Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Energy Profile Diagrams
Energy Profile Diagrams
Uploaded by
uttambaghel1110Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Energy Profile Diagrams
Energy Profile Diagrams
Uploaded by
uttambaghel1110Copyright:
Available Formats
316 A Textbook of Organic Chemistry – Volume I
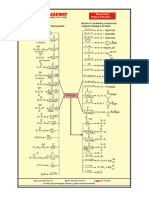
❖ Energy Profile Diagrams
The general mechanism for the aromatic electrophilic substitution involves two main steps which
must be discussed before we give an energy profile diagram of the same. The electrophile attacks the aromatic
ring to form resonance stabilized carbocations, followed by the detachment of leaving group.
A typical energy level profile of various intermediates and transition states in the course of electrophilic
substitution reactions in aromatic compounds is shown below.
Figure 1. Energy profile diagram for a typical aromatic electrophilic substitution.
Finally, it is also worthy to note that the rate of electrophilic substitution in already substituted
aromatic compounds depends upon the height of the potential barrier which will be different for different types
of attack i.e., o-, m- or p-attacks.
Copyright © Mandeep Dalal
LEGAL NOTICE
This document is an excerpt from the book entitled “A
Textbook of Organic Chemistry – Volume 1 by
Mandeep Dalal”, and is the intellectual property of the
Author/Publisher. The content of this document is
protected by international copyright law and is valid
only for the personal preview of the user who has
originally downloaded it from the publisher’s website
(www.dalalinstitute.com). Any act of copying (including
plagiarizing its language) or sharing this document will
result in severe civil and criminal prosecution to the
maximum extent possible under law.
This is a low resolution version only for preview purpose. If you
want to read the full book, please consider buying.
Buy the complete book with TOC navigation, high resolution
images and no watermark.
D DALAL
INSTITUTE
Home Classes Books Videos Location Contact Us About Us °' Followus: O O O G O
Home
CLASSES BOOKS VIDEOS
NET-JRF, llT-GATE, M.Sc Entrance & Publications Video Lectures
llT-JAM
Are you interested in books (Print and Ebook) Want video lectures in chemistry for CSIR UGC
Want to study chemistry for CSIR UGC - NET published by Dalal Institute? - NET JRF. llT-GATE. M.Sc Entrance, llT-JAM,
JRF, llT-GATE, M.Sc Entrance, llT-JAM, UPSC, READ MORE UPSC, ISRO, II Sc, TIFR, DRDO, BARC, JEST, GRE,
ISRO, II Sc, TIFR, DRDO, BARC, JEST, GRE, Ph.D Ph.D Entrance or any other competitive
Entrance or any other competitive examination where chemistry is a paper?
examination where chemistry is a paper? READ MORE
READ MORE
Postgraduate Level Senior-Secondary Level Undergraduate Level
Regular Program Regular Program Regular Program
Online Course Online Course Online Course
Result Result Result
Join the revolution by becoming a part of our community and get all of the member benefits
--------
like downloading any PDF document for your personal preview.
Share this article/info with your classmates and friends
Sign Up
join the revolution by becoming a part of our community and get all of the member benefits like downloading any PDF document for your personal preview.
Sign Up
Copyright© 2019 Dalal Institute
Table of Contents
CHAPTER 1 ................................................................................................................................................. 11
Nature of Bonding in Organic Molecules ............................................................................................... 11
❖ Delocalized Chemical Bonding ...................................................................................................... 11
❖ Conjugation .................................................................................................................................... 14
❖ Cross Conjugation .......................................................................................................................... 16
❖ Resonance....................................................................................................................................... 18
❖ Hyperconjugation ........................................................................................................................... 27
❖ Tautomerism ................................................................................................................................... 31
❖ Aromaticity in Benzenoid and Nonbenzenoid Compounds ............................................................ 33
❖ Alternant and Non-Alternant Hydrocarbons ................................................................................... 35
❖ Huckel’s Rule: Energy Level of π-Molecular Orbitals ................................................................... 3 7
❖ Annulenes ....................................................................................................................................... 44
❖ Antiaromaticity ............................................................................................................................... 46
❖ Homoaromaticity ............................................................................................................................ 48
❖ PMO Approach ............................................................................................................................... 50
❖ Bonds Weaker Than Covalent ........................................................................................................ 58
❖ Addition Compounds: Crown Ether Complexes and Cryptands, Inclusion Compounds,
Cyclodextrins ................................................................................................................................. 65
❖ Catenanes and Rotaxanes ............................................................................................................... 75
❖ Problems ......................................................................................................................................... 79
❖ Bibliography ................................................................................................................................... 80
CHAPTER 2 ................................................................................................................................................. 81
Stereochemistry ........................................................................................................................................ 81
❖ Chirality .......................................................................................................................................... 81
❖ Elements of Symmetry ................................................................................................................... 86
❖ Molecules with More Than One Chiral Centre: Diastereomerism .................................................. 90
❖ Determination of Relative and Absolute Configuration (Octant Rule Excluded) with Special
Reference to Lactic Acid, Alanine & Mandelic Acid ..................................................................... 92
❖ Methods of Resolution.................................................................................................................. 102
❖ Optical Purity ............................................................................................................................... 104
❖ Prochirality ................................................................................................................................... 105
❖ Enantiotopic and Diastereotopic Atoms, Groups and Faces ......................................................... 107
❖ Asymmetric Synthesis: Cram’s Rule and Its Modifications, Prelog’s Rule .................................. 113
❖ Conformational Analysis of Cycloalkanes (Upto Six Membered Rings) ...................................... 116
❖ Decalins ........................................................................................................................................ 122
❖ Conformations of Sugars .............................................................................................................. 126
❖ Optical Activity in Absence of Chiral Carbon (Biphenyls, Allenes and Spiranes) ....................... 132
❖ Chirality Due to Helical Shape ..................................................................................................... 137
❖ Geometrical Isomerism in Alkenes and Oximes ........................................................................... 140
❖ Methods of Determining the Configuration .................................................................................. 146
❖ Problems ....................................................................................................................................... 151
❖ Bibliography ................................................................................................................................. 152
CHAPTER 3 ............................................................................................................................................... 153
Reaction Mechanism: Structure and Reactivity .................................................................................. 153
❖ Types of Mechanisms ................................................................................................................... 153
❖ Types of Reactions ....................................................................................................................... 156
❖ Thermodynamic and Kinetic Requirements .................................................................................. 159
❖ Kinetic and Thermodynamic Control ........................................................................................... 161
❖ Hammond’s Postulate ................................................................................................................... 163
❖ Curtin-Hammett Principle ............................................................................................................ 164
❖ Potential Energy Diagrams: Transition States and Intermediates ................................................. 166
❖ Methods of Determining Mechanisms .......................................................................................... 168
❖ Isotope Effects .............................................................................................................................. 172
❖ Hard and Soft Acids and Bases ..................................................................................................... 174
❖ Generation, Structure, Stability and Reactivity of Carbocations, Carbanions, Free Radicals, Carbenes
and Nitrenes................................................................................................................................. 176
❖ Effect of Structure on Reactivity .................................................................................................. 200
❖ The Hammett Equation and Linear Free Energy Relationship ...................................................... 203
❖ Substituent and Reaction Constants .............................................................................................. 209
❖ Taft Equation ................................................................................................................................ 215
❖ Problems ....................................................................................................................................... 219
❖ Bibliography ................................................................................................................................. 220
CHAPTER 4 ............................................................................................................................................... 221
Carbohydrates ........................................................................................................................................ 221
❖ Types of Naturally Occurring Sugars ........................................................................................... 221
❖ Deoxy Sugars ............................................................................................................................... 227
❖ Amino Sugars ............................................................................................................................... 229
❖ Branch Chain Sugars .................................................................................................................... 230
❖ General Methods of Determination of Structure and Ring Size of Sugars with Particular Reference
to Maltose, Lactose, Sucrose, Starch and Cellulose ...................................................................... 231
❖ Problems ....................................................................................................................................... 239
❖ Bibliography ................................................................................................................................. 240
CHAPTER 5 ............................................................................................................................................... 241
Natural and Synthetic Dyes ................................................................................................................... 241
❖ Various Classes of Synthetic Dyes Including Heterocyclic Dyes ................................................. 241
❖ Interaction Between Dyes and Fibers ........................................................................................... 245
❖ Structure Elucidation of Indigo and Alizarin ................................................................................ 247
❖ Problems ....................................................................................................................................... 252
❖ Bibliography ................................................................................................................................. 253
CHAPTER 6 ............................................................................................................................................... 254
Aliphatic Nucleophilic Substitution ...................................................................................................... 254
❖ The SN2, SN1, Mixed SN1 and SN2, SNi, SN1′, SN2′, SNi′ and SET Mechanisms ......................... 254
The Neighbouring Group Mechanisms ......................................................................................... 263
❖
Neighbouring Group Participation by π and σ Bonds . .................................................................. 2 65
❖
Anchimeric Assistance ................................................................................................................. 269
❖
Classical and Nonclassical Carbocations ...................................................................................... 272
❖
Phenonium Ions ............................................................................................................................ 283
❖
Common Carbocation Rearrangements ........................................................................................ 284
❖
Applications of NMR Spectroscopy in the Detection of Carbocations ......................................... 286
❖
Reactivity – Effects of Substrate Structure, Attacking Nucleophile, Leaving Group and Reaction
❖
Medium ........................................................................................................................................ 288
❖ Ambident Nucleophiles and Regioselectivity ............................................................................... 294
❖ Phase Transfer Catalysis ............................................................................................................... 297
❖ Problems ....................................................................................................................................... 300
❖ Bibliography ................................................................................................................................. 301
CHAPTER 7 ............................................................................................................................................... 302
Aliphatic Electrophilic Substitution ...................................................................................................... 302
❖ Bimolecular Mechanisms − SE2 and SEi ...................................................................................... 3 02
❖ The SE1 Mechanism ..................................................................................................................... 305
❖ Electrophilic Substitution Accompanied by Double Bond Shifts ................................................. 307
❖ Effect of Substrates, Leaving Group and the Solvent Polarity on the Reactivity .......................... 308
❖ Problems ....................................................................................................................................... 310
❖ Bibliography ................................................................................................................................. 311
CHAPTER 8 ............................................................................................................................................... 312
Aromatic Electrophilic Substitution ..................................................................................................... 312
❖ The Arenium Ion Mechanism ....................................................................................................... 312
❖ Orientation and Reactivity ............................................................................................................ 314
❖ Energy Profile Diagrams .............................................................................................................. 316
❖ The Ortho/Para Ratio .................................................................................................................... 317
❖ ipso-Attack ................................................................................................................................... 319
❖ Orientation in Other Ring Systems ............................................................................................... 320
❖ Quantitative Treatment of Reactivity in Substrates and Electrophiles .......................................... 321
❖ Diazonium Coupling..................................................................................................................... 325
❖ Vilsmeier Reaction ....................................................................................................................... 326
❖ Gattermann-Koch Reaction .......................................................................................................... 327
❖ Problems ....................................................................................................................................... 329
❖ Bibliography ................................................................................................................................. 330
CHAPTER 9 ............................................................................................................................................... 331
Aromatic Nucleophilic Substitution ...................................................................................................... 331
❖ The ArSN1, ArSN2, Benzyne and SRN1 Mechanisms.................................................................... 331
❖ Reactivity – Effect of Substrate Structure, Leaving Group and Attacking Nucleophile................ 336
❖ The von Richter, Sommelet-Hauser, and Smiles Rearrangements ................................................ 339
❖ Problems ....................................................................................................................................... 343
❖ Bibliography ................................................................................................................................. 344
CHAPTER 10 ............................................................................................................................................. 345
Elimination Reactions ............................................................................................................................ 345
❖ The E2, E1 and E1CB Mechanisms ................................................................................................ 345
❖ Orientation of the Double Bond.................................................................................................... 348
❖ Reactivity – Effects of Substrate Structures, Attacking Base, the Leaving Group and The Medium
....................................................................................................................................................352
❖ Mechanism and Orientation in Pyrolytic Elimination ................................................................... 355
❖ Problems ....................................................................................................................................... 358
❖ Bibliography ................................................................................................................................. 359
CHAPTER 11 ............................................................................................................................................. 360
Addition to Carbon-Carbon Multiple Bonds ....................................................................................... 360
❖ Mechanistic and Stereochemical Aspects of Addition Reactions Involving Electrophiles,
Nucleophiles and Free Radicals .................................................................................................... 360
❖ Regio- and Chemoselectivity: Orientation and Reactivity ............................................................ 370
❖ Addition to Cyclopropane Ring .................................................................................................... 374
❖ Hydrogenation of Double and Triple Bonds ................................................................................. 375
❖ Hydrogenation of Aromatic Rings ................................................................................................ 377
❖ Hydroboration .............................................................................................................................. 378
❖ Michael Reaction .......................................................................................................................... 379
❖ Sharpless Asymmetric Epoxidation .............................................................................................. 380
❖ Problems ....................................................................................................................................... 382
❖ Bibliography ................................................................................................................................. 383
CHAPTER 12 ............................................................................................................................................. 384
Addition to Carbon-Hetero Multiple Bonds ......................................................................................... 384
❖ Mechanism of Metal Hydride Reduction of Saturated and Unsaturated Carbonyl Compounds, Acids,
Esters and Nitriles ......................................................................................................................... 384
❖ Addition of Grignard Reagents, Organozinc and Organolithium Reagents to Carbonyl and
Unsaturated Carbonyl Compounds ............................................................................................... 400
❖ Wittig Reaction ............................................................................................................................. 406
❖ Mechanism of Condensation Reactions Involving Enolates: Aldol, Knoevenagel, Claisen, Mannich,
Benzoin, Perkin and Stobbe Reactions .......................................................................................... 411
❖ Hydrolysis of Esters and Amides .................................................................................................. 433
❖ Ammonolysis of Esters ................................................................................................................. 437
❖ Problems ....................................................................................................................................... 439
❖ Bibliography ................................................................................................................................. 440
INDEX......................................................................................................................................................... 441
You might also like
- Deep Reinforcement Learning Hands-On - Second Edition: Apply modern RL methods to practical problems of chatbots, robotics, discrete optimization, web automation, and more, 2nd EditionFrom EverandDeep Reinforcement Learning Hands-On - Second Edition: Apply modern RL methods to practical problems of chatbots, robotics, discrete optimization, web automation, and more, 2nd EditionNo ratings yet
- HFL CPLDocument166 pagesHFL CPLHaneulbit SeoNo ratings yet
- Csir Net NotesDocument2 pagesCsir Net NotesPäwnî Bhärtî100% (1)
- A.P. Chapter 8 WebTestDocument9 pagesA.P. Chapter 8 WebTestNick PirainoNo ratings yet
- Vilsmeier ReactionDocument9 pagesVilsmeier ReactionMartha GraciaNo ratings yet
- ATOOCV1 6 3 Neighbouring Group Participation by π and σ BondsDocument12 pagesATOOCV1 6 3 Neighbouring Group Participation by π and σ Bonds20tamilselvi-ugcheNo ratings yet
- ATOOCV1!2!13 Optical Activity in Absence of Chiral Carbon Biphenyls Allenes and SpiranesDocument13 pagesATOOCV1!2!13 Optical Activity in Absence of Chiral Carbon Biphenyls Allenes and Spiranesvanshkhurana8077No ratings yet
- Racemization of Tris Chelate Complexes: Legal NoticeDocument11 pagesRacemization of Tris Chelate Complexes: Legal NoticeDebraj Dhar PurkayasthaNo ratings yet
- Ochem CH332KDocument17 pagesOchem CH332KfarahrayshukNo ratings yet
- Safari - 31-Jul-2019 at 1:08 PMDocument1 pageSafari - 31-Jul-2019 at 1:08 PMsavydhimanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Compounds TeacherDocument33 pagesChemistry Compounds TeacherKari Kristine Hoskins BarreraNo ratings yet
- RDVV PHD ThesisDocument6 pagesRDVV PHD Thesisteresaoakmanevansville100% (1)
- April 11-15Document18 pagesApril 11-15Lhester Jay SalaoNo ratings yet
- رسالة دكتوراةDocument449 pagesرسالة دكتوراةRagheb IbrahimNo ratings yet
- BIODEGRADABLE BIOMATERIALS For Orthopiedic DevicesDocument77 pagesBIODEGRADABLE BIOMATERIALS For Orthopiedic DevicesquzalbashNo ratings yet
- Research Paper Inorganic Chemistry PDFDocument4 pagesResearch Paper Inorganic Chemistry PDFafeawobfi100% (1)
- (Download PDF) Bionanocomposites Integrating Biological Processes For Bioinspired Nanotechnologies First Edition Aime Online Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument42 pages(Download PDF) Bionanocomposites Integrating Biological Processes For Bioinspired Nanotechnologies First Edition Aime Online Ebook All Chapter PDForlando.brennan371100% (14)
- Organic Chemistry Made Ridiculously SimpleDocument5 pagesOrganic Chemistry Made Ridiculously SimpleOrva Hospital0% (2)
- IBT P Coverage 23Document41 pagesIBT P Coverage 23Jaymae CaseresNo ratings yet
- Unit Outline SCC1226D - Tri 01,2023 PDFDocument9 pagesUnit Outline SCC1226D - Tri 01,2023 PDFKaumudi LiyanageNo ratings yet
- OCTOBER 09 13 2023 Grade 4 DLL MELCBASED MODULE1 WITH LR PORTAL Quarter 1 Week 7 EMILY O. ESTRELLA ESP ENGLISH AP SCIENCEDocument75 pagesOCTOBER 09 13 2023 Grade 4 DLL MELCBASED MODULE1 WITH LR PORTAL Quarter 1 Week 7 EMILY O. ESTRELLA ESP ENGLISH AP SCIENCENerissa BaricauaNo ratings yet
- Hussain Jeevakhan - Applied Physics II - AICTE Prescribed Textbook - English - With Lab Manual-KHANNA BOOK PUBLISHING CO. PVT. LTD. (2021)Document350 pagesHussain Jeevakhan - Applied Physics II - AICTE Prescribed Textbook - English - With Lab Manual-KHANNA BOOK PUBLISHING CO. PVT. LTD. (2021)Luiza LuzNo ratings yet
- Bio 218Document42 pagesBio 218odenigbo samuelNo ratings yet
- 11th STD Public Exam Question Paper For All Years: Both Tamil Medium and English Medium QuestionsDocument5 pages11th STD Public Exam Question Paper For All Years: Both Tamil Medium and English Medium Questionscasudha965No ratings yet
- (Ebook PDF) Environmental Biotechnology: Principles and Applications 2nd Edition Perry L. Mccarty - Ebook PDF All ChapterDocument50 pages(Ebook PDF) Environmental Biotechnology: Principles and Applications 2nd Edition Perry L. Mccarty - Ebook PDF All Chapterpugalmeluu100% (4)
- IeiejejeieknejekeDocument25 pagesIeiejejeieknejekePorn PorntrexNo ratings yet
- Textbook Studies of Intensified Small Scale Processes For Liquid Liquid Separations in Spent Nuclear Fuel Reprocessing 1St Edition Dimitrios Tsaoulidis Auth Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument54 pagesTextbook Studies of Intensified Small Scale Processes For Liquid Liquid Separations in Spent Nuclear Fuel Reprocessing 1St Edition Dimitrios Tsaoulidis Auth Ebook All Chapter PDFcarmen.mcdonald474100% (5)
- Esm 342 Eia and Ea - UneditedDocument75 pagesEsm 342 Eia and Ea - Uneditedpalmer okiemuteNo ratings yet
- ChE 426N OBE Course Syllabus Ver 2016-2017Document3 pagesChE 426N OBE Course Syllabus Ver 2016-2017EmmanuelDalesAlquizolaNo ratings yet
- Step-Down Transformer QuestionDocument8 pagesStep-Down Transformer QuestionAkanle MathewNo ratings yet
- Ib Biology Mark Scheme PhotosynthesisDocument8 pagesIb Biology Mark Scheme Photosynthesisafbsyebpu100% (2)
- ContinueDocument2 pagesContinuengulubetsereletso89No ratings yet
- CompoundPurificationFlashGuide SMDocument162 pagesCompoundPurificationFlashGuide SMSebastián FingerNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science 16Th Ed 16Th Edition Miller Full ChapterDocument51 pagesEnvironmental Science 16Th Ed 16Th Edition Miller Full Chapterpatricia.danner760100% (14)
- Full Download PDF of (Ebook PDF) Experiments in Biochemistry: A Hands-On Approach 2nd Edition All ChapterDocument43 pagesFull Download PDF of (Ebook PDF) Experiments in Biochemistry: A Hands-On Approach 2nd Edition All Chapterlathyudhay100% (7)
- Human Anatomy RespiratoryDocument36 pagesHuman Anatomy RespiratoryHafid JuniorNo ratings yet
- CHE 450 Module 3 2014 PDFDocument47 pagesCHE 450 Module 3 2014 PDFLad SlasNo ratings yet
- Entry Requirements Royal Conservatoire The HagueDocument1 pageEntry Requirements Royal Conservatoire The HagueYerdana YerbolNo ratings yet
- Bio 118 (Radiation Biology)Document18 pagesBio 118 (Radiation Biology)Emmanuel PardinanNo ratings yet
- PDF Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Pyrrole Imidazole Polyamide Probes For Visualization of Telomeres Yusuke Kawamoto Ebook Full ChapterDocument54 pagesPDF Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Pyrrole Imidazole Polyamide Probes For Visualization of Telomeres Yusuke Kawamoto Ebook Full Chaptersandra.wild393100% (1)
- File78555119dispersion of LightpdfDocument10 pagesFile78555119dispersion of LightpdfMario PelicanoNo ratings yet
- At Lesson Summary Week 10Document3 pagesAt Lesson Summary Week 10api-533864204No ratings yet
- New SyllabusDocument5 pagesNew SyllabusAnuNo ratings yet
- Textbook A Study On Antimicrobial Effects of Nanosilver For Drinking Water Disinfection 1St Edition Xu Yang Auth Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument39 pagesTextbook A Study On Antimicrobial Effects of Nanosilver For Drinking Water Disinfection 1St Edition Xu Yang Auth Ebook All Chapter PDFmaurice.thibodeau744100% (22)
- 3887supportingresourcesqualitativetests Final 83628Document15 pages3887supportingresourcesqualitativetests Final 83628GOURAV GOLANo ratings yet
- Sample Study Using CorrrelationDocument7 pagesSample Study Using Corrrelationblackcloverasta585No ratings yet
- Thesis Physics ExampleDocument7 pagesThesis Physics Exampleirywesief100% (2)
- Practical Guide For PHD Candidates at Epfl: Version: August 12, 2008Document91 pagesPractical Guide For PHD Candidates at Epfl: Version: August 12, 2008rjohn1No ratings yet
- PDF Bioelectrochemical Interface Engineering First Edition Navanietha Krishnaraj Ebook Full ChapterDocument53 pagesPDF Bioelectrochemical Interface Engineering First Edition Navanietha Krishnaraj Ebook Full Chapterstephanie.willis395100% (4)
- Electrochemical EnergyDocument12 pagesElectrochemical EnergySANTIAGO, ISAIAH MICAH L.No ratings yet
- Membranes For Olefin SeparationsDocument162 pagesMembranes For Olefin Separationsvu anh ducNo ratings yet
- Thesis Jin Jeon V08-AugmentedDocument137 pagesThesis Jin Jeon V08-Augmentedpandapriyanshu768034No ratings yet
- (Download PDF) A Microscale Approach To Organic Laboratory Techniques 6 Ed 6Th Edition Donald L Pavia Online Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument42 pages(Download PDF) A Microscale Approach To Organic Laboratory Techniques 6 Ed 6Th Edition Donald L Pavia Online Ebook All Chapter PDFbarbara.dodd666100% (13)
- Mod TA 220-1Document9 pagesMod TA 220-1Muhammed Azeem RehmanNo ratings yet
- Advanced Laser Process For Surface Enhancement Advanced Topics in Science and Technology in China 61 Jianhua YaoDocument70 pagesAdvanced Laser Process For Surface Enhancement Advanced Topics in Science and Technology in China 61 Jianhua Yaopaul.cate815100% (16)
- tawuwibapedDocument2 pagestawuwibapedRohan KumarNo ratings yet
- Imperial College London PHD Thesis FormatDocument7 pagesImperial College London PHD Thesis Formatelizabethjenkinsatlanta100% (2)
- PHD Thesis ZeolitesDocument4 pagesPHD Thesis ZeolitesKimberly Pulley100% (2)
- NetflixDocument29 pagesNetflixlaboop2121No ratings yet
- 18847Document45 pages18847jadhvnahrinNo ratings yet
- JORC Code ReportingDocument7 pagesJORC Code Reportingmozart pourvousNo ratings yet
- Reaction Kinetics of Biodiesel Synthesis From Waste Oil Using A Carbon-Based Solid Acid CatalystDocument6 pagesReaction Kinetics of Biodiesel Synthesis From Waste Oil Using A Carbon-Based Solid Acid Catalystsalonso93No ratings yet
- Nucleophilic SubstitutionDocument3 pagesNucleophilic SubstitutionayushNo ratings yet
- Molecular RearrangementsDocument9 pagesMolecular RearrangementsDhanaswamy Ilangeswaran67% (3)
- Chemical Equilibrium Chemistry Grade 12: Everything Science WWW - Everythingscience.co - ZaDocument10 pagesChemical Equilibrium Chemistry Grade 12: Everything Science WWW - Everythingscience.co - ZaWaqas LuckyNo ratings yet
- III 12 2009 UllmannEncycl HetCatal Turek Deutschmann-666931330Document153 pagesIII 12 2009 UllmannEncycl HetCatal Turek Deutschmann-666931330Dragon's Sin of Wrath MeliodasNo ratings yet
- Alkenes and Alkynes II:: Addition ReactionsDocument102 pagesAlkenes and Alkynes II:: Addition Reactionsfingil20032003No ratings yet
- Homolytic: Click A Box Below To Go To The MechanismDocument29 pagesHomolytic: Click A Box Below To Go To The Mechanismhknhat100% (1)
- Chapter 3 Chemical KineticsDocument46 pagesChapter 3 Chemical KineticsaadarshceoNo ratings yet
- RX Indol IodoDocument8 pagesRX Indol IodoFernando RSNo ratings yet
- Kinetics Study of Propylene Oxide and WaterDocument8 pagesKinetics Study of Propylene Oxide and WaterRisma RegiyantiNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Temperature and PH On The Enzyme Activity of Salivary AmylaseDocument9 pagesThe Effects of Temperature and PH On The Enzyme Activity of Salivary AmylaseCherisse TuazonNo ratings yet
- PMR v19 I1 012 014Document3 pagesPMR v19 I1 012 014Arianne Jayne G. GubaNo ratings yet
- Problems - SET-1 Org Without AnswersDocument19 pagesProblems - SET-1 Org Without AnswersNidhi SisodiaNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Vs Thermodynamic ControlDocument20 pagesKinetic Vs Thermodynamic ControlNgua GiaNo ratings yet
- Dr. Muhammad Yasir Akram: Presented ToDocument19 pagesDr. Muhammad Yasir Akram: Presented ToZee ShanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 4 - Benzene: Test Items For Mcmurry'S Organic Chemistry, Seventh Edition 145Document4 pagesTutorial Chapter 4 - Benzene: Test Items For Mcmurry'S Organic Chemistry, Seventh Edition 145Amrun RusrlNo ratings yet
- REDUCTIONS FinalDocument11 pagesREDUCTIONS Finalgamer boomerNo ratings yet
- EMGBS-Bio 11. U.3 NoteDocument37 pagesEMGBS-Bio 11. U.3 NoteDaniel GtsadkanNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium Core (SL HL) Questions Paper2Document2 pagesEquilibrium Core (SL HL) Questions Paper2RyanNo ratings yet
- Organic Reaction MechanismDocument15 pagesOrganic Reaction Mechanismrohit13339No ratings yet
- Grignard Reagents - Flash Cards - FinalDocument3 pagesGrignard Reagents - Flash Cards - FinalArchisman MisraNo ratings yet
- 6 Aldehydes and Ketones-ReactionsDocument33 pages6 Aldehydes and Ketones-ReactionsPrashant NalindeNo ratings yet
- Alkenes and Cycloalkenes: Alkenes Carbon - Carbon Double BondDocument22 pagesAlkenes and Cycloalkenes: Alkenes Carbon - Carbon Double BondМария МановаNo ratings yet
- Mevalonic Acid PathwayDocument4 pagesMevalonic Acid PathwayChandra ReddyNo ratings yet
- 3.1 FRP KineticsDocument9 pages3.1 FRP KineticsNazratul NajwaNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde and Ketone ReactionsDocument21 pagesAldehyde and Ketone ReactionsAinsssNo ratings yet
- ReactionsDocument33 pagesReactionsNicksonNo ratings yet
- Kinetics of Hydrogen Uptake and Release From Heteroaromatic Compounds For Hydrogen StorageDocument9 pagesKinetics of Hydrogen Uptake and Release From Heteroaromatic Compounds For Hydrogen Storagesj singhNo ratings yet
- 7.1 Dynamic EquilibriumDocument26 pages7.1 Dynamic EquilibriumScotrraaj GopalNo ratings yet