Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Adjectives and Adverbs
Adjectives and Adverbs
Uploaded by
2157011179Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Adjectives and Adverbs
Adjectives and Adverbs
Uploaded by
2157011179Copyright:
Available Formats
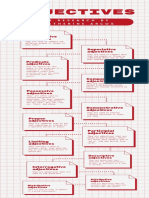
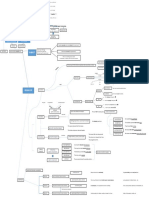
Words modifying nouns, expressing
DEFINITION physical and other qualities and the
writer’s opinion/attitude
Used before nouns: a strong man
Attributive
A word that describes or adds to the
Adjectives Many nouns used as attributive
meaning of a verb, an adjective, another adjectives: a paper cup
adverb, or a sentence, and which answers
such questions as how, where, or when Predicative Used after verbs (linking
verbs): The meal is delicious.
Adjectives
Adverbs cannot modify nouns
Having a certain property to a
greater or lesser degree
Adjuncts: part of the basic structure
of a clause or sentence in which it
TYPES Gradable
occurs, and modifies the verb Modified by very, enough, too: very tall
Ex: He died in England. Adjectives
I have almost finished.
Having comparative and superlative
Adverbial: any word, phrase, forms: taller, the tallest
Conjuncts: not part of the basic structure or clause that functions like DEFINITION
of a clause or sentence
Not having a certain property to
Ex: However, the weather was not good. an adverb a greater or lesser degree
➔ adverb = one-word adverbial Non-gradable
Disjuncts: (also called sentence adverbs)
Not modified by very, enough, too
adverbs which show the speaker’s
attitude to or evaluation of what is said
Adjectives
in the rest of the sentence Not having comparative and
Ex: Naturally, I paid for my own meal. superlative forms:
Most frequently used
Particle: a term used for a word
Simple Adjectives:
Adverb particle: a word such as in, which cannot readily be Often mono-syllabic and bi-
back, on, etc. When it modifies a Good, Bad, Fine, syllabic words: cold, happy
verb rather than a noun identified with any of the main
Short, Etc.
Ex: The train’s getting in. PARTS OF SPEECH/ WORD CLASS No distinctive form to mark as
Ex: She did not receive my email. adjectives
Some of native origin: greenish,
Adverbs frequently end in –ly: Derived from nouns, other hopeful, handy, etc.
slowly, quickly, etc. adjectives, or verbs by adding
certain suffixes Of foreign bases: apparent,
FORMS AND secondary, marvelous, etc.
Not all words end in –ly are
adverbs: friendly, lovely, etc. FORMATION Derived Adjectives Derived from adjectives by adding prefixes
to adjectives: unhappy, insecure, etc.
Some adverbs do not have an –ly ending:
Derived from verbs or adjectives by
always, well, etc.
adding prefix a-: asleep, alone, etc.
Some adverbs can have two forms: • Noun + adjective: tax-free
He has come late. vs. He has come lately. FORM AND Compound • Determiner + adjective: all-American
• Number + noun: four-wheel
She talked very loud. vs. She talked very loudly. Adjectives • Adverb + participle: well-balanced Exception: Little can be used as
FORMATION • Adverb + adverb: well-off predicative adjective when it
refers to age
Ex: When I was little.
Simple adverbs: just, only, well, back, down, pretty, etc. Little is mostly attributive: a
little cottage
Compound adverbs: somehow, somewhere, Same cannot be predicative
therefore, whereupon, hereby, etc. •Attributive only: chief, elder,
without the: Yes, I had the same
experience./Yes, my experience
eldest, eventual, former, indoor, was the same.
Derivational adverbs: inner, latter, main, mere, only,
o -ly: oddly, interestingly outdoor, outer, principal, sheer, A noun as modifier can only be
attributive: a tennis club, a
sole, upper, utter
o -wise: clockwise water pipe
o -ward(s): northward(s) Nouns saying what something
o -fashion: schoolboy-fashion is made of can go in either
position: It’s a metal pipe./The
o -ways: sideways pipe is metal.
o -style: cowboy-style
Some words with the prefix a-:
awake, ashamed, alike, etc.
• Before the subject
• Before the main verb
• After the verb “be”
Front: Yesterday something Many of these can be attributive if modified
Attributive And An Adjective Can Go Before A Noun (Attributive by an adverb: the wide awake children
• Between the auxiliary and the strange happened Position) Or As Complement After A Linking
main verb Predicative Verb (Predicative Position) Some words to do with health:
• After the first auxiliary verb (with Mid: He completely missed it. POSITIONS Positions Ex: It's A Big House. Vs The House Is Big. Predicative only well, fine, ill, unwell
more than 1 auxiliary)
Some words expressing feelings:
• Before a negative auxiliary verb
End: What are you doing tomorrow? content, glad, pleased, upset
• After the verb and object (not
between) Pleased, glad, and upset can be
attributive when not referring
Adverbs saying how directly to people: a pleased
expression, the glad news, an
something happens upset stomach
He generously paid for us. = It Adverbs of Manner
was generous of him to have Usually placed after the main
paid for us.
verb, after the object (if there is
one), or between the subject
He paid for us generously. = He
and the verb
ADJECTIVES
paid for us in a generous Different meanings in
ADJECTIVES
manner.
different positions
Adverbs indicating location (where),
direction (where to/ from) AND Sometimes adjectives can go after nouns
Ex: He has a face thin and worn, but eager
Ex: She still lives there now. and resolute.
ADVERBS
Adjective + prepositional phrase
Manner + place + time
Ex: They talked happily in the bedroom all night.
Adverbs of Place ADVERBS After nouns cannot go before the noun
Ex: He is a man greedy for money.
Adjectives After Sometimes the position depends on the meaning.
At the beginning of a sentence Ex: The amount of money involved is quite
Ex: Indoors it was nice and warm.
Nouns And small. (=relevant)
Pronouns It’s a rather involved story. (= complicated)
Adverbs of definite time: at the
end or beginning of a sentence Adjectives come after indefinite pronouns:
After pronouns You mustn't do anything silly.
Ex: I went shopping yesterday./
Yesterday I went shopping.
Two excellent public tennis
Adverbs of indefinite time: at the end or courts (opinion + type + purpose)
Adverbs indicating the
beginning of a sentence, or before the verb
Ex: She currently works as a journalist./
time when something Adverbs of Time The order can sometimes change: a In general, the adjective closest to the
Currently she works as a journalist./ She happens big horrible building
noun has the closest link in meaning
with the noun and expresses what is
works as a journalist currently.
POSITIONS
most permanent about it.
Old and young referring to
Adverbs of duration people often come next to the
Ex: She worked as a journalist for two years. noun: a dignified old lady
Adverbs of definite frequency: at the end or When two adjectives have similar
beginning of a sentence meanings, the shorter often comes
Ex: I pay my rent weekly. Adverbs telling how first: A bright, cheerful smile or a
Adverbs of soft, comfortable chair
often something
Adverbs of indefinite frequency: before the
happens Frequency
main (ordinary) verb, after the verb “be”, The Order Of Sometimes two orders are
between the auxiliary and the main verb
Ex: We usually go shopping on Sundays.
Attributive possible: a peaceful, happy face/
a happy, peaceful face
TYPES Adjectives
Adverbs answering the question And can be put between two adjectives:
a soft and comfortable chair
“To what extent...?”
Adverbs of Degree And is not used between adjectives
Before the adjective or adverb they modify with different meanings: beautiful
golden sands
Ex: He drove very fast.
But is used when the adjectives
Adverbs modifying the refer to two qualities in contrast: a
whole sentence cheap but effective solution
Sentence Adverbs -ing adjectives: people's/thing's
Usually at the beginning of the sentence features, characteristics
Ex: Unfortunately, Richard didn’t get to Participle As Ex: He's an interesting person.
the airport on time.
Adjectives -ed adjectives: people's feelings/emotions
Ex: I'm interested in him.
Adverbs indicating that what is being
communicated is limited to the part To refer to some groups of people in the
that is focused society: the poor, the rich
Focus Adverbs A few adjectives can come after a/an to
They limit the sense of the sentence or to act mean a specific person: Now as a
as an additive superstar, she was an unknown, only
Social groups two years ago.
Ex: He said he wanted to do only what was the
best for the country.
There are a few adjectives that can be
used as nouns: a black (= a black person)
Short adverbs: mono-syllabic adverbs
Short and Long The + Adjective For a whole people=> the + adjective of
Long adverbs: others (except EARLY)
Adverbs nationality: the English
To refer to things in general
It was almost dark. Abstract qualities having an abstract quality: the
new, the old, the unexplained
I have completely forgotten/I
have never forgotten/I will as + Adj + as
never have forgotten not so/as + Adj + as
completely, practically,
erb of Completeness follow
Emphatic used with "as many/much as" , "as few/little as" +
AUXILIARIES.
I kind of hope she win.
almost, nearly, quite,
ADVERB OF Equatives
number
I will have completely finished rather, partly, sort of, kind Ex: There are sometimes as many as 40 students in the class
by next June of, more or less, hardly, COMPLETENESS You can fly to Paris as little as 20 Euros.
Do you think the repair has
scarcely Twice/ two times / three times + as + adj/adv + as
Ex: My new laptop is twice as expensive as my old one/
been properly done?
My old laptop is half as expensive as my new one
When most is followed by an
One syllable --> Most adjectives BOTH: clear, free, keen, sage, sure, true, wise
adverb, THE is not used.
Ex: The reason is mentioned
MOST are short adjectives
(-ed; like; real; right; wrong)
most frequently.
BOTH: able, clever, common, cruel,
Inversion after adverbials of place/ position Regular (-er/the -est; feeble, gentle, handsome, narrow,
Ex: At the apple tree sat the boy. Inversion: a movement more/the most)
Short vs Long adjectives pleasant, polite, simple, sincere, stupid
Two-syllable: -ful; -less; -ing; -ed: LONG
operation by which the INVERSION (-y: SHORT)
Inversion after adverbials of movement
Ex: Down the hill ran the bus. order of two expressions WITH COMPARISON Three-syllable: LONG
is reversed ADVERBIALS (Exception: unhappy)
Inversion after negative adverbials
Ex: Under no circumstances can this ➔ subject-verb inversion
story be discussed with others. good - better - the best
bad - worse - the worst
many/much - more - the most
little - lest - the least
Irregular
far - further/farther - farthest/
furthest
Comparatives/
ill - worse - the worst
superlatives
few - fewer/less - the fewest/
least
-er and -er, more and more: The
colder it is, the hungrier I get.
The -er ... , the -er ...: The more,
DOUBLE
the merrier.
COMPARATIVES
The more ..., the more ...: The
more generous you are towards
others, the more generous they
are likely to be towards you.
The second method was less
complicated than the first one.
COMPARATIVE WITH
LESS This new laptop is not as fast as
my old one. I’m sorry I bought it
now.
You might also like
- Go Further Booklet 6Document56 pagesGo Further Booklet 6José Ramón Cruz Díaz100% (1)
- Berklee Shares - Essential Guide To Lyric Form and Structure - Lyrical Elements, The Great Juggling ArtDocument4 pagesBerklee Shares - Essential Guide To Lyric Form and Structure - Lyrical Elements, The Great Juggling Artkdnata19970% (2)
- Vocabulary RoutinesDocument13 pagesVocabulary Routineskim100% (1)
- THAI Grammar PDFDocument17 pagesTHAI Grammar PDFShirl100% (2)
- Parts of SpeechDocument2 pagesParts of SpeechТетяна ДармограйNo ratings yet
- Used To Express em Otional StatesDocument1 pageUsed To Express em Otional StatesClaudine S. UananNo ratings yet
- Mind Map 2Document1 pageMind Map 2Rizqy Dhinia100% (1)
- Fachri Meidiansyah - 06SIGE001 - SyntaxDocument8 pagesFachri Meidiansyah - 06SIGE001 - SyntaxFachri MeidiansyahNo ratings yet
- Adverbs 2Document1 pageAdverbs 2Minh Thuận Hoàng ThịNo ratings yet
- Basic Units of LanguageDocument1 pageBasic Units of LanguageAweekly EyesNo ratings yet
- Semantics: From Reference...Document1 pageSemantics: From Reference...Ma Minh HươngNo ratings yet
- Milton y Majo-MapasDocument4 pagesMilton y Majo-MapasJuddyNo ratings yet
- QUIZ Bahasa Inggris 1-Ikwan Nugroho RMIK-Smt 1Document2 pagesQUIZ Bahasa Inggris 1-Ikwan Nugroho RMIK-Smt 1ikwan nugrohoNo ratings yet
- Gramática Inglesa CN 2020Document11 pagesGramática Inglesa CN 2020PamelaNo ratings yet
- Mind Map - Unit 1Document1 pageMind Map - Unit 1freeloadtailieu2017No ratings yet
- Micor, Leijh Ann Jewel A. Ced-02-201P Mendiola, Aila O. ENG103Document1 pageMicor, Leijh Ann Jewel A. Ced-02-201P Mendiola, Aila O. ENG103Aila Obrero MendiolaNo ratings yet
- ADJECTIVESDocument4 pagesADJECTIVESPUTERI SOLEHAH BINTI ABDULLAH MoeNo ratings yet
- Adjective Clauses: Relative Pronouns & Relative ClausesDocument4 pagesAdjective Clauses: Relative Pronouns & Relative ClausesJaypee MelendezNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument31 pagesParts of Speechsergio alcazarNo ratings yet
- Pronoun MindmapDocument1 pagePronoun MindmapSlamet RiyadiNo ratings yet
- LL B GR VerbalsDocument10 pagesLL B GR VerbalsGuia Mae LondoñoNo ratings yet
- ADJECTIVESDocument3 pagesADJECTIVESKatherine ArcosNo ratings yet
- Adjectival ClausesDocument1 pageAdjectival ClausesPhương ThảoNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTIONDocument52 pagesINTRODUCTIONTannyNo ratings yet
- Phrases: Sebagai Subjek Predikat ObjekDocument1 pagePhrases: Sebagai Subjek Predikat ObjekTedhi Kerta KusumaNo ratings yet
- Tugas Bhs - InggrisDocument16 pagesTugas Bhs - InggrisFandy IrvansyahNo ratings yet
- I Bought From Him A BMW.: SemanticsDocument1 pageI Bought From Him A BMW.: Semantics--Kaki --No ratings yet
- Morphosyntax's Concept MapDocument2 pagesMorphosyntax's Concept MapFrancisco ReyesNo ratings yet
- Dictionary: Facilitates Learning. Quick, Accurate Search. Large Storage CapacityDocument1 pageDictionary: Facilitates Learning. Quick, Accurate Search. Large Storage CapacitypaolisNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Glossary For EnglishDocument20 pagesCurriculum Glossary For EnglishTUNGWAPE MIRIAMNo ratings yet
- Vocab Quiz Quiz Trade Cards PDFDocument6 pagesVocab Quiz Quiz Trade Cards PDFSteve XieNo ratings yet
- Concept Map/ Diagram: Perez, Angelika S. Bsed English 2ADocument4 pagesConcept Map/ Diagram: Perez, Angelika S. Bsed English 2AAngelika PerezNo ratings yet
- ADJECTIVESDocument1 pageADJECTIVESCHRISTIAN GEOVANNY ARIAS PARRANo ratings yet
- Generative Transformational Grammar: Syntactic ComponentsDocument2 pagesGenerative Transformational Grammar: Syntactic ComponentsNatali TorresNo ratings yet
- Adjectives and Adverbs PDFDocument72 pagesAdjectives and Adverbs PDFRenata RochaNo ratings yet
- Academic Word List (AWL) by Averil CoxheadDocument13 pagesAcademic Word List (AWL) by Averil CoxheadÇağatay CingözNo ratings yet
- Pronou Ns Are TheDocument1 pagePronou Ns Are TheArianne ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Parts of The SpeechDocument1 pageParts of The SpeechMoises HernandezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Figurative Language - Word MapDocument1 pageChapter 5 - Figurative Language - Word MapareszNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Language CurriculumDocument25 pagesGrade 7 Language CurriculumSkeeter MarshNo ratings yet
- Week 9 List 10Document1 pageWeek 9 List 10vscriven1803No ratings yet
- SENTENCES MergedDocument4 pagesSENTENCES MergedHuỳnh Võ Bích HuânNo ratings yet
- Framework RI.2.4 6thDocument3 pagesFramework RI.2.4 6thdirectora2012No ratings yet
- 00 Spanish Battle Plans All PDFDocument12 pages00 Spanish Battle Plans All PDFkhanik rajNo ratings yet
- 00 Spanish Battle Plans All PDFDocument12 pages00 Spanish Battle Plans All PDFRaka HadiyanNo ratings yet
- 00 Spanish Battle Plans All PDFDocument12 pages00 Spanish Battle Plans All PDFRaka HadiyanNo ratings yet
- Battle Plan: Grammar: The 8 Parts of SpeechDocument12 pagesBattle Plan: Grammar: The 8 Parts of SpeechasdfNo ratings yet
- NounFamily PDFDocument2 pagesNounFamily PDFЖанар ЖупбановаNo ratings yet
- Defining and Non Defining Group 1 (Ribbery, Kristian, Nova, Allegra)Document9 pagesDefining and Non Defining Group 1 (Ribbery, Kristian, Nova, Allegra)Fitria Permata SariNo ratings yet
- Pronou Ns Are TheDocument1 pagePronou Ns Are TheArianne ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Connecting Utterances To The Background - Word MapDocument1 pageChapter 9 - Connecting Utterances To The Background - Word MapareszNo ratings yet
- ADVERBSDocument1 pageADVERBSPUTERI SOLEHAH BINTI ABDULLAH MoeNo ratings yet
- Grammar and Punctuation Scope and SeqDocument2 pagesGrammar and Punctuation Scope and SeqMaureen WallNo ratings yet
- Super HandoutsDocument24 pagesSuper Handoutsvictoria tuazonNo ratings yet
- Adverbial ClausesDocument1 pageAdverbial ClausesMinh Thuận Hoàng ThịNo ratings yet
- Grammar 2Document6 pagesGrammar 2Roberto HerreraNo ratings yet
- Grammar HandbookDocument24 pagesGrammar Handbookgt211No ratings yet
- Edu Trans MidDocument5 pagesEdu Trans MidRismaNo ratings yet
- File 8 - Vocab - Making Adjectives and Adverbs - PracticeDocument1 pageFile 8 - Vocab - Making Adjectives and Adverbs - Practicelilianac02323No ratings yet
- Morphology Tema 1Document20 pagesMorphology Tema 1Melisa PontónNo ratings yet
- Apuntes de Ingles - VerbosDocument9 pagesApuntes de Ingles - VerbosJuan Francisco ValeroNo ratings yet
- The Passive Voice ClassDocument7 pagesThe Passive Voice ClassTeresa AdpNo ratings yet
- Rhyan Laufer Leal - 2º ANO - SIMPLE PRESENT AND SIMPLE PASTDocument2 pagesRhyan Laufer Leal - 2º ANO - SIMPLE PRESENT AND SIMPLE PASTRhyan LauferNo ratings yet
- Topic 11 H de La LenguaDocument11 pagesTopic 11 H de La LenguaMamenvsNo ratings yet
- Plural - Nouns RulesDocument13 pagesPlural - Nouns RulesLuis Catalan LeonNo ratings yet
- Clerk Final Syllabus Advt 15 of 2022Document3 pagesClerk Final Syllabus Advt 15 of 2022Pankaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Group 2Document9 pagesGroup 2MiaNo ratings yet
- Gram Exp U51 Infinitives of Purpose 3Document5 pagesGram Exp U51 Infinitives of Purpose 3api-515535366No ratings yet
- New Wordpad DocumentDocument10 pagesNew Wordpad DocumentBalach M. TheboNo ratings yet
- Sentence Types-1 PDFDocument2 pagesSentence Types-1 PDFGiovana Montenegro VacaNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech: AnthologyDocument23 pagesParts of Speech: Anthologyapi-540657733No ratings yet
- Simple Present - Simple PastDocument12 pagesSimple Present - Simple PastJuaKo NavidadNo ratings yet
- Dependent PrepositionsDocument4 pagesDependent PrepositionsChimera EarthaNo ratings yet
- Chapter IiDocument25 pagesChapter Iiahmad fahmiNo ratings yet
- Keys06 Grammar Boook English 2.0Document1 pageKeys06 Grammar Boook English 2.0acNo ratings yet
- TOEFL Meeting 12Document29 pagesTOEFL Meeting 12customer serviceNo ratings yet
- Verbs Past Present and Future TenseDocument2 pagesVerbs Past Present and Future Tensecarmelo3004100% (1)
- Tenses in EnglishDocument76 pagesTenses in Englishmusa_ks100% (1)
- Grammar Rules - List of Attached PhrasesDocument3 pagesGrammar Rules - List of Attached PhrasesMarlon KhanNo ratings yet
- AFFIXATIONDocument10 pagesAFFIXATIONHala Tawfik MakladNo ratings yet
- 2023 - 01 - 27 - RL ClassDocument19 pages2023 - 01 - 27 - RL ClassChristine OctaviaNo ratings yet
- Word OrderDocument80 pagesWord OrdernlrahmahNo ratings yet
- English Qualifier Exam Set BDocument8 pagesEnglish Qualifier Exam Set BAnkanPattanayakNo ratings yet
- Aymara 3Document2 pagesAymara 3Carla Gutierrez FloresNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Describing PeopleDocument5 pagesLesson 4 - Describing Peoplemahfud fajriansyahNo ratings yet
- Prefix and SuffixDocument14 pagesPrefix and Suffixmirza100% (2)
- 8 Parts of SpeechDocument1 page8 Parts of SpeechCharity PalerNo ratings yet