Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Concept Map 2
Concept Map 2
Uploaded by
cwissenb0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Concept Map 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesConcept Map 2
Concept Map 2
Uploaded by
cwissenbCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
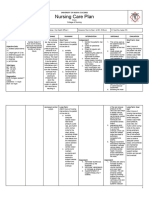
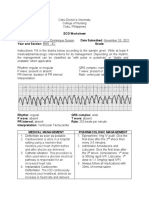
Medical Diagnosis Pathophysiology
Impaired cardiac function Right bundle branch block (RBBB) is a cardiac
conduction abnormality that affects the
Medications
electrical signaling within the heart. In a healthy
NACL 0.9
heart, electrical impulses travel from the
IV 75mL/hr
30 days/continuous sinoatrial node to the atrioventricular node and
Nursing Diagnosis then to the bundle of His, which divides into the
Zofran Impaired cardiac function related to right bundle left and right bundle branches to activate the
4 mg branch blockage as evidenced by ECG changes left and right ventricles. In RBBB, the electrical
q6hrs PRN Nausea and symptoms of dyspnea, chest pain, and impulses are delayed or blocked within the
IV Push dizziness. right bundle branch, causing a delay in the
Morphine activation of the right ventricle. This can lead to
2-4 mg impaired cardiac function, including a decrease
PRN Pain 7-10 in cardiac output and an increased risk of
IV Push arrhythmias. The ECG changes associated with
Goals RBBB include a widened QRS complex and a
Aspirin characteristic pattern of ST-T wave changes.
325 mg QID, PRN, PO Patient will maintain stable vital signs
Patients with RBBB may experience symptoms
within acceptable limits by end of shift.
Nitroglycerine such as dyspnea, chest pain, and dizziness,
Patient will demonstrate hemodynamic by
(Nitrostat) which can be attributed to reduced cardiac
end of shift
1 tab 2.5 mg output and decreased oxygenation. Treatment
nitroglycerine, if not of RBBB may involve medication or other
relieved within 5 min interventions such as pacemaker implantation
administer a second or catheter ablation to restore normal cardiac
tab. PO, PRN
conduction and improve cardiac function.
Assessment data to support nursing
diagnosis
Support system Developmental
Subjective Data:
Wife, 2 Pt reports SOB Despair vs.
daughters, 1 son. Pt reports, “I have pain in my chest”. Integrity
Objective Data: Pt falls into
Pt ECG shows RBBB and ST elevation. Capillary refill is despair due to
1+, O2 saturation is 86% on room air. inability to
complete ADL,
related to fatigue.
Concept map Copyright 2020 @ Unitek College All rights reserved
Diagnostic exams,
Complications Laboratory test and results
& information related to nursing diagnosis
to report to MD Nursing Interventions
Troponin I, Troponin T
h 1. Monitor the patient's oxygen saturation and (Cardiac Enzymes)
Elevated Troponin provide O2 via NC 4L. Results:
levels T1 (18:00) 16.4
2. Administer medications as prescribed. T2 (19:00) 25.5
Dyspnea w/low O2 T3 (20:00) 52
3. Monitor the patient's fluid balance and
stats electrolyte levels, and administer intravenous fluids
TT Positive
ECG
or diuretics as prescribed. 5 lead, continuous monitoring
ECG abnormalities Pt ECG shows widened QRS of
Chest Pain 1. Assess electrolytes levels q4hr. greater than 120 milliseconds,
elevated T waves, V6- showing
2.Asses troponin levels q1hrx3, asses q4hr inverted T waves
thereafter.
3. Administer medications and fluids as prescribed
to achieve hemodynamic stability.
Treatment
Plan/Procedures
Continuous 5 Lead cardiac monitoring
Monitor for DVTs
Continue monitoring Troponin Levels.
Monitor Pain
Scientific Rationale Monitor )2 stats
1. Pts w/ low O2 saturation need supplemental O2 due to the
heart’s inability to pump oxygen-rich blood to the body.
Patient Teaching
2. Vasodilators open arteries/veins to allow for decreased vascular
resistance, increasing cardiac output and reducing ventricular
workload. Morphine and anti-anxiety medications help with
relaxing and calming the patient which can reduce cardiac
Educate pt on activity limitations, provide guidance to
workload. Angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) lower blood
perform activities within limitations. Include
pressure and make pumping blood easier for the heart.
recommendations for modifying activities. Provide
information on the signs and symptoms of cardiac stress.
3. Pts with Mi have impaired heart function. Monitoring fluid
balance is important to identify and manage any imbalances to
Educate pt on activity modification to prevent
prevent complications like heart failure, pulmonary edema,
overexertion and keep vital signs WNL,
and renal failure.
1. An MI can cause electrolyte imbalances that effect heart function
leading to further complications.
2. MI can cause cardiac enzyme levels to elevate.
3. Administer morphine, O2, nitroglycerine, aspirin can help
manage symptoms of MI.
Evaluation of Interventions
Pt has maintained normal ECG pattern
within the last 4 ours.
Goal(s)Met Pt labs reveal a slow decrease in
Partially Met
Troponins.
1.Goal met. Pt shows Normal ECG &
decreasing Troponins. Pt electrolyte values showing a trend
toward normal limits.
2.Goal met: Pt electrolyte levels
stabilizing.
You might also like
- Precision Nutrition Coaching WorkbookDocument165 pagesPrecision Nutrition Coaching WorkbookJože Majcen86% (7)
- ORE - UK Dental Reference BooksDocument4 pagesORE - UK Dental Reference BooksKisshore Reddy50% (2)
- Coronary Artery Bypass Graph Concept MapDocument5 pagesCoronary Artery Bypass Graph Concept Mapnursing concept maps100% (1)
- Jake Yvan Dizon Case Study, Chapter 49, Assessment and Management of Patients With Hepatic DisordersDocument8 pagesJake Yvan Dizon Case Study, Chapter 49, Assessment and Management of Patients With Hepatic DisordersJake Yvan DizonNo ratings yet
- Anemia Concept Mapping. Group 1Document82 pagesAnemia Concept Mapping. Group 1Giselle EstoquiaNo ratings yet
- Acute Cardiac Care PDFDocument43 pagesAcute Cardiac Care PDFhuong LNo ratings yet
- CCRN-PCCN-CMC Review Cardiac Part 2Document21 pagesCCRN-PCCN-CMC Review Cardiac Part 2Giovanni Mictil100% (1)
- StudocuDocument83 pagesStudocuFreddy Mendoza CoronelNo ratings yet
- 9c5a4module 2 Self EsteemDocument14 pages9c5a4module 2 Self EsteemHarshita Jakhodia100% (1)
- TCMDocument4 pagesTCMxuxumoNo ratings yet
- Concept Map Isha PreeclampsiaDocument1 pageConcept Map Isha PreeclampsiaNoemi GabayNo ratings yet
- Asthma of Cardiac Origin in A 66 Year Ol 945c182cDocument4 pagesAsthma of Cardiac Origin in A 66 Year Ol 945c182cFransiska DelviaNo ratings yet
- L5 Heart Failure-Dr. Yagub S SalehDocument7 pagesL5 Heart Failure-Dr. Yagub S Salehnusaiba.alobaidyNo ratings yet
- INOTROPESDocument28 pagesINOTROPESsinghal297% (30)
- Study of The Role of Plasma Nt-Probnp in The Diagnosis of Heart FailureDocument5 pagesStudy of The Role of Plasma Nt-Probnp in The Diagnosis of Heart FailureMinerva Medical Treatment Pvt LtdNo ratings yet
- Cp201012 Learning Light-395Document2 pagesCp201012 Learning Light-395jyothiNo ratings yet
- DigoxinDocument4 pagesDigoxinJaessa FelicianoNo ratings yet
- Week 4. ARFDocument50 pagesWeek 4. ARFAira EspleguiraNo ratings yet
- L2 Hypertension 2 - Dr. Yagub S SalehDocument4 pagesL2 Hypertension 2 - Dr. Yagub S Salehnusaiba.alobaidyNo ratings yet
- 29-04-2021 Uremic + Severe Asidosis + CKD + Probable Pneumonia Covid-19Document3 pages29-04-2021 Uremic + Severe Asidosis + CKD + Probable Pneumonia Covid-19Firdha RositaNo ratings yet
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument4 pagesDecreased Cardiac Outputaudreyann.acobNo ratings yet
- NCP 2004Document6 pagesNCP 2004Kate WillisNo ratings yet
- Ivabradine Use in Heart Failure After Myocardial Infarction Can Help With The Titration of The Dose of ARB/ACEI or - Blockers: A Case ReportDocument4 pagesIvabradine Use in Heart Failure After Myocardial Infarction Can Help With The Titration of The Dose of ARB/ACEI or - Blockers: A Case ReportAzmia TabahNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy With His Bundle Pacing, 2018.Document7 pagesCardiac Resynchronization Therapy With His Bundle Pacing, 2018.Abel GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Children With Cardiac DisordersDocument3 pagesCase Study On Children With Cardiac DisordersAlyNo ratings yet
- Effects of An Antithrombin Drug in Patients With Subacute Exacerbations of Binswanger DiseaseDocument4 pagesEffects of An Antithrombin Drug in Patients With Subacute Exacerbations of Binswanger DiseaseFortune FireNo ratings yet
- Reversal of Tachycardiomyopathy Due To Left Atrial Tachycardia by IvabradineDocument3 pagesReversal of Tachycardiomyopathy Due To Left Atrial Tachycardia by Ivabradinedarlen bahriNo ratings yet
- Presented By, Dr. Likhit T House Surgeon Medicine D Unit MmcriDocument73 pagesPresented By, Dr. Likhit T House Surgeon Medicine D Unit MmcriVasu LohraNo ratings yet
- Final NCP (Jannel)Document6 pagesFinal NCP (Jannel)Zed P. EstalillaNo ratings yet
- Estudio DELayDocument20 pagesEstudio DELayOliver Danilo Cuenca MorenoNo ratings yet
- Heath Day 4 Care Plan 3Document12 pagesHeath Day 4 Care Plan 3api-639508852No ratings yet
- Diagnosis of Acute Myocardial InfarctDocument5 pagesDiagnosis of Acute Myocardial InfarctOscar SanNo ratings yet
- U2T1L3 InotropesDocument7 pagesU2T1L3 InotropesEscarlet FigueroaNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing and Midwifery: Mabini Colleges Daet, Camarines NorteDocument1 pageCollege of Nursing and Midwifery: Mabini Colleges Daet, Camarines NorteMa. Sheenadel ZamudioNo ratings yet
- A 17 Year Old With Becker Muscular Dystrophy and UDocument5 pagesA 17 Year Old With Becker Muscular Dystrophy and UagamerocallejasNo ratings yet
- Case Study of Anterior Wall MI 48Document32 pagesCase Study of Anterior Wall MI 48سوما الشمريNo ratings yet
- Cervical Dystonia and Constantin Brancus PDFDocument19 pagesCervical Dystonia and Constantin Brancus PDFDaniel HristescuNo ratings yet
- Nanda NCP BasedDocument14 pagesNanda NCP Baseddeliejoyce100% (1)
- Transient Electrocardiographic Changes FDocument2 pagesTransient Electrocardiographic Changes FEmil PyykönenNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2214027121001949 MainDocument5 pages1 s2.0 S2214027121001949 Mainachavisva0196No ratings yet
- Acute Kidney Injury W/ Hyperkalemia NCPDocument5 pagesAcute Kidney Injury W/ Hyperkalemia NCPMyrvic Ortiz La OrdenNo ratings yet
- Piis 2474870622018802Document9 pagesPiis 2474870622018802api-749207656No ratings yet
- Theuseofcardiotonic Drugsinneonates: Eugene Dempsey,, Heike RabeDocument18 pagesTheuseofcardiotonic Drugsinneonates: Eugene Dempsey,, Heike RabePaty JuárezNo ratings yet
- Complex Care Concept MapDocument6 pagesComplex Care Concept Mapapi-740628337No ratings yet
- ID Pengetahuan Remaja Putri Tentang Cara MeDocument3 pagesID Pengetahuan Remaja Putri Tentang Cara MeAyu Wita DewiNo ratings yet
- Brugada Electrocardiographic Pattern Induced By.14Document4 pagesBrugada Electrocardiographic Pattern Induced By.14Punnaphat Tinnaphop DaraswangNo ratings yet
- 01-10 2022 Pharm Acute Care in Cardiology 2022 R2Document62 pages01-10 2022 Pharm Acute Care in Cardiology 2022 R2Amira HelayelNo ratings yet
- PIIS2468644118301282Document5 pagesPIIS2468644118301282Lilly PattersonNo ratings yet
- STH 19 - Day 2 - Track 1 - Session 2 - Watson - Hypertension - SNDocument18 pagesSTH 19 - Day 2 - Track 1 - Session 2 - Watson - Hypertension - SNiqra uroojNo ratings yet
- ECG WorksheetDocument4 pagesECG WorksheetNikki GuisonNo ratings yet
- Brugada Electrocardiographic Pattern Induced By.14Document4 pagesBrugada Electrocardiographic Pattern Induced By.14Punnaphat Tinnaphop DaraswangNo ratings yet
- Review and Update On VasopressorsDocument9 pagesReview and Update On VasopressorspunkgatitNo ratings yet
- Sympathetic Modulation by Antihypertensive DrugsDocument3 pagesSympathetic Modulation by Antihypertensive Drugsthomas albertNo ratings yet
- Hypovolemic ShockDocument4 pagesHypovolemic ShockRATNo ratings yet
- Activity No1 Case Study On CADDocument3 pagesActivity No1 Case Study On CADVictor StevenNo ratings yet
- Ok 2012 CorrelationDocument3 pagesOk 2012 CorrelationsufaNo ratings yet
- Two Cases of BRASH Syndrome: A Diagnostic Challenge: European Journal Internal MedicineDocument4 pagesTwo Cases of BRASH Syndrome: A Diagnostic Challenge: European Journal Internal MedicineDesi MeliaNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension TopicDocument32 pagesPulmonary Arterial Hypertension Topicapi-668691030No ratings yet
- Heart Failure TodayDocument54 pagesHeart Failure TodaypoolchagoNo ratings yet
- Preemptive Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy To Prevent Cardiac Arrest in Peripartum Cardiomyopathy: A Case ReportDocument5 pagesPreemptive Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy To Prevent Cardiac Arrest in Peripartum Cardiomyopathy: A Case Reportvanilla wottledNo ratings yet
- Hypertensionaha 118 11180Document10 pagesHypertensionaha 118 11180Dayanti Nuroazi UtariNo ratings yet
- CHFDocument11 pagesCHFGwendolyn Talahiban LusaraNo ratings yet
- Natriuretic Peptides - Physiology, Pathophysiology and Clinical Use in Heart FailureDocument7 pagesNatriuretic Peptides - Physiology, Pathophysiology and Clinical Use in Heart FailuregunawanNo ratings yet
- Vertebral Canal Haematoma and Coagulopathy - BjaDocument2 pagesVertebral Canal Haematoma and Coagulopathy - BjaRENAULTNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Optimización del tratamiento de las fluctuaciones motoras en la enfermedad de Parkinson: Adaptando el tratamiento al pacienteFrom EverandFast Facts: Optimización del tratamiento de las fluctuaciones motoras en la enfermedad de Parkinson: Adaptando el tratamiento al pacienteNo ratings yet
- Exjade: (Deferasirox)Document13 pagesExjade: (Deferasirox)athayafebNo ratings yet
- Why Should The Students of Grade 10 - Passion - 7 From APEC Schools Marikina Heights Be in Favor of Vaccination Could This Be The Solution For The Face To Face Classes AgainDocument18 pagesWhy Should The Students of Grade 10 - Passion - 7 From APEC Schools Marikina Heights Be in Favor of Vaccination Could This Be The Solution For The Face To Face Classes AgainRanen Darren P. BenitoNo ratings yet
- 2020-10-01 St. Mary's County TimesDocument32 pages2020-10-01 St. Mary's County TimesSouthern Maryland OnlineNo ratings yet
- Open Letter To Minister Tell Re COVID-19 in Prisons - April 2, 2020Document4 pagesOpen Letter To Minister Tell Re COVID-19 in Prisons - April 2, 2020Thomas PillerNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 8.2: Shown Horizontally or VerticallyDocument1 pageWorksheet 8.2: Shown Horizontally or VerticallySangkasNo ratings yet
- Clinic SystemDocument21 pagesClinic Systemmarlon_tayagNo ratings yet
- AmiodaroneDocument2 pagesAmiodaroneEmmil BernardoNo ratings yet
- 12th - English - Answer KeyDocument5 pages12th - English - Answer Keyutharun3No ratings yet
- Dopamine NationDocument1 pageDopamine NationIntrovertNo ratings yet
- Amnestic DisordersDocument15 pagesAmnestic DisordersMaicah ShaneNo ratings yet
- Monthly Digest April 2018 Eng - PDF 92Document461 pagesMonthly Digest April 2018 Eng - PDF 92Naveen KumarNo ratings yet
- 2022 Nigeria Real Estate Market Outlook (Compressed)Document60 pages2022 Nigeria Real Estate Market Outlook (Compressed)Aminul IslamNo ratings yet
- English ProjectDocument17 pagesEnglish ProjectPreeti TiwariNo ratings yet
- BENJAMIN, Harry - Better Sight Without Glasses (1962) PDFDocument115 pagesBENJAMIN, Harry - Better Sight Without Glasses (1962) PDFKhoerNo ratings yet
- Part 1:-Safety On Workplace: Q 1) What Are The Health Hazards Mentioned inDocument5 pagesPart 1:-Safety On Workplace: Q 1) What Are The Health Hazards Mentioned inSalman AlshammariNo ratings yet
- Life Safety Code: ComparisonDocument48 pagesLife Safety Code: Comparisonmomen alrmzNo ratings yet
- Artikel Review Ratna DpsDocument5 pagesArtikel Review Ratna DpsRika AmeliaNo ratings yet
- Mind, Character and Personality Volume 2Document353 pagesMind, Character and Personality Volume 23angelsminconcepts100% (2)
- DLL Wellness WK 5Document5 pagesDLL Wellness WK 5Lorna CelarioNo ratings yet
- Practioner's Guide To Ethical Decision MakingDocument6 pagesPractioner's Guide To Ethical Decision Makingsaurav.das2030No ratings yet
- Cmca Lec ReviewerDocument32 pagesCmca Lec Reviewercuteathena11No ratings yet
- A Case Study On The Ayurvedic Management of Cerebral PalsyDocument10 pagesA Case Study On The Ayurvedic Management of Cerebral PalsyHiramandalam PatanjaliNo ratings yet
- My Learning Experience at Lung Center of The: PhilippinesDocument3 pagesMy Learning Experience at Lung Center of The: PhilippinesMarie Aurora Gielbert MarianoNo ratings yet
- Teaching Clinical Handover With ISBAR: Review Open AccessDocument8 pagesTeaching Clinical Handover With ISBAR: Review Open AccessFernando PintoNo ratings yet
- Physiology of 3 Gates (Qigong) or 3 Granthi (Yoga)Document10 pagesPhysiology of 3 Gates (Qigong) or 3 Granthi (Yoga)Test4DNo ratings yet