Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 viewsThe Nerve Cell
The Nerve Cell
Uploaded by
jonelllantero032Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Weekly AssignmentDocument7 pagesWeekly AssignmentBajwa AyeshaNo ratings yet
- Oral Exam ReviewerDocument48 pagesOral Exam ReviewerFayena JoseNo ratings yet
- Oral Exam ReviewerDocument39 pagesOral Exam ReviewerFayena JoseNo ratings yet
- Nervous TissuesDocument13 pagesNervous TissuesSafura IjazNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Neural TissueDocument15 pagesChapter 12 Neural TissueKatherine De San AgustinNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Transes 1Document6 pagesNervous System Transes 1Rhodie BatislaonNo ratings yet
- Unit 3.10 Neurons: Structure of A NeuronDocument5 pagesUnit 3.10 Neurons: Structure of A NeuronNeville Cheong (SPC)No ratings yet
- General Psychology - Biological FoundationDocument55 pagesGeneral Psychology - Biological FoundationKomala PodapatiNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Neuroscience and BehaviourDocument7 pages1.2 Neuroscience and BehaviourDiya MehtaNo ratings yet
- Structure of Brain Nervous System-20-04-2020Document3 pagesStructure of Brain Nervous System-20-04-2020Jethalal GadaNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Nervious Tissues.pptxDocument36 pages4.2 Nervious Tissues.pptxZaara RashéidNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Nervous SystemDocument32 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Nervous SystemLouise Murphy100% (1)
- 3.1 Nervous System NotesDocument8 pages3.1 Nervous System NotesabaybezawitNo ratings yet
- Nervous ControlDocument15 pagesNervous ControlzoeakatNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Biological Foundations of Behaviour - Student OutlineDocument43 pagesModule 2 Biological Foundations of Behaviour - Student OutlineDweep BajajNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument14 pagesNervous SystemJose-Miguel HernandezNo ratings yet
- Types of Neurons PDFDocument2 pagesTypes of Neurons PDFPerry Sin100% (2)
- Functions of THDocument12 pagesFunctions of THKarl KiwisNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Science 10Document3 pagesReviewer in Science 10Aaron ZephyrNo ratings yet
- Nscelec4-Week 15Document23 pagesNscelec4-Week 15Jeune Kristine OngNo ratings yet
- Presentation 2Document23 pagesPresentation 2Maria KhanNo ratings yet
- Coordinated Functions Nervoys SDocument3 pagesCoordinated Functions Nervoys SGwency Ross Alvarez (Gwen)No ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument86 pagesThe Nervous SystemNatukunda Dianah100% (1)
- CNS PNS NeuronsDocument20 pagesCNS PNS NeuronsTyrese SmithNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument15 pagesNervous SystemSatrioNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System-13 Dr. Hazim AL-RawiDocument16 pagesThe Nervous System-13 Dr. Hazim AL-RawiDrAli Al-FendiNo ratings yet
- Midterm NotesDocument14 pagesMidterm Notescassandra alexanderNo ratings yet
- Updated Central and Peripheral Nervous System TestDocument8 pagesUpdated Central and Peripheral Nervous System TestScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Nervous TissueDocument8 pagesModule 5 Nervous TissueHermione MalfoyNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesNervous SystemJavi OceansoulNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument20 pagesNervous SystemxoxogeloNo ratings yet
- Module 12 Handouts Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesModule 12 Handouts Nervous Systemgianarido30No ratings yet
- Science Sofie 10 3 RevDocument11 pagesScience Sofie 10 3 Revjinxtapperhat07No ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - An Introduction To The Nervous System: Peripheral Nerves)Document7 pagesChapter 12 - An Introduction To The Nervous System: Peripheral Nerves)tomorrow.today.yesterday .yesterdayNo ratings yet
- Class NotesDocument4 pagesClass Notesdaniel holmesNo ratings yet
- Botan's Cns and The Brain 2023Document115 pagesBotan's Cns and The Brain 2023Caamir Dek HaybeNo ratings yet
- 9SUMMARYNERVOUSSYSTEMDocument24 pages9SUMMARYNERVOUSSYSTEMArvenBitasNo ratings yet
- Neuro-Network: A Presentation About The Nervous SystemDocument14 pagesNeuro-Network: A Presentation About The Nervous Systemwellskyle891No ratings yet
- The Nervous System Is Divided Into Two PartsDocument5 pagesThe Nervous System Is Divided Into Two PartsTahir AzizNo ratings yet
- What Is Nervous System?: Presented By: TIP Grade 12 StudentDocument28 pagesWhat Is Nervous System?: Presented By: TIP Grade 12 StudentDreiza Patria SunodanNo ratings yet
- Midterm Reviewer Anaphy LectureDocument15 pagesMidterm Reviewer Anaphy LectureCarlito FantilaganNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument23 pagesNervous SystemAnonymous 3OKQDoiJNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument12 pagesNervous SystemLeon MarkoNo ratings yet
- BIOAA1BSP221E - Neutral Conduction - MendozaDocument6 pagesBIOAA1BSP221E - Neutral Conduction - MendozaCassandraNo ratings yet
- Neuropsychology Summary BookletDocument12 pagesNeuropsychology Summary Bookletapi-642709499No ratings yet
- UNIT 4 (Nervous System)Document14 pagesUNIT 4 (Nervous System)Workinesh Kaynabo KambaloNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology NSDocument73 pagesAnatomy & Physiology NSIsha Bhusal67% (3)
- Nervous System: Science 6 - Second QuarterDocument25 pagesNervous System: Science 6 - Second QuarterRegin BaguioNo ratings yet
- Neurology Assignment 1Document9 pagesNeurology Assignment 1workupindia7No ratings yet
- Animal Nervous System: Logo HereDocument32 pagesAnimal Nervous System: Logo HereAnne Claudette Capin TeofiloNo ratings yet
- NeurologyDocument42 pagesNeurologybuzz Q100% (2)
- Nervous System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument26 pagesNervous System Anatomy and PhysiologyKBD100% (3)
- The Nervous SystemDocument36 pagesThe Nervous SystemespirituronnierickNo ratings yet
- Nervous System 1Document13 pagesNervous System 1wasim akhtarNo ratings yet
- Ervous Ystem: Structural ClassificationDocument95 pagesErvous Ystem: Structural ClassificationJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Neurons Elements of BehaviourDocument3 pagesNeurons Elements of Behaviourchantefraser8No ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument28 pagesNervous SystemPhoebe dane M PandayNo ratings yet
- Module 2: Physiological Basis of BehaviorDocument23 pagesModule 2: Physiological Basis of BehaviorRoxie May Theresse AbagatnanNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument9 pagesNervous SystemMuhamad Hafiz Bin Mohd BakriNo ratings yet
The Nerve Cell
The Nerve Cell
Uploaded by
jonelllantero0320 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views9 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views9 pagesThe Nerve Cell
The Nerve Cell
Uploaded by
jonelllantero032Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 9
The Nerve Cell
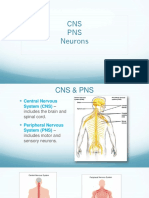
- The nervous system consists of the brain,
spinal cord, sense receptors and the nerves.
- The basic unit of the nervous system is
the Neuron or the nerve cells.
- It helps to perceive and send messages to
the parts of our body as required.
Structure of a Neuron
A neuron consists of the following three
parts:
1) The Cell body: It is also called the cyton
or perikaryon.
- It contains a nucleus with cytoplasm.
2) Dendrites: They are branched structures
of the cell body.
- They help to conduct the impulses to the
cell body.
3) Axon: It is an Elongated Dendrite. It is
surrounded by the Myelin Sheath, which
is again covered by Neurolemma.
- The Myelin sheath has gaps throughout its
length called the NODES OF RANVIER.
- The end portions are swollen like bulbs
called Neurotransmitters, which store
chemicals.
Types of Neurons
1. Brain Cells - These process information.
2. Sensory Neurons - These detect the
outside world and send signals to the CNS
3. Motor Neurons - These receive signals
from the CNS and pass them on to muscles
and glands.
Neurons are cells with the special ability
to carry signals or impulses. Thoughts,
emotions, learning, and many body
functions are carried by nerve impulses in
the neurons. A nerve impulse is a
combination of an electrical charge and a
chemical reaction.
Synapse
- is a small gap at the end of a neuron that
allows a signal to pass from one neuron to
the next. Neurons are cells that transmit
information between your brain and other
parts of the central nervous system.
- Synapses are found where neurons connect
with other neurons.
You might also like
- Weekly AssignmentDocument7 pagesWeekly AssignmentBajwa AyeshaNo ratings yet
- Oral Exam ReviewerDocument48 pagesOral Exam ReviewerFayena JoseNo ratings yet
- Oral Exam ReviewerDocument39 pagesOral Exam ReviewerFayena JoseNo ratings yet
- Nervous TissuesDocument13 pagesNervous TissuesSafura IjazNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Neural TissueDocument15 pagesChapter 12 Neural TissueKatherine De San AgustinNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Transes 1Document6 pagesNervous System Transes 1Rhodie BatislaonNo ratings yet
- Unit 3.10 Neurons: Structure of A NeuronDocument5 pagesUnit 3.10 Neurons: Structure of A NeuronNeville Cheong (SPC)No ratings yet
- General Psychology - Biological FoundationDocument55 pagesGeneral Psychology - Biological FoundationKomala PodapatiNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Neuroscience and BehaviourDocument7 pages1.2 Neuroscience and BehaviourDiya MehtaNo ratings yet
- Structure of Brain Nervous System-20-04-2020Document3 pagesStructure of Brain Nervous System-20-04-2020Jethalal GadaNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Nervious Tissues.pptxDocument36 pages4.2 Nervious Tissues.pptxZaara RashéidNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Nervous SystemDocument32 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Nervous SystemLouise Murphy100% (1)
- 3.1 Nervous System NotesDocument8 pages3.1 Nervous System NotesabaybezawitNo ratings yet
- Nervous ControlDocument15 pagesNervous ControlzoeakatNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Biological Foundations of Behaviour - Student OutlineDocument43 pagesModule 2 Biological Foundations of Behaviour - Student OutlineDweep BajajNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument14 pagesNervous SystemJose-Miguel HernandezNo ratings yet
- Types of Neurons PDFDocument2 pagesTypes of Neurons PDFPerry Sin100% (2)
- Functions of THDocument12 pagesFunctions of THKarl KiwisNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Science 10Document3 pagesReviewer in Science 10Aaron ZephyrNo ratings yet
- Nscelec4-Week 15Document23 pagesNscelec4-Week 15Jeune Kristine OngNo ratings yet
- Presentation 2Document23 pagesPresentation 2Maria KhanNo ratings yet
- Coordinated Functions Nervoys SDocument3 pagesCoordinated Functions Nervoys SGwency Ross Alvarez (Gwen)No ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument86 pagesThe Nervous SystemNatukunda Dianah100% (1)
- CNS PNS NeuronsDocument20 pagesCNS PNS NeuronsTyrese SmithNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument15 pagesNervous SystemSatrioNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System-13 Dr. Hazim AL-RawiDocument16 pagesThe Nervous System-13 Dr. Hazim AL-RawiDrAli Al-FendiNo ratings yet
- Midterm NotesDocument14 pagesMidterm Notescassandra alexanderNo ratings yet
- Updated Central and Peripheral Nervous System TestDocument8 pagesUpdated Central and Peripheral Nervous System TestScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Nervous TissueDocument8 pagesModule 5 Nervous TissueHermione MalfoyNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesNervous SystemJavi OceansoulNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument20 pagesNervous SystemxoxogeloNo ratings yet
- Module 12 Handouts Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesModule 12 Handouts Nervous Systemgianarido30No ratings yet
- Science Sofie 10 3 RevDocument11 pagesScience Sofie 10 3 Revjinxtapperhat07No ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - An Introduction To The Nervous System: Peripheral Nerves)Document7 pagesChapter 12 - An Introduction To The Nervous System: Peripheral Nerves)tomorrow.today.yesterday .yesterdayNo ratings yet
- Class NotesDocument4 pagesClass Notesdaniel holmesNo ratings yet
- Botan's Cns and The Brain 2023Document115 pagesBotan's Cns and The Brain 2023Caamir Dek HaybeNo ratings yet
- 9SUMMARYNERVOUSSYSTEMDocument24 pages9SUMMARYNERVOUSSYSTEMArvenBitasNo ratings yet
- Neuro-Network: A Presentation About The Nervous SystemDocument14 pagesNeuro-Network: A Presentation About The Nervous Systemwellskyle891No ratings yet
- The Nervous System Is Divided Into Two PartsDocument5 pagesThe Nervous System Is Divided Into Two PartsTahir AzizNo ratings yet
- What Is Nervous System?: Presented By: TIP Grade 12 StudentDocument28 pagesWhat Is Nervous System?: Presented By: TIP Grade 12 StudentDreiza Patria SunodanNo ratings yet
- Midterm Reviewer Anaphy LectureDocument15 pagesMidterm Reviewer Anaphy LectureCarlito FantilaganNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument23 pagesNervous SystemAnonymous 3OKQDoiJNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument12 pagesNervous SystemLeon MarkoNo ratings yet
- BIOAA1BSP221E - Neutral Conduction - MendozaDocument6 pagesBIOAA1BSP221E - Neutral Conduction - MendozaCassandraNo ratings yet
- Neuropsychology Summary BookletDocument12 pagesNeuropsychology Summary Bookletapi-642709499No ratings yet
- UNIT 4 (Nervous System)Document14 pagesUNIT 4 (Nervous System)Workinesh Kaynabo KambaloNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology NSDocument73 pagesAnatomy & Physiology NSIsha Bhusal67% (3)
- Nervous System: Science 6 - Second QuarterDocument25 pagesNervous System: Science 6 - Second QuarterRegin BaguioNo ratings yet
- Neurology Assignment 1Document9 pagesNeurology Assignment 1workupindia7No ratings yet
- Animal Nervous System: Logo HereDocument32 pagesAnimal Nervous System: Logo HereAnne Claudette Capin TeofiloNo ratings yet
- NeurologyDocument42 pagesNeurologybuzz Q100% (2)
- Nervous System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument26 pagesNervous System Anatomy and PhysiologyKBD100% (3)
- The Nervous SystemDocument36 pagesThe Nervous SystemespirituronnierickNo ratings yet
- Nervous System 1Document13 pagesNervous System 1wasim akhtarNo ratings yet
- Ervous Ystem: Structural ClassificationDocument95 pagesErvous Ystem: Structural ClassificationJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Neurons Elements of BehaviourDocument3 pagesNeurons Elements of Behaviourchantefraser8No ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument28 pagesNervous SystemPhoebe dane M PandayNo ratings yet
- Module 2: Physiological Basis of BehaviorDocument23 pagesModule 2: Physiological Basis of BehaviorRoxie May Theresse AbagatnanNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument9 pagesNervous SystemMuhamad Hafiz Bin Mohd BakriNo ratings yet