Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Parkinson's DIsease PCOL
Parkinson's DIsease PCOL
Uploaded by
chichandesuCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Parkinson's DIsease PCOL
Parkinson's DIsease PCOL
Uploaded by
chichandesuCopyright:
Available Formats
When medication is ineffective, surgery may be an option to control symptoms and improve
quality of life. However, not everyone is a good candidate for surgery. For example, if a patient
never responds or no longer responds to levodopa and carbidopa, surgery is unlikely to help.
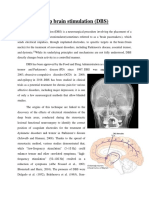
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) is a surgical procedure that involves implanting a small device
called a stimulator into the brain. The stimulator delivers electrical impulses to specific areas of
the brain that are affected by Parkinson's disease, helping to reduce symptoms such as
tremors, stiffness, and slowness of movement. DBS is considered a reversible treatment
because the device can be turned off or removed if necessary.
Neuroablative lesion surgeries involve destroying a small area of brain tissue that is causing
symptoms in Parkinson's disease patients. This can be done using radiation therapy,
radiofrequency, or other techniques. While this treatment can be effective at reducing
symptoms, it is considered irreversible because the destroyed tissue cannot be replaced or
regenerated.
Neural transplantation is a surgical procedure that involves implanting fetal brain tissue into
the brain of a Parkinson's disease patient. The hope is that the transplanted cells will produce
dopamine, a chemical that is deficient in Parkinson's disease patients, and help to alleviate
symptoms. However, this treatment is still in the experimental stage and has not yet been widely
adopted due to safety concerns and inconsistent results.
Stereotactic procedures are a group of surgical techniques used to precisely target and
manipulate specific areas of the brain. These procedures can be used for a variety of purposes,
including diagnosing brain tumors, treating epilepsy, and relieving pain. In the context of
Parkinson's disease, stereotactic procedures can be used to place electrodes or other devices
into the brain for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes.
Overall, surgical procedures for Parkinson's disease are typically reserved for advanced cases
that do not respond well to medication or for individuals with severe side effects from
medication. The choice of procedure will depend on the specific symptoms and the individual's
overall health and medical history
You might also like
- Efficacy of DBS in Parkinson - For NsiuDocument2 pagesEfficacy of DBS in Parkinson - For NsiushaffanaNo ratings yet
- Biology ProjectDocument14 pagesBiology ProjectVittal Rao LNo ratings yet
- Current Surgical Treatments For Parkinson's Disease and Potential Therapeutic TargetsDocument4 pagesCurrent Surgical Treatments For Parkinson's Disease and Potential Therapeutic TargetsRudolph MuliawanNo ratings yet
- Guide To DBS Stimulation TherapyDocument56 pagesGuide To DBS Stimulation TherapyAndres Rodriguez SeijoNo ratings yet
- Deep Brain Stimulation For Movement Disorders: Neurostimulator - A Programmable BatteryDocument6 pagesDeep Brain Stimulation For Movement Disorders: Neurostimulator - A Programmable BatteryZee GreiNo ratings yet
- Parkinson19 PDFDocument6 pagesParkinson19 PDFLorenaNo ratings yet
- Surgical Therapies For Parkinson DiseaseDocument13 pagesSurgical Therapies For Parkinson DiseaseAnali Durán CorderoNo ratings yet
- Deep Brain Stimulation Guide ParkinsonsDocument56 pagesDeep Brain Stimulation Guide ParkinsonsGaurav MehtaNo ratings yet
- Art. L Zrinzo - MRI-guided STN DBS in Parkinson's Disease Without Microelectrode Recording Efficacy and SafetyDocument7 pagesArt. L Zrinzo - MRI-guided STN DBS in Parkinson's Disease Without Microelectrode Recording Efficacy and SafetyEstereotaxia BrasilNo ratings yet
- The Newest ParkinsonDocument6 pagesThe Newest Parkinsonmykeyos1870No ratings yet
- Deep Brain StimulationDocument4 pagesDeep Brain StimulationCristian GondacNo ratings yet
- DBS2008Document48 pagesDBS2008Carol Artigas Gómez100% (1)
- Deep Brain StimulationDocument9 pagesDeep Brain StimulationKeerthanaNo ratings yet
- Dbs VnsDocument22 pagesDbs Vnswen tvaleNo ratings yet
- Neurosurgery For Parkinson - S DiseaseDocument12 pagesNeurosurgery For Parkinson - S DiseaseJesus German Loya ValladolidNo ratings yet
- Deep Brain Stimulation For Parkinson's Disease - Patient SelectionDocument9 pagesDeep Brain Stimulation For Parkinson's Disease - Patient SelectionAtul JainNo ratings yet
- Art. PA Star - Microelectrode-Guided Implantation of Deep Brain Stimulators Into The Globus Pallidus Internus For Dystonia Techniques, Electrode Locations, and OutcomesDocument14 pagesArt. PA Star - Microelectrode-Guided Implantation of Deep Brain Stimulators Into The Globus Pallidus Internus For Dystonia Techniques, Electrode Locations, and OutcomesPaul RodrigoNo ratings yet
- Role of Preclinical Data in PDDocument23 pagesRole of Preclinical Data in PDIrving ParraNo ratings yet
- Gene Therapy For Parkinson's DiseaseDocument2 pagesGene Therapy For Parkinson's DiseaseBhaswan Indu JanaNo ratings yet
- Fnins 14 558532Document16 pagesFnins 14 558532anita putri effendiNo ratings yet
- Awake CraniotomyDocument28 pagesAwake CraniotomyBeba EchevarriaNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Parkinson Disease With Motor Fluctuations and DyskinesiaDocument15 pagesTreatment of Parkinson Disease With Motor Fluctuations and DyskinesiaSalvador FigueroaNo ratings yet
- Parkinsons Disease Term PaperDocument4 pagesParkinsons Disease Term Paperc5t0jsyn100% (1)
- Clinical Outcomes Using Clearpoint Interventional Mri For Deep Brain Stimulation Lead Placement in Parkinson'S DiseaseDocument9 pagesClinical Outcomes Using Clearpoint Interventional Mri For Deep Brain Stimulation Lead Placement in Parkinson'S DiseasejoshbakhNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic EvaluationDocument67 pagesDiagnostic EvaluationMyzing OraaNo ratings yet
- Blueprint For Neurostimulation With Intranasal Light TherapyDocument28 pagesBlueprint For Neurostimulation With Intranasal Light Therapy456456456y45y45100% (1)
- Management of Parkinson's DiseaseDocument20 pagesManagement of Parkinson's DiseasePia S.No ratings yet
- Artículo15 - ParkinsonDocument15 pagesArtículo15 - ParkinsonRicardo FernandezNo ratings yet
- Subthalamic and Pallidal Stimulations in Patients With Parkinson's Disease - Common and Dissociable ConnectionsDocument13 pagesSubthalamic and Pallidal Stimulations in Patients With Parkinson's Disease - Common and Dissociable ConnectionsViviana TorresNo ratings yet
- Pi Is 1094715921064345Document7 pagesPi Is 1094715921064345syarifaNo ratings yet
- Update On Surgery For Parkinson's Disease: Jens VolkmannDocument5 pagesUpdate On Surgery For Parkinson's Disease: Jens VolkmannAkiNo ratings yet
- Parkinson's Disease & Deep Brain StimulationDocument31 pagesParkinson's Disease & Deep Brain Stimulationjesus20100No ratings yet
- Deep-Brain Stimulation For Parkinson's Disease: Clinical TherapeuticsDocument10 pagesDeep-Brain Stimulation For Parkinson's Disease: Clinical TherapeuticsanonimoNo ratings yet
- Cellular, Molecular, and Clinical Mechanisms of Action of Deep Brain StimulationDocument18 pagesCellular, Molecular, and Clinical Mechanisms of Action of Deep Brain StimulationAndrés BotelloNo ratings yet
- JOURNALDocument10 pagesJOURNALTin NatividadNo ratings yet
- Bio 212 GDocument11 pagesBio 212 GhugoivanstNo ratings yet
- Basal Ganglia Circuits As Targets For Neuromodulation in Parkinson DiseaseDocument7 pagesBasal Ganglia Circuits As Targets For Neuromodulation in Parkinson DiseaseSebastián GallegosNo ratings yet
- Eeg UsDocument6 pagesEeg UsnetoNo ratings yet
- New Trends by RodDocument11 pagesNew Trends by Rodmolukas101No ratings yet
- Biology Investigatory Project Class 12thDocument20 pagesBiology Investigatory Project Class 12thsupercelldarshil100% (1)
- Research Paper Parkinson DiseaseDocument5 pagesResearch Paper Parkinson Diseasem0d1p1fuwub2100% (1)
- Parkinsons Disease PHD ThesisDocument5 pagesParkinsons Disease PHD Thesischristinawestcharleston100% (2)
- Deep Brain Stimulation Research PaperDocument8 pagesDeep Brain Stimulation Research Papergipinin0jev2100% (1)
- Parkinsons Disease Thesis PDFDocument5 pagesParkinsons Disease Thesis PDFsararousesyracuse100% (2)
- Stereotactic Implantation of Deep BrainDocument28 pagesStereotactic Implantation of Deep Brainberna chuaNo ratings yet
- BSE656 Team 9Document5 pagesBSE656 Team 9juee chandrachudNo ratings yet
- Mosley Et Al. (2020)Document19 pagesMosley Et Al. (2020)Fie LarsenNo ratings yet
- Young Onset Parkinson Disease ProposalDocument10 pagesYoung Onset Parkinson Disease ProposalYT HungNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms Discovered in The Effect of Brain Stimulation in DepressionDocument3 pagesMechanisms Discovered in The Effect of Brain Stimulation in DepressionEcbNo ratings yet
- Methods To Study Brain and Behaviour. Ethical Considerations. - Biological Psychology Course - 3rd SemDocument37 pagesMethods To Study Brain and Behaviour. Ethical Considerations. - Biological Psychology Course - 3rd Semacademicwiz30No ratings yet
- New Strategic Management of Stem Cell TH in Movdis CasesDocument32 pagesNew Strategic Management of Stem Cell TH in Movdis CasesSafitri MuhlisaNo ratings yet
- França (2018) Brain StimulationDocument12 pagesFrança (2018) Brain StimulationAna paula CamargoNo ratings yet
- DaTscan For Parkinson PDFDocument9 pagesDaTscan For Parkinson PDFSuresh UmadiNo ratings yet
- Review DBSDocument8 pagesReview DBSEtonia PangNo ratings yet
- Franca (2019) World NeurosurgDocument8 pagesFranca (2019) World NeurosurgCarina FrançaNo ratings yet
- MSSPDocument2 pagesMSSPaira khanNo ratings yet
- From Diagnosis to Cure: Innovations in Disease Diagnosis and TreatmentFrom EverandFrom Diagnosis to Cure: Innovations in Disease Diagnosis and TreatmentNo ratings yet
- Echography and Doppler of the BrainFrom EverandEchography and Doppler of the BrainChiara RobbaNo ratings yet
- Sleep Disorders in Parkinson’s Disease: Management and Case StudyFrom EverandSleep Disorders in Parkinson’s Disease: Management and Case StudyChun-Feng LiuNo ratings yet