Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Plant Nutrition and Transport CIE iGCSE 0610 PPQ
Plant Nutrition and Transport CIE iGCSE 0610 PPQ
Uploaded by
dinakempho3Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Plant Nutrition and Transport CIE iGCSE 0610 PPQ
Plant Nutrition and Transport CIE iGCSE 0610 PPQ
Uploaded by
dinakempho3Copyright:
Available Formats
24
Plant nutrition and transport
CORE questions
Core 1
(a) The chemical equation for photosynthesis shown below is incomplete.
6H2 O CH O
+ ...................................
energy
plant pigment
→ 6 12 6 + ..............................
water glucose
(i) Complete the equation in either symbols or words. [2]
(ii) State the source of energy for this reaction.
[1]
(iii) Name the plant pigment necessary for this reaction.
[1]
(iv) Which mineral is needed by a plant to form this pigment?
[1]
(b) (i) Name the tissue in which the sugar produced in photosynthesis is carried to
other parts of the plant.
[1]
(ii) In many plants some of the sugar formed in photosynthesis is converted to
starch for storage. Explain the advantage of storing starch rather than sugar.
.......... [2]
(iii) Name the carbohydrate, formed from sugar produced in photosynthesis,
which is used to build cell walls.
[1]
[Total : 9]
v1 4Y11 Cambridge IGCSE Biology – past paper questions and answers
25
Core 2
Fig. 1 shows changes in the rate of water loss from a plant during part of a day. It also shows
changes in the temperature and light intensity over the same period.
Fig. 1
(a) Explain why the rate of water loss rises steeply between 0700 and 1200 hours.
[3]
(b) Suggest which factor, light intensity or temperature, has the greater effect on the rate
of water loss between 1200 and 1500 hours. Explain your answer.
Factor .............................................................................................................................
Explanation ....................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................... [2]
v1 4Y11 Cambridge IGCSE Biology – past paper questions and answers
26
Core 2
(c) Predict and explain the likely effect on the rate of water loss if there had been heavy
rainfall between 1100 and 1200 hours.
Prediction .......................................................................................................................
Explanation ....................................................................................................................
.......... [2]
[Total : 7]
v1 4Y11 Cambridge IGCSE Biology – past paper questions and answers
27
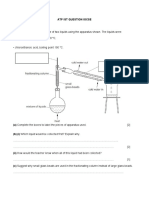
ALTERNATIVE TO PRACTICAL questions
Alternative to Practical 1
Fig. 2 shows three sets of apparatus, A, B and C, used to measure different biological
processes.
Fig. 2
(a) Name the process that can be measured by each apparatus.
A ...........................................................................................................................
B ...........................................................................................................................
C ....................................................................................................................... [3]
v1 4Y11 Cambridge IGCSE Biology – past paper questions and answers
28
Alternative to Practical 1
(b) (i) Name the gas which is produced by the process measured using apparatus
A.
[1]
(ii) Suggest one possible control for an experiment using apparatus A.
[1]
(c) When using apparatus B, it is possible to vary the external conditions. Suggest how
changing one named external condition would affect the biological process
measured by apparatus B.
[1]
(d) (i) Name the gas produced by the process measured using apparatus C.
[1]
(ii) How would you keep one named external factor constant when using
apparatus C?
[1]
[Total : 8]
v1 4Y11 Cambridge IGCSE Biology – past paper questions and answers
29
EXTENSION questions
Extension 1
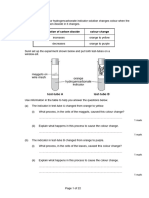
Fig. 3 shows part of the lower surface of a typical dicotyledonous leaf.
Fig. 3
(a) On Fig. 3, label part A and the cells B and C. [3]
The surfaces of the leaves of two species of plant were studied and the number of stomata
per unit area (stomatal frequency) was recorded.
Cobalt chloride paper changes colour in the presence of water.
Pieces of cobalt chloride paper were attached to the upper and lower surfaces of leaves on
both plants. The plants were set up for one hour during the day. Any colour changes were
recorded. The experiment was repeated for one hour at night. Table 1 shows the results.
Table 1
stomatal frequency colour change to cobalt chloride paper
plant day night Key
species lower upper lower upper lower upper ✔ colour
surface surface surface surface surface surface change
Cassia
0 18 ✘ ✔ ✘ ✘ ✘ no
fistula
Bauhinia colour
22 0 ✔ ✘ ✘ ✘ change
monandra
(b) Describe the differences in stomatal distribution between the two species of plant.
.......... [2]
v1 4Y11 Cambridge IGCSE Biology – past paper questions and answers
30
Extension 1
(c) (i) Explain the colour changes to the cobalt chloride paper during the day.
[3]
(ii) Suggest why there was no colour change for either plant at night.
[1]
(d) Outline the mechanism by which water in the roots reaches the leaf.
........................................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................... [3]
(e) State and explain the effect of the following on transpiration rate:
(i) increasing humidity;
.......... [2]
(ii) increasing temperature.
.......... [2]
[Total : 16]
v1 4Y11 Cambridge IGCSE Biology – past paper questions and answers
31
Extension 2
Fig. 4 shows an aphid feeding on a plant stem. Its mouthparts are hollow tubes which are
pushed into the stem to remove sugar solution.
Fig. 4
(a) Aphids are arthropods. State two features, visible in Fig. 4, which are common to all
arthropods.
1. ...........................................................................................................................
2 ........... ............................................................................................................ [2]
(b) In which tissue, and by what processes, does the sugar solution move through the
plant?
Tissue ............................................................................................................................
Processes ......................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................... [3]
v1 4Y11 Cambridge IGCSE Biology – past paper questions and answers
32
Extension 2
Some of the sugar solution was collected from the plant stem. Plant cells were placed on a
microscope slide and covered with this sugar solution.
(c) (i) Describe what changes would occur to each of the cell parts listed below, if
the sugar solution was more concentrated than the sap in the cell vacuole.
Sap vacuole
Cytoplasm
Cell wall
[3]
(ii) Explain, in terms of water potential gradient, how these changes occur.
[3]
(d) Systemic pesticides can be used to kill pests such as aphids. Describe how the
application of these pesticides to leaves kills aphids feeding on the stem.
.......... [2]
[Total : 13]
v1 4Y11 Cambridge IGCSE Biology – past paper questions and answers
33
Extension 3
A student carried out an experiment to investigate the growth of floating water plants taken
from a pond. Equal masses of the plants were placed into three separate glass containers A,
B and C, similar to the one shown in Fig. 5
Fig. 5
Container A was lit by a 250 W bulb, B was lit by a 75 W bulb and C was lit by a 250 W bulb
with a coloured filter in front of the lamp, as shown in Fig. 5
At weekly intervals, the plants were removed from each container in turn, gently dried,
weighed and returned to the containers after their mass had been recorded. Fig. 6 shows the
results plotted on a graph.
Fig. 6
v1 4Y11 Cambridge IGCSE Biology – past paper questions and answers
34
Extension 3
(a) With reference to Fig. 6 calculate the percentage increase in mass of the plants in
container A during the first five weeks of the experiment. (Show your working.)
% increase .................................[2]
(b) Suggest why the mass of plants in container A began to decrease after week 5, while
the mass of plants in B continued to increase.
Container A ....................................................................................................................
Container B ....................................................................................................................
.......... [2]
(c) During the eighth week, in which container would there be the least dissolved
oxygen? Explain your answer.
Container ........................
Explanation .................................................................................................................................
.......... [2]
v1 4Y11 Cambridge IGCSE Biology – past paper questions and answers
35
Plant nutrition and transport – answers
Core 1
a any three of these
light intensity increases
the stomata open
increase in temperature
greater rate of evaporation / transpiration / diffusion
b factor- temperature
explanation- as light decreases the rate of loss continues to rise / temperature and
water loss curves peak at the similar time
c prediction- rate of water loss / transpiration falls / lower
explanation- air saturated / humid (thus less evaporation)
Core 2
a(i) 6CO2 / carbon dioxide
6O2 / oxygen
(ii) sun / solar / sunlight
(iii) chlorophyll
(iv) magnesium / iron / nitrate / ammonium
b(i) phloem
(ii) starch is insoluble
has no osmotic effect / easier to retain in storage / prevent it being moved
(iii) cellulose
Alternative to Practical 1
a A respiration / use of oxygen
B transpiration / uptake of water / water loss
C photosynthesis
b(i) carbon dioxide / CO2
(ii) one from
glass beads
stones
empty tube
boiled, sterile, dry or dead seeds
v1 4Y11 Cambridge IGCSE Biology – past paper questions and answers
36
c one from
moving air / wind / fan / dry air speed up process
enclosed in a bag / increase humidity slow process
cold air slow process
hot air speed up process
in darkness slow process
in light / sunny speed up process
d(i) oxygen / O2
(ii) any one of these
light-intensity fixed position of bulb / keep light on / same wattage /
temperature- heat shield / in water bath / heat filter
carbon dioxide- add hydrogen carbonate to water
biotic idea- use same piece of waterweed
Extension 1
a any two from
presence of segmented body or abdomen
presence of jointed limbs or appendages
presence of head or eyes
presence of exoskeleton
b tissue phloem / sieve tubes
processes reference to translocation
reference to active transport or active uptake
c(i) sap vacuole gets smaller / shrinks / loses water / reference to increase in
concentration
cytoplasm moves away from (cell) wall
cell wall no longer curves outwards
(ii) any three points
water potential in vacuole / cell is higher than outside
due to lower concentration of sugar molecules / higher concentration if water
molecules in vacuole / cell
so water moves out by osmosis
through (cell) membrane
d pesticides are absorbed into the leaf / plant / stem
aphids feed on / suck / remove poisonous sap
Extension 2
a A stoma / stomatal pore
B guard cell
C epidermal cell / epidermis
b upper surface
C. Fistula has 18 stomata while B. Monhandra has none
lower surface
C. Fistula has no stomata while B. Monhandra has 22
v1 4Y11 Cambridge IGCSE Biology – past paper questions and answers
37
c(i) three of these points
water is only lost if stomata are present
stomata open during the day
so water (vapour) is lost
reference to transpiration
(ii) stomata are closed at night
d any three of these points
reference to xylem
water enters xylem vessel through pots in walls
reference to transpiration stream / pull
reference to capillary action
reference to root pressure
e(i) rate will decrease
reference to smaller gradient for diffusion
(ii) rate will increase
more energy for evaporation
warm air can hold more water vapour than cold air
Extension 3
300
a × 100
150
= 200%
b container A
depletion of salts / nutrients
seeds released
disease
shortage of carbon dioxide
reached end of life cycle
container B
photosynthesis
growth
nutrients not exhausted
food stores
sufficient carbon dioxide
c container C
least or no photosynthesis occurring
respiration exceeds photosynthesis
death of plant so bacteria active, using up oxygen
v1 4Y11 Cambridge IGCSE Biology – past paper questions and answers
You might also like
- Epigenetics How Environment Changes Your BiologyDocument144 pagesEpigenetics How Environment Changes Your BiologyAdje100% (1)
- Nguyễn Minh Hoàng 2021.08 Internal Ielts Test Reading Ver1 PassagesDocument7 pagesNguyễn Minh Hoàng 2021.08 Internal Ielts Test Reading Ver1 PassagesPhan Vinh PhongNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Molecular Diagnostics 3rd Edition Lela BuckinghamDocument10 pagesTest Bank For Molecular Diagnostics 3rd Edition Lela BuckinghamJustinReidmajof100% (31)
- LABORATORY ACTIVITY No. 4 - FROG DISSECTIONDocument6 pagesLABORATORY ACTIVITY No. 4 - FROG DISSECTIONNazarene Carlo Pagaspas100% (1)
- Role Play On Challenges of Middle AdolescenceDocument4 pagesRole Play On Challenges of Middle Adolescence「 」100% (2)
- Calculations and Organic Practice QuestionsDocument25 pagesCalculations and Organic Practice QuestionsPanagiotis ScordisNo ratings yet
- Bio 345 Evolution Module 1 & 2 Exam 1 Review GuideDocument17 pagesBio 345 Evolution Module 1 & 2 Exam 1 Review GuideTiffanie100% (1)
- 2d Movement of MoleculesDocument12 pages2d Movement of MoleculesRabia RafiqueNo ratings yet
- PDF Document 0BA95E32636B 1Document5 pagesPDF Document 0BA95E32636B 1Soo ZhixuanNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissues, Organs - Systems 1 QP PDFDocument22 pagesPlant Tissues, Organs - Systems 1 QP PDFAlexia Micallef GattNo ratings yet
- CIE A-Level Biology Topic 13 Photosynthesis Exam Questions: Alevelbiology - Co.ukDocument15 pagesCIE A-Level Biology Topic 13 Photosynthesis Exam Questions: Alevelbiology - Co.ukMaisarah HalimNo ratings yet
- Plant Transport Exam Q StudentsDocument3 pagesPlant Transport Exam Q StudentszwepzaungNo ratings yet
- Limiting Factors 6Document7 pagesLimiting Factors 6Khadija AhmedNo ratings yet
- Exam Prep Science Form 2Document11 pagesExam Prep Science Form 2lusubilosimbeye9No ratings yet
- 2.4 Bulk & Surface Properties of Matter 1 QPDocument24 pages2.4 Bulk & Surface Properties of Matter 1 QPksrlnnn.8No ratings yet
- Work Sheet (Topic - Plants and Food)Document22 pagesWork Sheet (Topic - Plants and Food)ananafra861No ratings yet
- Cycles Within EcosystemsDocument62 pagesCycles Within EcosystemsEmmaNo ratings yet
- Biology Paper 1 June 1998Document32 pagesBiology Paper 1 June 1998k391No ratings yet
- PapersDocument25 pagesPapersMush TNo ratings yet
- 1.5 Kinetics ExamproDocument33 pages1.5 Kinetics Examproannonymous oneNo ratings yet
- Populations in Ecosystems QPDocument7 pagesPopulations in Ecosystems QPJanine BertolottiNo ratings yet
- 1st Question Experimental DesignDocument16 pages1st Question Experimental DesignHayaa KhanNo ratings yet
- GCSE Biology: Photosynthesis - 1Document4 pagesGCSE Biology: Photosynthesis - 1Mr. Suit100% (1)
- Structured Questions 9C 2023Document16 pagesStructured Questions 9C 2023SomeonenamedmaazNo ratings yet
- NAME CLASS Topic Outline: Year 9 Term 3 Biology Work Book - 2017-2018Document30 pagesNAME CLASS Topic Outline: Year 9 Term 3 Biology Work Book - 2017-2018fatimaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument20 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Educationthreefold18 -BRAWL STARSNo ratings yet
- Plant Transport Exam QDocument5 pagesPlant Transport Exam QSeema QureshiNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: BIOLOGY 0610/31Document24 pagesCambridge IGCSE: BIOLOGY 0610/31DharaniNo ratings yet
- b4 Organisation in Plants Exam QsDocument26 pagesb4 Organisation in Plants Exam QsDarius “FlawlessStreak” OpreaNo ratings yet
- Exercise-U2-Topic 6 - EnergeticsDocument109 pagesExercise-U2-Topic 6 - EnergeticsLiang LuNo ratings yet
- Questions Paper 2 CHP 19Document5 pagesQuestions Paper 2 CHP 19FIKRIYE ONDEROLNo ratings yet
- CBSE Sample Paper Class 7 Science Set 4Document4 pagesCBSE Sample Paper Class 7 Science Set 4Sumanta PanNo ratings yet
- 11.1 Osmosis QuestionsDocument6 pages11.1 Osmosis Questionsnayabalish08No ratings yet
- G8 9 - Plant Nutrition HW QPDocument6 pagesG8 9 - Plant Nutrition HW QPSumayya P ANo ratings yet
- Edexcel Questions of Photosynthesis Only-2Document30 pagesEdexcel Questions of Photosynthesis Only-2Rokunuz Jahan Rudro100% (1)
- B3.1 Exam-Style QuestionsDocument4 pagesB3.1 Exam-Style QuestionsToni HeaterNo ratings yet
- B2 Questions and AnswersDocument22 pagesB2 Questions and Answersinaayairshad.17No ratings yet
- Energy Changes, Rate, Reversible, NH3, H2SO4Document5 pagesEnergy Changes, Rate, Reversible, NH3, H2SO4HudaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelDocument24 pagesCambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelSiya PathakNo ratings yet
- Entrance Exam Sample PaperDocument9 pagesEntrance Exam Sample PaperChloe IngersentNo ratings yet
- Catalysts 1 QPDocument12 pagesCatalysts 1 QPprettytakadiyiNo ratings yet
- Organisation of An Ecosystem 1 QPDocument23 pagesOrganisation of An Ecosystem 1 QPAlfie ArthurNo ratings yet
- Y11 Biology Lockdown Learning ReviewDocument9 pagesY11 Biology Lockdown Learning ReviewMohamedNo ratings yet
- Reversible Reactions & Dynamic Equilibrium 3 QPDocument18 pagesReversible Reactions & Dynamic Equilibrium 3 QPSam GreenNo ratings yet
- Changes of State and The Particle Model 1 QPDocument9 pagesChanges of State and The Particle Model 1 QPSamuraigistNo ratings yet
- Biology Perfect Score Module Form 4 Set 1Document21 pagesBiology Perfect Score Module Form 4 Set 1danish_35070% (1)
- Cambridge IGCSE: Combined Science 0653/32Document24 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Combined Science 0653/32tapiwa nyamundaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelDocument12 pagesCambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelMuhammad AhmedNo ratings yet
- Foundation Tier Biology 2: A.M. TUESDAY, 24 January 2012 45 MinutesDocument11 pagesFoundation Tier Biology 2: A.M. TUESDAY, 24 January 2012 45 Minutessureshthevan100% (1)
- 1.1 Cell Structure (Moderate) QPDocument14 pages1.1 Cell Structure (Moderate) QPehodariNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Cell Structure (Moderate) QP PDFDocument16 pages1.1 Cell Structure (Moderate) QP PDFBeyondShine Car Care zckidNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE Biology (0610) Past Paper Questions and AnswersDocument112 pagesCambridge IGCSE Biology (0610) Past Paper Questions and AnswersKiro XuNo ratings yet
- 2854 June 05Document15 pages2854 June 05ExamStuffNo ratings yet
- Ans 2 (Core)Document20 pagesAns 2 (Core)suhaankochhar2008No ratings yet
- Kcse 2012 Biology p1Document7 pagesKcse 2012 Biology p1Urex ZNo ratings yet
- Revision Exer 8Document6 pagesRevision Exer 8killer boyNo ratings yet
- IGedex2122 1.1-1.4Document34 pagesIGedex2122 1.1-1.4rkblsistemNo ratings yet
- End of Term Year 7 Chem 1Document9 pagesEnd of Term Year 7 Chem 1Barminga KamurenNo ratings yet
- Eco and Envir 2019 Sep SciDocument13 pagesEco and Envir 2019 Sep SciStudent Valeria Ferriol CebrianNo ratings yet
- Biomimetic Principles and Design of Advanced Engineering MaterialsFrom EverandBiomimetic Principles and Design of Advanced Engineering MaterialsNo ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Plant NutritionFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Plant NutritionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- GP4 ForcesDocument10 pagesGP4 Forcesdinakempho3No ratings yet
- Fats and OilsDocument4 pagesFats and Oilsdinakempho3No ratings yet
- Food SupplementsDocument3 pagesFood Supplementsdinakempho3No ratings yet
- Food LabellingDocument2 pagesFood Labellingdinakempho3No ratings yet
- November 2021 Question Paper 02Document8 pagesNovember 2021 Question Paper 02dinakempho3No ratings yet
- NEET CBSE Molecular Basic of Inheritance MCQ QADocument61 pagesNEET CBSE Molecular Basic of Inheritance MCQ QARavian Mhe BitonNo ratings yet
- QP - Class IX - Science - Mid-Term - Assessment - 2021 - 22 - Oct - 21Document6 pagesQP - Class IX - Science - Mid-Term - Assessment - 2021 - 22 - Oct - 21Ashish GambhirNo ratings yet
- Braxton Johns - Child Development Final PaperDocument6 pagesBraxton Johns - Child Development Final Paperapi-719543705No ratings yet
- RDB College of Nursing and Paramedical Science: DR M A Dawoodbatcha PH DDocument3 pagesRDB College of Nursing and Paramedical Science: DR M A Dawoodbatcha PH DYAMINIPRIYANNo ratings yet
- Isef Research Paper GuidelinesDocument5 pagesIsef Research Paper Guidelinesyqxvxpwhf100% (1)
- Module On LeavesDocument28 pagesModule On LeavesCharles Linelle MendozaNo ratings yet
- 2019-20 Academic Year Family Law-1Document18 pages2019-20 Academic Year Family Law-1Soham UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: Theorizing The ContemporaryDocument5 pagesPhotosynthesis: Theorizing The ContemporaryTadeoNo ratings yet
- The Plant KingdomDocument30 pagesThe Plant KingdomBenidick PascuaNo ratings yet
- Pagpaparami NG Purong Binhi NG Palay Sa Sariling BukidDocument36 pagesPagpaparami NG Purong Binhi NG Palay Sa Sariling BukidvladimirNo ratings yet
- Vol. IIDocument663 pagesVol. IICamila Alcantara100% (1)
- Verbal Ability HandoutDocument4 pagesVerbal Ability HandoutAnuj JainNo ratings yet
- POPULASI DAN SERANGAN LARVA Batocera Hercules Boisduv (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) Pada Tanaman Pala Di Kecamatan Kauditan Kabupaten Minahasa UtaraDocument13 pagesPOPULASI DAN SERANGAN LARVA Batocera Hercules Boisduv (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) Pada Tanaman Pala Di Kecamatan Kauditan Kabupaten Minahasa UtaraRajif ProtektionNo ratings yet
- Raisin in The Sun Quotes and Comparisons To Rosie The MovieDocument10 pagesRaisin in The Sun Quotes and Comparisons To Rosie The MovieAnita C.KNo ratings yet
- 1 - Intro To BiotechnologyDocument25 pages1 - Intro To BiotechnologynicoleNo ratings yet
- 4life Summit - Vol.31 2020Document24 pages4life Summit - Vol.31 2020AkpemiNo ratings yet
- Topical Approach To Lifespan Development 7th Edition Santrock Test Bank 1Document52 pagesTopical Approach To Lifespan Development 7th Edition Santrock Test Bank 1Arturo Newman100% (48)
- Insect Reproduction: Entomology (BIOL 409) Fall 2004, Lecture # 21Document18 pagesInsect Reproduction: Entomology (BIOL 409) Fall 2004, Lecture # 21Reube RonnyNo ratings yet
- Sequencing of DNA (Sanger Sequencing) : Sirjan BastolaDocument10 pagesSequencing of DNA (Sanger Sequencing) : Sirjan BastolaAnil YadavNo ratings yet
- Third Written Assignment - Do Ngoc LinhDocument3 pagesThird Written Assignment - Do Ngoc LinhLinh Đỗ NgọcNo ratings yet
- Science Form 1 Chapter 2 NoteDocument8 pagesScience Form 1 Chapter 2 NoteADAM LOHNo ratings yet
- Bentham and Hooker's System of Classification Drpunamjeswal bsc-IIDocument4 pagesBentham and Hooker's System of Classification Drpunamjeswal bsc-IIShreyas SNo ratings yet
- Correlation Coefficients: Find Pearson's Correlation CoefficientDocument5 pagesCorrelation Coefficients: Find Pearson's Correlation CoefficientMadison HartfieldNo ratings yet
- Detecting & Identifying TermitesDocument2 pagesDetecting & Identifying TermitesmackerelfishNo ratings yet