Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CARBOHYDRATES
CARBOHYDRATES
Uploaded by
Shenne Ann MaghuyopCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Solution Manual of Modern Semiconductor Devices For Integrated Circuits (Chenming Calvin Hu)Document122 pagesSolution Manual of Modern Semiconductor Devices For Integrated Circuits (Chenming Calvin Hu)hu leo86% (7)
- Chak de India Management Perspective ProjectDocument21 pagesChak de India Management Perspective ProjectMr. Umang PanchalNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 3 2D Shape With ReflectionDocument7 pagesLesson Plan 3 2D Shape With ReflectionfatimaNo ratings yet
- ASTM C-40 Tester: Ordering InformationDocument1 pageASTM C-40 Tester: Ordering InformationImber Rene Salgueiro HuancaNo ratings yet
- Character CreationDocument36 pagesCharacter CreationGracia Gagah100% (2)
- 314Document65 pages314dim4erema100% (3)
- Bio ChemDocument14 pagesBio Chemmary balansagNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates: General Characteristics and Various TestsDocument8 pagesCarbohydrates: General Characteristics and Various TestsMaw BerryNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument14 pagesCarbohydratesxubulavaxatiaNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates IAL Edexcel ChemistryDocument17 pagesCarbohydrates IAL Edexcel ChemistryIsaa gabNo ratings yet
- Biology As Unit 1Document4 pagesBiology As Unit 1tamara.haddadinNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument6 pagesCarbohydratesGale SatsatinNo ratings yet
- Biology Unit Review: I. CarbohydratesDocument11 pagesBiology Unit Review: I. CarbohydratesJOSHUA DICHOSONo ratings yet
- Edexcel Biology Unit 1 NotesDocument74 pagesEdexcel Biology Unit 1 NotesBene Bin100% (2)
- Biochem MidtermsDocument25 pagesBiochem MidtermsYuki MendezNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Week 4 - CarbohydrateDocument6 pagesBiochemistry Week 4 - CarbohydrateMicah JadeNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry M3 Pidlaoan AlexanderDocument5 pagesBiochemistry M3 Pidlaoan AlexanderPrincess M. De VeraNo ratings yet
- Micro para Transes 1.1Document4 pagesMicro para Transes 1.1Kyla Marie BadanaNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates, Lipids & Nucleic Acids:: Forms Chain Like Molecules-PolymersDocument8 pagesCarbohydrates, Lipids & Nucleic Acids:: Forms Chain Like Molecules-PolymersJojo LouNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates, Lipids, ProteinsDocument5 pagesCarbohydrates, Lipids, ProteinsJustine AsiloNo ratings yet
- Biomolecule: Carbohydrates: Philippine Christian Gospel SchoolDocument9 pagesBiomolecule: Carbohydrates: Philippine Christian Gospel SchoolTashi OngNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry CARBOHYDRATESDocument5 pagesBiochemistry CARBOHYDRATESPrincess M. De VeraNo ratings yet
- Group 7: Bisonaya Capillo FallurinDocument17 pagesGroup 7: Bisonaya Capillo FallurinSyndy BisonayaNo ratings yet
- CARBOHYDRATESDocument3 pagesCARBOHYDRATESEva Marie GaaNo ratings yet
- 2general Biology 1 Learning Package Final TermDocument19 pages2general Biology 1 Learning Package Final Termashleykategallo361No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 PDFDocument5 pagesChapter 3 PDFNafis KNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument21 pagesCarbohydratesidkmyname100% (5)
- Carbohydrates - BiochemistryDocument16 pagesCarbohydrates - Biochemistryquinsummer17No ratings yet
- Carbohydrate S: Prepared By: ROBIÑOS, Emily Ann ADocument13 pagesCarbohydrate S: Prepared By: ROBIÑOS, Emily Ann AMarilyn BagayNo ratings yet
- Outline: Biochemistry LEC CarbohydratesDocument8 pagesOutline: Biochemistry LEC CarbohydratesShardy Lyn RuizNo ratings yet
- Biochem Mod 8 PDFDocument3 pagesBiochem Mod 8 PDFtheaNo ratings yet
- Module 2.2 CarbohydratesDocument6 pagesModule 2.2 CarbohydratesZabelle BungarNo ratings yet
- Biological MoleculesDocument8 pagesBiological MoleculesQaran PrintingNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEM ReviewerDocument12 pagesBIOCHEM ReviewerKyla JuantaNo ratings yet
- HARPERS - IV Carbohydrates of Physiological SignificanceDocument4 pagesHARPERS - IV Carbohydrates of Physiological SignificancedandiNo ratings yet
- Bio Notes 2Document32 pagesBio Notes 2Sinin VegaNo ratings yet
- Bio Notes 2Document32 pagesBio Notes 2Sinin VegaNo ratings yet
- General and Specific Test For Carbohydrates BioChemDocument15 pagesGeneral and Specific Test For Carbohydrates BioChemwynNo ratings yet
- q4 Module 2 CompressedDocument4 pagesq4 Module 2 CompressedFELIX ROBERT VALENZUELANo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument29 pagesCarbohydratesreena aroraNo ratings yet
- Presentation Title: Your SubtitleDocument47 pagesPresentation Title: Your SubtitleDenize Faith Malagday AbellaNo ratings yet
- CN Unit-IiDocument25 pagesCN Unit-IiJohn Benedict Suiza VillaruelNo ratings yet
- STPM BIOLOGY Basic Chemistry of A CellDocument22 pagesSTPM BIOLOGY Basic Chemistry of A Cellwkwhui100% (2)
- Molecular Composition of CellsDocument3 pagesMolecular Composition of CellsThiody Hope Mongas100% (1)
- CARBOHYDRATESDocument12 pagesCARBOHYDRATESxenia rayaNo ratings yet
- Bio MoleculesDocument15 pagesBio MoleculessofiajanineganalNo ratings yet
- HYDROLYZE Means Undergo Chemical Breakdown Due To Reaction With WaterDocument3 pagesHYDROLYZE Means Undergo Chemical Breakdown Due To Reaction With Waterjohn paulNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4: Biomolecules: Major Types of Biomolecules: Carbohydrates, Lipids, Nucleic Acids, andDocument12 pagesLesson 4: Biomolecules: Major Types of Biomolecules: Carbohydrates, Lipids, Nucleic Acids, andJuselle Faith AtaNo ratings yet
- Science BiomoleculesDocument9 pagesScience BiomoleculesJulia OhNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - 1A2-3 Carbohydrates I & IIDocument30 pagesLesson 3 - 1A2-3 Carbohydrates I & IIAlex SmirnovNo ratings yet
- Biochem NotesDocument17 pagesBiochem NotesKate strangeNo ratings yet
- UNITI Biomolecules PDFDocument18 pagesUNITI Biomolecules PDFdrugdrug100% (1)
- Biological MoleculesDocument18 pagesBiological MoleculesPrince OycoNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer - FinaDocument3 pagesScience Reviewer - FinaAmamore Lorenzana PlazaNo ratings yet
- CARBOHYDRATESDocument5 pagesCARBOHYDRATESMicah YapNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IAL Biology Unit 1 Topic 1 - Molecules, Transport and HealthDocument40 pagesEdexcel IAL Biology Unit 1 Topic 1 - Molecules, Transport and HealthEshalNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2nd Quarter 1st Sem ReviewerDocument11 pagesGeneral Biology 2nd Quarter 1st Sem ReviewerIsmael Udrih Maglalang50% (2)
- Biochem Lec Prelim FinalsDocument11 pagesBiochem Lec Prelim FinalsJullia SollezaNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Biological MoleculesDocument48 pagesCH 2 Biological Molecules9G11 Aulia KayanaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry and Structure of The Cell Biological MacromoleculesDocument4 pagesChemistry and Structure of The Cell Biological MacromoleculesJohn ManciaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry ReviewerDocument20 pagesBiochemistry ReviewerabcdeniselimNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio - 1 2.5 - The Organic Molecules of Living OrganismsDocument7 pagesGen Bio - 1 2.5 - The Organic Molecules of Living OrganismsBlaire ReyesNo ratings yet
- CHE 461 Module 1Document20 pagesCHE 461 Module 1Danladi VictoriaNo ratings yet
- Biology ReportDocument64 pagesBiology ReportChelo IlagNo ratings yet
- General Biology - EnzymesDocument10 pagesGeneral Biology - EnzymesHaze dashvilNo ratings yet
- BUS 500 Skills in Business Communication PDFDocument8 pagesBUS 500 Skills in Business Communication PDFrakin tajwarNo ratings yet
- Doctor Kekalo Pinto Bean Whole Supplier: 1. Executive SummaryDocument12 pagesDoctor Kekalo Pinto Bean Whole Supplier: 1. Executive Summaryalemayehu tarikuNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Research NotesDocument8 pagesQualitative Research NotesAnanta SinhaNo ratings yet
- Fatigue Crack Propagation in Aluminium AlloysDocument3 pagesFatigue Crack Propagation in Aluminium AlloysNils VerkleijNo ratings yet
- Quotation - QT-230031Document2 pagesQuotation - QT-230031Hassan FahmiNo ratings yet
- Be Project Work BookDocument44 pagesBe Project Work BookCASTING DEPARTMENTNo ratings yet
- Pembelajaran Literasi Membaca Di Pondok Pesantren Sidogiri Kraton PasuruanDocument17 pagesPembelajaran Literasi Membaca Di Pondok Pesantren Sidogiri Kraton Pasuruanpriyo hartantoNo ratings yet
- Summary of US Class Size Reduction ResearchDocument7 pagesSummary of US Class Size Reduction ResearchLeonie HaimsonNo ratings yet
- Lu PDFDocument34 pagesLu PDFAlexanderNo ratings yet
- Sample Railing Calculation To Euro Code PDFDocument4 pagesSample Railing Calculation To Euro Code PDFphuckha2012100% (1)
- Belzona 5111 Product Data SheetDocument2 pagesBelzona 5111 Product Data SheetPeter RhoadsNo ratings yet
- Deep Learning in Mobile and Wireless Networking: A SurveyDocument67 pagesDeep Learning in Mobile and Wireless Networking: A SurveyBee MUNo ratings yet
- DzireDocument324 pagesDzireDaniel Lopez VenancioNo ratings yet
- Des-F1025p-E DSDocument3 pagesDes-F1025p-E DSNaing Win ZawNo ratings yet
- Computational Techniques in Quantum Chemistry and Molecular PhysicsDocument569 pagesComputational Techniques in Quantum Chemistry and Molecular PhysicsClóvis Batista Dos SantosNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument5 pagesQuestionsrajasamygopalNo ratings yet
- First Semester Summary ReportDocument21 pagesFirst Semester Summary ReportAkhila JoseNo ratings yet
- Industrial Crops & ProductsDocument10 pagesIndustrial Crops & ProductsShield YggdrasilNo ratings yet
- Partnerships BritAc & MoL Kate Rosser FrostDocument16 pagesPartnerships BritAc & MoL Kate Rosser FrostCulture CommsNo ratings yet
- FBFP UserGuide 2 21Document88 pagesFBFP UserGuide 2 21Zlatko OžanićNo ratings yet
- Cultural Variations and Social Differences (Ethnicity)Document19 pagesCultural Variations and Social Differences (Ethnicity)Jomar TeofiloNo ratings yet
- Diagrama 950H PDFDocument1 pageDiagrama 950H PDFDaniel Castillo PeñaNo ratings yet
- 01 eLMS Activity 1 Network TechnologyDocument2 pages01 eLMS Activity 1 Network Technologybasahara sengokuNo ratings yet
CARBOHYDRATES
CARBOHYDRATES
Uploaded by
Shenne Ann MaghuyopCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CARBOHYDRATES
CARBOHYDRATES
Uploaded by
Shenne Ann MaghuyopCopyright:
Available Formats
BIOCHEMISTRY
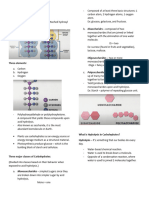
CARBOHYDRATES (CH2O) carbon,hydrogen,oxygen FUNCTIONS
called saccharides - Energy source
Building blocks and primary source of energy - Macronutrient
Hydrated carbon - Nutrient provider
Most widespread organic subtances - Dietary fiber
Chemically carbohydrates are - Heart health
polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones, their simple - Weight management
derivatives or their polymers. - Diabetes management
which produce units of such type on hydrolysis
Hydrolysis- water is mostly used to break down the Diabetes Insipidus- blood sugar is normal yet can’t
chemical bonds that exists between a particular properly urinate
substance. - Makes you feel thirsty because many fluis
“sugar” is the sucrose disaccharide are leaving the body.
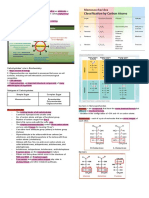
CLASSIFICATIONS Diabetes Mellitus- blood sugar is too high and can
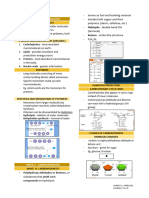
SIMPLE CARBOHYDRATE - basic type of carbs. urinate.
Monosaccharides- one sugar unit - Feeling thirst because of too much glucose
- the smallest of the carbohydrates. in blood.
- Digestion and metabolism Gestational diabetes- is a type of diabetes that can
Glucose – simple sugar develop during pregnancy in women who don't already
have diabetes.
Fructose – fruit sugar
Type 1 Diabetes- juvenile diabetes or insulin-dependent
Galactose – brain sugar
diabetes, pancreas produces little or no insulin by
Diasaccharides- two sugar unit
itself.
- two monosaccharides (simple sugars) are Type 2 Diabetes- most common type, when body is
joined by glycosidic linkage. resistant to insulin or doesn’tmake enough insulin.
- Energy source Type 3 Diabetes- describe the theory that insulin
Maltose (plants) glucose + glucose resistance and insulin-like growth factor dysfunction in
lactose(milk) glucose + galactose the brain may cause Alzheimer's disease.
sucrose(sugar cane) glucose + fructose
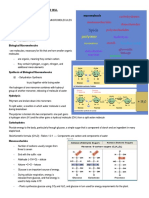
glycosidic linkage- chemical bond in the form of a Anaerobic- without oxygen.
covalent connection that connects a carbohydrate Adenosine Triphosphate ATP- "energy currency" of the
(sugar) molecule to another group. cell, as it provides readily releasable energy in the bond
between the second and third phosphate groups.
GLYCONE- sugar group
REACTIONS
AGLYCONE- non- sugar group
GLYCOLYSIS- glucose to pyruvate
GLUCONEOGENESIS- glucose from non-curb
COMPLEX CARBOHYDRATES - often single units GLYCONEOGENESIS-glycogen from glucose (formation)
(monosaccharides), which are bound together. GLYCOGENOLYSIS-glycogen from glucose (breakdown)
Oligosaccharides- contain two to ten simple CELLUALR RESPIRATION-oxidation of glucose
units of sugar. PHOTOSYNTHESIS-carbon dioxide and water into
Polysaccharides- contain hundreds and glucose
thousands of monosaccharides which are FERMENTATION-breakdown of glucose
related. DEHYDRATION SYSTHESIS-glycosidic bond of mono and
- joined by glycosidic linkage. poly
- Starch (plants)
- Glycogen (animals) Anabolism- is the building of complex molecules from
- Fiber(soluble and insoluble) numerous simple ones.
Catabolism- is the breakdown of complex molecules
into numerous simple ones.
redox reactions- are reactions that involve the transfer
of electrons from one species to another.
BIOCHEMISTRY
Chemical
Other mososaccharides- they occur in the form of 1. Reducing power-they reduce alkaline metals
complex carbohydrates like pentosans, gums, xylans, and are themselves transformed into organic
and arabans, which on hydrolysis yield pentoses. acids.
2. Osazone formation-this property is attributed
Desoxy sugars- are true carbohydrates but the to the presence of aldehyde or ketone group in
hydrogen and oxygen in their molecules are not their molecules.
in such proportion as that found in a molecule 3. Action of alkalies-this is due to the liberation of
of water. aldehyde which subsequently polymerizes to for
Monosaccharides esters-monosaccharides form resinous substance, caramel.
esters with phosphoric acid which appears to be 4. Actions of acids- in the presence of an acid,
a prerequisite to many physiological reactions. dissacharides.
Trisaccharides-it is also called milose or Molisch test: a violet ring is formed at
melitriose, and is found in cotton seed the junction of the two liquids.
Anthrone test-a keto form of 9-
hydroxyathracene.
GENERAL PROPERTIES OF CARBOHYDRATES
Seliwannoff’s test-this involves the
physical and chemical properties
action of resorcinol and HCI on sugar.
5. Fermentation-this is the decomposition of
Physical
carbohydrates brought about by the action of
1. The mono and disachharides are white
microorganism such as yeast, mold, bacteria,
crystalline substances.
etc.
Starches are amorphous powder.
6. Reduction- all sugars except sucrose undergo
Fibrous the most complex cellulose.
reduction with the absorption of energy and the
2. The solubility to ordinary solvents is inversely
formation of products convertible into fats.
proportional to the complexity of their
7. Electrification-this is subsequently transformed
structures.
into lactic acid with the simultaneous liberation
Both mono and dissacharides are
of energy.
readily dissolved in water.
Higher carbohydrates like starch
Inulin-is found in the bulb of onions and garlic.
dissolve only slightly.
Glycogen-it is also called animal starch, found mostly in
Cellulose is practically insoluble.
the liver as storage material.
3.
Dextrins- are precipitated from their clear, colorless
Both mono and dissacharides are sweet,
solution of alcohol.
while starches and celluloses are
cellulose-is the most abundant organic compound,
tasteless.
making up around 50% or more of the carbon
vegetation.
Sugar is a generic name applied to all carbohydrates
hyaluronic acid-is a complex mucopolysaccharide made
possessing sweet taste.
up of d-gluronic acid, d-glucosamine and acetic acid in
equimolecular amounts.
Three variesties of sugars.
Cane sugar-sugar cane
Grape sugar-fruits
Milk sugar-from milk
Fructose is the sweetest of the common sugars.
Lactose is the least sweet.
Sucrose is taken as the standard (100%) of sweetness.
You might also like
- Solution Manual of Modern Semiconductor Devices For Integrated Circuits (Chenming Calvin Hu)Document122 pagesSolution Manual of Modern Semiconductor Devices For Integrated Circuits (Chenming Calvin Hu)hu leo86% (7)
- Chak de India Management Perspective ProjectDocument21 pagesChak de India Management Perspective ProjectMr. Umang PanchalNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 3 2D Shape With ReflectionDocument7 pagesLesson Plan 3 2D Shape With ReflectionfatimaNo ratings yet
- ASTM C-40 Tester: Ordering InformationDocument1 pageASTM C-40 Tester: Ordering InformationImber Rene Salgueiro HuancaNo ratings yet
- Character CreationDocument36 pagesCharacter CreationGracia Gagah100% (2)
- 314Document65 pages314dim4erema100% (3)
- Bio ChemDocument14 pagesBio Chemmary balansagNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates: General Characteristics and Various TestsDocument8 pagesCarbohydrates: General Characteristics and Various TestsMaw BerryNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument14 pagesCarbohydratesxubulavaxatiaNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates IAL Edexcel ChemistryDocument17 pagesCarbohydrates IAL Edexcel ChemistryIsaa gabNo ratings yet
- Biology As Unit 1Document4 pagesBiology As Unit 1tamara.haddadinNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument6 pagesCarbohydratesGale SatsatinNo ratings yet
- Biology Unit Review: I. CarbohydratesDocument11 pagesBiology Unit Review: I. CarbohydratesJOSHUA DICHOSONo ratings yet
- Edexcel Biology Unit 1 NotesDocument74 pagesEdexcel Biology Unit 1 NotesBene Bin100% (2)
- Biochem MidtermsDocument25 pagesBiochem MidtermsYuki MendezNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Week 4 - CarbohydrateDocument6 pagesBiochemistry Week 4 - CarbohydrateMicah JadeNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry M3 Pidlaoan AlexanderDocument5 pagesBiochemistry M3 Pidlaoan AlexanderPrincess M. De VeraNo ratings yet
- Micro para Transes 1.1Document4 pagesMicro para Transes 1.1Kyla Marie BadanaNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates, Lipids & Nucleic Acids:: Forms Chain Like Molecules-PolymersDocument8 pagesCarbohydrates, Lipids & Nucleic Acids:: Forms Chain Like Molecules-PolymersJojo LouNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates, Lipids, ProteinsDocument5 pagesCarbohydrates, Lipids, ProteinsJustine AsiloNo ratings yet
- Biomolecule: Carbohydrates: Philippine Christian Gospel SchoolDocument9 pagesBiomolecule: Carbohydrates: Philippine Christian Gospel SchoolTashi OngNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry CARBOHYDRATESDocument5 pagesBiochemistry CARBOHYDRATESPrincess M. De VeraNo ratings yet
- Group 7: Bisonaya Capillo FallurinDocument17 pagesGroup 7: Bisonaya Capillo FallurinSyndy BisonayaNo ratings yet
- CARBOHYDRATESDocument3 pagesCARBOHYDRATESEva Marie GaaNo ratings yet
- 2general Biology 1 Learning Package Final TermDocument19 pages2general Biology 1 Learning Package Final Termashleykategallo361No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 PDFDocument5 pagesChapter 3 PDFNafis KNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument21 pagesCarbohydratesidkmyname100% (5)
- Carbohydrates - BiochemistryDocument16 pagesCarbohydrates - Biochemistryquinsummer17No ratings yet
- Carbohydrate S: Prepared By: ROBIÑOS, Emily Ann ADocument13 pagesCarbohydrate S: Prepared By: ROBIÑOS, Emily Ann AMarilyn BagayNo ratings yet
- Outline: Biochemistry LEC CarbohydratesDocument8 pagesOutline: Biochemistry LEC CarbohydratesShardy Lyn RuizNo ratings yet
- Biochem Mod 8 PDFDocument3 pagesBiochem Mod 8 PDFtheaNo ratings yet
- Module 2.2 CarbohydratesDocument6 pagesModule 2.2 CarbohydratesZabelle BungarNo ratings yet
- Biological MoleculesDocument8 pagesBiological MoleculesQaran PrintingNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEM ReviewerDocument12 pagesBIOCHEM ReviewerKyla JuantaNo ratings yet
- HARPERS - IV Carbohydrates of Physiological SignificanceDocument4 pagesHARPERS - IV Carbohydrates of Physiological SignificancedandiNo ratings yet
- Bio Notes 2Document32 pagesBio Notes 2Sinin VegaNo ratings yet
- Bio Notes 2Document32 pagesBio Notes 2Sinin VegaNo ratings yet
- General and Specific Test For Carbohydrates BioChemDocument15 pagesGeneral and Specific Test For Carbohydrates BioChemwynNo ratings yet
- q4 Module 2 CompressedDocument4 pagesq4 Module 2 CompressedFELIX ROBERT VALENZUELANo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument29 pagesCarbohydratesreena aroraNo ratings yet
- Presentation Title: Your SubtitleDocument47 pagesPresentation Title: Your SubtitleDenize Faith Malagday AbellaNo ratings yet
- CN Unit-IiDocument25 pagesCN Unit-IiJohn Benedict Suiza VillaruelNo ratings yet
- STPM BIOLOGY Basic Chemistry of A CellDocument22 pagesSTPM BIOLOGY Basic Chemistry of A Cellwkwhui100% (2)
- Molecular Composition of CellsDocument3 pagesMolecular Composition of CellsThiody Hope Mongas100% (1)
- CARBOHYDRATESDocument12 pagesCARBOHYDRATESxenia rayaNo ratings yet
- Bio MoleculesDocument15 pagesBio MoleculessofiajanineganalNo ratings yet
- HYDROLYZE Means Undergo Chemical Breakdown Due To Reaction With WaterDocument3 pagesHYDROLYZE Means Undergo Chemical Breakdown Due To Reaction With Waterjohn paulNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4: Biomolecules: Major Types of Biomolecules: Carbohydrates, Lipids, Nucleic Acids, andDocument12 pagesLesson 4: Biomolecules: Major Types of Biomolecules: Carbohydrates, Lipids, Nucleic Acids, andJuselle Faith AtaNo ratings yet
- Science BiomoleculesDocument9 pagesScience BiomoleculesJulia OhNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - 1A2-3 Carbohydrates I & IIDocument30 pagesLesson 3 - 1A2-3 Carbohydrates I & IIAlex SmirnovNo ratings yet
- Biochem NotesDocument17 pagesBiochem NotesKate strangeNo ratings yet
- UNITI Biomolecules PDFDocument18 pagesUNITI Biomolecules PDFdrugdrug100% (1)
- Biological MoleculesDocument18 pagesBiological MoleculesPrince OycoNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer - FinaDocument3 pagesScience Reviewer - FinaAmamore Lorenzana PlazaNo ratings yet
- CARBOHYDRATESDocument5 pagesCARBOHYDRATESMicah YapNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IAL Biology Unit 1 Topic 1 - Molecules, Transport and HealthDocument40 pagesEdexcel IAL Biology Unit 1 Topic 1 - Molecules, Transport and HealthEshalNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2nd Quarter 1st Sem ReviewerDocument11 pagesGeneral Biology 2nd Quarter 1st Sem ReviewerIsmael Udrih Maglalang50% (2)
- Biochem Lec Prelim FinalsDocument11 pagesBiochem Lec Prelim FinalsJullia SollezaNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Biological MoleculesDocument48 pagesCH 2 Biological Molecules9G11 Aulia KayanaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry and Structure of The Cell Biological MacromoleculesDocument4 pagesChemistry and Structure of The Cell Biological MacromoleculesJohn ManciaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry ReviewerDocument20 pagesBiochemistry ReviewerabcdeniselimNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio - 1 2.5 - The Organic Molecules of Living OrganismsDocument7 pagesGen Bio - 1 2.5 - The Organic Molecules of Living OrganismsBlaire ReyesNo ratings yet
- CHE 461 Module 1Document20 pagesCHE 461 Module 1Danladi VictoriaNo ratings yet
- Biology ReportDocument64 pagesBiology ReportChelo IlagNo ratings yet
- General Biology - EnzymesDocument10 pagesGeneral Biology - EnzymesHaze dashvilNo ratings yet
- BUS 500 Skills in Business Communication PDFDocument8 pagesBUS 500 Skills in Business Communication PDFrakin tajwarNo ratings yet
- Doctor Kekalo Pinto Bean Whole Supplier: 1. Executive SummaryDocument12 pagesDoctor Kekalo Pinto Bean Whole Supplier: 1. Executive Summaryalemayehu tarikuNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Research NotesDocument8 pagesQualitative Research NotesAnanta SinhaNo ratings yet
- Fatigue Crack Propagation in Aluminium AlloysDocument3 pagesFatigue Crack Propagation in Aluminium AlloysNils VerkleijNo ratings yet
- Quotation - QT-230031Document2 pagesQuotation - QT-230031Hassan FahmiNo ratings yet
- Be Project Work BookDocument44 pagesBe Project Work BookCASTING DEPARTMENTNo ratings yet
- Pembelajaran Literasi Membaca Di Pondok Pesantren Sidogiri Kraton PasuruanDocument17 pagesPembelajaran Literasi Membaca Di Pondok Pesantren Sidogiri Kraton Pasuruanpriyo hartantoNo ratings yet
- Summary of US Class Size Reduction ResearchDocument7 pagesSummary of US Class Size Reduction ResearchLeonie HaimsonNo ratings yet
- Lu PDFDocument34 pagesLu PDFAlexanderNo ratings yet
- Sample Railing Calculation To Euro Code PDFDocument4 pagesSample Railing Calculation To Euro Code PDFphuckha2012100% (1)
- Belzona 5111 Product Data SheetDocument2 pagesBelzona 5111 Product Data SheetPeter RhoadsNo ratings yet
- Deep Learning in Mobile and Wireless Networking: A SurveyDocument67 pagesDeep Learning in Mobile and Wireless Networking: A SurveyBee MUNo ratings yet
- DzireDocument324 pagesDzireDaniel Lopez VenancioNo ratings yet
- Des-F1025p-E DSDocument3 pagesDes-F1025p-E DSNaing Win ZawNo ratings yet
- Computational Techniques in Quantum Chemistry and Molecular PhysicsDocument569 pagesComputational Techniques in Quantum Chemistry and Molecular PhysicsClóvis Batista Dos SantosNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument5 pagesQuestionsrajasamygopalNo ratings yet
- First Semester Summary ReportDocument21 pagesFirst Semester Summary ReportAkhila JoseNo ratings yet
- Industrial Crops & ProductsDocument10 pagesIndustrial Crops & ProductsShield YggdrasilNo ratings yet
- Partnerships BritAc & MoL Kate Rosser FrostDocument16 pagesPartnerships BritAc & MoL Kate Rosser FrostCulture CommsNo ratings yet
- FBFP UserGuide 2 21Document88 pagesFBFP UserGuide 2 21Zlatko OžanićNo ratings yet
- Cultural Variations and Social Differences (Ethnicity)Document19 pagesCultural Variations and Social Differences (Ethnicity)Jomar TeofiloNo ratings yet
- Diagrama 950H PDFDocument1 pageDiagrama 950H PDFDaniel Castillo PeñaNo ratings yet
- 01 eLMS Activity 1 Network TechnologyDocument2 pages01 eLMS Activity 1 Network Technologybasahara sengokuNo ratings yet