Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is AC Current
What Is AC Current
Uploaded by
Maha BalaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Direct CurrentDocument1 pageDirect CurrentShra 1537No ratings yet
- Unit-II Beee Ac-I NewDocument19 pagesUnit-II Beee Ac-I NewParikshit SinghNo ratings yet
- Alternating and Direct Current: War of The CurrentsDocument1 pageAlternating and Direct Current: War of The CurrentsAmey KhawaleNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current: Group 1Document20 pagesAlternating Current: Group 1nichinichi_14No ratings yet
- Chapter Three DC and AC CircuitsDocument19 pagesChapter Three DC and AC CircuitsShaker HusienNo ratings yet
- Current.: ModulatedDocument1 pageCurrent.: ModulatedmmgcourrielNo ratings yet
- Activity4 Ac&Dc Gacosta NicoleDocument8 pagesActivity4 Ac&Dc Gacosta NicolenicsNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current: Frequency Hertz RFDocument2 pagesAlternating Current: Frequency Hertz RFKenneth BarberNo ratings yet
- Direction. An Electric Charge Would For Instance Move Forward, Then Backward, Then Forward, ThenDocument2 pagesDirection. An Electric Charge Would For Instance Move Forward, Then Backward, Then Forward, ThenjovitawayawayNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current (Ac) CircuitsDocument34 pagesAlternating Current (Ac) CircuitsGabriel Carl AlpuertoNo ratings yet
- Comparision of Ac & DCDocument11 pagesComparision of Ac & DCdevshakya885No ratings yet
- En M Wikipedia Org Wiki Alternating CurrentDocument16 pagesEn M Wikipedia Org Wiki Alternating CurrentMayurNo ratings yet
- Physics Project - Eddy Current 4Document17 pagesPhysics Project - Eddy Current 4margobuilders106No ratings yet
- Alternating CurrentDocument2 pagesAlternating CurrentYveth MacionNo ratings yet
- Soldering IronDocument12 pagesSoldering IronfjsabNo ratings yet
- Direct Current Only Flows in One Direction. Alternating Current Changes Direction PeriodicallyDocument1 pageDirect Current Only Flows in One Direction. Alternating Current Changes Direction PeriodicallyCarl Justine Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- (Basics) : 1. What Are Electrical Currents?Document7 pages(Basics) : 1. What Are Electrical Currents?Raedler MarcaidaNo ratings yet
- Comparision of Ac & DCDocument11 pagesComparision of Ac & DCdevshakya885No ratings yet
- Section Review:: Foundation Electrical Engineering: Basic AC Theory KuphaldtDocument2 pagesSection Review:: Foundation Electrical Engineering: Basic AC Theory KuphaldtVanesa JeronimoNo ratings yet
- AC To DC ParametersDocument4 pagesAC To DC ParametersJehnen BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Principle of ElectricDocument66 pagesPrinciple of ElectricSyahmi FadziNo ratings yet
- What and How To Acquire Voltage Power Resistor CurrentDocument8 pagesWhat and How To Acquire Voltage Power Resistor CurrentNie TofuNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuit Analysis HandoutDocument34 pagesElectric Circuit Analysis Handoutmeseret sisayNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current (AC) vs. Direct Current (DC) : Thunderstruck!Document11 pagesAlternating Current (AC) vs. Direct Current (DC) : Thunderstruck!deon balramNo ratings yet
- AC: An Electric Current That Continually Reverses DirectionDocument3 pagesAC: An Electric Current That Continually Reverses DirectionYveth MacionNo ratings yet
- Ex. No. 1Document5 pagesEx. No. 1roneali098No ratings yet
- Physics Ac DC ProDocument6 pagesPhysics Ac DC Prohi_scribdNo ratings yet
- L3-Principle of ElectricDocument66 pagesL3-Principle of ElectricIzzah AfiqahNo ratings yet
- RoneDocument9 pagesRoneroneali098No ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits 2Document231 pagesElectrical Circuits 2RJ MCNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2-Electricity and MagnesiumDocument24 pagesUNIT 2-Electricity and MagnesiumAar PeeNo ratings yet
- 3 Phase Power Vs Single Phase PowerDocument5 pages3 Phase Power Vs Single Phase PowerMuhammad AmeerNo ratings yet
- Brany Alejandro Gomezzz Physics..!!!Document8 pagesBrany Alejandro Gomezzz Physics..!!!Brany Alejandro Gomez AlvarezNo ratings yet
- ElectronicsDocument11 pagesElectronicsChris Benedict LatosaNo ratings yet
- Current ElectricityDocument23 pagesCurrent ElectricityGavin SamuelsNo ratings yet
- Building Services-Iii (Ar V 2116) 2014-15: B. Arch III SemesterDocument28 pagesBuilding Services-Iii (Ar V 2116) 2014-15: B. Arch III SemesterAmandeepKaurNo ratings yet
- What Is Alternating CurrentDocument49 pagesWhat Is Alternating CurrentRajeev ValunjkarNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current (AC) vs. Direct Current (DC) - Learn - SparkfunDocument12 pagesAlternating Current (AC) vs. Direct Current (DC) - Learn - SparkfunDeepakDeep100% (1)
- EEE 101 CH6: Ac Circuits and MeasurementsDocument30 pagesEEE 101 CH6: Ac Circuits and MeasurementsSERHAT YILDIRIMNo ratings yet
- PHYS101L LabReport9Document13 pagesPHYS101L LabReport9Leidee Charmellie SerranoNo ratings yet
- Electronics BasicsDocument21 pagesElectronics BasicsK a l o n M u s i kNo ratings yet
- MachinesDocument1 pageMachinesAkbar SNo ratings yet
- Phy3 Chapter1Document26 pagesPhy3 Chapter1kokoh20No ratings yet
- Research Electronics 4 19 9 19Document7 pagesResearch Electronics 4 19 9 19HarshilNo ratings yet
- Alternating CurrentDocument10 pagesAlternating Currentanand011100% (1)
- CT1 Unit 2Document29 pagesCT1 Unit 2Ali khan7No ratings yet
- Grade 9 IctDocument18 pagesGrade 9 IctJohn Carl ToledoNo ratings yet
- Describe AC DCDocument2 pagesDescribe AC DCNancy NursiamNo ratings yet
- Alternative Current (AC) and Direct Current (DC)Document4 pagesAlternative Current (AC) and Direct Current (DC)MonirNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity Chp-8 General Science 9th 10thDocument11 pagesCurrent Electricity Chp-8 General Science 9th 10thKamran AbdullahNo ratings yet
- 14 InvertersDocument52 pages14 InvertersEwerton Serafim100% (1)
- Illut Ee Lab Research 1Document15 pagesIllut Ee Lab Research 1carlverano0428No ratings yet
- Ac DC CircuitDocument3 pagesAc DC CircuitMark Dennis AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Electron Current Voltage Semiconductor Frequency Hertz RFDocument1 pageElectron Current Voltage Semiconductor Frequency Hertz RFDean ParconNo ratings yet
- Electric Current: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument46 pagesElectric Current: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaBerny ManalangNo ratings yet
- Present 2Document35 pagesPresent 2Jayesh JainNo ratings yet
- Getting Started. Conventional Electricity Supply 2021-22Document19 pagesGetting Started. Conventional Electricity Supply 2021-22Leeroy ZizhouNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Electricity Supply and Regulation in IndiaFrom EverandIntroduction to Electricity Supply and Regulation in IndiaNo ratings yet
What Is AC Current
What Is AC Current
Uploaded by
Maha BalaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What Is AC Current
What Is AC Current
Uploaded by
Maha BalaCopyright:
Available Formats
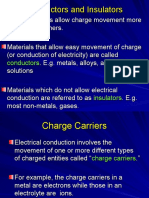
Alternating current (AC) is an electric current which periodically reverses
direction and changes its magnitude continuously with time, in contrast to direct
current (DC), which flows only in one direction. Alternating current is the form in
which electric power is delivered to businesses and residences, and it is the form
of electrical energy that consumers typically use when they plug kitchen
appliances, televisions, fans and electric lamps into a wall socket. A common
source of DC power is a battery cell in a flashlight. The abbreviations AC and DC
are often used to mean simply alternating and direct, respectively, as when they
modify current or voltage.[1][2]
The usual waveform of alternating current in most electric power circuits is a sine
wave, whose positive half-period corresponds with positive direction of the current
and vice versa (the full period is called a cycle). In certain applications, like
guitar amplifiers, different waveforms are used, such as triangular waves or square
waves. Audio and radio signals carried on electrical wires are also examples of
alternating current. These types of alternating current carry information such as
sound (audio) or images (video) sometimes carried by modulation of an AC carrier
signal. These currents typically alternate at higher frequencies than those used in
power transmission.
You might also like
- Direct CurrentDocument1 pageDirect CurrentShra 1537No ratings yet
- Unit-II Beee Ac-I NewDocument19 pagesUnit-II Beee Ac-I NewParikshit SinghNo ratings yet
- Alternating and Direct Current: War of The CurrentsDocument1 pageAlternating and Direct Current: War of The CurrentsAmey KhawaleNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current: Group 1Document20 pagesAlternating Current: Group 1nichinichi_14No ratings yet
- Chapter Three DC and AC CircuitsDocument19 pagesChapter Three DC and AC CircuitsShaker HusienNo ratings yet
- Current.: ModulatedDocument1 pageCurrent.: ModulatedmmgcourrielNo ratings yet
- Activity4 Ac&Dc Gacosta NicoleDocument8 pagesActivity4 Ac&Dc Gacosta NicolenicsNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current: Frequency Hertz RFDocument2 pagesAlternating Current: Frequency Hertz RFKenneth BarberNo ratings yet
- Direction. An Electric Charge Would For Instance Move Forward, Then Backward, Then Forward, ThenDocument2 pagesDirection. An Electric Charge Would For Instance Move Forward, Then Backward, Then Forward, ThenjovitawayawayNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current (Ac) CircuitsDocument34 pagesAlternating Current (Ac) CircuitsGabriel Carl AlpuertoNo ratings yet
- Comparision of Ac & DCDocument11 pagesComparision of Ac & DCdevshakya885No ratings yet
- En M Wikipedia Org Wiki Alternating CurrentDocument16 pagesEn M Wikipedia Org Wiki Alternating CurrentMayurNo ratings yet
- Physics Project - Eddy Current 4Document17 pagesPhysics Project - Eddy Current 4margobuilders106No ratings yet
- Alternating CurrentDocument2 pagesAlternating CurrentYveth MacionNo ratings yet
- Soldering IronDocument12 pagesSoldering IronfjsabNo ratings yet
- Direct Current Only Flows in One Direction. Alternating Current Changes Direction PeriodicallyDocument1 pageDirect Current Only Flows in One Direction. Alternating Current Changes Direction PeriodicallyCarl Justine Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- (Basics) : 1. What Are Electrical Currents?Document7 pages(Basics) : 1. What Are Electrical Currents?Raedler MarcaidaNo ratings yet
- Comparision of Ac & DCDocument11 pagesComparision of Ac & DCdevshakya885No ratings yet
- Section Review:: Foundation Electrical Engineering: Basic AC Theory KuphaldtDocument2 pagesSection Review:: Foundation Electrical Engineering: Basic AC Theory KuphaldtVanesa JeronimoNo ratings yet
- AC To DC ParametersDocument4 pagesAC To DC ParametersJehnen BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Principle of ElectricDocument66 pagesPrinciple of ElectricSyahmi FadziNo ratings yet
- What and How To Acquire Voltage Power Resistor CurrentDocument8 pagesWhat and How To Acquire Voltage Power Resistor CurrentNie TofuNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuit Analysis HandoutDocument34 pagesElectric Circuit Analysis Handoutmeseret sisayNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current (AC) vs. Direct Current (DC) : Thunderstruck!Document11 pagesAlternating Current (AC) vs. Direct Current (DC) : Thunderstruck!deon balramNo ratings yet
- AC: An Electric Current That Continually Reverses DirectionDocument3 pagesAC: An Electric Current That Continually Reverses DirectionYveth MacionNo ratings yet
- Ex. No. 1Document5 pagesEx. No. 1roneali098No ratings yet
- Physics Ac DC ProDocument6 pagesPhysics Ac DC Prohi_scribdNo ratings yet
- L3-Principle of ElectricDocument66 pagesL3-Principle of ElectricIzzah AfiqahNo ratings yet
- RoneDocument9 pagesRoneroneali098No ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits 2Document231 pagesElectrical Circuits 2RJ MCNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2-Electricity and MagnesiumDocument24 pagesUNIT 2-Electricity and MagnesiumAar PeeNo ratings yet
- 3 Phase Power Vs Single Phase PowerDocument5 pages3 Phase Power Vs Single Phase PowerMuhammad AmeerNo ratings yet
- Brany Alejandro Gomezzz Physics..!!!Document8 pagesBrany Alejandro Gomezzz Physics..!!!Brany Alejandro Gomez AlvarezNo ratings yet
- ElectronicsDocument11 pagesElectronicsChris Benedict LatosaNo ratings yet
- Current ElectricityDocument23 pagesCurrent ElectricityGavin SamuelsNo ratings yet
- Building Services-Iii (Ar V 2116) 2014-15: B. Arch III SemesterDocument28 pagesBuilding Services-Iii (Ar V 2116) 2014-15: B. Arch III SemesterAmandeepKaurNo ratings yet
- What Is Alternating CurrentDocument49 pagesWhat Is Alternating CurrentRajeev ValunjkarNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current (AC) vs. Direct Current (DC) - Learn - SparkfunDocument12 pagesAlternating Current (AC) vs. Direct Current (DC) - Learn - SparkfunDeepakDeep100% (1)
- EEE 101 CH6: Ac Circuits and MeasurementsDocument30 pagesEEE 101 CH6: Ac Circuits and MeasurementsSERHAT YILDIRIMNo ratings yet
- PHYS101L LabReport9Document13 pagesPHYS101L LabReport9Leidee Charmellie SerranoNo ratings yet
- Electronics BasicsDocument21 pagesElectronics BasicsK a l o n M u s i kNo ratings yet
- MachinesDocument1 pageMachinesAkbar SNo ratings yet
- Phy3 Chapter1Document26 pagesPhy3 Chapter1kokoh20No ratings yet
- Research Electronics 4 19 9 19Document7 pagesResearch Electronics 4 19 9 19HarshilNo ratings yet
- Alternating CurrentDocument10 pagesAlternating Currentanand011100% (1)
- CT1 Unit 2Document29 pagesCT1 Unit 2Ali khan7No ratings yet
- Grade 9 IctDocument18 pagesGrade 9 IctJohn Carl ToledoNo ratings yet
- Describe AC DCDocument2 pagesDescribe AC DCNancy NursiamNo ratings yet
- Alternative Current (AC) and Direct Current (DC)Document4 pagesAlternative Current (AC) and Direct Current (DC)MonirNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity Chp-8 General Science 9th 10thDocument11 pagesCurrent Electricity Chp-8 General Science 9th 10thKamran AbdullahNo ratings yet
- 14 InvertersDocument52 pages14 InvertersEwerton Serafim100% (1)
- Illut Ee Lab Research 1Document15 pagesIllut Ee Lab Research 1carlverano0428No ratings yet
- Ac DC CircuitDocument3 pagesAc DC CircuitMark Dennis AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Electron Current Voltage Semiconductor Frequency Hertz RFDocument1 pageElectron Current Voltage Semiconductor Frequency Hertz RFDean ParconNo ratings yet
- Electric Current: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument46 pagesElectric Current: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaBerny ManalangNo ratings yet
- Present 2Document35 pagesPresent 2Jayesh JainNo ratings yet
- Getting Started. Conventional Electricity Supply 2021-22Document19 pagesGetting Started. Conventional Electricity Supply 2021-22Leeroy ZizhouNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Electricity Supply and Regulation in IndiaFrom EverandIntroduction to Electricity Supply and Regulation in IndiaNo ratings yet