Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BT21EE008 - Experiment-14 Group-01
BT21EE008 - Experiment-14 Group-01
Uploaded by
BT21EE013 Pratima0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views8 pagesOriginal Title
BT21EE008_Experiment-14 Group-01
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views8 pagesBT21EE008 - Experiment-14 Group-01
BT21EE008 - Experiment-14 Group-01
Uploaded by
BT21EE013 PratimaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 8
Name – Prashant Kumar
Enrollment Number – BT21EE008 (Group-01)
Subject – EEP-1505
Experiment Name - Perform the open circuit characteristics of
synchronous generator
Experiment Number -01
Aim :- Perform the open circuit characteristics of a synchronous
generator.
Objective:
The objective of this experiment is to investigate the open circuit
characteristics of a synchronous generator to understand its voltage
regulation, synchronous reactance, and determine the magnetization
curve.
Apparatus Required:
Sl. Appartus Specification Quantity
No
1. Three phase synchronous Power Rating: 3 HP 01
generator Voltage Rating: 440 V
Current Rating: 4.8
Speed Rating: 1440 rpm
2. Ammeter (0-20) A 01
3. Voltmeter (0-300) volt 01
4. Tachometer Digital Contact type 01
5. Variable DC supply (0-230) volt 01
6. Connecting Wires As per Requirement 01
7. Rheostat 400V,2.3A 01
Theory:
The open circuit characteristics of a synchronous generator provide
insights into its voltage regulation, synchronous reactance, and the
magnetization curve. These characteristics help engineers and
researchers understand the generator's behavior under different
operating conditions.
1. Voltage Regulation:
Voltage regulation in a synchronous generator refers to its ability to
maintain a nearly constant terminal voltage when subjected to varying
loads or changes in excitation. The terminal voltage, V, can be
expressed in terms of the generator's synchronous reactance, X_s, and
the armature current, I_a, as follows:
V = E - I_a * X_s
Where:
V is the terminal voltage.
E is the generated electromotive force (EMF).
I_a is the armature current.
X_s is the synchronous reactance.
Voltage regulation, expressed as a percentage, can be calculated using
the following formula:
Voltage Regulation (%) = (V_no-load - V_full-load) / V_full-load *
100%
Where:
V_no-load is the terminal voltage at no-load condition.
V_full-load is the terminal voltage at full-load condition.
2. Synchronous Reactance:
The synchronous reactance (X_s) represents the impedance of the
synchronous generator when it is operating under open circuit
conditions. It is a measure of the generator's opposition to the flow of
current in its armature winding. The synchronous reactance is
calculated as:
X_s = V_no-load / I_excitation
Where:
V_no-load is the terminal voltage at no-load condition.
I_excitation is the excitation current.
3. Magnetization Curve:
The magnetization curve, also known as the no-load saturation curve,
depicts the relationship between the terminal voltage (V) and the
rotational speed (N) of the generator when it operates under open
circuit conditions.
The generator's electromotive force (E) is proportional to its speed N
and excitation current I_excitation:
E = k * N * I_excitation
Where:
E is the generated electromotive force (EMF).
k is a constant depending on the generator's design and construction.
By plotting terminal voltage (V) against rotational speed (N), you can
determine the magnetization curve, which provides valuable
information about the generator's performance characteristics.
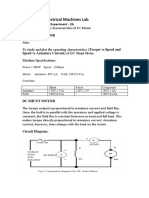
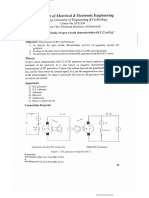
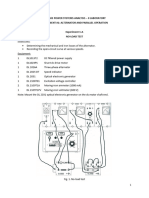
Circuit Diagram :
Fig 1.1:- circuit diagram for experimental open circuit test of Three
phase synchronous generator
Procedure:
1. Connect the synchronous generator to the excitation source using
suitable wiring, ensuring the polarity is correct.
2. Connect an ammeter in series with the excitation circuit to
measure the excitation current.
3. Connect a voltmeter to measure the terminal voltage of the
generator.
4. Connect a tachometer to measure the rotational speed of the
generator.
5. Connect a multimeter to measure any other necessary electrical
parameters.
Observation Table :-
Sl. No V(volt ) I(A) Speed(rpm)
1) 111 0.1 1491
2) 136 0.14 1490
3) 171 0.19 1485
4) 186 0.21 1497
5) 234 0.28 1484
6) 262 0.32 1498
7) 292 0.36 1509
8) 345 0.47 1510
9) 350 0.49 1466
Result:-
1. Voltage Regulation:
The following data was collected to calculate voltage regulation:
Terminal voltage at no-load condition (V_no-load) = 240 V
Terminal voltage at full-load condition (V_full-load) = 230 V
Voltage Regulation (%) = [(240 V - 230 V) / 230 V] * 100% = 4.35%
The generator exhibits a voltage regulation of approximately 4.35%
from no-load to full-load conditions, indicating good voltage control
capabilities.
Conclusion:-
In conclusion, the open circuit characteristics of the synchronous
generator were studied. The generator demonstrated a voltage
regulation of approximately 4.35% from no-load to full-load conditions,
indicating its capability to maintain a stable terminal voltage. The
synchronous reactance was calculated to be approximately 48 ohms,
showing its impedance under open circuit conditions. The
magnetization curve provided insights into how the terminal voltage
varies with rotational speed and excitation current. These findings
contribute to a better understanding of the generator's behavior and its
suitability for specific applications in power generation and
distribution.
Precautions:-
1. Always disconnect the generator from the main power source
before starting the experiment to avoid electrical accidents.
2. Ensure all electrical connections are secure and insulated to
prevent short circuits or electrical shocks.
3. Thoroughly inspect all equipment and wiring to ensure they are in
good working condition before starting the experiment.
4. Report any damaged or malfunctioning equipment to the
supervisor.
You might also like
- Prismic A 30 AVR Manual Rev DDocument132 pagesPrismic A 30 AVR Manual Rev DOperadores Termosuria TermosuriaNo ratings yet
- LAB REPORT NO 12 (Electrical Engineering)Document8 pagesLAB REPORT NO 12 (Electrical Engineering)Malik Hassaan SangraalNo ratings yet
- Exp. 3 - Load Test and Equivalent Circuit Determination On Three Phase Squirrel Cage Induction Motor andDocument9 pagesExp. 3 - Load Test and Equivalent Circuit Determination On Three Phase Squirrel Cage Induction Motor andSanjay MeenaNo ratings yet
- The Synchronous Generator: 2.1. Synchronizing A Generator To An AC SystemDocument10 pagesThe Synchronous Generator: 2.1. Synchronizing A Generator To An AC SystemsantoshkumarNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Generator - Lab ReportDocument8 pagesSynchronous Generator - Lab ReportBarbara Coelho40% (5)
- Generator Protection Relay SettingsDocument59 pagesGenerator Protection Relay SettingsRamakrishna86% (7)
- Exp. 2 - OCC and Load Test On AlternatorDocument7 pagesExp. 2 - OCC and Load Test On AlternatorKailash Jagarwal100% (1)
- Em Lab-II ManualDocument45 pagesEm Lab-II Manualrkadiraj701160% (5)
- Experiment - No.10 Load Test On DC Shunt Motor: DATE:10/12/2021Document6 pagesExperiment - No.10 Load Test On DC Shunt Motor: DATE:10/12/2021Baba YagaNo ratings yet
- Eep 203 Electromechanics LaboratoryDocument65 pagesEep 203 Electromechanics Laboratorysourabh_rohillaNo ratings yet
- M.A.M School of Engineering TRICHY - 621 105Document97 pagesM.A.M School of Engineering TRICHY - 621 105Preethi RanganathanNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.2: Operation of D.C Motors, Running and ReversingDocument10 pagesExperiment No.2: Operation of D.C Motors, Running and Reversingwrya hussainNo ratings yet
- 2 Machine LabDocument4 pages2 Machine LabManoj GuptaNo ratings yet
- P1 - DC Motor Position Control PDFDocument10 pagesP1 - DC Motor Position Control PDFSeptiani DitaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5Document8 pagesExperiment 5rastgonikoNo ratings yet
- Modul P2Document10 pagesModul P2Wahjue AjhiieNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1Document7 pagesExperiment 1عبدالعزيز شقحانNo ratings yet
- Open Circuit Saturation Curve of An Alternator I. ObjectivesDocument4 pagesOpen Circuit Saturation Curve of An Alternator I. ObjectivesArnel Pamaos Lopiba MontañezNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines-II (EX-503) : Practical Work BookDocument25 pagesElectrical Machines-II (EX-503) : Practical Work BookFilipe Braga CoutoNo ratings yet
- ME 39-Electrical Engineering Lab ManualDocument111 pagesME 39-Electrical Engineering Lab ManualSuma Rani GNo ratings yet
- Machine Manual PDFDocument35 pagesMachine Manual PDFh1169104No ratings yet
- Machines Lab ManualDocument124 pagesMachines Lab ManualpurushothNo ratings yet
- ME2143-1 Lab ManualDocument10 pagesME2143-1 Lab ManualJoshua ChooNo ratings yet
- Three Phase Induction MotorDocument6 pagesThree Phase Induction MotorCønstäh Van Der WüppertälärîanskíhNo ratings yet
- E M 1 Lab ManualDocument63 pagesE M 1 Lab ManualdsparanthamanNo ratings yet
- DC Motor Speed Control System - ED4400BDocument14 pagesDC Motor Speed Control System - ED4400BDanang Pradika Purnomo100% (1)
- Chapter 1 DC Drives Part2Document75 pagesChapter 1 DC Drives Part2Mohammad MunzirNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines Lab: Experiment 2ADocument9 pagesElectrical Machines Lab: Experiment 2AARTI RAWATNo ratings yet
- Yahya 1210983 Ex4Document18 pagesYahya 1210983 Ex4yahya333.pNo ratings yet
- Terco MTR InduksiDocument51 pagesTerco MTR InduksiNovan A ImanNo ratings yet
- EMMPRA3 PracticalGuide - 2021Document14 pagesEMMPRA3 PracticalGuide - 2021Tshepo MolotoNo ratings yet
- Experiment For IEDocument8 pagesExperiment For IEUzma IlyasNo ratings yet
- Machine - Lab Manual Merged PDFDocument14 pagesMachine - Lab Manual Merged PDFMubin LikhonNo ratings yet
- Besic Electrical Engineering Lab: Experiment - 8Document9 pagesBesic Electrical Engineering Lab: Experiment - 8Rajesh RajNo ratings yet
- 120EE1098 - Vennela Medaboina - Merged BEE Report-CompressedDocument83 pages120EE1098 - Vennela Medaboina - Merged BEE Report-CompressedSahasrabda Sai PradhanNo ratings yet
- Prosedur Percobaan Motor SinkronSinkron Generator SinkronDocument10 pagesProsedur Percobaan Motor SinkronSinkron Generator SinkronDara AmeliaNo ratings yet
- EE6365 EE Lab ManualDocument58 pagesEE6365 EE Lab Manualjk100% (1)
- EEE363 (Exp 10) Study of The Operating Characteristics and Torque Speed Relationship of Capacitor Start Motor & Run MotorDocument8 pagesEEE363 (Exp 10) Study of The Operating Characteristics and Torque Speed Relationship of Capacitor Start Motor & Run Motorsalad.ass420420No ratings yet
- Experiment No:01 Name of The Experiment: Observation of No Load and Full Load Characteristics of A Three-PhaseDocument16 pagesExperiment No:01 Name of The Experiment: Observation of No Load and Full Load Characteristics of A Three-PhaseRupalNo ratings yet
- EEM483 Experiment1Document10 pagesEEM483 Experiment1Onat ŞenelNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Induction MotorsDocument17 pagesLaboratory Induction MotorsEsteban GilNo ratings yet
- CSLABMANUALDocument99 pagesCSLABMANUALGOKUL RNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Act 2 Group4Document10 pagesLaboratory Act 2 Group4Danielle Aubrey TerencioNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines Lab ManualDocument41 pagesElectrical Machines Lab Manualsohaib hashmatNo ratings yet
- Exp 7Document11 pagesExp 7John Renzel RiveraNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2Document4 pagesExperiment 2dhruvmistry300No ratings yet
- Electrical Machines-I Lab ManualDocument24 pagesElectrical Machines-I Lab Manualankur_sharma_95No ratings yet
- Starting, Speed Control....Document6 pagesStarting, Speed Control....dickmjoloNo ratings yet
- s5 Lab Manual Full FinalDocument45 pagess5 Lab Manual Full FinalananyadeviashokkumarNo ratings yet
- Machine Based Experiments Lab Report-1 Name: Karthickeien E BY: CH - EN.U4CCE21024 Group: A TopicDocument14 pagesMachine Based Experiments Lab Report-1 Name: Karthickeien E BY: CH - EN.U4CCE21024 Group: A TopicKartheepan KaNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronics Lab Manual For Mechanical EngineeringDocument21 pagesElectrical and Electronics Lab Manual For Mechanical EngineeringSreerag Kunnathu SugathanNo ratings yet
- Beee Lab ManualDocument36 pagesBeee Lab ManualChanduVarmaKalidindiNo ratings yet
- Power Generation Transmission Lab ManualDocument69 pagesPower Generation Transmission Lab ManualMuzammil NaeemNo ratings yet
- Some Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSome Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlFrom EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1From EverandNewnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- CompositeinsulatorDocument13 pagesCompositeinsulatorBT21EE013 PratimaNo ratings yet
- Assignment SolutionDocument4 pagesAssignment SolutionBT21EE013 PratimaNo ratings yet
- Sample ProgramsDocument3 pagesSample ProgramsBT21EE013 PratimaNo ratings yet
- Vision-Based UAV Collision Avoidance With 2D Dynamic Safety EnvelopeDocument11 pagesVision-Based UAV Collision Avoidance With 2D Dynamic Safety EnvelopeBT21EE013 PratimaNo ratings yet
- CSM (Charge Simulation Method)Document9 pagesCSM (Charge Simulation Method)BT21EE013 PratimaNo ratings yet
- Energy-Constrained Delivery of Goods With Drones Under Varying Wind Conditions 1Document13 pagesEnergy-Constrained Delivery of Goods With Drones Under Varying Wind Conditions 1BT21EE013 PratimaNo ratings yet
- D8.048.06.0.00 User Manual of KG541 ControllerDocument36 pagesD8.048.06.0.00 User Manual of KG541 ControllerAlfiya AnamNo ratings yet
- Excitation Contactors From 80 To 7500 A v06rDocument46 pagesExcitation Contactors From 80 To 7500 A v06rMridu Ranjan SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- University Question Bank For PSP - Unit 05Document2 pagesUniversity Question Bank For PSP - Unit 05ptarwatkar123No ratings yet
- LR-G200 Rebar Scanner PDFDocument65 pagesLR-G200 Rebar Scanner PDFJohn Carlo AmodiaNo ratings yet
- Field Flashing A GeneratorDocument2 pagesField Flashing A GeneratorJJNo ratings yet
- Static Excitation EquipmentDocument54 pagesStatic Excitation EquipmentSwathi PrasadNo ratings yet
- Hydro GeneratorDocument34 pagesHydro Generatorhardy113100% (1)
- EM10Document5 pagesEM10Waleed AlzuodNo ratings yet
- DCA-Series July.2023Document20 pagesDCA-Series July.2023Nguyen Thang LongNo ratings yet
- UCDI274K 311 1P TD EN - Rev - ADocument10 pagesUCDI274K 311 1P TD EN - Rev - AMuntasir MunirNo ratings yet
- TR13 - REF NCT - Old CT - NCT PH - REF CT - 1 - Copy (3 Files Merged)Document104 pagesTR13 - REF NCT - Old CT - NCT PH - REF CT - 1 - Copy (3 Files Merged)SARAVANAN ANo ratings yet
- Rich Operation Experiences and New Technologies On Adjustable Speed Pumped Storage Systems in JapanDocument8 pagesRich Operation Experiences and New Technologies On Adjustable Speed Pumped Storage Systems in JapanR0B0T2013100% (1)
- 13-Thermal-Power-Plant-Plomin2 (Thermo Power Plant Plomin 2 - Končar KET) PDFDocument20 pages13-Thermal-Power-Plant-Plomin2 (Thermo Power Plant Plomin 2 - Končar KET) PDFdayiroNo ratings yet
- Tutorial1 (SynchronousMchines)Document3 pagesTutorial1 (SynchronousMchines)Zamira JamilNo ratings yet
- Stamford MX321 Avr PDFDocument4 pagesStamford MX321 Avr PDFAhmed Sherif CupoNo ratings yet
- Excellence in Generator Control: Hycon Thyricon ExcitationDocument11 pagesExcellence in Generator Control: Hycon Thyricon Excitationcosty_transNo ratings yet
- TUGASAN KUMPULAN (DC Generator)Document43 pagesTUGASAN KUMPULAN (DC Generator)Zainuddin BusuNo ratings yet
- Lab 08 - DC GeneratorsDocument9 pagesLab 08 - DC GeneratorsGaloenkz100% (1)
- Aaaaaa Electrical Generators and Excitation Systems TOKOLOGO MOTORS MPUMALANGADocument7 pagesAaaaaa Electrical Generators and Excitation Systems TOKOLOGO MOTORS MPUMALANGAcraig pretoriusNo ratings yet
- MEO Orals On Marine Electro Technology Function 5Document2 pagesMEO Orals On Marine Electro Technology Function 5Salih Tuğrul SarıNo ratings yet
- DM110Document2 pagesDM1103efooNo ratings yet
- EEM Electric MachinesDocument17 pagesEEM Electric Machinesgilles vanexeNo ratings yet
- Review of Free Energy GeneratorDocument7 pagesReview of Free Energy GeneratorAmode OlamideNo ratings yet
- 2 Unit 35-61Document25 pages2 Unit 35-61806 Ansh gargNo ratings yet
- Brochure JeumontDocument20 pagesBrochure JeumontMarioNo ratings yet
- DC Motor TypesDocument20 pagesDC Motor TypesHans Paolo Palomaria CamNo ratings yet
- Lab Compre Question Bank 2017 2018Document4 pagesLab Compre Question Bank 2017 2018Vaibhav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Objective: TH THDocument27 pagesObjective: TH THMerina AdhikariNo ratings yet