Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Linkers of Purpose
Linkers of Purpose
Uploaded by
clauuuulooopez2481Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Linkers of Purpose
Linkers of Purpose
Uploaded by
clauuuulooopez2481Copyright:
Available Formats
Linking Words. Connectors of PURPOSE. Unit 6.
Page 84
CONNECTORS OF PURPOSE
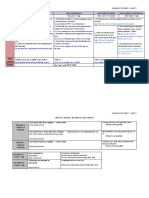
We distinguish 3 different types of purpose clauses.
A) (1) We use FOR + -ING when we describe the purpose of an object; that
- FOR is to say, when we describe what the object is used for.
Example: - What is a pen used for? It is used for writing
- That cake isn’t for eating. It’s just for looking at.
- A kettle is used for boiling water
(2) FOR + NOUN → **I went for a walk
Example: I went to the café for a coffee
I went to the café for having a coffee = wrong!
I went to the café to have a coffee. = correct!
-TO
-IN ORDER (not) TO
-SO AS (not) TO B) When the subject is the same as the main clause.
Affirmative: TO + infinitive.
Example: She wrote to tell him the news.
Affirmative & negative: IN ORDER (not) TO / SO AS (not) TO + infinitive.
Example: He gave up a permanent job in order to / so as to freelance.
He left early in order NOT to / so as NOT to miss the train
- SO (THAT)
-IN ORDER THAT
C) When we have a different subject or the repetition of the same subject in
the purpose clause.
- C.1) Simple present: SO THAT / IN ORDER THAT + SENTENCE {subject
+ can/may/will/ or present simple}
Examples:
- I will help him so that/ in order that he can finish early.
may finish early.
will finish early.
- I’ll pick you up from the station so that you can’t take a taxi
may not take a taxi
won’t take a taxi
don’t need to take a taxi.
-C.2) Simple past:
Example:
- I helped him so that/ in order that he could finish early.
might finish early
would finish early
- He got a taxi so that/ in order that he couldn’t be late.
mightn’t be late
wouldn’t be late
You might also like
- Learning Japanese For JLPT N5Document88 pagesLearning Japanese For JLPT N5Sienna68% (19)
- Jieun Kiaer - Emoji SpeakDocument217 pagesJieun Kiaer - Emoji SpeakAura BălanNo ratings yet
- Manual For Note-TakingDocument17 pagesManual For Note-TakingWilliams Paul Us Grajales100% (2)
- Project Av4Document9 pagesProject Av4Loresmey Roman AcuñaNo ratings yet
- Preposiciones TeoriaDocument13 pagesPreposiciones TeoriadecoletiNo ratings yet
- Starter Unit: Used To/ Be, Get Used ToDocument13 pagesStarter Unit: Used To/ Be, Get Used ToMaria BigiNo ratings yet
- VerbulDocument5 pagesVerbulAna MNo ratings yet
- ADVERBIAL CLAUSE EnglishDocument3 pagesADVERBIAL CLAUSE Englishfayan fayanNo ratings yet
- Forms: Affirmative: Subject + Will + Verb - 1 FormDocument9 pagesForms: Affirmative: Subject + Will + Verb - 1 FormagapisandreeaNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentenceDocument6 pagesConditional SentencePutri AisyahNo ratings yet
- Subject + Was/were/v II + Object/ComplementDocument6 pagesSubject + Was/were/v II + Object/ComplementRini TiaraNo ratings yet
- Ekonomska I Upravna Škola, Split Obrazovanje OdraslihDocument9 pagesEkonomska I Upravna Škola, Split Obrazovanje OdraslihKlara GalićNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Indicative TensesDocument8 pagesChapter 1 - Indicative TensesAndreea DascaluNo ratings yet
- Chuyên Đề Tenses PhượngDocument20 pagesChuyên Đề Tenses PhượngLy BùiNo ratings yet
- Past PerfectDocument2 pagesPast Perfectnagdee.bNo ratings yet
- Dory TOEIC 3 - Grammar - TensesDocument20 pagesDory TOEIC 3 - Grammar - TensesHuyền Trinh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- To Help: 1. To + V1 (Long Infinitive)Document3 pagesTo Help: 1. To + V1 (Long Infinitive)Alina Marius FratilaNo ratings yet
- B. Possible Variations: A. Basic FormDocument3 pagesB. Possible Variations: A. Basic FormLittleSerenaNo ratings yet
- English Sem1Document14 pagesEnglish Sem1Aloha AlohaNo ratings yet
- TeoriDocument10 pagesTeoriMarlia SalehNo ratings yet
- So That/Such That/Too To/Enough To So That/So As ToDocument2 pagesSo That/Such That/Too To/Enough To So That/So As Tolinh nguyen hungNo ratings yet
- Futere TenseDocument11 pagesFutere TenseRidwan SulmaNo ratings yet
- Future TensesDocument6 pagesFuture Tensesdragos.spinuNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Past TensesDocument2 pagesUnit 2 - Past TensesLaura Luque BruguéNo ratings yet
- Ly Thuyet Va Bai Tap Cau Bi DongDocument9 pagesLy Thuyet Va Bai Tap Cau Bi DongThanh TrúcNo ratings yet
- Engleski - VremenaDocument8 pagesEngleski - VremenasreckoNo ratings yet
- TÓM TẮT NGỮ PHÁP - tiếng anh toeicDocument262 pagesTÓM TẮT NGỮ PHÁP - tiếng anh toeicNgọc TrâmNo ratings yet
- Present TensesDocument4 pagesPresent TensesAna MNo ratings yet
- Grammar Past Simple and ContinuousDocument4 pagesGrammar Past Simple and ContinuousElla MachaalanyNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument11 pagesTensesD MNo ratings yet
- ĐỀ CƯƠNG HK2 Môn Anh-Khối 10-NH 22-23Document25 pagesĐỀ CƯƠNG HK2 Môn Anh-Khối 10-NH 22-23원정초No ratings yet
- General RevisionDocument5 pagesGeneral Revisionimen djefourNo ratings yet
- De Cuong On Tap Hoc Ki 1 Mon Tieng Anh 11 Global SuccessDocument42 pagesDe Cuong On Tap Hoc Ki 1 Mon Tieng Anh 11 Global SuccessKhổngThuTrangNo ratings yet
- Sentence Completion RulesDocument7 pagesSentence Completion RulesGlowing Angel100% (1)
- Chapter 3: Kinds of Sentences: ObjectivesDocument8 pagesChapter 3: Kinds of Sentences: ObjectivesPhạm Ngọc Khánh An lớp 1.10No ratings yet
- Đề Cương Hk2 Môn Anh-khối 10-Nh 22-23-Đáp ÁnDocument25 pagesĐề Cương Hk2 Môn Anh-khối 10-Nh 22-23-Đáp ÁnPhuong HaNo ratings yet
- So That/Such That/Too To/Enough To So That/So As ToDocument2 pagesSo That/Such That/Too To/Enough To So That/So As Tolinh nguyen hungNo ratings yet
- Day 1Document41 pagesDay 1Phươngg ThảooNo ratings yet
- Infinitive Clause, Purpose Clause and Reason ClauseDocument4 pagesInfinitive Clause, Purpose Clause and Reason ClauseBilal Kafkan MammeriNo ratings yet
- ADvanced GrammarDocument9 pagesADvanced GrammarakhmedjanoffNo ratings yet
- BachillerDocument5 pagesBachillerFatima VazquezNo ratings yet
- st06 Lessons Eng-Tenses PDFDocument3 pagesst06 Lessons Eng-Tenses PDFHafa ApbNo ratings yet
- L.2 Compound SentenceDocument6 pagesL.2 Compound Sentenceabdelkarim.bouhrakNo ratings yet
- Types of Sentences L1Document4 pagesTypes of Sentences L1Mohamed BenNo ratings yet
- Tense - Lecture1Document7 pagesTense - Lecture1SM TANVIR AHAMMADNo ratings yet
- Xercise Conditional Sentences Type 1,2,3Document9 pagesXercise Conditional Sentences Type 1,2,3FlashNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 - Simple Past and Present PerfectDocument19 pagesUNIT 2 - Simple Past and Present PerfectOliver TorresNo ratings yet
- Offer and RequestDocument15 pagesOffer and Requestgabi_calciu1032No ratings yet
- Past Tenses ChartDocument1 pagePast Tenses ChartSonia GabaldonNo ratings yet
- Past Perfect Simple+KEYDocument4 pagesPast Perfect Simple+KEYpsychelookinforerosNo ratings yet
- E11 5banDocument7 pagesE11 5bannguyendohoangvyNo ratings yet
- Essential Grammar2Document2 pagesEssential Grammar2belenNo ratings yet
- TenseDocument7 pagesTensePradipta DasNo ratings yet
- Grammar Notes: (E.g. Advice, Information, Luggage, Baggage, Garbage, Rubbish, Trash, Litter, News)Document9 pagesGrammar Notes: (E.g. Advice, Information, Luggage, Baggage, Garbage, Rubbish, Trash, Litter, News)Ritsa BlNo ratings yet
- Times EnglishDocument6 pagesTimes EnglishAngelina HarabagiuNo ratings yet
- Tenses CamilaDocument12 pagesTenses CamilaWanda FernandezNo ratings yet
- Past Simple 2. Past ContinuousDocument8 pagesPast Simple 2. Past ContinuousGeraldine QuirogaNo ratings yet
- Perfect TensesDocument14 pagesPerfect TensesAmerica solis lealNo ratings yet
- Tobe - in The Simple Present: Eventually Enrolls at Harvard UniversityDocument8 pagesTobe - in The Simple Present: Eventually Enrolls at Harvard UniversitybadoomtskNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument24 pagesTenseskuntayuniNo ratings yet
- Tenses Notes DocumentDocument16 pagesTenses Notes DocumentA BhavyaNo ratings yet
- (Module 1) Grammar - Sentences TypesDocument9 pages(Module 1) Grammar - Sentences TypesNguyễn Vân KhánhNo ratings yet
- Noun Clause Self-Test: Directions: Underline The Noun Clause in The SentenceDocument2 pagesNoun Clause Self-Test: Directions: Underline The Noun Clause in The SentenceFernando Valdivia EscobarNo ratings yet
- Conjunction NotesDocument3 pagesConjunction NotesThwayyiba PKNo ratings yet
- Bai Chua Band 6.5 - Ngoc BachDocument3 pagesBai Chua Band 6.5 - Ngoc Bachvantienbk100% (1)
- Keen Holy Handout of WritingDocument5 pagesKeen Holy Handout of Writingkamran imtiazNo ratings yet
- Expressing PurposeDocument2 pagesExpressing PurposepeacestabilityNo ratings yet
- Spoken English For Industry & Commerce: Information PackDocument14 pagesSpoken English For Industry & Commerce: Information PackRashi LoyalNo ratings yet
- Herre - English Cae PreparationDocument2 pagesHerre - English Cae PreparationZabdiel KaneNo ratings yet
- KindergartenMorningWorkBinder PDFDocument68 pagesKindergartenMorningWorkBinder PDFMolly Maree100% (1)
- Error Correction Observation Sheet-2Document8 pagesError Correction Observation Sheet-2Fathalla El MansouryNo ratings yet
- SPAG Paper 1 Short Answer QuestionsDocument28 pagesSPAG Paper 1 Short Answer QuestionsJax the trans100% (1)
- Great Writing 1 (Unit1)Document28 pagesGreat Writing 1 (Unit1)M MNo ratings yet
- ENGLISHDocument20 pagesENGLISHBarbaraNo ratings yet
- Literacy Eng Fal (Lea301-Dl-sg-e2) WMDocument123 pagesLiteracy Eng Fal (Lea301-Dl-sg-e2) WMcaitlynstarkey123No ratings yet
- Functional Grammar 3.3 3.4 HallidayDocument21 pagesFunctional Grammar 3.3 3.4 HallidayKate221192No ratings yet
- Map EssayDocument11 pagesMap EssayIrma NovriyaniNo ratings yet
- 9 Branches of Social ScienceDocument10 pages9 Branches of Social ScienceMaricar Cajala Bonete100% (1)
- Three Sentence Stories PDFDocument1 pageThree Sentence Stories PDFAlf GrantNo ratings yet
- Developmental MilestonesDocument8 pagesDevelopmental Milestones3aces100% (1)
- W 24 Test Units 13-16Document3 pagesW 24 Test Units 13-16Mada TuicaNo ratings yet
- Got It Level 2 Unit 6 TestDocument2 pagesGot It Level 2 Unit 6 TestSophie Cor - Pé0% (2)
- Islcollective Word Formation 1 221444dc2b67c2bbf23 76110063Document2 pagesIslcollective Word Formation 1 221444dc2b67c2bbf23 76110063Danilo A. PereiraNo ratings yet
- Early Phonological Training Preceding KindergartenDocument23 pagesEarly Phonological Training Preceding Kindergartenasma sariNo ratings yet
- ЛексикологіяDocument2 pagesЛексикологіяQwerty1488 No nameNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Group 2 (Reading)Document7 pagesWeek 4 Group 2 (Reading)TESL10621 Shameen Farah Binti Mohd AminNo ratings yet
- Test de Evaluare - Badalan SofiaDocument4 pagesTest de Evaluare - Badalan SofiasofiaNo ratings yet
- Innateness Theory PresentationDocument9 pagesInnateness Theory PresentationMarisol LealNo ratings yet
- Basics 1Document4 pagesBasics 1Andi ANo ratings yet