Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Beee306l Power-Systems-Analysis TH 1.0 70 Beee306l
Beee306l Power-Systems-Analysis TH 1.0 70 Beee306l
Uploaded by
Divya JagwaniOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Beee306l Power-Systems-Analysis TH 1.0 70 Beee306l
Beee306l Power-Systems-Analysis TH 1.0 70 Beee306l
Uploaded by
Divya JagwaniCopyright:
Available Formats
Agenda Item 65/44 - Annexure - 40
BEEE306L Power Systems Analysis L T P C
3 0 0 3
Pre-requisite BEEE304L Syllabus version
1.0
Course Objectives
1. Familiarize with the modelling of components for power system studies.
2. Apply the concepts to design and construct the power system.
3. Design and develop protection schemes for the secured and reliable power grid operation.
Course Outcomes
On completion of this course, the students will be able to:
1. Formulate the network matrices and compute load flow solutions for power systems.
2. Identify and analyze different types of faults to calculate the transient rating of protection
devices.
3. Examine different power system stability issues and apply appropriate solution methods.
4. Design and implement protection schemes for power system.
5. Differentiate the working of a conventional SCADA and wide area monitoring system in a
power grid.
Module:1 Power System Network Modelling 6 hours
Need for system analysis in planning and operation of power system; distinction between
steady state and transient state; general aspects of power flow, short circuit and stability
analysis; Admittance (YBUS), sparse matrix and impedance (ZBUS) matrix; Equivalent circuit
of transformer with off-nominal tap ratio; Phase shifting transformers.
Module:2 Load Flow Analysis 7 hours
Problem definition; Derivation of power flow equation; Bus classification; Po w e r f l o w,
Newton-Raphson and fast decoupled methods; DC load flow; P-V bus adjustment;
computation of slack bus power; transmission loss and line flows.
Module:3 Symmetrical Short Circuit Analysis 7 hours
Need for short circuit study; Approximations in modeling; Short circuit capacity;
Symmetrical short circuit analysis; Algorithm for short circuit studies; Fault calculations
using ZBUS.
Module:4 Unsymmetrical Short Circuit Analysis 6 hours
Symmetrical component transformation; Positive, negative and zero sequence impedances;
Unsymmetrical Faults; L-G, L-L and L-L-G fault analysis using sequence networks.
Module:5 Stability Analysis 6 hours
Swing equation in state space form; Equal area criterion; Critical clearing angle and time;
Voltage stability analysis.
Module:6 Real-time Monitoring and Control of Power Systems 6 hours
Requirements for monitoring control and operation; Dynamics and control time scales;
Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) system; Concepts of synchrophasors;
Wide Area Monitoring Systems (WAMS); Phasor Measurement Units (PMUs); Augmentation
of Wide Area Monitoring Systems (WAMS) for real time control with SCADA systems.
Module:7 Power System Protection 5 hours
Power system protection concepts and relaying; Electromagnetic and static relays;
Overcurrent and differential protection; Distance protection; Relay coordination.
Module:8 Contemporary Topics 2 hours
Total Lecture hours: 45 hours
Proceedings of the 65th Academic Council (17.03.2022) 1177
Agenda Item 65/44 - Annexure - 40
Text Books
1. John J. Grainger, William D. Stevenson, Jr, Gary W Chang, Power System Analysis,
2016, Tata McGraw Hill Education
2. Hadi Saadat, Power System Analysis, 2015, Tata McGraw Hill Education
Reference Books
1. Ulf Hager, Christian Rehtanz, Nikolai Voropai, Monitoring Control and Protection of
Interconnected Power Systems, 2014, Springer
2. D. P. Kothari and I. J. Nagrath, Modern Power System Analysis, 4th Edition, 2011, Tata
McGraw Hill Education
Mode of Evaluation: CAT, Quiz, Assignments, FAT
Recommended by Board of Studies 19-02-2022
Approved by Academic Council No. 65 Date 17-03-2022
Proceedings of the 65th Academic Council (17.03.2022) 1178
You might also like
- BEEE303L - CONTROL-SYSTEMS - TH - 1.0 - 67 - Control SystemsDocument3 pagesBEEE303L - CONTROL-SYSTEMS - TH - 1.0 - 67 - Control SystemsMohit SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- PSE PG Structure ModifedDocument61 pagesPSE PG Structure ModifedAnkit YadavNo ratings yet
- ,J, K,, KCDocument2 pages,J, K,, KCAnonymous 9Zc6KcHmdNo ratings yet
- M Tech, II-sem, r16 Eee Syllabus (PS Only)Document14 pagesM Tech, II-sem, r16 Eee Syllabus (PS Only)sambana pavankumarNo ratings yet
- Eee4009 Fac 39 Eee4009Document3 pagesEee4009 Fac 39 Eee4009Satbir singhNo ratings yet
- Syllabus of Power SystemDocument2 pagesSyllabus of Power SystemdhoniNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument3 pagesPDFDaryAntoNo ratings yet
- Nptel: Computer Aided Power System Analysis - Video CourseDocument3 pagesNptel: Computer Aided Power System Analysis - Video Coursejrrb_jaivik100% (1)
- Power System 1: CO1 CO2 CO3 CO4 CO5 CO6Document2 pagesPower System 1: CO1 CO2 CO3 CO4 CO5 CO6Anonymous HyOfbJ6100% (1)
- Powwer System Operation and Control PDFDocument3 pagesPowwer System Operation and Control PDFmitulNo ratings yet
- Circuit BreakerDocument3 pagesCircuit BreakerNAVEED ISHRAQNo ratings yet
- Co and Po MappingDocument41 pagesCo and Po MappingRajesh ChidambaramNo ratings yet
- PSP 2710707 SyllabusDocument3 pagesPSP 2710707 SyllabusMadhav ManavadariaNo ratings yet
- Ymca College 5 Sem Btech ElectricalDocument12 pagesYmca College 5 Sem Btech Electricalvinit kumarNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19Document3 pagesGujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19Pratham VaghelaNo ratings yet
- SG SyllabusDocument2 pagesSG SyllabusVaibhavNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityBhavik PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- 2 FullDocument8 pages2 FullDhaval MerNo ratings yet
- Power System Analysis of A Microgrid Using ETAPDocument5 pagesPower System Analysis of A Microgrid Using ETAP陆华林No ratings yet
- Bmee308l Control-Systems TH 1.0 67 Bmee308lDocument3 pagesBmee308l Control-Systems TH 1.0 67 Bmee308lKrijayNo ratings yet
- 6th Sem EEE 18Document28 pages6th Sem EEE 18Iqbal Ahammed KaladgikarNo ratings yet
- B.Tech, EE, 5th Sem, 2018-19 BatchDocument19 pagesB.Tech, EE, 5th Sem, 2018-19 BatchBijayKumarDasNo ratings yet
- SVUCE MTech PowerSystemsDocument42 pagesSVUCE MTech PowerSystemsTejaRam AugusthyaNo ratings yet
- PSOC Lession PlanDocument7 pagesPSOC Lession PlanskdwarakanathNo ratings yet
- Electrical 2 of 2Document124 pagesElectrical 2 of 2xevokov579No ratings yet
- CBGS 7 Sem 20-21290521110137Document18 pagesCBGS 7 Sem 20-21290521110137kushagra vashishthaNo ratings yet
- Power System Analysis - IIDocument2 pagesPower System Analysis - IIPratikTiwari0% (2)
- 3.1 Control Systems: RationaleDocument15 pages3.1 Control Systems: RationaleSoumya BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Cmps QB PDFDocument80 pagesCmps QB PDFDse YtNo ratings yet
- MTech EE Power Common Syllabus 10.04.14!2!2Document22 pagesMTech EE Power Common Syllabus 10.04.14!2!2alfred_googleNo ratings yet
- 10ee81 Electrical Design, Estimating and CostingDocument16 pages10ee81 Electrical Design, Estimating and CostingFzs LohiNo ratings yet
- ME Drives and Control SyllabusDocument34 pagesME Drives and Control SyllabusHarshal VaidyaNo ratings yet
- Be Electrical Engg 2008 SyllabusDocument40 pagesBe Electrical Engg 2008 SyllabusGaurav sNo ratings yet
- Power System AnalysisDocument21 pagesPower System AnalysisCheryl FernandezNo ratings yet
- To Understand The Method of Representation of Power System Components To Know About Loacation and Components of A Distribution SubstationDocument2 pagesTo Understand The Method of Representation of Power System Components To Know About Loacation and Components of A Distribution SubstationBhupesh yadavNo ratings yet
- 13advanced Power System Simulation LaboratoryDocument1 page13advanced Power System Simulation Laboratorypurushotham1982No ratings yet
- ELECTRIC POWER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM-SyllabusDocument2 pagesELECTRIC POWER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM-SyllabusTanvi IsraniNo ratings yet
- Dilan Jayaweera Eds. Smart Power Systems and Renewable Energy System IntegrationDocument207 pagesDilan Jayaweera Eds. Smart Power Systems and Renewable Energy System IntegrationkalokosNo ratings yet
- Power System Protection and Switchgear (BTEE3013) : Dr. Sheetla PrasadDocument16 pagesPower System Protection and Switchgear (BTEE3013) : Dr. Sheetla PrasadSarthakNo ratings yet
- Course Outline For Power System ProtectionDocument2 pagesCourse Outline For Power System ProtectionNasib IgaNo ratings yet
- 7th Sem SyllabusDocument14 pages7th Sem SyllabusS D ManjunathNo ratings yet
- Sem6 SyllabusDocument5 pagesSem6 SyllabusSamsung TabletNo ratings yet
- Eighth Semester: Flexible AC Transmission System (EL20811) ObjectivesDocument10 pagesEighth Semester: Flexible AC Transmission System (EL20811) ObjectivesSai SanjeevareddyNo ratings yet
- Psoc 2180909Document3 pagesPsoc 2180909himanshuNo ratings yet
- Ece668: Distribution System Engineering Winter Term 2022Document2 pagesEce668: Distribution System Engineering Winter Term 2022Chan DavidNo ratings yet
- MTech PSOC 06 ModifiedDocument26 pagesMTech PSOC 06 ModifiedrahulludhaniNo ratings yet
- Application of Intelligent Control Algorithms To Study The Dynamics of Hybrid Power SystemDocument216 pagesApplication of Intelligent Control Algorithms To Study The Dynamics of Hybrid Power System洪維晨No ratings yet
- Mmha506l - Advanced-Control-Systems - TH - 1.0 - 73 - Mmha506l - 67 AcpDocument2 pagesMmha506l - Advanced-Control-Systems - TH - 1.0 - 73 - Mmha506l - 67 AcpSoumi RayNo ratings yet
- Linear Control TheoryDocument1 pageLinear Control TheorySanjay SinhaNo ratings yet
- M.Tech PEESDocument14 pagesM.Tech PEEScharinathrNo ratings yet
- 8th Sem SyllabusDocument4 pages8th Sem SyllabusSanjay PandeyNo ratings yet
- BE EEE VI Sem MergedDocument12 pagesBE EEE VI Sem MergedNatarajan RajaNo ratings yet
- Course OutlineDocument5 pagesCourse Outlinegui0381No ratings yet
- RE Grid Integration and Distributed Generation Specialization Syllabus - 100916Document8 pagesRE Grid Integration and Distributed Generation Specialization Syllabus - 100916malini72No ratings yet
- Mtech PS SyllabusDocument25 pagesMtech PS SyllabusJithendra NathNo ratings yet
- VII Sem EX SyllabusDocument17 pagesVII Sem EX SyllabusAbhinav RajNo ratings yet
- Semester VIDocument16 pagesSemester VIمحمدضيأ الدينNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Control of Power Electronic Converters for Microgrid ApplicationsFrom EverandModeling and Control of Power Electronic Converters for Microgrid ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Practical Guidance for Defining a Smart Grid Modernization Strategy: The Case of DistributionFrom EverandPractical Guidance for Defining a Smart Grid Modernization Strategy: The Case of DistributionNo ratings yet
- Kinetic and Potential Energy WorksheetDocument3 pagesKinetic and Potential Energy WorksheetAvril NavarroNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 (Part 2) : Use of Micropipettor and Analytical BalanceDocument4 pagesExperiment 1 (Part 2) : Use of Micropipettor and Analytical BalanceCara JaenNo ratings yet
- Trig Exam Example 20-2Document10 pagesTrig Exam Example 20-2api-267824245No ratings yet
- N2HYROPEDocument9 pagesN2HYROPEAraby Gamal GamalNo ratings yet
- EITN90 Radar and Remote Sensing Lecture 4: Characteristics of ClutterDocument56 pagesEITN90 Radar and Remote Sensing Lecture 4: Characteristics of Cluttertdtiog hohdedkkNo ratings yet
- Topic 1.1 Linear EquationsDocument24 pagesTopic 1.1 Linear EquationsnshoulyNo ratings yet
- Ok 83.28Document1 pageOk 83.28joe_frangiehNo ratings yet
- EWWP KBW Operation ManualDocument20 pagesEWWP KBW Operation ManualHoàngViệtAnhNo ratings yet
- CHM 451 F-12 Exam 3 AnswersDocument10 pagesCHM 451 F-12 Exam 3 AnswersAbdul Mueez Lone100% (1)
- PIEAS 1 Past Paper PakLearningSpotDocument13 pagesPIEAS 1 Past Paper PakLearningSpotMuhammad HammadNo ratings yet
- Castigliano's Theorem - GDLCDocument17 pagesCastigliano's Theorem - GDLCjohnvchristy7No ratings yet
- Strength Science 2012 by SullivanDocument64 pagesStrength Science 2012 by SullivanAndrew ShirekNo ratings yet
- 740-Upd8 Global Warming Swindle PresentationDocument11 pages740-Upd8 Global Warming Swindle PresentationDipanjan DasNo ratings yet
- Exer 2 - PH and BuffersDocument4 pagesExer 2 - PH and BuffersAsi JenNo ratings yet
- Pple Assignment-4Document7 pagesPple Assignment-4Subhangi KashyapNo ratings yet
- Spherical Plain Bearings, Plain Bushes, Rod Ends: Catalogue 238Document181 pagesSpherical Plain Bearings, Plain Bushes, Rod Ends: Catalogue 238durvalmedinasNo ratings yet
- Productflyer - 978 0 387 74364 6Document1 pageProductflyer - 978 0 387 74364 6Dhruv PatelNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Analysis of The Macromolecular Complex of Iron (III) Hydroxide With Polymaltose in Liquid Dosage FormsDocument5 pagesQuantitative Analysis of The Macromolecular Complex of Iron (III) Hydroxide With Polymaltose in Liquid Dosage FormsLipsi MerchánNo ratings yet
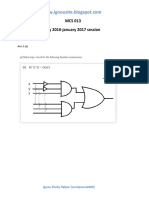
- MCS 013Document16 pagesMCS 013Mamta GuptaNo ratings yet
- Detail Schedule For Three Days Work ShopDocument3 pagesDetail Schedule For Three Days Work ShopNeeraj ChavdaNo ratings yet
- Cable Supply, Electrical and I&C Installation Works: 1 PurposeDocument13 pagesCable Supply, Electrical and I&C Installation Works: 1 PurposeAhmed ShoaibNo ratings yet
- PWHTDocument79 pagesPWHTnguyenNo ratings yet
- Ansys Progamming, UpfDocument5 pagesAnsys Progamming, UpfshirbhatenjNo ratings yet
- The Coefficient of Earth Pressure at Rest: Canadian Geotechnical Journal January 2011Document21 pagesThe Coefficient of Earth Pressure at Rest: Canadian Geotechnical Journal January 2011Adefi AbiogaNo ratings yet
- CITATION HTT /L 1033Document2 pagesCITATION HTT /L 1033Ahmad NajibNo ratings yet
- Mounded Stoarge Vessel C P SystemDocument5 pagesMounded Stoarge Vessel C P SystemRakesh AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Exercise 11Document3 pagesExercise 11api-270901668No ratings yet
- LWL MiniguideDocument28 pagesLWL MiniguidePaoloNo ratings yet
- Chapter at A GlanceDocument18 pagesChapter at A GlanceproodootNo ratings yet
- Master BatchDocument12 pagesMaster Batchskimmer05100% (1)