Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Notes
Notes
Uploaded by
mohamed.hassan0310 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as rtf, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesNotes
Notes
Uploaded by
mohamed.hassan031Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as rtf, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
· The objective is to determine the control torque applied to
the motor crank
· The windshield wiper mechanisms are vehicle-specific
systems in which the wiping
motion is transferred from the wiper motor to the pivot-shaft
assemblies via linkages. A
compact wiper system consists of the following components:
wiper motor with thermoswitch, wiper gearing, motor crank,
steel base-plate, crank linkage, pivot-shaft assembly
with oscillating crank, and second pivot-shaft assembly with
plate (for parallel wipe
pattern), respectively.
· is used to obtain the crank turning moment, which is the
input parameter in the dynamic analysis.
· build - create parts, constrain the parts (using geometric
restrictions), create forces and
torques acting on the parts; test - measure characteristics,
perform simulations, review
animations, review numeric results as plots; validate - import
test data, superimpose test data on plots; refine - add friction,
define flexible bodies, define controls and others.
· In the kinematic & inverse dynamic models, the degree of
mobility is kinematically
controlled by using a motion generator, 1(t). Considering the
input speed for the motor
crank n1=65 rot/min, will results: 1 = n1 /30 = 6.803
rad/sec 1 = 1t = 6.803t. For
the dynamic model, the kinematic constraint is replaced with
the torque applied on the
motor crank; therefore, the dynamic model has one
independent generalized coordinate
· The friction force that acts on the wiper lamella depends
on the friction coefficient
between rubber blade and windshield, and the normal force
generated by the spring
mounted between wiper arm and oscillating crank. Considering
the dry wiping regime, the
friction force, which is applied in the connection point between
wiper arm and lamella (see
fig. 1), will be Ff = 8.7 N.
{1} ANNALS of the ORADEA UNIVERSITY.
Fascicle of Management and Technological Engineering, Volume
XI (XXI), 2012, NR1
You might also like
- Machines and Mechanisms CourseworkDocument30 pagesMachines and Mechanisms Courseworksaad hussainNo ratings yet
- Study of a reluctance magnetic gearbox for energy storage system applicationFrom EverandStudy of a reluctance magnetic gearbox for energy storage system applicationRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Design and Analysis of Globoidal Cam Index DriveDocument6 pagesDesign and Analysis of Globoidal Cam Index DriveijsretNo ratings yet
- 2004 - 04 Study of Stability of A Two Wheeled Vehicle MODENADocument11 pages2004 - 04 Study of Stability of A Two Wheeled Vehicle MODENARenan Alves100% (1)
- Technical Paper For Students and Young Engineers: - Fisita World Automotive Congress, Barcelona 2004Document15 pagesTechnical Paper For Students and Young Engineers: - Fisita World Automotive Congress, Barcelona 2004rike.spNo ratings yet
- Important Short Questions DYNAMICS AND DESIGN OF MACHINERYDocument32 pagesImportant Short Questions DYNAMICS AND DESIGN OF MACHINERYramos mingoNo ratings yet
- 9 - Optimal Decoupled Control For Dry Clutch EngagementDocument6 pages9 - Optimal Decoupled Control For Dry Clutch EngagementMehdi NiksereshtNo ratings yet
- The Study of Continuous Rolling Mill Inter-Stand T PDFDocument8 pagesThe Study of Continuous Rolling Mill Inter-Stand T PDFSantosh Kumar Pandey100% (1)
- Mathematical Model For Torsional Vibration Analysis in Internal Combustion EnginesDocument6 pagesMathematical Model For Torsional Vibration Analysis in Internal Combustion Enginesstefanovicana1No ratings yet
- Annals 2013 2 19 PDFDocument4 pagesAnnals 2013 2 19 PDFLohith B.YNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Locomotive Motor Torque Impact at Changeable Dynamic Operation ConditionsDocument9 pagesAnalysis of Locomotive Motor Torque Impact at Changeable Dynamic Operation Conditionsharshads1502No ratings yet
- Open Ended LabDocument7 pagesOpen Ended LabSaad AliKhanNo ratings yet
- Bridge Deck Active Damper Wind Tunnel Test PreprintDocument10 pagesBridge Deck Active Damper Wind Tunnel Test PreprintJose Manuel Gonzalez ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Dokument - Pub Dom Assignment Flipbook PDFDocument22 pagesDokument - Pub Dom Assignment Flipbook PDFMuhammad SaboorNo ratings yet
- STA 2013 LiliaDocument6 pagesSTA 2013 LiliaHAFEDH ABIDNo ratings yet
- A Novel Gear Test Rig With Adjustable Shaft Compliance and Misalignments Part I: DesignDocument10 pagesA Novel Gear Test Rig With Adjustable Shaft Compliance and Misalignments Part I: DesignjgjNo ratings yet
- A Novel Gear Test Rig With Adjustable PDFDocument10 pagesA Novel Gear Test Rig With Adjustable PDFjgjNo ratings yet
- VCS REPORT FinalDocument7 pagesVCS REPORT Finalasd108533No ratings yet
- Infunce of Electrical Assistance Steering System On VehicleDocument18 pagesInfunce of Electrical Assistance Steering System On VehicleAmiroNo ratings yet
- Paper CT4 Load Assumptions For Pitch System Manj 041Document5 pagesPaper CT4 Load Assumptions For Pitch System Manj 041mbreuking6943No ratings yet
- Hiroaki HOSHINO - Simulation On Synchronization MechanismDocument8 pagesHiroaki HOSHINO - Simulation On Synchronization Mechanismelah1No ratings yet
- Lab Work 8: Aim of The WorkDocument4 pagesLab Work 8: Aim of The WorkvirenNo ratings yet
- есть данные комбайнаDocument19 pagesесть данные комбайнаdimaNo ratings yet
- Gait Phase-Based Control For A Rotary Series Elastic Actuator Assisting The Knee JointDocument6 pagesGait Phase-Based Control For A Rotary Series Elastic Actuator Assisting The Knee JointYazdan RastegarNo ratings yet
- 1991 - Bearings MathmodelDocument22 pages1991 - Bearings MathmodelChiara GastaldiNo ratings yet
- George Constantinesco Torque Converter Analysis by Simulink PDFDocument6 pagesGeorge Constantinesco Torque Converter Analysis by Simulink PDFslysoft.20009951No ratings yet
- Manual TransmissionDocument5 pagesManual Transmissionstolen mechieducNo ratings yet
- A Mechatronic Approach For Anti-Slip Control in Railway TractionDocument6 pagesA Mechatronic Approach For Anti-Slip Control in Railway TractionLoftie DeyzelNo ratings yet
- A Design Proposal of Driving SystemDocument5 pagesA Design Proposal of Driving SystemlukaszNo ratings yet
- Wang 2018Document5 pagesWang 2018R Prabhu SekarNo ratings yet
- GC Cam Design and Analysis PDFDocument6 pagesGC Cam Design and Analysis PDFrahulNo ratings yet
- Analysis of The Instability Phenomena Caused by Steam in High-Pressure TurbinesDocument20 pagesAnalysis of The Instability Phenomena Caused by Steam in High-Pressure Turbinesbaca88No ratings yet
- An Experimental Study of Whirling Characteristics of Gear-Pinion Rotor SystemDocument4 pagesAn Experimental Study of Whirling Characteristics of Gear-Pinion Rotor SystemBunty PereraNo ratings yet
- 11a Motor Sizing and Selection For Geared Hoisting Systems Rev 1 071221 CCuploadDocument9 pages11a Motor Sizing and Selection For Geared Hoisting Systems Rev 1 071221 CCuploadnaga531No ratings yet
- Modelling The Elastodynamic Behaviour of A DesmodrDocument11 pagesModelling The Elastodynamic Behaviour of A DesmodrIkshwakNo ratings yet
- Application of Adaptive Controlnext Term To The Fluctuation of Engine Speed at IdleDocument15 pagesApplication of Adaptive Controlnext Term To The Fluctuation of Engine Speed at IdleIkhwanul KhairiNo ratings yet
- Machine Tool Feed DrivesDocument18 pagesMachine Tool Feed DrivesDoris ParaschivNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Force AnalysisDocument42 pagesDynamic Force Analysisdhruv001No ratings yet
- Identification and Quantification of Stick-Slip Induced Brake Groan Events Using Experimental and Analytical InvestigationsDocument21 pagesIdentification and Quantification of Stick-Slip Induced Brake Groan Events Using Experimental and Analytical Investigationsthierry42No ratings yet
- Assessment of Dynamic Parameters of Heavy-Duty GearsDocument6 pagesAssessment of Dynamic Parameters of Heavy-Duty GearsMohammad HosseiniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Spur Gear DesignDocument122 pagesChapter 9 Spur Gear DesignJimmy Silvera OtañeNo ratings yet
- Technical Paper For Students and Young Engineers: - Fisita World Automotive Congress, Barcelona 2004Document7 pagesTechnical Paper For Students and Young Engineers: - Fisita World Automotive Congress, Barcelona 2004hadiNo ratings yet
- Design On Torsion Test-Bed of Automobile Drive Shaft: Dongmei Yuan, Qiang Liang and Xihong ZouDocument3 pagesDesign On Torsion Test-Bed of Automobile Drive Shaft: Dongmei Yuan, Qiang Liang and Xihong ZouAlberto hdez FonsecaNo ratings yet
- Mechatronics CEP 2 Designing Control System For Suspension SystemDocument12 pagesMechatronics CEP 2 Designing Control System For Suspension SystemFaizan SamdaniNo ratings yet
- li2011Document14 pagesli2011Ismail IsmailNo ratings yet
- Final ReportDocument20 pagesFinal ReportMuhammad Hussain Bilal100% (1)
- Performance Enhancement of Internal Combustion Engines Through Vibration Control: State of The Art and ChallengesDocument30 pagesPerformance Enhancement of Internal Combustion Engines Through Vibration Control: State of The Art and Challengesachraf zegnaniNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Rigid Dynamic of A Spatial Slider-Crank Mechanism With Spherical Clearance Joints Using ANSYS Software Huynh Ngoc Thai, SHYH-CHOUR HUANGDocument5 pagesAnalysis of Rigid Dynamic of A Spatial Slider-Crank Mechanism With Spherical Clearance Joints Using ANSYS Software Huynh Ngoc Thai, SHYH-CHOUR HUANGThaiHuynhNgocNo ratings yet
- Freq. Response ParametersDocument4 pagesFreq. Response ParametersPPMNo ratings yet
- Developing A Proposed Satellite Reaction Wheel Model With Current Mode ControlDocument5 pagesDeveloping A Proposed Satellite Reaction Wheel Model With Current Mode ControlJahnavi VurityNo ratings yet
- Estimation and Active Damping of Unbalance Forces in Jeffcott-Like Rotor-Bearing SystemsDocument22 pagesEstimation and Active Damping of Unbalance Forces in Jeffcott-Like Rotor-Bearing SystemsAnonymous LU3Dz3TKtVNo ratings yet
- mei2008Document10 pagesmei2008engineeringtipsaNo ratings yet
- Symposium On The Lift and Escalator Technologies: Vibrations in A Lift SystemDocument4 pagesSymposium On The Lift and Escalator Technologies: Vibrations in A Lift SystemfreddyjoertyNo ratings yet
- Model Based Fault Identi Cation of UnbalanceDocument10 pagesModel Based Fault Identi Cation of UnbalanceJulio CesarNo ratings yet
- Theoretical and Experimental Efficiency Analysis of Multi-Degrees-of-Freedom Epicyclic Gear TrainsDocument21 pagesTheoretical and Experimental Efficiency Analysis of Multi-Degrees-of-Freedom Epicyclic Gear TrainsAmin ShafanezhadNo ratings yet
- Discrete-Time For Traction: RobustDocument7 pagesDiscrete-Time For Traction: RobustfenasikarimNo ratings yet
- Mechanism and Machine Theory: К. Bissembayev, Zh. IskakovDocument18 pagesMechanism and Machine Theory: К. Bissembayev, Zh. IskakovDennis AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Control of DC Motor Using Different Control StrategiesFrom EverandControl of DC Motor Using Different Control StrategiesNo ratings yet
- QuizDocument1 pageQuizmohamed.hassan031No ratings yet
- 9 Mechanical Weld QualityDocument36 pages9 Mechanical Weld Qualitymohamed.hassan031No ratings yet
- Impact SheetDocument2 pagesImpact Sheetmohamed.hassan031No ratings yet
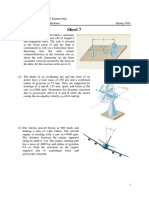
- Sheet 7 GyroscopeDocument1 pageSheet 7 Gyroscopemohamed.hassan031No ratings yet
- Sheet 6 FlywheelDocument2 pagesSheet 6 Flywheelmohamed.hassan031No ratings yet
- Creep SheetDocument3 pagesCreep Sheetmohamed.hassan031No ratings yet
- Final 2021Document3 pagesFinal 2021mohamed.hassan031No ratings yet
- Design of IC Engine ComponentsDocument52 pagesDesign of IC Engine Componentsmohamed.hassan031No ratings yet
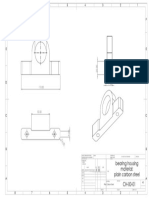
- Bearin HousingDocument1 pageBearin Housingmohamed.hassan031No ratings yet
- Final 2023Document3 pagesFinal 2023mohamed.hassan031No ratings yet
- Final 2023Document16 pagesFinal 2023mohamed.hassan031No ratings yet
- Torsion MEDocument24 pagesTorsion MEmohamed.hassan031No ratings yet
- Welding MetallurgyDocument46 pagesWelding Metallurgymohamed.hassan031No ratings yet
- Study Elastic and Plastic Bending of A Sheet BlankDocument11 pagesStudy Elastic and Plastic Bending of A Sheet Blankmohamed.hassan031No ratings yet
- 10 Heat Flow in WeldingDocument20 pages10 Heat Flow in Weldingmohamed.hassan031No ratings yet
- Failure Analysis of A Spring For A Fuel Pump BrackDocument5 pagesFailure Analysis of A Spring For A Fuel Pump Brackmohamed.hassan031No ratings yet