Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 viewsDrugs For Respiratory System
Drugs For Respiratory System
Uploaded by
aliyahalexie6Nursing pharma
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Postpartum Teaching PlanDocument3 pagesPostpartum Teaching Plan6bigstar991% (11)
- Comprehensive Board Exam ENT PDFDocument644 pagesComprehensive Board Exam ENT PDFdrskbarla50% (2)
- Pharmacotherapy of CoughDocument51 pagesPharmacotherapy of CoughIqra Butt100% (3)
- Midterm PharmaDocument25 pagesMidterm PharmaKaye Honeylee ManibogNo ratings yet
- Respiratory MedicationsDocument14 pagesRespiratory MedicationsissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- Module 3.2 - Respiratory DrugsDocument3 pagesModule 3.2 - Respiratory DrugsCatherine Sinen ObinqueNo ratings yet
- Pharm Exam Ii NotesDocument24 pagesPharm Exam Ii Noteskatiana louisNo ratings yet
- Notes For Respiratory AgentsDocument4 pagesNotes For Respiratory AgentsZella ViaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory DrugsDocument56 pagesRespiratory DrugsIra G. Delos Santos100% (1)
- Printed Material ModuleeeeDocument56 pagesPrinted Material ModuleeeeShang MacarayonNo ratings yet
- 4.l - Respiratory System Pharmacology by IGMRIDocument13 pages4.l - Respiratory System Pharmacology by IGMRIclaw foreSK TeamNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Topic SummaryDocument7 pagesRespiratory Topic SummaryShingie MatemaNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On Functions of Respiratory SystemDocument73 pagesDrugs Acting On Functions of Respiratory SystemMarin ChianuNo ratings yet
- Cough PharmacotherapyDocument27 pagesCough PharmacotherapySalifyanji SimpambaNo ratings yet
- Module 14 - Drugs-affecting-the-Respiratory-System-3Document48 pagesModule 14 - Drugs-affecting-the-Respiratory-System-3weissNo ratings yet
- Upper Respiratory Disorders: ObjectivesDocument16 pagesUpper Respiratory Disorders: ObjectivesJennie QuachNo ratings yet
- Pharma Reviewer (Midterm)Document7 pagesPharma Reviewer (Midterm)SaidinaNo ratings yet
- Asthma Treatment and PreventionDocument5 pagesAsthma Treatment and PreventionJohn Paul MatienzoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System DrugsDocument5 pagesRespiratory System DrugsHamad AlshabiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Drugs Actiong On Respiratory SystemDocument6 pagesChapter 6 - Drugs Actiong On Respiratory SystemMohit SoniNo ratings yet
- Dr. Swagath, HassanDocument29 pagesDr. Swagath, HassanSwagath NNo ratings yet
- Bronchial Asthma: Sudhakar Lakavath Dept - Of.PharmacologyDocument50 pagesBronchial Asthma: Sudhakar Lakavath Dept - Of.PharmacologySudhakar LakavathNo ratings yet
- CombiventDocument2 pagesCombiventunkown userNo ratings yet
- Drug Study IMDocument2 pagesDrug Study IMAbigail BrillantesNo ratings yet
- V. Drug StudyDocument5 pagesV. Drug StudyJopaii TanakaNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting The Respiratory System PPPDocument35 pagesDrugs Affecting The Respiratory System PPPChristopher VelonzaNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting The Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesDrugs Affecting The Respiratory SystemJerica Jaz F. Vergara100% (1)
- PHL1 - Pharmacotherapy Bronchial AsthmaDocument7 pagesPHL1 - Pharmacotherapy Bronchial AsthmaFadhlina OmarNo ratings yet
- 5.1 5.4Document24 pages5.1 5.4Nim DCNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Upper Drugs NotesDocument3 pagesRespiratory Upper Drugs NotesAngela PonceNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Cough: - Cough Is of Two TypesDocument5 pagesDrugs For Cough: - Cough Is of Two TypesKahlon JotNo ratings yet
- Janine Vega BSM 3 Phama Midterm ActivityDocument8 pagesJanine Vega BSM 3 Phama Midterm ActivityJanine VegaNo ratings yet
- Pulmonology May 28Document76 pagesPulmonology May 28Brielle ShoppNo ratings yet
- NCM 106 FinalsDocument55 pagesNCM 106 FinalsKyle BagacNo ratings yet
- E Kart DrugsDocument3 pagesE Kart DrugsNichole CastleNo ratings yet
- 16 Drugs Affecting RespiDocument3 pages16 Drugs Affecting RespiAdriwayne Francis GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Romero, Deinielle Ingrid M. (Pulmo)Document3 pagesRomero, Deinielle Ingrid M. (Pulmo)Deinielle Magdangal RomeroNo ratings yet
- 15 Patients With Altered VentilationDocument66 pages15 Patients With Altered VentilationErshelle Mae MorlaNo ratings yet
- Case Study 4 CVD Infarct CAP MR HUD RDU DementiaDocument21 pagesCase Study 4 CVD Infarct CAP MR HUD RDU DementiaVictoria Mae Irong CabahugNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument62 pagesRespiratory SystemSravani SravsNo ratings yet
- Cough: PHR Sangita ShakyaDocument21 pagesCough: PHR Sangita ShakyaCurex QANo ratings yet
- Pharma Midterm ReviewerDocument45 pagesPharma Midterm ReviewerCarlos Miguel AndalNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyZek Comidoy100% (1)
- Note 1Document3 pagesNote 1HossamJamaykaNo ratings yet
- Midterms RLEDocument11 pagesMidterms RLEgungonfiona28No ratings yet
- Antihistamine BlockersDocument12 pagesAntihistamine Blockersyra capiliNo ratings yet
- Rhinitis Guidelines: Classification and Differential DiagnosisDocument5 pagesRhinitis Guidelines: Classification and Differential DiagnosisEricaNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Respiratory SystemDocument18 pagesDrugs For Respiratory SystemKaye CorNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Disorders (Asthma & COPD ..)Document5 pagesRespiratory System Disorders (Asthma & COPD ..)KC PalattaoNo ratings yet
- Ipratroprium Drug CardDocument3 pagesIpratroprium Drug CardXiaoDuckyNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgCoxAEPf B5bFXXj0n0ogZgNdJimPp0HP25fR0kWmUQfj5aodpDMX Y2yxgw FKGZR QuqtH7SZyDlG8F4JVDjQOuJN8At7iKpg7xji x2zqAMu YaQmBFHVDJ12jag4khHkNk5gAYOo25zDocument6 pagesACFrOgCoxAEPf B5bFXXj0n0ogZgNdJimPp0HP25fR0kWmUQfj5aodpDMX Y2yxgw FKGZR QuqtH7SZyDlG8F4JVDjQOuJN8At7iKpg7xji x2zqAMu YaQmBFHVDJ12jag4khHkNk5gAYOo25zRheeanne AmilasanNo ratings yet
- WEEK 9 - NCMA216 - PHARMA - Respiratory System AgentsDocument50 pagesWEEK 9 - NCMA216 - PHARMA - Respiratory System AgentsOther AccountNo ratings yet
- Treating The Severely Dyspneic Patient - : Covid-19 Training For Healthcare WorkersDocument4 pagesTreating The Severely Dyspneic Patient - : Covid-19 Training For Healthcare WorkersDefo SandiNo ratings yet
- 02 Bronchial AsthmaDocument6 pages02 Bronchial AsthmaahmedNo ratings yet
- CHF Drug StudyDocument11 pagesCHF Drug StudySeth Michael Daniel BenauroNo ratings yet
- Autacoids Final PDFDocument22 pagesAutacoids Final PDFIqra ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Fluorescein Wall ChartDocument1 pageFluorescein Wall ChartbijujcNo ratings yet
- 1.chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease 2. Allergic RhinitisDocument18 pages1.chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease 2. Allergic Rhinitisيحيى اسماعيل الجميليNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting The Respiratory SystemDocument89 pagesDrugs Affecting The Respiratory SystemkayarohanamNo ratings yet
- Local Anesthesia Made Easy: Complete Guide on How to make your Local Anesthetic Procedure a Success (Including a List of Anesthetic Equipment and their Uses)From EverandLocal Anesthesia Made Easy: Complete Guide on How to make your Local Anesthetic Procedure a Success (Including a List of Anesthetic Equipment and their Uses)No ratings yet
- Differentiating Anesthesia Equipment: Identify and Understand Anesthesia Equipment in 1 Hour (Including the most popular manufacturers and suppliers to buy Anesthesia Equipment)From EverandDifferentiating Anesthesia Equipment: Identify and Understand Anesthesia Equipment in 1 Hour (Including the most popular manufacturers and suppliers to buy Anesthesia Equipment)No ratings yet
- Leann Li ResumeDocument2 pagesLeann Li Resumeapi-660140781No ratings yet
- Vice and DrugDocument8 pagesVice and DrugTIPAY, EMELIE L.No ratings yet
- Do You Need To Drink 8 Glasses of Water TranscriptDocument2 pagesDo You Need To Drink 8 Glasses of Water TranscriptHarold Saldy CasalemNo ratings yet
- MD India Preauth FormDocument2 pagesMD India Preauth FormM/s MicrotechNo ratings yet
- Palliative Care in Parkinson's Disease: ReviewDocument4 pagesPalliative Care in Parkinson's Disease: ReviewAnonymous lwYEylQhNo ratings yet
- Cholesterol PDFDocument32 pagesCholesterol PDFAkshad PatilNo ratings yet
- Csa Form Serology Clearance Certificate s7 Oct 2014Document2 pagesCsa Form Serology Clearance Certificate s7 Oct 2014Thomas EyreNo ratings yet
- Heart AnatomyDocument11 pagesHeart AnatomyJohn FisherNo ratings yet
- Are Repeat COVID Infections DangerousDocument3 pagesAre Repeat COVID Infections DangerousJuan MNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plankarla joy sta teresaNo ratings yet
- Growth of Analytical Thinking Skills Over Time As Measured With The MATCH TestDocument7 pagesGrowth of Analytical Thinking Skills Over Time As Measured With The MATCH TestFrederico PóvoaNo ratings yet
- Abg Analysis ReviewerDocument21 pagesAbg Analysis ReviewerAyiessa_AJNo ratings yet
- By MBBS Gang: ENT Examination ProcedureDocument23 pagesBy MBBS Gang: ENT Examination ProcedureYour DaddyNo ratings yet
- Master's Degree in Periodontology: COURSE 2023-2024Document14 pagesMaster's Degree in Periodontology: COURSE 2023-2024Liseth CarreñoNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology MCQsDocument18 pagesPharmacology MCQsjerry garcia50% (2)
- CV TemplateDocument4 pagesCV TemplateWan HakimiNo ratings yet
- Covid 19 Myths and FactsDocument13 pagesCovid 19 Myths and FactsPrince KatiyarNo ratings yet
- CMC Pedia Batch 2Document43 pagesCMC Pedia Batch 2Marrione CalinawanNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument1 pageCase StudyGemina Leah MaeNo ratings yet
- A Glimmer of Hope, The Non-Surgical Wand For The Aesthetic Correction of Black Triangles - A Case SeriesDocument5 pagesA Glimmer of Hope, The Non-Surgical Wand For The Aesthetic Correction of Black Triangles - A Case SeriesIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Frcpath Part 1 Previous Questions: Document1Document11 pagesFrcpath Part 1 Previous Questions: Document1Ali LaftaNo ratings yet
- Quizlet PDFDocument4 pagesQuizlet PDFsgkismetNo ratings yet
- NP1 NotesDocument59 pagesNP1 NotesBrianMarBeltranNo ratings yet
- ASGE 2012 Endoscopy in Pregnant and Lactating WomenDocument7 pagesASGE 2012 Endoscopy in Pregnant and Lactating WomenjordanNo ratings yet
- Principles of Drug Therapy For The Elderly PatientDocument16 pagesPrinciples of Drug Therapy For The Elderly PatientGalih Maygananda Putra100% (1)
- Clinicopathological Study of Gall Bladder Lesions in Tertiary Care HospitalDocument28 pagesClinicopathological Study of Gall Bladder Lesions in Tertiary Care HospitalHappy SinghNo ratings yet
- LESSON PLAN FOR PLACENTA EXAMINATION NHDHFDocument10 pagesLESSON PLAN FOR PLACENTA EXAMINATION NHDHFjrkedridgemwanakalandoNo ratings yet
- Supta Sarkar HHM-2013-10 M.SC Foods & Nutrition: Presented byDocument31 pagesSupta Sarkar HHM-2013-10 M.SC Foods & Nutrition: Presented byGirum SolomonNo ratings yet
Drugs For Respiratory System
Drugs For Respiratory System
Uploaded by
aliyahalexie60 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views3 pagesNursing pharma
Original Title
DRUGS-FOR-RESPIRATORY-SYSTEM
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentNursing pharma
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views3 pagesDrugs For Respiratory System
Drugs For Respiratory System
Uploaded by
aliyahalexie6Nursing pharma
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
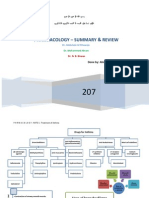
DRUGS FOR THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
DRUGS FOR THE UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT Nursing Intervention:
1. Assess the character of cough before therapy
I. SYMPATHOMIMETICS Side effects:
MOA: stimulate the alpha adrenergic receptors of 1. Drowsiness alert patient if operating machines
the nasal mucosa, vasoconstriction, shrinking of 2. Constipation increase in fiber intake
engorged nasal turbinates and nasal mucosa,
promotes sinus drainage and improves nasal air II. MUCOLYTICS
passages MOA: break disulphide bridges between the
• **DOC for nasal congestion macromolecules within the mucus, decreased
• **available in P.O. & intranasal spray mucus viscosity, and easily removed by coughing,
Nursing Interventions: bronchial clapping and postural drainage
1. Check history of HPN, DM, arrythmias, • ** for emphysema, bronchitis, asthma,
hyperthyroidism, glaucoma, prostatic hyperplasia
pneumonia
2. Take vital signs
Nursing Interventions:
Side effects:
1. Nasal irritation- stinging or burning sensation 1. Assess characteristics of cough
2. HPN – due to excessive use; monitor BP 2. Monitor VS
3. Observe for GIT symptoms
II. ANTIHISTAMINES 4. Baseline assessment of mental status
MOA: compete for H1 receptors on the surface to Side effects:
the arterioles, capilliaries and secretory glands of 1. Nausea & vomiting – due to pungent odor
the mucus membranes and prevents histamine (NAC); smell of rotten egg; have an emesis basin
release ready
• **DOC for allergic rhinitis & allergic 2. Bronchospasm – use a bronchodilating agent
conjunctivitis
Nursing Interventions:
1. Review history of glaucoma, prostatic III. EXPECTORANTS
hyperplasia or asthma refer to MD Actions:
2. Assess patient’s work environment a) enhances output of respiratory tract fluid
Side effects: b) decreases mucus viscosity
1. Sedation and drowsiness most common side c) promotes cilliary action
effect; give during bedtime; provide personal • for dry productive cough; can be used in
safety at work combination of other cough agents
2. Impaired expectoration dry mouth and throat • do not give if cough lasts for a week
suck ice chips Nursing Intervetion:
3. Blurred vision, constipation, urinary retention 1. Assess character of cough
• ** increase fluid intake to 8-10 glasses of Side effects:
water/day ** rare
The best expectorant is water
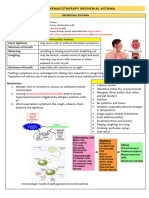
III. INTRA-NASAL CORTICOSTEROIDS
MOA: inhibit generation of pro- inflammatory IV. BETA ADRENERGIC BRONCHODILATING AGENTS/
cytokines BETA 2 ADRENERGIC AGONISTS
• ** for allergic rhinitis to control symptoms; MOA: stimulates beta 2 receptors thus open up the
discontinue if no improvement within 3 airways
weeks
Nursing Interventions: ** mainstay treatment for asthma usually given as
1. Clear nose with decongestant nebulization for acute asthma attacks
2. Blow nose thoroughly before spray
Side effects Nursing Interventions:
1. Nasal burning 1. Baseline VS
2. Assess palpitations and arrythmias
DRUGS FOR THE LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT 3. Baseline mental status (anxiety, nervousness,
alertness)
I. ANTI-TUSSIVE AGENTS Side effects:
MOA: suppress the cough center of the brain 1. Tachycardia, palpitations increase of 20
beats/mins report to physician
• ** for severe, dry, hacking, non- 2. Tremors adjust dose
productive cough that wakes up the
patient at night
3. Nervousness, restlessness, headache due to a) decrease bronchoconstriction
increase effect of the drug b) inflammatory responses
4. Nausea and vomiting
• inhibit trigger symptoms of asthma
V. METHYLXANTHINES • second line drugs
MOA: relaxes the smooth muscles of the bronchi • used if inhaled glucocorticoids does not
thus dilates the airways work
• for asthma and COPD
Nursing Interventions:
Nursing Interventions: 1. Baseline VS
1. Check history of angina, PUD, hyperthyroidism, 2. Pulmonary function test
glaucoma, DM
Side effects:
2. Baseline VS
no serious adverse reactions
3. Baseline mental status (anxiety, restlessness,
nervousness
Side effects: RESPIRATORY DRUGS
1. Nausea and vomiting; epigastric pain; A. DRUGS FOR UPPER RESPIRATORY DISEASES
abdominal cramps
2. Report palpitations
SYMPATHOMIMETIC DECONGESTANTS
3. Nervousness, alertness, anxiety due to
Phenylephrine (Dimetapp Reformulated)
the increased effects of the drugs report to the
physician Phenylpropanolamine ( Disudrin, Neozep,
Sinutab)
VI. ANTICHOLINERGIC AGENTS Ephidrine (Ephedrine)
MOA: blocks the muscarinic receptors of the Pseudoephedrine (Sudafed)
bronchi reducing bronchoconstriction Oxymetazoline (Drixine)
• for long term treatment of COPD
ANTI-HISTAMINES
Nursing Interventions: Diphenhydramine (Bendryl)
1. Baseline VS Chlorphenarmine maleate (Colvan, Ritemed)
2. Determine for any history of glaucoma Hydroxazine (Iterax)
Side effects: Loratadine (Claritin; Alerta; Loradex)
1. dry mouth suck ice chips or hard candy Desloratadine (Aerius, Deslogen)
2. throat irritation mouthwash of Cetirizine (Virlix; Zyrtec)
1 tbsp of hydrogen peroxide + 6-8 ounces of
Levocetirizine (Zyzal)
water; commercial mouthwashes are prohibited
Promethazine (Phenergan)
3. report tachycardia and urinary retention
Clemastine (Tavegyl)
Bilastine (Bilaxten)
VII. GLUCOCORTICOIDS (CORTICOSTERIODS)
MOA: suppressing inflammation thus INTRA-NASAL CORTICOSTEROIDS
a) reduce bronchial hyperactivity Mometasone fuorate (Mosaspray, Nasonex,
b) decrease airway mucus production Zymocort)
Fluticasone fuorate (Aramys)
• for long term airway inflammation
• prophylaxis for chronic asthma
B. DRUGS FOR LOWER RESPIRATORY DISEASES
• given only if unresponsive to previous drugs
mentioned
ANTI-TUSSIVE
Nursing Interventions: Dextromethorphan (Robitussin DM;Tuseran)
1. counseling and compliance Diphenhydramine (Benadryl)
2. preparation before administration Codeine (Robitussin AC)
3. mainating therapy Hydrocodone bitartarate (Hyocdan)
4. assess severe stress or acute asthma attack
Side effects: MUCOLYTIC
1. hoarseness and dry mouth Acetylcisteine (Fluimucil; Mucomyst)
2. oral thrush – advice mouthwash Carbocisteine (Solmux; Loviscol)
VIII. LEUKOTRIENE MODIFIERS/ ANTI
EXPECTORANT
LEUKOTRIENES
Guaifenesin (Robitussin)
MOA: suppress effects of leukotrienes thus Potassium iodide (SSKI)
BETA-ADRENERGIC BRONCHODILATING AGENTS
Salbutamol (Ventolin;Volmax)
Terbutaline (Bricanyl)
Salmeterol (Servent)
Isoproterenol (Isuprel)
Metaproterenol (Allupent)
XANTHINE DERIVATIVES
Aminophylline
Theophylline (Theodur; Nuelin; Asmasolon)
BRONCHODILATING AGENTS
Ipratropium bromide (Atrovent)
Iprsatropium bromide + salbutamol
(Pulmodual)
Ipratropium bromide + fenoterol (Berodual)
Ipratropium bromide + albuterol (Duavent)
CORTICOSTEROIDS
Prednisone (Organon; Pred)
Hydrocortisone (Solu-cortef)
Dexamethasone (Decadron)
ANTI-LEUKOTRIENE
Montelukast (Singulair; Montemax; Montiget)
Montelukast + levocetirizine (Zykast, Co-Altria;
Monte Plus)
Zafirlukast (Accolate)
You might also like
- Postpartum Teaching PlanDocument3 pagesPostpartum Teaching Plan6bigstar991% (11)
- Comprehensive Board Exam ENT PDFDocument644 pagesComprehensive Board Exam ENT PDFdrskbarla50% (2)
- Pharmacotherapy of CoughDocument51 pagesPharmacotherapy of CoughIqra Butt100% (3)
- Midterm PharmaDocument25 pagesMidterm PharmaKaye Honeylee ManibogNo ratings yet
- Respiratory MedicationsDocument14 pagesRespiratory MedicationsissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- Module 3.2 - Respiratory DrugsDocument3 pagesModule 3.2 - Respiratory DrugsCatherine Sinen ObinqueNo ratings yet
- Pharm Exam Ii NotesDocument24 pagesPharm Exam Ii Noteskatiana louisNo ratings yet
- Notes For Respiratory AgentsDocument4 pagesNotes For Respiratory AgentsZella ViaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory DrugsDocument56 pagesRespiratory DrugsIra G. Delos Santos100% (1)
- Printed Material ModuleeeeDocument56 pagesPrinted Material ModuleeeeShang MacarayonNo ratings yet
- 4.l - Respiratory System Pharmacology by IGMRIDocument13 pages4.l - Respiratory System Pharmacology by IGMRIclaw foreSK TeamNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Topic SummaryDocument7 pagesRespiratory Topic SummaryShingie MatemaNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On Functions of Respiratory SystemDocument73 pagesDrugs Acting On Functions of Respiratory SystemMarin ChianuNo ratings yet
- Cough PharmacotherapyDocument27 pagesCough PharmacotherapySalifyanji SimpambaNo ratings yet
- Module 14 - Drugs-affecting-the-Respiratory-System-3Document48 pagesModule 14 - Drugs-affecting-the-Respiratory-System-3weissNo ratings yet
- Upper Respiratory Disorders: ObjectivesDocument16 pagesUpper Respiratory Disorders: ObjectivesJennie QuachNo ratings yet
- Pharma Reviewer (Midterm)Document7 pagesPharma Reviewer (Midterm)SaidinaNo ratings yet
- Asthma Treatment and PreventionDocument5 pagesAsthma Treatment and PreventionJohn Paul MatienzoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System DrugsDocument5 pagesRespiratory System DrugsHamad AlshabiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Drugs Actiong On Respiratory SystemDocument6 pagesChapter 6 - Drugs Actiong On Respiratory SystemMohit SoniNo ratings yet
- Dr. Swagath, HassanDocument29 pagesDr. Swagath, HassanSwagath NNo ratings yet
- Bronchial Asthma: Sudhakar Lakavath Dept - Of.PharmacologyDocument50 pagesBronchial Asthma: Sudhakar Lakavath Dept - Of.PharmacologySudhakar LakavathNo ratings yet
- CombiventDocument2 pagesCombiventunkown userNo ratings yet
- Drug Study IMDocument2 pagesDrug Study IMAbigail BrillantesNo ratings yet
- V. Drug StudyDocument5 pagesV. Drug StudyJopaii TanakaNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting The Respiratory System PPPDocument35 pagesDrugs Affecting The Respiratory System PPPChristopher VelonzaNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting The Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesDrugs Affecting The Respiratory SystemJerica Jaz F. Vergara100% (1)
- PHL1 - Pharmacotherapy Bronchial AsthmaDocument7 pagesPHL1 - Pharmacotherapy Bronchial AsthmaFadhlina OmarNo ratings yet
- 5.1 5.4Document24 pages5.1 5.4Nim DCNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Upper Drugs NotesDocument3 pagesRespiratory Upper Drugs NotesAngela PonceNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Cough: - Cough Is of Two TypesDocument5 pagesDrugs For Cough: - Cough Is of Two TypesKahlon JotNo ratings yet
- Janine Vega BSM 3 Phama Midterm ActivityDocument8 pagesJanine Vega BSM 3 Phama Midterm ActivityJanine VegaNo ratings yet
- Pulmonology May 28Document76 pagesPulmonology May 28Brielle ShoppNo ratings yet
- NCM 106 FinalsDocument55 pagesNCM 106 FinalsKyle BagacNo ratings yet
- E Kart DrugsDocument3 pagesE Kart DrugsNichole CastleNo ratings yet
- 16 Drugs Affecting RespiDocument3 pages16 Drugs Affecting RespiAdriwayne Francis GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Romero, Deinielle Ingrid M. (Pulmo)Document3 pagesRomero, Deinielle Ingrid M. (Pulmo)Deinielle Magdangal RomeroNo ratings yet
- 15 Patients With Altered VentilationDocument66 pages15 Patients With Altered VentilationErshelle Mae MorlaNo ratings yet
- Case Study 4 CVD Infarct CAP MR HUD RDU DementiaDocument21 pagesCase Study 4 CVD Infarct CAP MR HUD RDU DementiaVictoria Mae Irong CabahugNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument62 pagesRespiratory SystemSravani SravsNo ratings yet
- Cough: PHR Sangita ShakyaDocument21 pagesCough: PHR Sangita ShakyaCurex QANo ratings yet
- Pharma Midterm ReviewerDocument45 pagesPharma Midterm ReviewerCarlos Miguel AndalNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyZek Comidoy100% (1)
- Note 1Document3 pagesNote 1HossamJamaykaNo ratings yet
- Midterms RLEDocument11 pagesMidterms RLEgungonfiona28No ratings yet
- Antihistamine BlockersDocument12 pagesAntihistamine Blockersyra capiliNo ratings yet
- Rhinitis Guidelines: Classification and Differential DiagnosisDocument5 pagesRhinitis Guidelines: Classification and Differential DiagnosisEricaNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Respiratory SystemDocument18 pagesDrugs For Respiratory SystemKaye CorNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Disorders (Asthma & COPD ..)Document5 pagesRespiratory System Disorders (Asthma & COPD ..)KC PalattaoNo ratings yet
- Ipratroprium Drug CardDocument3 pagesIpratroprium Drug CardXiaoDuckyNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgCoxAEPf B5bFXXj0n0ogZgNdJimPp0HP25fR0kWmUQfj5aodpDMX Y2yxgw FKGZR QuqtH7SZyDlG8F4JVDjQOuJN8At7iKpg7xji x2zqAMu YaQmBFHVDJ12jag4khHkNk5gAYOo25zDocument6 pagesACFrOgCoxAEPf B5bFXXj0n0ogZgNdJimPp0HP25fR0kWmUQfj5aodpDMX Y2yxgw FKGZR QuqtH7SZyDlG8F4JVDjQOuJN8At7iKpg7xji x2zqAMu YaQmBFHVDJ12jag4khHkNk5gAYOo25zRheeanne AmilasanNo ratings yet
- WEEK 9 - NCMA216 - PHARMA - Respiratory System AgentsDocument50 pagesWEEK 9 - NCMA216 - PHARMA - Respiratory System AgentsOther AccountNo ratings yet
- Treating The Severely Dyspneic Patient - : Covid-19 Training For Healthcare WorkersDocument4 pagesTreating The Severely Dyspneic Patient - : Covid-19 Training For Healthcare WorkersDefo SandiNo ratings yet
- 02 Bronchial AsthmaDocument6 pages02 Bronchial AsthmaahmedNo ratings yet
- CHF Drug StudyDocument11 pagesCHF Drug StudySeth Michael Daniel BenauroNo ratings yet
- Autacoids Final PDFDocument22 pagesAutacoids Final PDFIqra ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Fluorescein Wall ChartDocument1 pageFluorescein Wall ChartbijujcNo ratings yet
- 1.chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease 2. Allergic RhinitisDocument18 pages1.chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease 2. Allergic Rhinitisيحيى اسماعيل الجميليNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting The Respiratory SystemDocument89 pagesDrugs Affecting The Respiratory SystemkayarohanamNo ratings yet
- Local Anesthesia Made Easy: Complete Guide on How to make your Local Anesthetic Procedure a Success (Including a List of Anesthetic Equipment and their Uses)From EverandLocal Anesthesia Made Easy: Complete Guide on How to make your Local Anesthetic Procedure a Success (Including a List of Anesthetic Equipment and their Uses)No ratings yet
- Differentiating Anesthesia Equipment: Identify and Understand Anesthesia Equipment in 1 Hour (Including the most popular manufacturers and suppliers to buy Anesthesia Equipment)From EverandDifferentiating Anesthesia Equipment: Identify and Understand Anesthesia Equipment in 1 Hour (Including the most popular manufacturers and suppliers to buy Anesthesia Equipment)No ratings yet
- Leann Li ResumeDocument2 pagesLeann Li Resumeapi-660140781No ratings yet
- Vice and DrugDocument8 pagesVice and DrugTIPAY, EMELIE L.No ratings yet
- Do You Need To Drink 8 Glasses of Water TranscriptDocument2 pagesDo You Need To Drink 8 Glasses of Water TranscriptHarold Saldy CasalemNo ratings yet
- MD India Preauth FormDocument2 pagesMD India Preauth FormM/s MicrotechNo ratings yet
- Palliative Care in Parkinson's Disease: ReviewDocument4 pagesPalliative Care in Parkinson's Disease: ReviewAnonymous lwYEylQhNo ratings yet
- Cholesterol PDFDocument32 pagesCholesterol PDFAkshad PatilNo ratings yet
- Csa Form Serology Clearance Certificate s7 Oct 2014Document2 pagesCsa Form Serology Clearance Certificate s7 Oct 2014Thomas EyreNo ratings yet
- Heart AnatomyDocument11 pagesHeart AnatomyJohn FisherNo ratings yet
- Are Repeat COVID Infections DangerousDocument3 pagesAre Repeat COVID Infections DangerousJuan MNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plankarla joy sta teresaNo ratings yet
- Growth of Analytical Thinking Skills Over Time As Measured With The MATCH TestDocument7 pagesGrowth of Analytical Thinking Skills Over Time As Measured With The MATCH TestFrederico PóvoaNo ratings yet
- Abg Analysis ReviewerDocument21 pagesAbg Analysis ReviewerAyiessa_AJNo ratings yet
- By MBBS Gang: ENT Examination ProcedureDocument23 pagesBy MBBS Gang: ENT Examination ProcedureYour DaddyNo ratings yet
- Master's Degree in Periodontology: COURSE 2023-2024Document14 pagesMaster's Degree in Periodontology: COURSE 2023-2024Liseth CarreñoNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology MCQsDocument18 pagesPharmacology MCQsjerry garcia50% (2)
- CV TemplateDocument4 pagesCV TemplateWan HakimiNo ratings yet
- Covid 19 Myths and FactsDocument13 pagesCovid 19 Myths and FactsPrince KatiyarNo ratings yet
- CMC Pedia Batch 2Document43 pagesCMC Pedia Batch 2Marrione CalinawanNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument1 pageCase StudyGemina Leah MaeNo ratings yet
- A Glimmer of Hope, The Non-Surgical Wand For The Aesthetic Correction of Black Triangles - A Case SeriesDocument5 pagesA Glimmer of Hope, The Non-Surgical Wand For The Aesthetic Correction of Black Triangles - A Case SeriesIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Frcpath Part 1 Previous Questions: Document1Document11 pagesFrcpath Part 1 Previous Questions: Document1Ali LaftaNo ratings yet
- Quizlet PDFDocument4 pagesQuizlet PDFsgkismetNo ratings yet
- NP1 NotesDocument59 pagesNP1 NotesBrianMarBeltranNo ratings yet
- ASGE 2012 Endoscopy in Pregnant and Lactating WomenDocument7 pagesASGE 2012 Endoscopy in Pregnant and Lactating WomenjordanNo ratings yet
- Principles of Drug Therapy For The Elderly PatientDocument16 pagesPrinciples of Drug Therapy For The Elderly PatientGalih Maygananda Putra100% (1)
- Clinicopathological Study of Gall Bladder Lesions in Tertiary Care HospitalDocument28 pagesClinicopathological Study of Gall Bladder Lesions in Tertiary Care HospitalHappy SinghNo ratings yet
- LESSON PLAN FOR PLACENTA EXAMINATION NHDHFDocument10 pagesLESSON PLAN FOR PLACENTA EXAMINATION NHDHFjrkedridgemwanakalandoNo ratings yet
- Supta Sarkar HHM-2013-10 M.SC Foods & Nutrition: Presented byDocument31 pagesSupta Sarkar HHM-2013-10 M.SC Foods & Nutrition: Presented byGirum SolomonNo ratings yet