Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EAPP Reviewer
EAPP Reviewer
Uploaded by
Veronica Hycinth SabidoCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- 000 - Solar Photovoltaic Generators With MPPT and Battery Storage in Microgrids-File Exchange - MATLAB Central PDFDocument20 pages000 - Solar Photovoltaic Generators With MPPT and Battery Storage in Microgrids-File Exchange - MATLAB Central PDFTrần Quang TuyênNo ratings yet
- CS8 - Reading and Writing: Module 6/7Document67 pagesCS8 - Reading and Writing: Module 6/7Patrick BaleNo ratings yet
- Essay WritingDocument4 pagesEssay WritingShaimaa MNo ratings yet
- Library: Essay WritingDocument4 pagesLibrary: Essay WritingFrancisco RosaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document4 pagesChapter 3MaJo VdzNo ratings yet
- EAPP ReviewerDocument3 pagesEAPP ReviewerArchie BaldescoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For Reading and Writing Skills 11Document3 pagesReviewer For Reading and Writing Skills 11Nariza BasilioNo ratings yet
- Freshman Writing Bootcamp (Teacher Copy)Document22 pagesFreshman Writing Bootcamp (Teacher Copy)Sibila Patricia Acevedo TapiaNo ratings yet
- Eapp Reviewer 11 Stem DDocument3 pagesEapp Reviewer 11 Stem Dmanansalastarring100% (1)
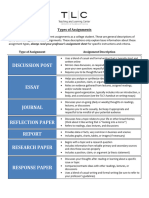
- Accs Types-Of-Assignments Rev2016Document2 pagesAccs Types-Of-Assignments Rev2016ThabangNo ratings yet
- EAPP-Q1 Module1 Lesson-1Document9 pagesEAPP-Q1 Module1 Lesson-1Johnpatrick CiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Writing Academic Texts: Steps On The Pre-Writing ProcessDocument2 pagesChapter 3: Writing Academic Texts: Steps On The Pre-Writing ProcessJT AlipioNo ratings yet
- Critical Reading Involves Using Logical and Rhetorical Skills. Identifying The Author PDFDocument5 pagesCritical Reading Involves Using Logical and Rhetorical Skills. Identifying The Author PDFemysamehNo ratings yet
- Essay Writing 1. Understanding The TaskDocument3 pagesEssay Writing 1. Understanding The Tasksky9213No ratings yet
- G11 ENGLISH Fourth QuarterDocument13 pagesG11 ENGLISH Fourth QuarterFrancis Aaron RafananNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: The Nature of Academic TextsDocument13 pagesLesson 1: The Nature of Academic Textsmillanarashleynicole04No ratings yet
- Academic Meeting 1Document16 pagesAcademic Meeting 1RifqyRujaniNo ratings yet
- Reading and Writing PDFDocument12 pagesReading and Writing PDFRashier AquinoNo ratings yet
- EAPP ReviewerDocument7 pagesEAPP Reviewerbepaca6152No ratings yet
- How To Write A Research Paper - A Beginner's GuideDocument17 pagesHow To Write A Research Paper - A Beginner's GuideshalalfeNo ratings yet
- APP 002 (English For Academic and Professional Purposes) : Day 01 Explaining The Nature of Academic Test Academic WritingDocument4 pagesAPP 002 (English For Academic and Professional Purposes) : Day 01 Explaining The Nature of Academic Test Academic WritingCaye Jamilah NatividadNo ratings yet
- Legal Skills Open Lecture Series: Effective Essay WritingDocument29 pagesLegal Skills Open Lecture Series: Effective Essay WritingEryn MunzirNo ratings yet
- EPQ Guidance Booklet CompressedDocument12 pagesEPQ Guidance Booklet CompressedRamesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- EnglishDocument7 pagesEnglishJona BugarinNo ratings yet
- Eapp Monthly TestDocument6 pagesEapp Monthly TestPhoebe GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Communication For Academic PurposesDocument15 pagesCommunication For Academic PurposesJahnine BaisNo ratings yet
- Basic Introduction To Academic WritingDocument15 pagesBasic Introduction To Academic WritingRifqyRujaniNo ratings yet
- Essay Writing SkillsDocument7 pagesEssay Writing SkillsjennywrenwattsNo ratings yet
- Engacad 1ST Grading ReviewerDocument5 pagesEngacad 1ST Grading ReviewerTodo RokiNo ratings yet
- Ch4 Note-Taking Paraphrasing SummarizingDocument27 pagesCh4 Note-Taking Paraphrasing SummarizingBilly BillNo ratings yet
- Biology: The Scientific ManuscriptDocument4 pagesBiology: The Scientific ManuscriptGksNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6: Reading A Critical Evaluation PaperDocument6 pagesLesson 6: Reading A Critical Evaluation PaperSophia ManubayNo ratings yet
- Eng ReviewerDocument12 pagesEng ReviewerBeefWith PorkNo ratings yet
- Eapp ReviewerDocument3 pagesEapp ReviewerJean GarciaNo ratings yet
- (App 1) Study GuideDocument4 pages(App 1) Study GuideMJ AlolorNo ratings yet
- A Brief Guide To Designing Essay Assignments: Writing ProgramDocument2 pagesA Brief Guide To Designing Essay Assignments: Writing ProgramGe HaxNo ratings yet
- LECTURES IN READING AND WRITING SKILLS CompleteDocument10 pagesLECTURES IN READING AND WRITING SKILLS CompleteAdrian BulawanNo ratings yet
- Reading and WritingDocument9 pagesReading and WritingEmziey ComendadorNo ratings yet
- EAPP (Reviewer q1)Document3 pagesEAPP (Reviewer q1)Joash Charlotte VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Writing An Academic Essay: 1.1 Analyse Your PromptDocument5 pagesWriting An Academic Essay: 1.1 Analyse Your PromptMasyhur MasyhurNo ratings yet
- Oua Essay WritingDocument4 pagesOua Essay Writingapi-397789138No ratings yet
- OutlinesDocument8 pagesOutlinesprincefigueNo ratings yet
- Pre WritingDocument6 pagesPre WritingMoyosore OderindeNo ratings yet
- Rws-Final ModuleDocument12 pagesRws-Final ModuleDharsinero SabandalNo ratings yet
- CRWT MidtermsDocument6 pagesCRWT MidtermsDenise Rina de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Eapp FinalsDocument5 pagesEapp FinalsSolstice OshiroNo ratings yet
- Eapp 2ND Quiz Reviewer LPLDocument3 pagesEapp 2ND Quiz Reviewer LPLAriaane Grace DaquioagNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in RWS 11Document4 pagesReviewer in RWS 11Arch GarciaNo ratings yet
- Eapp ReviewerDocument4 pagesEapp ReviewerMelon SerinNo ratings yet
- Pkewm MidsDocument4 pagesPkewm MidsSkrt brrt brtNo ratings yet
- Essay Writing The Fundamentals PDFDocument4 pagesEssay Writing The Fundamentals PDFhei shun TangNo ratings yet
- Academic Writing Final 1Document21 pagesAcademic Writing Final 1Syahrial KareaNo ratings yet
- Essay TipsDocument13 pagesEssay TipsGordon InformationNo ratings yet
- 5 60 66172 Com21st3e Ch07Document2 pages5 60 66172 Com21st3e Ch07Muhammad Ali buttNo ratings yet
- Essay Structure (2019)Document2 pagesEssay Structure (2019)Roy Estate (Sajila Roy)No ratings yet
- Module 1 - Reading and Writing SkillsDocument36 pagesModule 1 - Reading and Writing SkillsMonnn DragonnnNo ratings yet
- Academic Writing: by Dian A.N. Nurmala DewiDocument10 pagesAcademic Writing: by Dian A.N. Nurmala DewiRoberto Velasco MabulacNo ratings yet
- Academic Writing Guide 3 EssaysDocument30 pagesAcademic Writing Guide 3 EssaysDavyieNo ratings yet
- Academic Writing - School and College Students: Learn Academic Writing EasilyFrom EverandAcademic Writing - School and College Students: Learn Academic Writing EasilyNo ratings yet
- The Skanda Cult in IndiaDocument30 pagesThe Skanda Cult in Indiatadepalli729No ratings yet
- Practical Exercies in English and Spanich Tenses and MoodsDocument4 pagesPractical Exercies in English and Spanich Tenses and MoodsRonaldo MarroquínNo ratings yet
- English Test 10Document6 pagesEnglish Test 10Tuệ Minh ĐỗNo ratings yet
- Debate Task SheetDocument2 pagesDebate Task Sheetapi-405233129No ratings yet
- Englishin Southern AfricaDocument29 pagesEnglishin Southern AfricaSara FerrãoNo ratings yet
- LE Oral Com-Speech WritingDocument2 pagesLE Oral Com-Speech WritingSigrid FadrigalanNo ratings yet
- Foxboro Evo™ SCD6000 Wide Range Input Power Supply ModuleDocument8 pagesFoxboro Evo™ SCD6000 Wide Range Input Power Supply ModuleWisnu HartonoNo ratings yet
- Presentation Different VoicesDocument12 pagesPresentation Different VoicesMarinaProlyginaNo ratings yet
- Java GenericsDocument6 pagesJava GenericsUday DesirajNo ratings yet
- Hard TimesDocument23 pagesHard TimesRehab ShabanNo ratings yet
- ADMS - Chapter SixDocument35 pagesADMS - Chapter SixAtaklti TekaNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Faith: Shepherdville CollegeDocument4 pagesFoundations of Faith: Shepherdville CollegeKatherine Joyce ContanteNo ratings yet
- Narratives of InsecurityDocument11 pagesNarratives of Insecurityion irauliNo ratings yet
- 2A - QA1 ReviewDocument3 pages2A - QA1 ReviewzilbersepulvedaNo ratings yet
- Athena Nightshade - Enochian RitualDocument4 pagesAthena Nightshade - Enochian Ritualanthonyh80No ratings yet
- BaktiothaTheOriginofaMagicalNameinP Mac I1Document10 pagesBaktiothaTheOriginofaMagicalNameinP Mac I1Susana López SeguraNo ratings yet
- Ali Bin Abi TalibDocument5 pagesAli Bin Abi TalibOla AlKhateebNo ratings yet
- Anthem For Doomed YouthDocument3 pagesAnthem For Doomed YouthSufyan SarwarNo ratings yet
- Mirror RingDocument5 pagesMirror RingheadpncNo ratings yet
- APM - 9.5 - Java Agent Implementation GuideDocument357 pagesAPM - 9.5 - Java Agent Implementation Guideggen_mail.ruNo ratings yet
- The Bicol RegionDocument18 pagesThe Bicol RegionAikoDesuNo ratings yet
- A Motivational Video by Nick VujicicDocument2 pagesA Motivational Video by Nick VujicicLee MarquezNo ratings yet
- Set 3Document11 pagesSet 3tttttttttttNo ratings yet
- Theravāda Spirituality in The WestDocument14 pagesTheravāda Spirituality in The WestgustavogknNo ratings yet
- The Maulana Who Loved Krishna PDFDocument8 pagesThe Maulana Who Loved Krishna PDFarjun_nbrNo ratings yet
- Ed A User GuideDocument91 pagesEd A User GuideMarco TomasNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Technology and SocietyDocument6 pagesUnit 1 Technology and Societyyaritza millanNo ratings yet
- 10 Aaa21310adDocument7 pages10 Aaa21310adkędzierzawyNo ratings yet
- Api Use r12Document32 pagesApi Use r12Partha KatariNo ratings yet
EAPP Reviewer
EAPP Reviewer
Uploaded by
Veronica Hycinth SabidoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
EAPP Reviewer
EAPP Reviewer
Uploaded by
Veronica Hycinth SabidoCopyright:
Available Formats
ENGLISH FOR ACADEMIC AND PROFESSIONAL THE WRITING PROCESS
PURPOSES
- Developing your thesis statement. A thesis
statement is the claim or stand that you will
develop in your paper. It is the controlling idea
TEXT
of your essay. It gives your readers idea of what
- It is composed of letters, words, symbols, your paper is all about
phrases, and numbers - Organizing your paper. Your next task as a
writer is to support your thesis statement with
ACADEMIC TEXT/WRITING
sufficient evidence, data, and examples.
- is a clear, concise, focused, structured, and - Organizing your ideas. Means finding the
backed up by evidence. Its purpose is to aid the connections of one point to another and
reader’s understanding. It has a normal tone establishing a link from. Outlining is an
and style, but it is not complex and does not effective way of ensuing the logical flow of
require the use of long sentences and your ideas. You may opt to use the standard
complicated vocabulary. outline complete with roman numerals and
indentions or you may use lists, diagrams, or
PROFESSIONAL WRITING
maps.
- is a style of writing that is clear, concise, and • The introduction for academic essay
seeks to convey information and ideas quickly provides a background of your topic, poses
in a professional setting. a question regarding the topic, explains
how the question is problematic and
SKIMMING
significant, and gives the writer’s thesis
- the action of reading something quickly to statement.
note only the important points. • After this one-or-two paragraph
introduction to your essay, develop the
SCANNING
body of your essay. This is where the bulk
- reading rapidly in order to find specific facts. of the essay is found and where you
develop an answer or propose a solution to
the thesis statement that you have given in
PRE-WRITING PROCESS
the introduction. You have to support your
1. Brainstorming- when you responded with main points and include the other details
ideas and concepts related to the broad that you would support your thesis
concept that your teacher gave you, you were statement.
already generating possible topics for your • Your conclusion should bring together the
paper. points made in your paper and emphasize
2. Free-writing- aside from brainstorming, you your final point. The conclusion may also
can also use free-writing to generate ideas. leave a thought-provoking idea that you
Free-writing is like brainstorming in that you wish your audience to consider.
just write any idea that comes to your mind.
3. Clustering- this technique provides a graphic
representation of your ideas, allowing you to THE POST-WRITING PROCESS
visualize the connections and/or relationships
There are two processes involved in post-
of your ideas.
writing: revising and editing. According to Murray
(2005: 273);
• REVISING is re-seeing the entire draft so that
the writer can deal with the large issues that
must be resolved before he or she deals with
the line-by-line, word-by-word issues involved the texts by giving their thoughts or opinions
in EDITING. on an original text or certain piece of work.
• It is an avenue for students to share their
feelings on the topic.
AVOIDING PLAGIARISM
Before you start the actual process of
writing you need to make sure that the HOW TO WRITE A REACTION PAPER?
assumptions that you have about your topic can be
• Read and analyze the work thoroughly. It is
supported by evidence. This can be done by
crucial that you fully understand why you are
making sure that you have enough resources on
writing and what you are reacting to.
that topic
• Craft your thesis statement. Know the idea of
your overarching angle.
PLAGIARISM COULD BE ANY OF THE FOLLOWING:
• Create the paper’s outline (prewriting).
• Deliberate copying of somebody else’s work
• Compose the first draft (writing).
and claiming that the work to be his/her own.
• Using somebody else’s work or ideas without • Polish and repeat (post writing).
proper acknowledgement or citation; and
• Copying the text without paraphrasing it.
WHAT IS THE IMPORTANCE OF THE REACTION
PAPER IN THE SOCIETY?
AVOIDING PLAGIARISM
• It will allow the writers to articulate their
• PARAPHRASING is one of the ways to avoid thoughts/opinions about issues familiar and
plagiarism. It is rendering the essential ideas in relevant to them as they express their views,
a text (sentence or paragraph) using your own enabling them to share their point or a
words. When you paraphrase, it is advised that contrary viewpoint.
you first understand what the text is about and
then write your rendition of the text without
referring to it as you write. APA FORMAT 7TH EDITION
• QUOTATIONS must be identical to the original JOURNAL ARTICLE
text. DIRECT QUOTATION is preferred to a
paraphrase when the author’s ideas are so
important that paraphrasing them will change
the essence of those ideas.
• SUMMARIZING is selecting out key features of
a text to create a shorter version. It is a brief
restatement of a text’s main points.
WHAT IS A REACTION PAPER?
• A reaction paper is typically a 2–5-page
document in which the writer responds to one
or more texts.
• Its aim is to encourage students to think
critically about texts as they reflect and analyze
BOOK JOURNAL ARTICLE FROM DATABASE
Works Cited List:
Author Last Name, First Name. “Title”.
Journal/Magazine/Newspaper Title, Publication
Information [volume, issue/number, year, pages].
Name of Database, DOI, Permalink or shortened
URL for article in the database.
In-text:
(Author Last Name Page Number)
CHAPTER IN AN EDITED BOOK WEBSITE
Works Cited List:
Author Last Name. First Name. “Title of Page or
Article. “Title of Site, Sponsor or Publisher [include
only if different from website title or author], Date
of publication or Update Date, URL. Accessed Date
[optional; include date you accessed source if it is
likely to help readers].
In-text:
DOCUMENTING SOURCES IN MLA STYLE (Author Last Name or page title)
BOOK
Works cited List:
Author Last Name, First Name. Title. Publisher,
Year.
In-text:
(Author Last Name Page Number)
E- BOOK
Format:
Author’s Last Name, First Name. Title. Edition if
given and is not first edition, Publisher Name often
shortened, Year of publication. Name of Library
Database, Permalink URL.
You might also like
- 000 - Solar Photovoltaic Generators With MPPT and Battery Storage in Microgrids-File Exchange - MATLAB Central PDFDocument20 pages000 - Solar Photovoltaic Generators With MPPT and Battery Storage in Microgrids-File Exchange - MATLAB Central PDFTrần Quang TuyênNo ratings yet
- CS8 - Reading and Writing: Module 6/7Document67 pagesCS8 - Reading and Writing: Module 6/7Patrick BaleNo ratings yet
- Essay WritingDocument4 pagesEssay WritingShaimaa MNo ratings yet
- Library: Essay WritingDocument4 pagesLibrary: Essay WritingFrancisco RosaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document4 pagesChapter 3MaJo VdzNo ratings yet
- EAPP ReviewerDocument3 pagesEAPP ReviewerArchie BaldescoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For Reading and Writing Skills 11Document3 pagesReviewer For Reading and Writing Skills 11Nariza BasilioNo ratings yet
- Freshman Writing Bootcamp (Teacher Copy)Document22 pagesFreshman Writing Bootcamp (Teacher Copy)Sibila Patricia Acevedo TapiaNo ratings yet
- Eapp Reviewer 11 Stem DDocument3 pagesEapp Reviewer 11 Stem Dmanansalastarring100% (1)
- Accs Types-Of-Assignments Rev2016Document2 pagesAccs Types-Of-Assignments Rev2016ThabangNo ratings yet
- EAPP-Q1 Module1 Lesson-1Document9 pagesEAPP-Q1 Module1 Lesson-1Johnpatrick CiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Writing Academic Texts: Steps On The Pre-Writing ProcessDocument2 pagesChapter 3: Writing Academic Texts: Steps On The Pre-Writing ProcessJT AlipioNo ratings yet
- Critical Reading Involves Using Logical and Rhetorical Skills. Identifying The Author PDFDocument5 pagesCritical Reading Involves Using Logical and Rhetorical Skills. Identifying The Author PDFemysamehNo ratings yet
- Essay Writing 1. Understanding The TaskDocument3 pagesEssay Writing 1. Understanding The Tasksky9213No ratings yet
- G11 ENGLISH Fourth QuarterDocument13 pagesG11 ENGLISH Fourth QuarterFrancis Aaron RafananNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: The Nature of Academic TextsDocument13 pagesLesson 1: The Nature of Academic Textsmillanarashleynicole04No ratings yet
- Academic Meeting 1Document16 pagesAcademic Meeting 1RifqyRujaniNo ratings yet
- Reading and Writing PDFDocument12 pagesReading and Writing PDFRashier AquinoNo ratings yet
- EAPP ReviewerDocument7 pagesEAPP Reviewerbepaca6152No ratings yet
- How To Write A Research Paper - A Beginner's GuideDocument17 pagesHow To Write A Research Paper - A Beginner's GuideshalalfeNo ratings yet
- APP 002 (English For Academic and Professional Purposes) : Day 01 Explaining The Nature of Academic Test Academic WritingDocument4 pagesAPP 002 (English For Academic and Professional Purposes) : Day 01 Explaining The Nature of Academic Test Academic WritingCaye Jamilah NatividadNo ratings yet
- Legal Skills Open Lecture Series: Effective Essay WritingDocument29 pagesLegal Skills Open Lecture Series: Effective Essay WritingEryn MunzirNo ratings yet
- EPQ Guidance Booklet CompressedDocument12 pagesEPQ Guidance Booklet CompressedRamesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- EnglishDocument7 pagesEnglishJona BugarinNo ratings yet
- Eapp Monthly TestDocument6 pagesEapp Monthly TestPhoebe GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Communication For Academic PurposesDocument15 pagesCommunication For Academic PurposesJahnine BaisNo ratings yet
- Basic Introduction To Academic WritingDocument15 pagesBasic Introduction To Academic WritingRifqyRujaniNo ratings yet
- Essay Writing SkillsDocument7 pagesEssay Writing SkillsjennywrenwattsNo ratings yet
- Engacad 1ST Grading ReviewerDocument5 pagesEngacad 1ST Grading ReviewerTodo RokiNo ratings yet
- Ch4 Note-Taking Paraphrasing SummarizingDocument27 pagesCh4 Note-Taking Paraphrasing SummarizingBilly BillNo ratings yet
- Biology: The Scientific ManuscriptDocument4 pagesBiology: The Scientific ManuscriptGksNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6: Reading A Critical Evaluation PaperDocument6 pagesLesson 6: Reading A Critical Evaluation PaperSophia ManubayNo ratings yet
- Eng ReviewerDocument12 pagesEng ReviewerBeefWith PorkNo ratings yet
- Eapp ReviewerDocument3 pagesEapp ReviewerJean GarciaNo ratings yet
- (App 1) Study GuideDocument4 pages(App 1) Study GuideMJ AlolorNo ratings yet
- A Brief Guide To Designing Essay Assignments: Writing ProgramDocument2 pagesA Brief Guide To Designing Essay Assignments: Writing ProgramGe HaxNo ratings yet
- LECTURES IN READING AND WRITING SKILLS CompleteDocument10 pagesLECTURES IN READING AND WRITING SKILLS CompleteAdrian BulawanNo ratings yet
- Reading and WritingDocument9 pagesReading and WritingEmziey ComendadorNo ratings yet
- EAPP (Reviewer q1)Document3 pagesEAPP (Reviewer q1)Joash Charlotte VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Writing An Academic Essay: 1.1 Analyse Your PromptDocument5 pagesWriting An Academic Essay: 1.1 Analyse Your PromptMasyhur MasyhurNo ratings yet
- Oua Essay WritingDocument4 pagesOua Essay Writingapi-397789138No ratings yet
- OutlinesDocument8 pagesOutlinesprincefigueNo ratings yet
- Pre WritingDocument6 pagesPre WritingMoyosore OderindeNo ratings yet
- Rws-Final ModuleDocument12 pagesRws-Final ModuleDharsinero SabandalNo ratings yet
- CRWT MidtermsDocument6 pagesCRWT MidtermsDenise Rina de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Eapp FinalsDocument5 pagesEapp FinalsSolstice OshiroNo ratings yet
- Eapp 2ND Quiz Reviewer LPLDocument3 pagesEapp 2ND Quiz Reviewer LPLAriaane Grace DaquioagNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in RWS 11Document4 pagesReviewer in RWS 11Arch GarciaNo ratings yet
- Eapp ReviewerDocument4 pagesEapp ReviewerMelon SerinNo ratings yet
- Pkewm MidsDocument4 pagesPkewm MidsSkrt brrt brtNo ratings yet
- Essay Writing The Fundamentals PDFDocument4 pagesEssay Writing The Fundamentals PDFhei shun TangNo ratings yet
- Academic Writing Final 1Document21 pagesAcademic Writing Final 1Syahrial KareaNo ratings yet
- Essay TipsDocument13 pagesEssay TipsGordon InformationNo ratings yet
- 5 60 66172 Com21st3e Ch07Document2 pages5 60 66172 Com21st3e Ch07Muhammad Ali buttNo ratings yet
- Essay Structure (2019)Document2 pagesEssay Structure (2019)Roy Estate (Sajila Roy)No ratings yet
- Module 1 - Reading and Writing SkillsDocument36 pagesModule 1 - Reading and Writing SkillsMonnn DragonnnNo ratings yet
- Academic Writing: by Dian A.N. Nurmala DewiDocument10 pagesAcademic Writing: by Dian A.N. Nurmala DewiRoberto Velasco MabulacNo ratings yet
- Academic Writing Guide 3 EssaysDocument30 pagesAcademic Writing Guide 3 EssaysDavyieNo ratings yet
- Academic Writing - School and College Students: Learn Academic Writing EasilyFrom EverandAcademic Writing - School and College Students: Learn Academic Writing EasilyNo ratings yet
- The Skanda Cult in IndiaDocument30 pagesThe Skanda Cult in Indiatadepalli729No ratings yet
- Practical Exercies in English and Spanich Tenses and MoodsDocument4 pagesPractical Exercies in English and Spanich Tenses and MoodsRonaldo MarroquínNo ratings yet
- English Test 10Document6 pagesEnglish Test 10Tuệ Minh ĐỗNo ratings yet
- Debate Task SheetDocument2 pagesDebate Task Sheetapi-405233129No ratings yet
- Englishin Southern AfricaDocument29 pagesEnglishin Southern AfricaSara FerrãoNo ratings yet
- LE Oral Com-Speech WritingDocument2 pagesLE Oral Com-Speech WritingSigrid FadrigalanNo ratings yet
- Foxboro Evo™ SCD6000 Wide Range Input Power Supply ModuleDocument8 pagesFoxboro Evo™ SCD6000 Wide Range Input Power Supply ModuleWisnu HartonoNo ratings yet
- Presentation Different VoicesDocument12 pagesPresentation Different VoicesMarinaProlyginaNo ratings yet
- Java GenericsDocument6 pagesJava GenericsUday DesirajNo ratings yet
- Hard TimesDocument23 pagesHard TimesRehab ShabanNo ratings yet
- ADMS - Chapter SixDocument35 pagesADMS - Chapter SixAtaklti TekaNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Faith: Shepherdville CollegeDocument4 pagesFoundations of Faith: Shepherdville CollegeKatherine Joyce ContanteNo ratings yet
- Narratives of InsecurityDocument11 pagesNarratives of Insecurityion irauliNo ratings yet
- 2A - QA1 ReviewDocument3 pages2A - QA1 ReviewzilbersepulvedaNo ratings yet
- Athena Nightshade - Enochian RitualDocument4 pagesAthena Nightshade - Enochian Ritualanthonyh80No ratings yet
- BaktiothaTheOriginofaMagicalNameinP Mac I1Document10 pagesBaktiothaTheOriginofaMagicalNameinP Mac I1Susana López SeguraNo ratings yet
- Ali Bin Abi TalibDocument5 pagesAli Bin Abi TalibOla AlKhateebNo ratings yet
- Anthem For Doomed YouthDocument3 pagesAnthem For Doomed YouthSufyan SarwarNo ratings yet
- Mirror RingDocument5 pagesMirror RingheadpncNo ratings yet
- APM - 9.5 - Java Agent Implementation GuideDocument357 pagesAPM - 9.5 - Java Agent Implementation Guideggen_mail.ruNo ratings yet
- The Bicol RegionDocument18 pagesThe Bicol RegionAikoDesuNo ratings yet
- A Motivational Video by Nick VujicicDocument2 pagesA Motivational Video by Nick VujicicLee MarquezNo ratings yet
- Set 3Document11 pagesSet 3tttttttttttNo ratings yet
- Theravāda Spirituality in The WestDocument14 pagesTheravāda Spirituality in The WestgustavogknNo ratings yet
- The Maulana Who Loved Krishna PDFDocument8 pagesThe Maulana Who Loved Krishna PDFarjun_nbrNo ratings yet
- Ed A User GuideDocument91 pagesEd A User GuideMarco TomasNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Technology and SocietyDocument6 pagesUnit 1 Technology and Societyyaritza millanNo ratings yet
- 10 Aaa21310adDocument7 pages10 Aaa21310adkędzierzawyNo ratings yet
- Api Use r12Document32 pagesApi Use r12Partha KatariNo ratings yet