Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Med Org Topic 234
Med Org Topic 234
Uploaded by
barbadillojames419Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Intro To FSM Handouts BWDocument30 pagesIntro To FSM Handouts BWroberto_celio_2100% (5)
- Outline For Assessment of HEENTDocument3 pagesOutline For Assessment of HEENTpauchanmnl50% (2)
- Microbiology and Parasitology ReviewerDocument4 pagesMicrobiology and Parasitology ReviewerChrister Jon AcostaNo ratings yet
- Fungus PDFDocument4 pagesFungus PDFPrashant MishraNo ratings yet
- Mycology TransDocument11 pagesMycology TransKita kitaNo ratings yet
- Clinical AND ADVANCE Pathology: TopicDocument7 pagesClinical AND ADVANCE Pathology: TopicNestley TiongsonNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Fungi: Ex - Aspergillus, DermatophytesDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Fungi: Ex - Aspergillus, DermatophytesBanana CakeNo ratings yet
- Fungal InfectionDocument3 pagesFungal InfectionNicole TorralbaNo ratings yet
- FUNGAL and PARASITIC INFECTIONSDocument3 pagesFUNGAL and PARASITIC INFECTIONSKathleen Hazel AndresNo ratings yet
- Klinis Dan Diagnosa Laboratorium Jamur 10,11Document36 pagesKlinis Dan Diagnosa Laboratorium Jamur 10,11H PNo ratings yet
- MycosesDocument7 pagesMycosesJazmine Rose DelrosarioNo ratings yet
- Activity 8 MycologyDocument3 pagesActivity 8 MycologyBrent Lee100% (1)
- Birao Sas 14 Microbiology and ParasitologyDocument6 pagesBirao Sas 14 Microbiology and ParasitologyFrancis Jacob Dejecacion GarcesNo ratings yet
- FungiDocument1 pageFungiRaveenaNo ratings yet
- Micro Chart #3 - Italics OnlyDocument27 pagesMicro Chart #3 - Italics Onlyapi-26938624100% (1)
- MycosisDocument27 pagesMycosisIalyn RodrigoNo ratings yet
- Mycology 170328040158Document84 pagesMycology 170328040158Zainab KhadharNo ratings yet
- ED Na STR FUNGIDocument46 pagesED Na STR FUNGIdw21541No ratings yet
- Fungal InfectionsDocument76 pagesFungal InfectionsHrishikesh NachinolkarNo ratings yet
- Unit v. Fungal Diseases Rev.3Document56 pagesUnit v. Fungal Diseases Rev.3Vda RmehrNo ratings yet
- Mycology SOM CJBDocument91 pagesMycology SOM CJBYlia MastarsNo ratings yet
- Micro Chart Test 3Document8 pagesMicro Chart Test 3api-26938624No ratings yet
- Medically Important FungihandoutDocument55 pagesMedically Important FungihandoutHervis FantiniNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Cutaneous and Subcutaneous MycosesDocument46 pagesLecture 2 Cutaneous and Subcutaneous MycoseschiyeoncherryNo ratings yet
- (Internal) The Epidermis That Grow On The Keratin Present On TheseDocument8 pages(Internal) The Epidermis That Grow On The Keratin Present On TheseAthena Irish LastimosaNo ratings yet
- Superficial MycosisDocument17 pagesSuperficial Mycosisapi-19969058100% (3)
- Fungal Infections Mycotic Infections MycosesDocument12 pagesFungal Infections Mycotic Infections MycosesHussein QasimNo ratings yet
- Myco Myco OwnDocument4 pagesMyco Myco OwnMarielle Anne TuazonNo ratings yet
- Ankur Vashishtha S Ubharti University MeerutDocument34 pagesAnkur Vashishtha S Ubharti University MeerutKana FajarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MycologyDocument35 pagesIntroduction To MycologyTheBoss 20No ratings yet
- Mikosis SuperfisialDocument46 pagesMikosis SuperfisialAdipuraAtmadjaEgokNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Superficial Cutaneous Mycosis HandoutsDocument8 pagesLesson 2 Superficial Cutaneous Mycosis HandoutsKhay Mae DonascoNo ratings yet
- Cutaneous and Subcutaneous mycoses-FMS2-2558Document68 pagesCutaneous and Subcutaneous mycoses-FMS2-2558Marl EstradaNo ratings yet
- Title of The LecDocument22 pagesTitle of The LecWeird BoiNo ratings yet
- FungiDocument3 pagesFungikrystal TortolaNo ratings yet
- Systemic Mycoses: A. BlastomycosisDocument3 pagesSystemic Mycoses: A. Blastomycosisbaihern24No ratings yet
- Mikologi Kedokteran: Ilmu Yang Mempelajari Jamur Serta Penyakit Yang Ditimbulkan Pada ManusiaDocument100 pagesMikologi Kedokteran: Ilmu Yang Mempelajari Jamur Serta Penyakit Yang Ditimbulkan Pada ManusiazafiharoNo ratings yet
- Bios - FungiDocument7 pagesBios - FungicalebleuNo ratings yet
- DMS. K07. Jamur Penyebab Penyakit KulitDocument120 pagesDMS. K07. Jamur Penyebab Penyakit KulitmissirenaNo ratings yet
- 05 Systemic MycosesDocument3 pages05 Systemic MycosesThea MallariNo ratings yet
- Cut MycosesDocument56 pagesCut MycosesHafsa ImranNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Microbiology and Parasitology (PHMP211)Document59 pagesPharmaceutical Microbiology and Parasitology (PHMP211)Crisamor Rose Pareja ClarisaNo ratings yet
- MCB 409 Pathogenic MycologyDocument49 pagesMCB 409 Pathogenic Mycologyejohn8340No ratings yet
- Modul #3 - Student Activity Sheet - CUTANEOUS MYCOSESDocument7 pagesModul #3 - Student Activity Sheet - CUTANEOUS MYCOSESYlia MastarsNo ratings yet
- Antifungal Agents General Introduction To Fungi: Medical Mycology Cutaneous Infections (Dermatophytoses)Document4 pagesAntifungal Agents General Introduction To Fungi: Medical Mycology Cutaneous Infections (Dermatophytoses)Ad Rianne DeniseNo ratings yet
- MycosesDocument2 pagesMycosesMadabout MusicNo ratings yet
- Microbial Diseases (Skin Eyes)Document23 pagesMicrobial Diseases (Skin Eyes)Hazel Mae FestinNo ratings yet
- Jamur-Jamur Penyebab: Mikosis Superfisial Dermatofitosis Mikosis SubkutanDocument104 pagesJamur-Jamur Penyebab: Mikosis Superfisial Dermatofitosis Mikosis SubkutanJimmy Fran IINo ratings yet
- Fungal Infections-SubcutaneousDocument24 pagesFungal Infections-SubcutaneousKato CalebNo ratings yet
- Opportunistic MycosesDocument6 pagesOpportunistic MycosesJullana Rondina EscondeNo ratings yet
- Classification of Fungal InfectionsDocument26 pagesClassification of Fungal Infectionstev26100% (1)
- Dermatophytes 20240314 214707 0000Document18 pagesDermatophytes 20240314 214707 0000khushi.gupta2122No ratings yet
- Branching, Aerobic, Partially Acid Fast and Non-Acid Fast Gram (+) BacilliDocument2 pagesBranching, Aerobic, Partially Acid Fast and Non-Acid Fast Gram (+) BacilliJustine Marie RevillaNo ratings yet
- Infection of The Skin, Soft Tissue, Etc.Document84 pagesInfection of The Skin, Soft Tissue, Etc.fmds100% (1)
- Pharmaceutical Chemistry (Midterm)Document11 pagesPharmaceutical Chemistry (Midterm)Majeddah Aliudin TalambunganNo ratings yet
- Microbiology - 19Document4 pagesMicrobiology - 19karmylle andradeNo ratings yet
- Superficial MycosisDocument8 pagesSuperficial MycosisLuqman Al-Bashir FauziNo ratings yet
- Mycology MycosesDocument7 pagesMycology MycosesSarah Grace KamlaniNo ratings yet
- Classifications of FungiDocument11 pagesClassifications of FungiRusselNo ratings yet
- Dermatology Notes for Medical StudentsFrom EverandDermatology Notes for Medical StudentsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- A Simple Guide to Skin Fungal Infections, (Updated 2023) Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Skin Fungal Infections, (Updated 2023) Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- LECTURE-1 MedDocument2 pagesLECTURE-1 Medbarbadillojames419No ratings yet
- Pharm 17 Chapter 17Document15 pagesPharm 17 Chapter 17barbadillojames419No ratings yet
- Pharm 17 Activity 1.PDF ADocument3 pagesPharm 17 Activity 1.PDF Abarbadillojames419No ratings yet
- Pharm 17 Chapter 19Document14 pagesPharm 17 Chapter 19barbadillojames419No ratings yet
- DHQ Flowcharts v2 1 Prep Pep ArtDocument49 pagesDHQ Flowcharts v2 1 Prep Pep ArtNatasha MendozaNo ratings yet
- The Spanish Flu Pandemic of 1918Document5 pagesThe Spanish Flu Pandemic of 1918jellNo ratings yet
- Script For PPT PresentationDocument4 pagesScript For PPT PresentationJanine Airah MorgadoNo ratings yet
- Herbal PlantsDocument11 pagesHerbal PlantsDechy Lyn PalmaNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument32 pagesRheumatoid ArthritisWoro Nugroho100% (5)
- Asma AnakDocument53 pagesAsma AnakAsri Rasyid LaskarIRDNo ratings yet
- Kinesia ParadoxaDocument7 pagesKinesia ParadoxaArcenciel26No ratings yet
- ShinglesDocument8 pagesShinglesapi-3366481170% (1)
- Asthma: Topic OutlineDocument2 pagesAsthma: Topic OutlineKdamnzNo ratings yet
- Carpal Tunnel SyndromeDocument9 pagesCarpal Tunnel SyndromeMaha RajaNo ratings yet
- Antenatal CorticosteroidsDocument2 pagesAntenatal CorticosteroidsFaizaShabirAhmedNo ratings yet
- Abdominal EpilepsyDocument4 pagesAbdominal EpilepsyErnesto Ochoa MonroyNo ratings yet
- Complications Druing HemodialysisDocument30 pagesComplications Druing HemodialysisMD Hajj83% (6)
- Special Education ClassificationsDocument3 pagesSpecial Education ClassificationsEdmar AgarpaoNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- Emskfjek-Intravenous IV Fluid Prescribing in AdultsDocument14 pagesEmskfjek-Intravenous IV Fluid Prescribing in AdultsAli SemajNo ratings yet
- GeneXpert - Monthly - Report - JAN, FEB, MARCH 2019 (GIMS) GAMBAT)Document12 pagesGeneXpert - Monthly - Report - JAN, FEB, MARCH 2019 (GIMS) GAMBAT)shakeelNo ratings yet
- Inflammation AvianDocument4 pagesInflammation Avianamit vishen75% (4)
- Practitioner Sample O and P Written ExamDocument4 pagesPractitioner Sample O and P Written ExamBapina Kumar RoutNo ratings yet
- Gonorrhea Infection in Women: Prevalence, Effects, Screening, and ManagementDocument12 pagesGonorrhea Infection in Women: Prevalence, Effects, Screening, and Managementilham hamkaNo ratings yet
- Question Paper 2023 AIAPGETDocument20 pagesQuestion Paper 2023 AIAPGETrohinibrajole123No ratings yet
- Hypoxia: Lori HolmesDocument5 pagesHypoxia: Lori HolmesDanson Githinji ENo ratings yet
- Heat Tolerance Test PDFDocument7 pagesHeat Tolerance Test PDFMonica LapusNo ratings yet
- SAGES Consent 2019 2023Document16 pagesSAGES Consent 2019 2023cNo ratings yet
- Types of Food ContaminationDocument13 pagesTypes of Food ContaminationHelena MbangoNo ratings yet
- Sarcomas SurgeryDocument8 pagesSarcomas SurgeryJüdith Marie Reyes BauntoNo ratings yet
- LabyrinthitisDocument7 pagesLabyrinthitisChristie ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology of Oral CancerDocument12 pagesEpidemiology of Oral Cancerعدي عبدالالهNo ratings yet
Med Org Topic 234
Med Org Topic 234
Uploaded by
barbadillojames419Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Med Org Topic 234
Med Org Topic 234
Uploaded by
barbadillojames419Copyright:
Available Formats
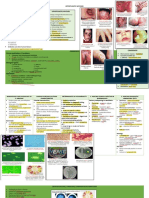
TOPIC 2: ANTIFUNGAL AGENTS
Clinical Types of Fungal Agents
Superficial Infections
Cutaneous Infections - Dermatomycoses / Dermatophytoses
• Epidermophyton (skin and nails)
• Microsporum (skin and hair)
• Tricophyton (skin, hair, and nails)-
Dermatophytes
Subcutaneous Infections - refers to a group of fungal diseases in w/c both the
skin and subcutaneous tissues are involved/ mostly
caused by saprophytic fungi lives in soil
Systemic Infections - have the ability to adapt to the internal
environment of the host; inhalation of fungal spores
Opportunistic Infections
Superficial Mycoses
Black Piedra/ Tinea nodosa CA: Piedrai hortae
White Piedra CA: Trichosporon asahii/ Trichosporon beigelii
Pityriasis/ Tinea versícolor CA: Malasezzia furfur
(ap-ap)
Tinea nigra - CA: Hortae werneckii
Locations on the Most Common Types of Ringworm
Tinea mannum Hands
Tinea cruris Groin
Tinea sycosis Beards
Tinea capitis Scalp
Tinea unguium Nails
Tinea corporis Trunk/body
SUBCUTANEOUS INFECTIONS
- refers to a group of fungal diseases in w/ both the skin and subcutaneous tissues are
involved/ mostly caused by saprophytic fungi lives in soil
Chromoblastomycoses - CM: Primary lesion are warty-like/ verrucous
appearance found along the draining lymphatics
Mycetoma - CA: Bacteria: Actinomycetes, Mycotic mycetoma
(Fungi)
- CM: Formation of draining sinuses with granules,
- Abscess formation
- Can spread to bones, muscles and nearby tissues
Sporotrichosis - CA: Sporothrix schenck
- CM: nodular lesions
Organic Medicinal Chemistry Kriszelle C. Mancera
- Occupational disease of gardeners *
Phaeohyphomycoses - Caused by the dermataceous fungi
- CA:
• Exophiala jeanselmei,
• Phialaphora richardsiae
• Bipolaris spicifera
• Wangiella dermatitidis
• Exorhilum rostratum
Systemic Mycoses
Coccidioidomycoses - CM: Valley Fever/ Desert Rheumatis
Histoplasmosis - Most common respiratory infections
- CA: Histoplasma capsulatum
- CM: Spelunker's disease
South American - CA: Paracoccidioiodes brasiliensis
Blastomycoses
North American - CA: Blastomyces dermatitidis
Blastomycoses - More contagious
Opportunistic Fungal Infections
Candidiasis - Most common opportunistic mycoses in humans
- CA: Candida ablicans
Cryptococcosis - CA: Crytpococcus neoformans
- Dx: Staining technique employing the india ink
- CM: Meningitis
- Tx. Flucytosine + Amphotericin B
Pneumocystis jirovecii - Tx: Co-trimoxazole
Aspergillosis - CA: Aspergillus fumigatus (more common)
- Fungal balls visible in the lungs
- DOC: Voriconazole
Organic Medicinal Chemistry Kriszelle C. Mancera
ANTI-FUNGAL AGENT
FATTY ACIDS
- all fatty acids and their salts have fungicidal properties
Propionic acid
- present in perspiration in low concentrations (around 0.01%)
Undecylenic Acid
- obtained from the destructive distillation of castor oil
NUCLEOSIDES
Flucytosine
- used only in combination with Amphotericin B for the treatment of systemic mycoses
and meningitis caused by Cryptococcus neoformans and Candida
ANTI FUNGAL ANTIBIOTICS
Polyenes
Amphotericin B (Fungizone®) - naturally occurring produced by Streptomyces
nodosus
- MOA: binds to ergosterol present in the cell
membrane disrupting membrane function,
allowing electrolytes to leak out from the cell
resulting in cell death
- Drug of Choice for systemic mycoses
Nystatin - Streptomyces noursei
- cereal like odor
- used for the treatment of candida * infections
- administered as an oral agent for the treatment
of oral candidiasis
- negligibly absorbed from the GIT tract so
adverse effects are rare
Natamycin - obtained from Streptomyces natalensis
ANTI-FUNGAL AGENT
Azoles - MOA: interacts with C-14 α-demethylase to block
demethylation of lanosterol t0 ergosterol, the
principal sterol of fungal membranes. This
inhibition disrupts membrane function & increases
permeability
Ketoconazole (Nizoral®) - only administered orally for systemic infection
- inhibits CYP450 and adrenal steroid synthesis
- has endocrine effects: gynecosmastia,
decreased libido, impotence, menstrual
irregularities
Itraconazole (Sporanox®) - it lacks the endocrinologic effects of
ketoconazole
Organic Medicinal Chemistry Kriszelle C. Mancera
Fluconazole (Diflucan) - administered orally and intravenously
- it has Excellent penetrability into the CSF
- Drug of Choice for cryptococcal meningitis
(Cryptococcus neoformans)
Ketoconazole, Itraconazole, - for SC & Systemic mycoses
Fluconazole
Clotrimazole, Miconazole, - for superficial mycoses
Econazole
TOPOC 3: ANTI-PARASITIC AGENTS
Protozoal Infection
Disease Causative Agent
Amebiasis
Trichomoniasis
Giardiasis
Leishmaniasis
African Trypanosomiasis
Toxoplasmosis
Malaria
Organic Medicinal Chemistry Kriszelle C. Mancera
Metronidazole (Flagyl)
- Drugs of choice for infections:
• T – Trichomonas vaginalis
• A – Entamoeba histolytica
• G – Giargia intestinalis
• S- Spore formers (C. difficile)
- Unpleasant metallic taste is often experienced
- If taken with alcohol, a disulfiram-like effect occurs
Anti-Protozoal Drugs
Diloxanide - Asymptomatic E. histolytica carriers
8-hydroquinoline
Iodoquinol - DOC for asymptomatic amebiasis
Emetine and Dehydroemetine - Protoplasmic poison that (x) protein synthesizing
protozoal and mammalian cells by preventing
protein elongation
Pentamidine isethionate - Alternative treatment of PCP
- Alternative treatment of visceral leishmaniasis
(esp. when stibogluconate is unresponsive or
contraindicated)
- S/E: cough and bronchospasm(inhalation);
Hypertension and Hypoglycemia (injection)
- Prophylaxis and treatment of African
trypanosomiasis
Atovaquone - Original: P. falciparum (tolerated rapidly)
- Aletrnative: to TMP-SMX against PCP (treatment
and prophylaxis)
- Absorption is increased by fatty food
Eflornithine - West African Sleeping Sickness
- (Meningoencephalitic stage) (T. brucei var.
gambiense)
- Myelosuppressive ↑ incidence of anemia,
leukopenia and thrombocytopenia → CBC
counting monitor
Nifurtimox - T. cruzi (South American Sleeping Sickness) →
the only clinically proven regimen for both acute
and chronic forms of the disease
Benznidazole - Treatment of Chaga’s disease (Similat effect
with Nifurtimox)
Melarsoprol - Prepared by reduction of a corresponding
pentavalent arsanilate to the trivalent
arsenoxide followed by reaction of the latter
with BAL
- OLD DOC for txt of latter stages of African
trypanosomiasis
- Adv: excellent penetration into the CNS;
therefore, effective against
meningoencephalitis form
Organic Medicinal Chemistry Kriszelle C. Mancera
Sodium stibogluconate - Pentavalent antimonial compound
- Schistosomiasis and other flukes
• Pentavalent → Trivalent
• Anti-Leishmaniasis (DOC),
Dimercaprol - 2,3-dimercapto-1-propanol
- Developed by the British during WWII; an
antidote to German Nazi’s Lewisite
- Antidote for As, Sb, Hg, Au and Pb toxicity
Suramin Sodium - Prophylaxis for Trypanosomiasis &
Onchocerciasis
- DOC for African Trypanosomiasis early stage
(but not Chaga's disease)
- not absorbed in the GIT & is given parenterally
- Early stage: Suramin alone; Late Stage (CNS
involvement) spoor penetration of suramin &
pentamidine, requires melarsoprol
ANTHELMINTIC AGENTS
Piperazine - MOA: blocks the response of the Ascaris muscle
to acetylcholine, causing flaccid paralysis
- Paralyses ascaris by acting as an agonist at
GABA receptors
Diethylcarbamazine Citrate - Immobilizes microfilariae by an unknown
mechanism, increasing their susceptibility to host
defense mechanisms
- DOC for Filariasis / Elephantiasis
• Causative agent:?
Pyrantel Pamoate - stimulates nicotinic receptors present at
neuromuscular junctions of nematodes →
contraction of a muscle occurs, followed by a
depolarization-induced paralysis
- The drug has no actions on flukes or ringworms
Mebendazole - Mebendazole irreversibly blocks glucose uptake
in susceptible helminths, thereby depleting
glycogen stored in the parasite
- KATZUNG: acts by selectively inhibiting
microtubule synthesis & glucose uptake in
nematodes
Thiabendazole - structural congener of mebendazole and has a
similar action on microtubules
- DOG for Threadworm infection
Albendazole - Arrest cell division in metaphase by interfering w/
microtubule assembly. They exhibit a high
affinity for tubular, the precursor protein of
microtubule synthesis
Niclosamide - MOA: uncoupling oxidative phosphorylation or
by activating ATPases
Bithionol - MOA: Unknown
Organic Medicinal Chemistry Kriszelle C. Mancera
- co-Drug of Choice (Triclabendazole) for
treatment of fascioliasis (Sheep liver fluke)
Praziquantel - increases cell membrane permeability of
susceptible worms, resulting in loss of
extracellular Cal+ ions causing massive
contraction & ultimate paralysis
Ivermectin - Isolated from S. avermitilis
- Intensifies GABA mediated
neurotransmission in nematodes & causes
immobilization of parasites, facilitating their
removal by the reticuloendothelial system
- DOC for River blindness / Onchocerciasis
TOPIC 4: ANTIMALARIAL DRUG
MALARIAL SPECIES
- Plasmodium falciparum
- Plasmodium vivax
- Plasmodium ovale
- Plasmodium malaria
- Plasmodium knowlesi
Organic Medicinal Chemistry Kriszelle C. Mancera
CHEMISTRY
- have one common structural feature-a-quinoline ring or a "quinoline with an
additional benzene added" (an acridine ring)
CINCHONA ALKALOIDS
QUININE
- reserved for malarial strains resistant to other agents
- Major adverse effect: Cinchonism
• Nausea, vomiting, tinnitus, vertigo
- General Protoplasm
- Quinoclidine ring
- Adverse Effect:
• Cinchonism
▪ Tinnitus, Visual disturbances, Flushing, Dizziness, Headache, Nausea
- Hypoglycaemia - insulin release & glucose consumption of parasite
- QT prolongation (IV Quinidine)
- Blackwater Fever
7-CHLORO-4-AMINOQUINOLINES
Chloroquine
- DOC in txt of erythrocytic malaria
- Anti-inflammatory action explains its occasional use in RA and SLE
- Prophylaxis (in areas with no resistance)
Amodiaquine
- highly suppressive in P. vivax & falciparum
- has curative activity against P. falciparum
- S/E: prolonged use pigmentation of the palate, nail & skin, agranulocytosis
8-AMINOQUINOLONES
Primaquine
- The only drug effective against exocrythrocytic stages of malaria
- only agent that can lead to “radical cures? of the P. vivid & ovale
- Gametocidal for all 4 plasmodia species
9-AMINOACRIDINES
Quinacrine - primarily used in txt of Giardiasis, but also
effective against tapeworm and malaria, and
topically against leishmaniasis ® should not be
Organic Medicinal Chemistry Kriszelle C. Mancera
given w/ primaquine because of increased
toxicity
Mefloquine - effective single agent for suppressing and
cutting multi-drug resistant forms of P. falciparum
Artemisinin, Artesunate, - Artemisinin (Quinghaosu) (PO)
Artemether - Artesunate (PO, IV, IM, Rectal)
- Artemether (PO, IM, Rectal)
• Very rapidly acting blood schizonticides
against all malaria parasites
• Rapidly metabolised to the active
metabolite Dihydroartemisinin
• A/E: N & V, Diarrhea
- Clinical Uses:
• treatment of multidrug-resistant P.
falciparum malaria
- only drugs reliably effective against Quinine-
resistant strains
Artesunate - treatment of severe malaria
- treatment of uncomplicated & severe
falciparum malaria
- treatment of highly resistant falciparum malaria
in Thailand (with Mefloquine)
Organic Medicinal Chemistry Kriszelle C. Mancera
You might also like
- Intro To FSM Handouts BWDocument30 pagesIntro To FSM Handouts BWroberto_celio_2100% (5)
- Outline For Assessment of HEENTDocument3 pagesOutline For Assessment of HEENTpauchanmnl50% (2)
- Microbiology and Parasitology ReviewerDocument4 pagesMicrobiology and Parasitology ReviewerChrister Jon AcostaNo ratings yet
- Fungus PDFDocument4 pagesFungus PDFPrashant MishraNo ratings yet
- Mycology TransDocument11 pagesMycology TransKita kitaNo ratings yet
- Clinical AND ADVANCE Pathology: TopicDocument7 pagesClinical AND ADVANCE Pathology: TopicNestley TiongsonNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Fungi: Ex - Aspergillus, DermatophytesDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Fungi: Ex - Aspergillus, DermatophytesBanana CakeNo ratings yet
- Fungal InfectionDocument3 pagesFungal InfectionNicole TorralbaNo ratings yet
- FUNGAL and PARASITIC INFECTIONSDocument3 pagesFUNGAL and PARASITIC INFECTIONSKathleen Hazel AndresNo ratings yet
- Klinis Dan Diagnosa Laboratorium Jamur 10,11Document36 pagesKlinis Dan Diagnosa Laboratorium Jamur 10,11H PNo ratings yet
- MycosesDocument7 pagesMycosesJazmine Rose DelrosarioNo ratings yet
- Activity 8 MycologyDocument3 pagesActivity 8 MycologyBrent Lee100% (1)
- Birao Sas 14 Microbiology and ParasitologyDocument6 pagesBirao Sas 14 Microbiology and ParasitologyFrancis Jacob Dejecacion GarcesNo ratings yet
- FungiDocument1 pageFungiRaveenaNo ratings yet
- Micro Chart #3 - Italics OnlyDocument27 pagesMicro Chart #3 - Italics Onlyapi-26938624100% (1)
- MycosisDocument27 pagesMycosisIalyn RodrigoNo ratings yet
- Mycology 170328040158Document84 pagesMycology 170328040158Zainab KhadharNo ratings yet
- ED Na STR FUNGIDocument46 pagesED Na STR FUNGIdw21541No ratings yet
- Fungal InfectionsDocument76 pagesFungal InfectionsHrishikesh NachinolkarNo ratings yet
- Unit v. Fungal Diseases Rev.3Document56 pagesUnit v. Fungal Diseases Rev.3Vda RmehrNo ratings yet
- Mycology SOM CJBDocument91 pagesMycology SOM CJBYlia MastarsNo ratings yet
- Micro Chart Test 3Document8 pagesMicro Chart Test 3api-26938624No ratings yet
- Medically Important FungihandoutDocument55 pagesMedically Important FungihandoutHervis FantiniNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Cutaneous and Subcutaneous MycosesDocument46 pagesLecture 2 Cutaneous and Subcutaneous MycoseschiyeoncherryNo ratings yet
- (Internal) The Epidermis That Grow On The Keratin Present On TheseDocument8 pages(Internal) The Epidermis That Grow On The Keratin Present On TheseAthena Irish LastimosaNo ratings yet
- Superficial MycosisDocument17 pagesSuperficial Mycosisapi-19969058100% (3)
- Fungal Infections Mycotic Infections MycosesDocument12 pagesFungal Infections Mycotic Infections MycosesHussein QasimNo ratings yet
- Myco Myco OwnDocument4 pagesMyco Myco OwnMarielle Anne TuazonNo ratings yet
- Ankur Vashishtha S Ubharti University MeerutDocument34 pagesAnkur Vashishtha S Ubharti University MeerutKana FajarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MycologyDocument35 pagesIntroduction To MycologyTheBoss 20No ratings yet
- Mikosis SuperfisialDocument46 pagesMikosis SuperfisialAdipuraAtmadjaEgokNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Superficial Cutaneous Mycosis HandoutsDocument8 pagesLesson 2 Superficial Cutaneous Mycosis HandoutsKhay Mae DonascoNo ratings yet
- Cutaneous and Subcutaneous mycoses-FMS2-2558Document68 pagesCutaneous and Subcutaneous mycoses-FMS2-2558Marl EstradaNo ratings yet
- Title of The LecDocument22 pagesTitle of The LecWeird BoiNo ratings yet
- FungiDocument3 pagesFungikrystal TortolaNo ratings yet
- Systemic Mycoses: A. BlastomycosisDocument3 pagesSystemic Mycoses: A. Blastomycosisbaihern24No ratings yet
- Mikologi Kedokteran: Ilmu Yang Mempelajari Jamur Serta Penyakit Yang Ditimbulkan Pada ManusiaDocument100 pagesMikologi Kedokteran: Ilmu Yang Mempelajari Jamur Serta Penyakit Yang Ditimbulkan Pada ManusiazafiharoNo ratings yet
- Bios - FungiDocument7 pagesBios - FungicalebleuNo ratings yet
- DMS. K07. Jamur Penyebab Penyakit KulitDocument120 pagesDMS. K07. Jamur Penyebab Penyakit KulitmissirenaNo ratings yet
- 05 Systemic MycosesDocument3 pages05 Systemic MycosesThea MallariNo ratings yet
- Cut MycosesDocument56 pagesCut MycosesHafsa ImranNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Microbiology and Parasitology (PHMP211)Document59 pagesPharmaceutical Microbiology and Parasitology (PHMP211)Crisamor Rose Pareja ClarisaNo ratings yet
- MCB 409 Pathogenic MycologyDocument49 pagesMCB 409 Pathogenic Mycologyejohn8340No ratings yet
- Modul #3 - Student Activity Sheet - CUTANEOUS MYCOSESDocument7 pagesModul #3 - Student Activity Sheet - CUTANEOUS MYCOSESYlia MastarsNo ratings yet
- Antifungal Agents General Introduction To Fungi: Medical Mycology Cutaneous Infections (Dermatophytoses)Document4 pagesAntifungal Agents General Introduction To Fungi: Medical Mycology Cutaneous Infections (Dermatophytoses)Ad Rianne DeniseNo ratings yet
- MycosesDocument2 pagesMycosesMadabout MusicNo ratings yet
- Microbial Diseases (Skin Eyes)Document23 pagesMicrobial Diseases (Skin Eyes)Hazel Mae FestinNo ratings yet
- Jamur-Jamur Penyebab: Mikosis Superfisial Dermatofitosis Mikosis SubkutanDocument104 pagesJamur-Jamur Penyebab: Mikosis Superfisial Dermatofitosis Mikosis SubkutanJimmy Fran IINo ratings yet
- Fungal Infections-SubcutaneousDocument24 pagesFungal Infections-SubcutaneousKato CalebNo ratings yet
- Opportunistic MycosesDocument6 pagesOpportunistic MycosesJullana Rondina EscondeNo ratings yet
- Classification of Fungal InfectionsDocument26 pagesClassification of Fungal Infectionstev26100% (1)
- Dermatophytes 20240314 214707 0000Document18 pagesDermatophytes 20240314 214707 0000khushi.gupta2122No ratings yet
- Branching, Aerobic, Partially Acid Fast and Non-Acid Fast Gram (+) BacilliDocument2 pagesBranching, Aerobic, Partially Acid Fast and Non-Acid Fast Gram (+) BacilliJustine Marie RevillaNo ratings yet
- Infection of The Skin, Soft Tissue, Etc.Document84 pagesInfection of The Skin, Soft Tissue, Etc.fmds100% (1)
- Pharmaceutical Chemistry (Midterm)Document11 pagesPharmaceutical Chemistry (Midterm)Majeddah Aliudin TalambunganNo ratings yet
- Microbiology - 19Document4 pagesMicrobiology - 19karmylle andradeNo ratings yet
- Superficial MycosisDocument8 pagesSuperficial MycosisLuqman Al-Bashir FauziNo ratings yet
- Mycology MycosesDocument7 pagesMycology MycosesSarah Grace KamlaniNo ratings yet
- Classifications of FungiDocument11 pagesClassifications of FungiRusselNo ratings yet
- Dermatology Notes for Medical StudentsFrom EverandDermatology Notes for Medical StudentsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- A Simple Guide to Skin Fungal Infections, (Updated 2023) Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Skin Fungal Infections, (Updated 2023) Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- LECTURE-1 MedDocument2 pagesLECTURE-1 Medbarbadillojames419No ratings yet
- Pharm 17 Chapter 17Document15 pagesPharm 17 Chapter 17barbadillojames419No ratings yet
- Pharm 17 Activity 1.PDF ADocument3 pagesPharm 17 Activity 1.PDF Abarbadillojames419No ratings yet
- Pharm 17 Chapter 19Document14 pagesPharm 17 Chapter 19barbadillojames419No ratings yet
- DHQ Flowcharts v2 1 Prep Pep ArtDocument49 pagesDHQ Flowcharts v2 1 Prep Pep ArtNatasha MendozaNo ratings yet
- The Spanish Flu Pandemic of 1918Document5 pagesThe Spanish Flu Pandemic of 1918jellNo ratings yet
- Script For PPT PresentationDocument4 pagesScript For PPT PresentationJanine Airah MorgadoNo ratings yet
- Herbal PlantsDocument11 pagesHerbal PlantsDechy Lyn PalmaNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument32 pagesRheumatoid ArthritisWoro Nugroho100% (5)
- Asma AnakDocument53 pagesAsma AnakAsri Rasyid LaskarIRDNo ratings yet
- Kinesia ParadoxaDocument7 pagesKinesia ParadoxaArcenciel26No ratings yet
- ShinglesDocument8 pagesShinglesapi-3366481170% (1)
- Asthma: Topic OutlineDocument2 pagesAsthma: Topic OutlineKdamnzNo ratings yet
- Carpal Tunnel SyndromeDocument9 pagesCarpal Tunnel SyndromeMaha RajaNo ratings yet
- Antenatal CorticosteroidsDocument2 pagesAntenatal CorticosteroidsFaizaShabirAhmedNo ratings yet
- Abdominal EpilepsyDocument4 pagesAbdominal EpilepsyErnesto Ochoa MonroyNo ratings yet
- Complications Druing HemodialysisDocument30 pagesComplications Druing HemodialysisMD Hajj83% (6)
- Special Education ClassificationsDocument3 pagesSpecial Education ClassificationsEdmar AgarpaoNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- Emskfjek-Intravenous IV Fluid Prescribing in AdultsDocument14 pagesEmskfjek-Intravenous IV Fluid Prescribing in AdultsAli SemajNo ratings yet
- GeneXpert - Monthly - Report - JAN, FEB, MARCH 2019 (GIMS) GAMBAT)Document12 pagesGeneXpert - Monthly - Report - JAN, FEB, MARCH 2019 (GIMS) GAMBAT)shakeelNo ratings yet
- Inflammation AvianDocument4 pagesInflammation Avianamit vishen75% (4)
- Practitioner Sample O and P Written ExamDocument4 pagesPractitioner Sample O and P Written ExamBapina Kumar RoutNo ratings yet
- Gonorrhea Infection in Women: Prevalence, Effects, Screening, and ManagementDocument12 pagesGonorrhea Infection in Women: Prevalence, Effects, Screening, and Managementilham hamkaNo ratings yet
- Question Paper 2023 AIAPGETDocument20 pagesQuestion Paper 2023 AIAPGETrohinibrajole123No ratings yet
- Hypoxia: Lori HolmesDocument5 pagesHypoxia: Lori HolmesDanson Githinji ENo ratings yet
- Heat Tolerance Test PDFDocument7 pagesHeat Tolerance Test PDFMonica LapusNo ratings yet
- SAGES Consent 2019 2023Document16 pagesSAGES Consent 2019 2023cNo ratings yet
- Types of Food ContaminationDocument13 pagesTypes of Food ContaminationHelena MbangoNo ratings yet
- Sarcomas SurgeryDocument8 pagesSarcomas SurgeryJüdith Marie Reyes BauntoNo ratings yet
- LabyrinthitisDocument7 pagesLabyrinthitisChristie ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology of Oral CancerDocument12 pagesEpidemiology of Oral Cancerعدي عبدالالهNo ratings yet