Uploaded by
anniemusyimiCopyright:
Available Formats
MACHAKOS UNIVERSITY
University Examinations 2018/2019
SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL AND MANUFACTURING ENGINEERING
THIRD YEAR SPECIAL/SUPPLEMENTARY EXAMINATION FOR
BACHELOR OF SCIENCE IN MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
EMM 302: SOLID AND STRUCTURAL MECHANICS 1
DATE: 22/7/2019 TIME: 2.00-4.00 PM
INSTRUCTIONS:
Answer Question One and Any Other Two Questions
QUESTION ONE (30 MARKS)
a) The following data were recorded during the tensile test of a 14-mm-diameter mild steel
rod. The gage length was 50 mm.
Plot the stress-strain diagram and determine the following mechanical properties: (a)
modulus of elasticity; (c) yield point; (d) ultimate strength; and (e) rupture strength.
(12 marks)
b) Define the following types of stresses:
i. Compressive stresses (2 marks)
ii. Shear stresses (2 marks)
Examination Irregularity is punishable by expulsion Page 1 of 4
c) A hollow steel tube with an inside diameter of 100 mm must carry a tensile load of 400
kN. Determine the outside diameter of the tube if the stress is limited to 120 MN/m2.
(4 marks)
d) Differentiate between Von Mises and Tresca’s yield theories (4 marks)
e) Define “Torsion” and state the torsion equation defining all the variables in the equation
(4 marks)
f) Define bulk modulus and shear modulus (2 marks)
QUESTIONS TWO (20 MARKS)
a) The structure in Figure Q2(a) is a truss which is pinned to the floor at point A, and
supported by a roller at point D. Determine the force to all members of the truss.
Figure Q2(a)
b) A hollow bronze shaft of 75 mm outer diameter and 50mm inner diameter is slipped
over a solid steel shaft 50mm diameter and of the same length as the hollow shaft as
shown in figure Q2(b). The two shafts are then fastened rigidly together at their ends.
For bronze, G = 41 GPa, and for steel, G = 80 GPa. What torque can be applied to the
composite shaft without exceeding a shearing stress of 55 MPa in the bronze or 83 MPa
in the steel? (10 marks)
Figure Q2(b)
Examination Irregularity is punishable by expulsion Page 2 of 4
QUESTIONS THREE (20 MARKS)
a) i Differentiate between thick and thin shell pressure vessels (2 marks)
ii A cylindrical pressure vessel is fabricated from steel plating that has a thickness
of 20 mm. The diameter of the pressure vessel is 450 mm and its length is 2.0
m. determine the maximum internal pressure that can be applied if the
longitudinal stress is limited to 140 MPa, and the circumferential stress is
limited to 60 MPa. (6 marks)
b) Letting D = Mean diameter of the spring; d = diameter of the spring; n = number of
active coils; G = modulus of rigidity of spring material; W = axial load on the spring; τ
= maximum shear stress induced in the wire; C = spring index = D/d; p = pitch of coils;
δ = deflection of the spring as a result of axial load, W and Ks = shear stress factor;
i. Derive the spring rate, W/ δ in terms of G, d, C and n. (4 marks)
ii. A helical spring is made from a wire 6 mm diameter and has an outside diameter
of 75 mm. if the permissible shear stress is 350 MPa and modulus of rigidity 84
KN/mm2, find the axial load, W , which the spring can carry and the deflection
per active turn. (8 marks)
QUESTIONS FOUR (20 MARKS)
a) Steel railroad reels 10 m long are laid with a clearance of 3 mm at a temperature of
15°C. At what temperature will the rails just touch? What stress would be induced in
the rails at that temperature if there were no initial clearance? Assume α = 11.7
μm/(m·°C) and E = 200 GPa. (8 marks)
b) A rectangular steel block is loaded as shown in Figure Q4(b)
i. Determine the strain in the direction of each force
ii. Calculate the change in volume
iii. Determine the bulk modulus K and Modulus of rigidity G.
(Assume Poisson’s ratio = 0.25 and Elastic Modulus = 200 GPa)
Examination Irregularity is punishable by expulsion Page 3 of 4
1000 KN
x
480 KN
0.08 m
y
0.25 m
900 KN
Figure Q4(b)
(12 marks)
QUESTIONS FIVE (20 MARKS)
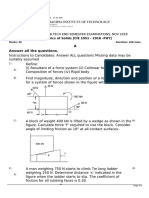
a) An element in plane stress is subjected to stresses = 84 , = −30 and
= −32 . Determine
i. The stresses acting on an element rotated through an angle = 40°
ii. The principal stresses, and
iii. The maximum shear stresses. Show all results on sketches of properly oriented
elements. (15 marks)
b) A short hollow circular cast iron cylinder is to support an axial compressive load
P = 580 kN. The ultimate tensile strength (UTS) of cast iron on compression is 270
Mpa. It is decided to design the cylinder with a wall thickness t = 25mm and a factor of
safety. Calculate the minimum required outside diameter (5 marks)
Examination Irregularity is punishable by expulsion Page 4 of 4
You might also like
- 2019 Summer Question Paper (Msbte Study Resources)Document5 pages2019 Summer Question Paper (Msbte Study Resources)Ashish pathareNo ratings yet
- 3 Hours / 70 Marks: Seat NoDocument5 pages3 Hours / 70 Marks: Seat NoMadao111No ratings yet
- 3 Hours / 70 Marks: Seat NoDocument4 pages3 Hours / 70 Marks: Seat NoKkNo ratings yet
- Previous Year Question Paper With AnswersDocument108 pagesPrevious Year Question Paper With AnswersTejasPatilNo ratings yet
- SOMDocument14 pagesSOMAditya ojhaNo ratings yet
- Ashok Dmm1Document4 pagesAshok Dmm1Praveen KumarNo ratings yet
- EMT 3102 SUPP Solids & Structural Mechanics 1 SUPPDocument4 pagesEMT 3102 SUPP Solids & Structural Mechanics 1 SUPPGausss TjNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Solids GTU PapersDocument17 pagesMechanics of Solids GTU Papersvaibhav shahNo ratings yet
- Model Question Paper - 1 With Effect From 2020-21 (CBCS Scheme) Fifth Semester B.E. Degree ExaminationDocument10 pagesModel Question Paper - 1 With Effect From 2020-21 (CBCS Scheme) Fifth Semester B.E. Degree ExaminationSharath KotegarNo ratings yet
- R5 210304 Mechanics of SolidsDocument2 pagesR5 210304 Mechanics of SolidssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- r059210303 Mechanics of SolidsDocument8 pagesr059210303 Mechanics of SolidsSrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- CE8301-Strength of Materials IDocument4 pagesCE8301-Strength of Materials Isyed1188No ratings yet
- (2008 Course) : S.E. (Mech.) (Ii Seni,) Examination, 2010 Strength of Machine ElementsDocument10 pages(2008 Course) : S.E. (Mech.) (Ii Seni,) Examination, 2010 Strength of Machine ElementsdramiltNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityJaineshNo ratings yet
- Dme Question BankDocument4 pagesDme Question BankRavi Patil100% (1)
- MOM OU Old Question PaperDocument2 pagesMOM OU Old Question PaperAmmineni Syam PrasadNo ratings yet
- 3 Hours / 70 Marks: Instructions: (1) All Questions Are CompulsoryDocument4 pages3 Hours / 70 Marks: Instructions: (1) All Questions Are CompulsoryCE Div A 15 shivraj DhakneNo ratings yet
- Diploma QPDocument4 pagesDiploma QPSundarasetty HarishbabuNo ratings yet
- Diploma Quasion PapersDocument4 pagesDiploma Quasion PapersSundarasetty HarishbabuNo ratings yet
- 3 Hours / 70 Marks: Seat NoDocument5 pages3 Hours / 70 Marks: Seat Noopwigs444No ratings yet
- Internal Assessment Examination-II: Part-A (Answer All The Questions)Document2 pagesInternal Assessment Examination-II: Part-A (Answer All The Questions)VVCET - MechNo ratings yet
- AsdfasdfasdfDocument8 pagesAsdfasdfasdfFleight Vandollin100% (1)
- Som I Iat Ques 2019Document3 pagesSom I Iat Ques 2019Siva RamanNo ratings yet
- 2014 Summer Question PaperDocument4 pages2014 Summer Question PaperPrajwal V DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- EMT 3253 Solid Structural Mechanics IDocument4 pagesEMT 3253 Solid Structural Mechanics IezraNo ratings yet
- Design of Machine Elements Question Paper SampleDocument6 pagesDesign of Machine Elements Question Paper SampleK V SATHEESHKUMAR MECHNo ratings yet
- DME-I Question BankDocument6 pagesDME-I Question BankLohith AcharyaNo ratings yet
- EMM7241-Advanced Machine Design Examination June 2016Document8 pagesEMM7241-Advanced Machine Design Examination June 2016Charles OndiekiNo ratings yet
- Candidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarksDocument4 pagesCandidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarksMadan PanditNo ratings yet
- Som Ese 2021Document7 pagesSom Ese 2021Gaurav ManeNo ratings yet
- B C192020 Pages: 3: Answer Any Two Full Questions, Each Carries 15 MarksDocument3 pagesB C192020 Pages: 3: Answer Any Two Full Questions, Each Carries 15 Markslakshmi dileepNo ratings yet
- Paper ID (A08011: B.Tech. (Sem. - 3'd)Document3 pagesPaper ID (A08011: B.Tech. (Sem. - 3'd)bravo16893No ratings yet
- Rr211402 Mechanics of SolidsDocument8 pagesRr211402 Mechanics of SolidsSrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering SET ADocument16 pagesCivil Engineering SET Aishak789No ratings yet
- Btech Me 5 Sem Machine Design 1 Rme501 2021Document2 pagesBtech Me 5 Sem Machine Design 1 Rme501 2021aalumirchi167No ratings yet
- Robin in DuDocument8 pagesRobin in DuRobin George RejiNo ratings yet
- Question Bank: Module 1:design For Static StrengthDocument22 pagesQuestion Bank: Module 1:design For Static Strengthcrazy hjNo ratings yet
- 2014 Winter Question PaperDocument6 pages2014 Winter Question PaperPrajwal V DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Mom Sem 1 (09-10)Document12 pagesMom Sem 1 (09-10)Jenylex KumilNo ratings yet
- Mechanic Sof Solids (CIE 1051)Document4 pagesMechanic Sof Solids (CIE 1051)Alok KumarNo ratings yet
- Diploma Board Examination - June 2021Document4 pagesDiploma Board Examination - June 2021Maruthi Groupof InstitutionsNo ratings yet
- Copy of BCV301 Super Important - 22SCHEMEDocument3 pagesCopy of BCV301 Super Important - 22SCHEMEdarshandach0626No ratings yet
- 2nd Preboard Design Nov 2018 EditedDocument12 pages2nd Preboard Design Nov 2018 EditedXprts Review100% (1)
- Uganda Technical College - Lira: IMPORTANT SAMPLE QUESTIONS (Design of Concrete Structures To Eurocode 2)Document38 pagesUganda Technical College - Lira: IMPORTANT SAMPLE QUESTIONS (Design of Concrete Structures To Eurocode 2)Mugara Waitega PeterNo ratings yet
- Smat Quiz QuestionnairreDocument12 pagesSmat Quiz QuestionnairreGielyn DiwaNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Solids Oct-Nov 2020Document2 pagesMechanics of Solids Oct-Nov 2020nasty gammersNo ratings yet
- 9A03504 Design of Machine Elements 21Document8 pages9A03504 Design of Machine Elements 21slv_prasaadNo ratings yet
- Design of Machine Elements Question Paper SampleDocument7 pagesDesign of Machine Elements Question Paper SampleK V SATHEESHKUMAR MECHNo ratings yet
- ME401 RegularDocument3 pagesME401 RegularAmal SNo ratings yet
- Machine Design QP KtuDocument3 pagesMachine Design QP KtuAbhijith JoseNo ratings yet
- Design Preboard Exam NOV 2021Document17 pagesDesign Preboard Exam NOV 2021Glaiza Marie100% (1)
- (Join AICTE Telegram Group) 22303 (MOS) Mechanics of StructuralDocument4 pages(Join AICTE Telegram Group) 22303 (MOS) Mechanics of StructuralVivek Sharma0% (1)
- 21 ME63 Set 1&2Document7 pages21 ME63 Set 1&2prathapkumar2403No ratings yet
- Strength of Materials: at Least TWO Questions From Each PartDocument2 pagesStrength of Materials: at Least TWO Questions From Each PartnvnrevNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 FinalDocument2 pagesTutorial 5 FinalAtul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Design of Machine Elements Question Paper SampleDocument7 pagesDesign of Machine Elements Question Paper SampleK V SATHEESHKUMAR MECHNo ratings yet
- 3 Hours / 70 Marks: Seat NoDocument5 pages3 Hours / 70 Marks: Seat NoMadao111No ratings yet
- Ce8353 SomDocument2 pagesCe8353 Somsrinithims78No ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Tata Motors's AchivementsDocument105 pagesTata Motors's AchivementsSunny SinghNo ratings yet
- TM-Editor 25.04.2016 Seite 1 050-Meteorology - LTMDocument308 pagesTM-Editor 25.04.2016 Seite 1 050-Meteorology - LTMIbrahim Med100% (1)
- 2.High-Confidence Behavior at Work The Exec SkillsDocument27 pages2.High-Confidence Behavior at Work The Exec SkillsRamiro BernalesNo ratings yet
- Blank 7E Lesson Plan TemplateDocument5 pagesBlank 7E Lesson Plan TemplateJoshuel AgpasaNo ratings yet
- Apollo Valves: 94A / 95A SeriesDocument1 pageApollo Valves: 94A / 95A Seriesmaruthappan sundaramNo ratings yet
- Sensor Manual 1Document11 pagesSensor Manual 1Tame PcAddictNo ratings yet
- LOPC-mech Seal FailureDocument26 pagesLOPC-mech Seal FailureSanjeevi Kumar SpNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 6 SolutionsDocument7 pagesAssignment - 6 SolutionsGopal Iswarpur Ghosh100% (1)
- Chapter 1: Scientific Understanding of Behavior: Learning ObjectivesDocument13 pagesChapter 1: Scientific Understanding of Behavior: Learning Objectiveshallo BroNo ratings yet
- Tag Heuer Movement FinishesDocument2 pagesTag Heuer Movement FinishesDevil GodNo ratings yet
- Noc19 Me17 Assignment5Document3 pagesNoc19 Me17 Assignment5mechanicalNo ratings yet
- December 2016Document192 pagesDecember 2016Ramesh MankaniNo ratings yet
- DISS Q2 Week1 Learning-Activity-SheetDocument2 pagesDISS Q2 Week1 Learning-Activity-SheetBryanNo ratings yet
- Terraformer D TsDocument7 pagesTerraformer D TsprogramhNo ratings yet
- Rudder - Steering Gear Speed RulesDNVGL-RU-SHIP-Pt4Ch10 19Document1 pageRudder - Steering Gear Speed RulesDNVGL-RU-SHIP-Pt4Ch10 19Tolias EgwNo ratings yet
- CDAP006 Subfloor Protection PDFDocument2 pagesCDAP006 Subfloor Protection PDFGustavo Márquez TorresNo ratings yet
- Ingeteam Catalogo Cms Mayo2019 Eng MailDocument7 pagesIngeteam Catalogo Cms Mayo2019 Eng MailChrist Rodney MAKANANo ratings yet
- SS 113 QuizDocument2 pagesSS 113 QuizAlbette Amor Improgo SeposoNo ratings yet
- Aide Memoire On UtilitiesDocument11 pagesAide Memoire On UtilitiesFaress RabiNo ratings yet
- Vietnam SPC - Vinyl Price ListDocument9 pagesVietnam SPC - Vinyl Price ListThe Cultural CommitteeNo ratings yet
- Caserm/D: Publication Ordering InformationDocument326 pagesCaserm/D: Publication Ordering InformationjohnNo ratings yet
- DB Broadcast PM300 ManualDocument108 pagesDB Broadcast PM300 Manualfransferdinand2001100% (1)
- Science Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesScience Lesson Planapi-285283157No ratings yet
- CA Level 1Document43 pagesCA Level 1Cikya ComelNo ratings yet
- MC Practicals 2Document12 pagesMC Practicals 2Adi AdnanNo ratings yet
- HP LaserJet Managed MFP E72425-E72430 - CPMDDocument526 pagesHP LaserJet Managed MFP E72425-E72430 - CPMDDaniel GarciaNo ratings yet
- Ch6-Mechanical PropertiesDocument39 pagesCh6-Mechanical PropertiesSaif AlbaddawiNo ratings yet
- P1NN Gallardo - Pinal - ErikaDocument17 pagesP1NN Gallardo - Pinal - ErikaOnda ElectromagnéticaNo ratings yet
- Ecm 9Document1 pageEcm 9Misa GamezNo ratings yet
- Colah Github Io Posts 2015 08 Understanding LSTMsDocument16 pagesColah Github Io Posts 2015 08 Understanding LSTMsMithun PantNo ratings yet