Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Calculation of Wind Load ASCE7 16 Chapter26&27For Open Build
Calculation of Wind Load ASCE7 16 Chapter26&27For Open Build
Uploaded by
John Leoanrd L FerrerOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Calculation of Wind Load ASCE7 16 Chapter26&27For Open Build
Calculation of Wind Load ASCE7 16 Chapter26&27For Open Build
Uploaded by
John Leoanrd L FerrerCopyright:
Available Formats
Phnom Penh, Cambodia Project: ...
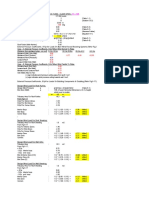
Calculation of Wind Load for Open Building Monoslope Roof
1-Input Delta
> Eave height heave ≔ 4.6 m
> Mean roof height hmain_roof ≔ 5 m
> Width of building W ≔ 20 m
> Length of building L ≔ 10 m
> Angle of plan of roof from horizontal θ ≔ 18.5 deg
> Wind flow WindFlow ≔ Clear Wind Flow
2-Calculation of Wind Velocity Pressure
km m
> Basic wind speed V ≔ 149 ―― = 41.389 ―
hr s
> Wind directionality factor Kd ≔ 0.85 (Table 26.6-1)
> Exposure category Exposure ≔ C (Section 26.7)
> Topographic factor Kzt ≔ 1 (Figure 26.8-1)
> Ground elevation factor Ke ≔ 1 (Section 26.9)
> Gust-effect facto G ≔ 0.85 (Section 26.11)
> Enclosure classification Enclose ≔ Open building (Section 26.12)
> The velocity pressure exposure coefficient (Table 26.10-1)
Kz = 0.85
N ⎛ V ⎞2 kN
> Velocity pressure qh ≔ 0.613 ―― ⋅ Kz ⋅ K zt ⋅ Kd ⋅ K e ⋅ ⎜ ―― ⎟ = 0.759 ―― (section 26.10)
m2 m
⎜ ―⎟ m 2
> Internal pressure coefficient ⎜⎝ s ⎟⎠ (Table 26.13-1)
⎡ GCpi_pos ⎤ ⎡ 0 ⎤
⎢ ⎥≔⎢ ⎥ (Table 26.13-1)
⎣ GCpi_ne ⎦ ⎣ 0 ⎦
Structural Analysis and Design Report Page 1
Phnom Penh, Cambodia Project: ...
3-Calculation External Pressure Coefficient Cn
(Figure 27.3-4)
> Wind direction 0 Degree For load Case A (Clear Wind Flow)
⎡ CNW_A_Clear_Direct0° ⎤ ⎡ -1.18 ⎤
⎢ ⎥=⎢ ⎥
⎣ CNL_A_Clear_Direct0° ⎦ ⎣ -1.44 ⎦
> Wind direction 0 Degree For load Case B (Clear Wind Flow)
⎡ CNW_B_Clear_Direct0° ⎤ ⎡ -2.133 ⎤
⎢ ⎥=⎢ ⎥
⎣ CNL_B_Clear_Direct0° ⎦ ⎣ -0.14 ⎦
> Wind direction 0 Degree For load Case A (Obstructed Flow)
⎡ CNW_A_Obstruct_Direct0° ⎤ ⎡ -1.287 ⎤
⎢ ⎥=⎢ ⎥
⎣ CNL_A_Obstruct_Direct0° ⎦ ⎣ -1.593 ⎦
> Wind direction 0 Degree For load Case B (Obstructed Flow)
⎡ CNW_B_Obstruct_Direct0° ⎤ ⎡ -2.193 ⎤
⎢ ⎥=⎢ ⎥
⎣ CNL_B_Obstruct_Direct0° ⎦ ⎣ -0.74 ⎦
> Wind direction 180 Degree For load Case A (Clear Wind Flow)
⎡ CNW_A_Clear_Direct180° ⎤ ⎡ 1.487 ⎤
⎢ ⎥=⎢ ⎥
⎣ CNL_A_Clear_Direct180° ⎦ ⎣ 1.693 ⎦
> Wind direction 180 Degree For load Case B (Clear Wind Flow)
⎡ CNW_B_Clear_Direct180° ⎤ ⎡ 1.987 ⎤
⎢ ⎥=⎢ ⎥
⎣ CNL_B_Clear_Direct180° ⎦ ⎣ 0.647 ⎦
Structural Analysis and Design Report Page 2
Phnom Penh, Cambodia Project: ...
> Wind direction 180 Degree For load Case A (Obstructed Flow)
⎡ CNW_A_Obstruct_Direct180° ⎤ ⎡ 0.447 ⎤
⎢ ⎥=⎢ ⎥
⎣ CNL_A_Obstruct_Direct180° ⎦ ⎣ -1.053 ⎦
> Wind direction 180 Degree For load Case B (Obstructed Flow)
⎡ CNW_B_Obstruct_Direct180° ⎤ ⎡ 1.247 ⎤
⎢ ⎥=⎢ ⎥
⎣ CNL_B_Obstruct_Direct180° ⎦ ⎣ -0.16 ⎦
3-Calculation the Net Pressure Coefficient
> Wind direction =Case 0 degree A
⎡ CNW_A_Diretion0° ⎤ ⎡ -1.18 ⎤
⎢ ⎥=⎢ ⎥
⎣ CNL_A_Diretion0° ⎦ ⎣ -1.44 ⎦
> Wind direction =180 degree Case A
⎡ CNW_A_Diretion180° ⎤ ⎡ 1.487 ⎤
⎢ ⎥=⎢ ⎥
⎣ CNL_A_Diretion180° ⎦ ⎣ 1.693 ⎦
> Wind direction =0 degree Case B
⎡ CNW_B_Diretion0° ⎤ ⎡ -2.133 ⎤
⎢ ⎥=⎢ ⎥
⎣ CNL_B_Diretion0° ⎦ ⎣ -0.14 ⎦
> Wind direction =180 degree Case B
⎡ CNW_B_Diretion180° ⎤ ⎡ 1.987 ⎤
⎢ ⎥=⎢ ⎥
⎣ CNL_B_Diretion180° ⎦ ⎣ 0.647 ⎦
Structural Analysis and Design Report Page 3
Phnom Penh, Cambodia Project: ...
4-Calculation Wind Pressure Apply on Frame
> Wind direction =0 degree Load Case A > Wind direction =180 degree Load Case A
kN kN
qA1 ≔ qh ⋅ G ⋅ CNW_A_Diretion0° = -0.761 ―― qA3 ≔ qh ⋅ G ⋅ CNW_A_Diretion180° = 0.959 ――
m2 m2
kN kN
qA2 ≔ qh ⋅ G ⋅ CNL_A_Diretion0° = -0.929 ―― qA4 ≔ qh ⋅ G ⋅ CNL_A_Diretion180° = 1.092 ――
m2 m2
> Wind direction =0 degree Load Case B > Wind direction =180 degree Load Case B
kN kN
qB1 ≔ qh ⋅ G ⋅ CNW_B_Diretion0° = -1.376 ―― 2
qB3 ≔ qh ⋅ G ⋅ CNW_B_Diretion180° = 1.281 ――
m m2
kN kN
qB2 ≔ qh ⋅ G ⋅ CNL_B_Diretion0° = -0.09 ――2
qB4 ≔ qh ⋅ G ⋅ CNL_B_Diretion180° = 0.417 ――
m m2
Note: >The value of pressure p is positive (+), it means that the force is PUSH IN.
>If the value of pressure p is negative (-), means that the force is PUSH OUT.
Structural Analysis and Design Report Page 4
You might also like
- Ranger - Manual de Peças M5R1 M5R2 RKEDocument6 pagesRanger - Manual de Peças M5R1 M5R2 RKEWanderson Wadjô100% (3)
- 1 Storey Structural AnalysisDocument26 pages1 Storey Structural AnalysisBrin Entong50% (2)
- SAUDI Lighting CodeDocument14 pagesSAUDI Lighting CodeIBRAHIM ESMAIL50% (2)
- Wind Analysis For Open Structure (Solar Panels) Based On ASCE 7-16 Input DataDocument8 pagesWind Analysis For Open Structure (Solar Panels) Based On ASCE 7-16 Input DataDonald HamiltonNo ratings yet
- Switching Power Supply Design: A Concise Practical HandbookFrom EverandSwitching Power Supply Design: A Concise Practical HandbookNo ratings yet
- Chapter-0 Control Valves Handbook PDFDocument60 pagesChapter-0 Control Valves Handbook PDFOscarGomezMecanico100% (2)
- Ollessos Technical Training Institute Proposeed Three Storey Building For Civil Engineering DepartmentDocument89 pagesOllessos Technical Training Institute Proposeed Three Storey Building For Civil Engineering DepartmentCarol SoiNo ratings yet
- Determining of Wind Load According To ASCE 7-16: H Z ZT D e 2Document2 pagesDetermining of Wind Load According To ASCE 7-16: H Z ZT D e 2Primož KozlevčarNo ratings yet
- Monoslope Wind NSCPDocument8 pagesMonoslope Wind NSCPNicole100% (1)
- Structural Calculations For Metal Structure and Fence Legalization PlansDocument34 pagesStructural Calculations For Metal Structure and Fence Legalization PlansAlejandro MorelNo ratings yet
- An Example Problem On Wind Load Calculation According To NSCP 2010Document32 pagesAn Example Problem On Wind Load Calculation According To NSCP 2010Danilo NeryNo ratings yet
- Canteen 3-2-19Document41 pagesCanteen 3-2-19EngelMerlDeVillaNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Final Exam Problem & SolutionsDocument8 pagesHeat Transfer Final Exam Problem & SolutionsRonard Pa–a0% (1)
- TrussDocument3 pagesTrussAashish MaharjanNo ratings yet
- Final Plate Design of Roof Truss Ce 153-Timber DesignDocument37 pagesFinal Plate Design of Roof Truss Ce 153-Timber DesignJohn Lloyd JuanoNo ratings yet
- GRP 6 Wind Loads On Building Using Directional ProdecureDocument2 pagesGRP 6 Wind Loads On Building Using Directional ProdecureJade ParrenoNo ratings yet
- Wind LoadDocument7 pagesWind LoadChristelle Nicole TargaNo ratings yet
- Manual Compu Barangay Affairs BuildingDocument38 pagesManual Compu Barangay Affairs BuildingMeanne AzucenaNo ratings yet
- 2-Wind Load Calculation Monoslop RoofDocument4 pages2-Wind Load Calculation Monoslop Roofkheang mengNo ratings yet
- Calculation Vacuum Bay (ADNOC)Document152 pagesCalculation Vacuum Bay (ADNOC)Jaman AliNo ratings yet
- Wind Load: Velocity, V 150 KPHDocument6 pagesWind Load: Velocity, V 150 KPHBernadeth TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Open Building With Gable Roof: ProcedureDocument7 pagesOpen Building With Gable Roof: ProcedureFranklin Lucas HilarionNo ratings yet
- L0Ad Parameters: Dead LoadDocument11 pagesL0Ad Parameters: Dead LoadJuNe RaMos JavierNo ratings yet
- CALC - Roof Loadingsv02-Asnp3Document13 pagesCALC - Roof Loadingsv02-Asnp3axl skid santosNo ratings yet
- Design Check Calculation of Tension PolesDocument34 pagesDesign Check Calculation of Tension Polesirshad khanNo ratings yet
- Analiza Opterecenja VetarDocument5 pagesAnaliza Opterecenja VetarNevena SakovicNo ratings yet
- Annexure-1 Wind Load ReportDocument4 pagesAnnexure-1 Wind Load ReportPrabartak DasNo ratings yet
- Determining Risk Category of Building or Other Structure. Table 103 - 1 Occupancy CategoryDocument10 pagesDetermining Risk Category of Building or Other Structure. Table 103 - 1 Occupancy CategoryDaisy Jane LulabNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Wind Loads: CE 115 Structural Theory IiDocument12 pagesEstimation of Wind Loads: CE 115 Structural Theory IiKim SomeraNo ratings yet
- Wind - PZ CalculationDocument4 pagesWind - PZ CalculationPradip NikamNo ratings yet
- Windload by BNBC 1993 (Shoyeeb)Document3 pagesWindload by BNBC 1993 (Shoyeeb)Shoyeeb Ahmed100% (1)
- Wind Loadn CalculationDocument1 pageWind Loadn CalculationSiddiqui RanaNo ratings yet
- Example 1Document10 pagesExample 1Pagal KumarNo ratings yet
- Aldrin Leyte (12-7-19) (Recovered) (Autosaved) (Autosaved2) (Autosaved) (Version1)Document98 pagesAldrin Leyte (12-7-19) (Recovered) (Autosaved) (Autosaved2) (Autosaved) (Version1)Mohamad Siddik DimasangkayNo ratings yet
- Wind Load EnclosedDocument1 pageWind Load EnclosedronyNo ratings yet
- Seismic Load STG BuildingDocument6 pagesSeismic Load STG BuildingWahyu MunajatNo ratings yet
- 1-Load ParametersDocument97 pages1-Load ParametersJuNe RaMos JavierNo ratings yet
- Wind - PZ CalculationDocument4 pagesWind - PZ CalculationPradip NikamNo ratings yet
- Minimum Loads: Thayer's Formula (From Steel Structures 3rd Ed 2012 by Z.A. Siddiqi, p.261)Document17 pagesMinimum Loads: Thayer's Formula (From Steel Structures 3rd Ed 2012 by Z.A. Siddiqi, p.261)JHON CLYDE SEPADANo ratings yet
- Wind Load Dusit BangkokDocument1 pageWind Load Dusit BangkokleoNo ratings yet
- Design of Purlins and Load Calc.Document2 pagesDesign of Purlins and Load Calc.Anabelle Olimba SantillanNo ratings yet
- Determining Risk Category of Building or Other StructureDocument12 pagesDetermining Risk Category of Building or Other StructureJet JavierNo ratings yet
- CanopyDocument2 pagesCanopySuchitra PandaNo ratings yet
- Wind Load Calculation As Per ASCE7-05Document1 pageWind Load Calculation As Per ASCE7-05S A K ClostreNo ratings yet
- Arena Print July 26Document50 pagesArena Print July 26Angelo Gardiola MaglinaoNo ratings yet
- Wind Load Section B - Method 1 (For All Heights) - Open Buildings - Monoslope Free RoofDocument2 pagesWind Load Section B - Method 1 (For All Heights) - Open Buildings - Monoslope Free Rooffred anthony UeraNo ratings yet
- An Example Problem On Wind Load Calculation According To NSCP 2010 )Document32 pagesAn Example Problem On Wind Load Calculation According To NSCP 2010 )joshua humirangNo ratings yet
- R.R. Rojo and AssociatesDocument4 pagesR.R. Rojo and AssociatesMarkNo ratings yet
- WIND LOADING ANALYSIS - Main Wind-Force Resisting System: Input DataDocument4 pagesWIND LOADING ANALYSIS - Main Wind-Force Resisting System: Input Datawaquarstr100% (1)
- 9) Stability of Tank Against Wind Load (Ref: ASCE - 7)Document4 pages9) Stability of Tank Against Wind Load (Ref: ASCE - 7)SachinNo ratings yet
- Design of Chemical BoltDocument54 pagesDesign of Chemical BoltEmdadul HuqNo ratings yet
- Base Plate Design (Pin) Asd For CompressionDocument54 pagesBase Plate Design (Pin) Asd For CompressionEmdadul HuqNo ratings yet
- Wind LoadDocument21 pagesWind LoadMilan KarkiNo ratings yet
- Minimum Loads: Thayer's Formula (From Steel Structures 3rd Ed 2012 by Z.A. Siddiqi, p.261)Document25 pagesMinimum Loads: Thayer's Formula (From Steel Structures 3rd Ed 2012 by Z.A. Siddiqi, p.261)JHON CLYDE SEPADANo ratings yet
- A.1.Input Data: Wind Analysis For Shade Open Structure Based On ASCE 7-05Document3 pagesA.1.Input Data: Wind Analysis For Shade Open Structure Based On ASCE 7-05Antonysamy SanthanamNo ratings yet
- Wind Load (EIT)Document3 pagesWind Load (EIT)thongchai_007No ratings yet
- Calc Steel Metal PerporatedDocument13 pagesCalc Steel Metal PerporatedOecoep Iteem100% (1)
- Wind Load Data Sheet For RCC & STRL Steel in STAAD & ETABSDocument46 pagesWind Load Data Sheet For RCC & STRL Steel in STAAD & ETABSmaruthiinfra structuresNo ratings yet
- BS Wind Application BS 6399 P2Document15 pagesBS Wind Application BS 6399 P2taka731220100% (6)
- Sabrina Ricambi 2021-02Document77 pagesSabrina Ricambi 2021-02Yayah Nya ShandaNo ratings yet
- 5 DPS AlbaniaDocument22 pages5 DPS AlbaniaCarlos A GonzaNo ratings yet
- Fuji Finepix s5200 s5600Document121 pagesFuji Finepix s5200 s5600zilikonNo ratings yet
- PIC16C7XDocument36 pagesPIC16C7XBoopathi ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Craig Hacking KiosksDocument54 pagesCraig Hacking KioskschepimancaNo ratings yet
- Dynetics GremlinsDocument2 pagesDynetics GremlinsartikidNo ratings yet
- ES8388 Control Register - ES8388 RegisterDocument1 pageES8388 Control Register - ES8388 Registerfahmy integration partnerNo ratings yet
- ASTM B666 WWW - QCEXPERT.irDocument7 pagesASTM B666 WWW - QCEXPERT.ireka putriNo ratings yet
- Debate Thorium #1Document430 pagesDebate Thorium #1Asher Lasday100% (2)
- Turningtorso 160210123821 PDFDocument25 pagesTurningtorso 160210123821 PDFDavidGustavoEBNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor Starting ParametersDocument10 pagesInduction Motor Starting ParametersДејан ПејовскиNo ratings yet
- Learning MicroStation VBADocument941 pagesLearning MicroStation VBABill100% (3)
- Assambly ch03Document33 pagesAssambly ch03Mypdfsite100% (1)
- Series Wta Asme Hydro-Pneumatic TanksDocument4 pagesSeries Wta Asme Hydro-Pneumatic TankscaballerolangNo ratings yet
- Installation, Operating and Maintenance Manual: Double Eccentric Butterfly ValvesDocument8 pagesInstallation, Operating and Maintenance Manual: Double Eccentric Butterfly ValveszaidNo ratings yet
- Boiler Shutdown ActivitiesDocument13 pagesBoiler Shutdown ActivitiesMohammad salmanNo ratings yet
- XLR UserGuideDocument209 pagesXLR UserGuideSobhy GendykhelaNo ratings yet
- Quick Reference - Programming CodesDocument2 pagesQuick Reference - Programming CodesjjdjacksonNo ratings yet
- Shortening of Waiting Period For Closure Pour in Bridge ConstructionDocument19 pagesShortening of Waiting Period For Closure Pour in Bridge ConstructionHao LuoNo ratings yet
- The ASTM Copper Strip Corrosion Test: Application To Propane With Carbonyl Sulfide and Hydrogen SulfideDocument7 pagesThe ASTM Copper Strip Corrosion Test: Application To Propane With Carbonyl Sulfide and Hydrogen SulfideAJ ManurungNo ratings yet
- Irf 200 B 211Document10 pagesIrf 200 B 211betodias30No ratings yet
- Agarwood Classification: A Case-Based Reasoning Approach Based On E-NoseDocument7 pagesAgarwood Classification: A Case-Based Reasoning Approach Based On E-NoseLily SyafinazNo ratings yet
- SAP Memory ManagementDocument16 pagesSAP Memory ManagementDevender5194No ratings yet
- Wee Chieftain Steam Factsheet - Mar 15Document1 pageWee Chieftain Steam Factsheet - Mar 15Bia AkramNo ratings yet
- Ar. Classical ArchitectureDocument160 pagesAr. Classical ArchitectureAmit GurjarNo ratings yet