Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Vocabulary 1 - Anatomy of The Eye
Vocabulary 1 - Anatomy of The Eye
Uploaded by
Osvaldo Ariel TonelloCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Katsushi Ikeuchi (Editor) - Computer Vision - A Reference Guide-Springer (2021)Document1,436 pagesKatsushi Ikeuchi (Editor) - Computer Vision - A Reference Guide-Springer (2021)Wendy Contreras100% (1)
- Traffic Engineering Module - 1Document35 pagesTraffic Engineering Module - 1Shri Deer100% (1)
- Preparing and Trying A Civil CaseDocument82 pagesPreparing and Trying A Civil CaseOsvaldo Ariel TonelloNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Eye Ear and SkinDocument7 pagesAnatomy of Eye Ear and Skina62882975No ratings yet
- D Out About Different Parts of The EyeDocument2 pagesD Out About Different Parts of The EyeAljhon DelfinNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The EyeDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The EyeBryan Espanol100% (1)
- Physiology of The Eye and Visual Trans Duct IonDocument9 pagesPhysiology of The Eye and Visual Trans Duct IonJoie Sheen BastianNo ratings yet
- Eyes Health AssessmenttDocument34 pagesEyes Health AssessmenttMhiaBuenafeNo ratings yet
- Sense Organs: Structure of Human EyeDocument8 pagesSense Organs: Structure of Human EyeRanveer SinghNo ratings yet
- Special Sense Pathway: Visual, Auditory, VestibularDocument56 pagesSpecial Sense Pathway: Visual, Auditory, Vestibularmyka brilliant cristobalNo ratings yet
- Visual OrganDocument43 pagesVisual Organmahdia18No ratings yet
- Sensory OrgansDocument11 pagesSensory OrgansCurex QANo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The EyeDocument3 pagesAnatomy of The EyeKina KinaNo ratings yet
- Human Eye NotesDocument2 pagesHuman Eye Notesndee072No ratings yet
- Unit 13 Sence OrganDocument132 pagesUnit 13 Sence OrganChandan ShahNo ratings yet
- Olfactory, Eye, Ear'nOTESDocument23 pagesOlfactory, Eye, Ear'nOTESTida TpNo ratings yet
- C1 F3 BiodiversityDocument112 pagesC1 F3 BiodiversityNurul Shafiah Mustafa KamalNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of The EyesDocument5 pagesStructure and Function of The EyesPreeti ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Physiology of EyeDocument17 pagesPhysiology of EyeHanna ShibuNo ratings yet
- Eye and VisionDocument19 pagesEye and VisionVincent PolicarNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual (Special Senses)Document6 pagesLab Manual (Special Senses)Francis GarcesNo ratings yet
- Fact Sheet Eye How The Eye and Brain Work Together PDFDocument4 pagesFact Sheet Eye How The Eye and Brain Work Together PDFWy TeayNo ratings yet
- Sense Organ: Diyah Candra AnitaDocument35 pagesSense Organ: Diyah Candra AnitaNamulondo Mwajib Bogere100% (1)
- Sheena The EyeDocument9 pagesSheena The EyeSheena Yen de Pano-PagdalianNo ratings yet
- Iris Muscle - (Most Anterior Extension: EyeballDocument8 pagesIris Muscle - (Most Anterior Extension: EyeballBianx Flores DosdosNo ratings yet
- L5 - 2 - Special SensesDocument87 pagesL5 - 2 - Special Sensesbotchwaylilian17No ratings yet
- Structure of EyeDocument24 pagesStructure of Eyedipendrakumarkushawaha44No ratings yet
- Each Eyeball Is Positioned in A Bony Depression in The Skull Called Orbit. - Only The Anterior One-Sixth of The Eye's Surface Can Normally Be SeenDocument14 pagesEach Eyeball Is Positioned in A Bony Depression in The Skull Called Orbit. - Only The Anterior One-Sixth of The Eye's Surface Can Normally Be SeenMark AngeloNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The EyesDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The EyesNkk Aqnd MgdnglNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Eyes-BiopsyDocument20 pagesAnatomy of Eyes-BiopsynandanitriadiningsihNo ratings yet
- Visual and AuditoryDocument7 pagesVisual and AuditoryChristi EspinosaNo ratings yet
- The Eye The Eyeball Has Three TunicsDocument6 pagesThe Eye The Eyeball Has Three TunicsLara ShayaNo ratings yet
- The Sensory Organs: Anatomy Department Hasanuddin UniversityDocument117 pagesThe Sensory Organs: Anatomy Department Hasanuddin UniversityamiraNo ratings yet
- The EyeDocument6 pagesThe EyeDebiprasad GhoshNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of An EyeDocument12 pagesAnatomy of An EyeSuahniNo ratings yet
- Presentation1 (2) 4Document10 pagesPresentation1 (2) 4Shokunbi TolaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 f3Document113 pagesChapter 1 f3FAthiyah Abdul RahimNo ratings yet
- Sense Organs NotesDocument13 pagesSense Organs NotesVijay Laxmi MundhraNo ratings yet
- Technical College of Health ShekhanDocument9 pagesTechnical College of Health ShekhanSaadNo ratings yet
- Part 13 - Human Sensory Organs AnatomyDocument21 pagesPart 13 - Human Sensory Organs AnatomyAmal Naeem JHNo ratings yet
- 1-Anatomy of The EyeDocument2 pages1-Anatomy of The EyeRadhwanNo ratings yet
- Structure of Eye !Document11 pagesStructure of Eye !Leonora KadriuNo ratings yet
- Your Eye AnatomyDocument4 pagesYour Eye AnatomyAljhon DelfinNo ratings yet
- Vision: Chapter 9: SensesDocument21 pagesVision: Chapter 9: SenseshoneykrizelNo ratings yet
- Special Senses EYEDocument4 pagesSpecial Senses EYEDevendra RawatNo ratings yet
- An Organ That Receives and Relays Information About The Body's Senses To The BrainDocument59 pagesAn Organ That Receives and Relays Information About The Body's Senses To The BrainIsarra AmsaluNo ratings yet
- Perception and Coordination Lesson 1.2Document4 pagesPerception and Coordination Lesson 1.2Lovely CruzxNo ratings yet
- Bionic Eye EB KNS 2019Document58 pagesBionic Eye EB KNS 2019Lalitaditya DivakarlaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The EyeDocument2 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The EyeKeanu Jay MaltosNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The EyeDocument4 pagesAnatomy of The EyeSabrinaAyuPutriNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY OF THE EYE (Organ of Vision) by DR Omeje EmmanuelDocument31 pagesANATOMY OF THE EYE (Organ of Vision) by DR Omeje Emmanuelchidera100% (2)
- Info Sheet 4 - 1Document8 pagesInfo Sheet 4 - 1Francis ObmergaNo ratings yet
- Assignment Submitted To: Sir Muneeb Ahmad Submitted By: Ayesha Farooq Roll No: 19010920-104 Course: PSY 101 Section: Bba (B)Document9 pagesAssignment Submitted To: Sir Muneeb Ahmad Submitted By: Ayesha Farooq Roll No: 19010920-104 Course: PSY 101 Section: Bba (B)Ayesha FarooqNo ratings yet
- Human Eye 13Document1 pageHuman Eye 13Dorcas CuevasNo ratings yet
- Lo Week 3 Blok Sss - April 2Document12 pagesLo Week 3 Blok Sss - April 2mellyNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology 1st SessionDocument26 pagesOphthalmology 1st SessionWais samarNo ratings yet
- Creating 3D Eyes: One: The Anatomy of The Human EyeDocument2 pagesCreating 3D Eyes: One: The Anatomy of The Human Eyekora_c995No ratings yet
- Health Assessment Nursing Chapter 11: EyesDocument3 pagesHealth Assessment Nursing Chapter 11: EyesRobin OommenNo ratings yet
- EENT Review ManualDocument19 pagesEENT Review ManualJohn Darvin TanNo ratings yet
- EyeballDocument14 pagesEyeballMirko BelanNo ratings yet
- Special SensesDocument21 pagesSpecial SensesJhemDelfinNo ratings yet
- Human Senses: Monique MavronicolasDocument10 pagesHuman Senses: Monique MavronicolasMonique MavronicolasNo ratings yet
- Low Vision: Assessment and Educational Needs: A Guide to Teachers and ParentsFrom EverandLow Vision: Assessment and Educational Needs: A Guide to Teachers and ParentsNo ratings yet
- Test On Past Tenses and Filming VocabularyDocument2 pagesTest On Past Tenses and Filming VocabularyOsvaldo Ariel TonelloNo ratings yet
- Hello, Hello - SongDocument1 pageHello, Hello - SongOsvaldo Ariel TonelloNo ratings yet
- Differences Between American and British EnglishDocument3 pagesDifferences Between American and British EnglishOsvaldo Ariel TonelloNo ratings yet
- English Test Dietetics - 30-Minute VersionDocument1 pageEnglish Test Dietetics - 30-Minute VersionOsvaldo Ariel TonelloNo ratings yet
- Dictionary of Health Related Terms English SpanishDocument77 pagesDictionary of Health Related Terms English Spanishjosemiguel100% (4)
- Colors DocDocument12 pagesColors DocTeorija PajaclukaNo ratings yet
- TaxanomyDocument32 pagesTaxanomyChucho Reach100% (1)
- ABE 313 Properties of AB Materials Module 6Document21 pagesABE 313 Properties of AB Materials Module 6Eloisa Marie SilausoNo ratings yet
- 691566643060unit-6 - Housing and Interior DesignDocument13 pages691566643060unit-6 - Housing and Interior DesignGaganpreet Kaur Fashion Designing100% (1)
- Vrinda ThesisDocument58 pagesVrinda ThesisArun FizardoNo ratings yet
- Cyborg Parts and Implants - Fallout 2d20Document22 pagesCyborg Parts and Implants - Fallout 2d20PoohatyNo ratings yet
- Eye PhysiologyDocument11 pagesEye PhysiologyAmanuel DinaNo ratings yet
- Vision Development - Childhood - American Academy of OphthalmologyDocument1 pageVision Development - Childhood - American Academy of Ophthalmologysneha duttaNo ratings yet
- Leonardo Da Vinci's Study of Light and Optics: A Synthesis of Fields in The Last Supper by Nicole BitlerDocument9 pagesLeonardo Da Vinci's Study of Light and Optics: A Synthesis of Fields in The Last Supper by Nicole BitlerAllie IelanNo ratings yet
- Places and LandscapeDocument113 pagesPlaces and LandscapeJimson SolisNo ratings yet
- Science of ColorsDocument6 pagesScience of Colorsprateeksaxena88100% (1)
- Material Color Code Identification - BarzanDocument1 pageMaterial Color Code Identification - BarzanMadhavMitruNo ratings yet
- Latihan PTS PEC Pamulang 1,2Document2 pagesLatihan PTS PEC Pamulang 1,2Pec Pamulang 1No ratings yet
- Es2 SC 179 The Sense of Sight Labelling Activity SheetDocument4 pagesEs2 SC 179 The Sense of Sight Labelling Activity Sheethamsat_eshq_51681625No ratings yet
- Humanities 11 - Introduction To Arts Color WheelDocument9 pagesHumanities 11 - Introduction To Arts Color Wheelmarangen125No ratings yet
- PG 03 TextDocument25 pagesPG 03 TextMohammed JammaNo ratings yet
- Is The Visual PoliticalDocument108 pagesIs The Visual PoliticalAbidin ZeinNo ratings yet
- Rethinking Psychological Anthropology - Continuity and Change in The Study of Human Action (2nd Ed)Document317 pagesRethinking Psychological Anthropology - Continuity and Change in The Study of Human Action (2nd Ed)bakbolom100% (3)
- Print-Testing-Tools-Mir - Copy-MergedDocument2 pagesPrint-Testing-Tools-Mir - Copy-Mergedbelive itNo ratings yet
- GE 106 Art Appreciation WK 3Document18 pagesGE 106 Art Appreciation WK 3daryl.pradoNo ratings yet
- Flock Color Scheme Worksheets - 1Document5 pagesFlock Color Scheme Worksheets - 1Olivia GogasNo ratings yet
- Computational Ethics - 1-S2.0-S1364661322000456-MainDocument18 pagesComputational Ethics - 1-S2.0-S1364661322000456-MainIRWA BUCHNo ratings yet
- Ingold SurfaceVisions PDFDocument10 pagesIngold SurfaceVisions PDFDirceu MauésNo ratings yet
- Ecological Approach: James Gibson'SDocument13 pagesEcological Approach: James Gibson'SmmtruffautNo ratings yet
- Sway Trumpet PDFDocument1 pageSway Trumpet PDFOleg Zaiat0% (1)
- Eye Examination: OSCE ChecklistDocument2 pagesEye Examination: OSCE ChecklistMohamed Anas SayedNo ratings yet
- Chart - Stitch FiddleDocument3 pagesChart - Stitch FiddleKnot by AlkiNo ratings yet
- Children and Their Development 6th Edition Kail Test BankDocument33 pagesChildren and Their Development 6th Edition Kail Test Bankdaywoman.frachozbkywc100% (35)
Vocabulary 1 - Anatomy of The Eye
Vocabulary 1 - Anatomy of The Eye
Uploaded by
Osvaldo Ariel TonelloOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Vocabulary 1 - Anatomy of The Eye
Vocabulary 1 - Anatomy of The Eye
Uploaded by
Osvaldo Ariel TonelloCopyright:
Available Formats
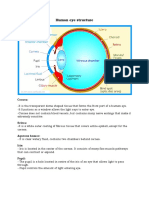
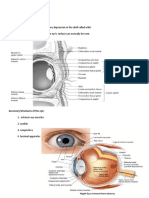
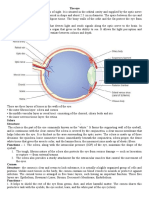
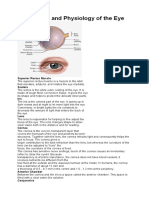
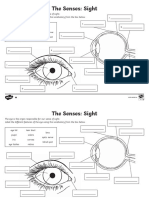
Anatomy of the Eye
Accommodation - Accommodation - The process by which the eye changes optical power to maintain a clear
image or focus on an object as its distance changes.
Anterior chamber - Chambre antérieure - The fluid-filled space inside the eye between the iris and the
cornea's innermost surface.
Aqueous humor - Humour aqueux - The clear fluid in the front part of the eye, helping to maintain intraocular
pressure and nourish the cornea and lens.
Binocular vision - Vision binoculaire - The ability to maintain visual focus on an object with both eyes,
creating a single visual image.
Blind spot - Tache aveugle - The point in the visual field that corresponds to the lack of light-detecting
photoreceptor cells on the optic disc of the retina where the optic nerve passes through to the brain.
Choroid - Choroïde - The vascular layer of the eye between the retina and the sclera that provides oxygen and
nourishment to the outer layers of the retina.
Ciliary body - Corps ciliaire - A ring of tissue behind the iris that is responsible for the production of aqueous
humor and contains the ciliary muscle, which controls the shape of the lens.
Color vision - Vision des couleurs - The capacity of the eye to detect and differentiate visible light in terms of
colors.
Conjunctiva - Conjonctive - A thin, clear membrane that covers the white part of the eye and the inner surfaces
of the eyelids.
Cornea - Cornée - The transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris, pupil, and anterior chamber.
Depth perception - Perception de la profondeur - The ability to perceive the world in three dimensions (3D)
and the distance of an object.
Eyebrow - Sourcil - The strip of hair growing on the ridge above
Eyelashes - Cils - The hair growing at the edge of the eyelids, offering protection from small particles.
Eyelid - Paupière - The movable pieces of skin that cover and protect the eye.
Field of vision - Champ visuel - The entire area that can be seen when the eye is directed forward, including
peripheral vision.
Fovea - Fovéa - A tiny pit located in the macula of the retina that provides the clearest vision of all.
Iris - Iris - The colored part of the eye, responsible for controlling the diameter and size of the pupil.
Lens (of the eye) - Cristallin - The transparent structure inside the eye that focuses light rays onto the retina.
Macula - Macula - A small central part of the retina, responsible for detailed vision.
Night vision - Vision nocturne - The ability to see in low-light conditions.
Optic disc - Papille optique - The point on the retina where the optic nerve fibers leave the eye, creating the
blind spot.
Optic nerve - Nerf optique - The nerve that transmits visual information from the retina to the brain.
Peripheral vision - Vision périphérique - The part of vision that occurs outside the very center of gaze.
Posterior chamber - Chambre postérieure - The fluid-filled space behind the iris but in front of the lens.
Pupil - Pupille - The opening in the center of the iris that allows light to strike the retina.
Retina - Rétine - A thin layer of tissue at the back of the eye where light is converted into neural signals to the
brain.
Sclera - Sclérotique - The white outer layer of the eyeball, providing structure and protection.
Visual cortex - Cortex visuel - The part of the cerebral cortex responsible for processing visual information.
Vitreous body - Corps vitré - The clear gel that fills the space between the lens and the retina, supporting the
shape of the eye.
Zonule fibers - Fibres zonulaires - The fibers that connect the ciliary body to the lens of the eye, helping to
hold it in place.
You might also like
- Katsushi Ikeuchi (Editor) - Computer Vision - A Reference Guide-Springer (2021)Document1,436 pagesKatsushi Ikeuchi (Editor) - Computer Vision - A Reference Guide-Springer (2021)Wendy Contreras100% (1)
- Traffic Engineering Module - 1Document35 pagesTraffic Engineering Module - 1Shri Deer100% (1)
- Preparing and Trying A Civil CaseDocument82 pagesPreparing and Trying A Civil CaseOsvaldo Ariel TonelloNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Eye Ear and SkinDocument7 pagesAnatomy of Eye Ear and Skina62882975No ratings yet
- D Out About Different Parts of The EyeDocument2 pagesD Out About Different Parts of The EyeAljhon DelfinNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The EyeDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The EyeBryan Espanol100% (1)
- Physiology of The Eye and Visual Trans Duct IonDocument9 pagesPhysiology of The Eye and Visual Trans Duct IonJoie Sheen BastianNo ratings yet
- Eyes Health AssessmenttDocument34 pagesEyes Health AssessmenttMhiaBuenafeNo ratings yet
- Sense Organs: Structure of Human EyeDocument8 pagesSense Organs: Structure of Human EyeRanveer SinghNo ratings yet
- Special Sense Pathway: Visual, Auditory, VestibularDocument56 pagesSpecial Sense Pathway: Visual, Auditory, Vestibularmyka brilliant cristobalNo ratings yet
- Visual OrganDocument43 pagesVisual Organmahdia18No ratings yet
- Sensory OrgansDocument11 pagesSensory OrgansCurex QANo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The EyeDocument3 pagesAnatomy of The EyeKina KinaNo ratings yet
- Human Eye NotesDocument2 pagesHuman Eye Notesndee072No ratings yet
- Unit 13 Sence OrganDocument132 pagesUnit 13 Sence OrganChandan ShahNo ratings yet
- Olfactory, Eye, Ear'nOTESDocument23 pagesOlfactory, Eye, Ear'nOTESTida TpNo ratings yet
- C1 F3 BiodiversityDocument112 pagesC1 F3 BiodiversityNurul Shafiah Mustafa KamalNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of The EyesDocument5 pagesStructure and Function of The EyesPreeti ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Physiology of EyeDocument17 pagesPhysiology of EyeHanna ShibuNo ratings yet
- Eye and VisionDocument19 pagesEye and VisionVincent PolicarNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual (Special Senses)Document6 pagesLab Manual (Special Senses)Francis GarcesNo ratings yet
- Fact Sheet Eye How The Eye and Brain Work Together PDFDocument4 pagesFact Sheet Eye How The Eye and Brain Work Together PDFWy TeayNo ratings yet
- Sense Organ: Diyah Candra AnitaDocument35 pagesSense Organ: Diyah Candra AnitaNamulondo Mwajib Bogere100% (1)
- Sheena The EyeDocument9 pagesSheena The EyeSheena Yen de Pano-PagdalianNo ratings yet
- Iris Muscle - (Most Anterior Extension: EyeballDocument8 pagesIris Muscle - (Most Anterior Extension: EyeballBianx Flores DosdosNo ratings yet
- L5 - 2 - Special SensesDocument87 pagesL5 - 2 - Special Sensesbotchwaylilian17No ratings yet
- Structure of EyeDocument24 pagesStructure of Eyedipendrakumarkushawaha44No ratings yet
- Each Eyeball Is Positioned in A Bony Depression in The Skull Called Orbit. - Only The Anterior One-Sixth of The Eye's Surface Can Normally Be SeenDocument14 pagesEach Eyeball Is Positioned in A Bony Depression in The Skull Called Orbit. - Only The Anterior One-Sixth of The Eye's Surface Can Normally Be SeenMark AngeloNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The EyesDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The EyesNkk Aqnd MgdnglNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Eyes-BiopsyDocument20 pagesAnatomy of Eyes-BiopsynandanitriadiningsihNo ratings yet
- Visual and AuditoryDocument7 pagesVisual and AuditoryChristi EspinosaNo ratings yet
- The Eye The Eyeball Has Three TunicsDocument6 pagesThe Eye The Eyeball Has Three TunicsLara ShayaNo ratings yet
- The Sensory Organs: Anatomy Department Hasanuddin UniversityDocument117 pagesThe Sensory Organs: Anatomy Department Hasanuddin UniversityamiraNo ratings yet
- The EyeDocument6 pagesThe EyeDebiprasad GhoshNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of An EyeDocument12 pagesAnatomy of An EyeSuahniNo ratings yet
- Presentation1 (2) 4Document10 pagesPresentation1 (2) 4Shokunbi TolaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 f3Document113 pagesChapter 1 f3FAthiyah Abdul RahimNo ratings yet
- Sense Organs NotesDocument13 pagesSense Organs NotesVijay Laxmi MundhraNo ratings yet
- Technical College of Health ShekhanDocument9 pagesTechnical College of Health ShekhanSaadNo ratings yet
- Part 13 - Human Sensory Organs AnatomyDocument21 pagesPart 13 - Human Sensory Organs AnatomyAmal Naeem JHNo ratings yet
- 1-Anatomy of The EyeDocument2 pages1-Anatomy of The EyeRadhwanNo ratings yet
- Structure of Eye !Document11 pagesStructure of Eye !Leonora KadriuNo ratings yet
- Your Eye AnatomyDocument4 pagesYour Eye AnatomyAljhon DelfinNo ratings yet
- Vision: Chapter 9: SensesDocument21 pagesVision: Chapter 9: SenseshoneykrizelNo ratings yet
- Special Senses EYEDocument4 pagesSpecial Senses EYEDevendra RawatNo ratings yet
- An Organ That Receives and Relays Information About The Body's Senses To The BrainDocument59 pagesAn Organ That Receives and Relays Information About The Body's Senses To The BrainIsarra AmsaluNo ratings yet
- Perception and Coordination Lesson 1.2Document4 pagesPerception and Coordination Lesson 1.2Lovely CruzxNo ratings yet
- Bionic Eye EB KNS 2019Document58 pagesBionic Eye EB KNS 2019Lalitaditya DivakarlaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The EyeDocument2 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The EyeKeanu Jay MaltosNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The EyeDocument4 pagesAnatomy of The EyeSabrinaAyuPutriNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY OF THE EYE (Organ of Vision) by DR Omeje EmmanuelDocument31 pagesANATOMY OF THE EYE (Organ of Vision) by DR Omeje Emmanuelchidera100% (2)
- Info Sheet 4 - 1Document8 pagesInfo Sheet 4 - 1Francis ObmergaNo ratings yet
- Assignment Submitted To: Sir Muneeb Ahmad Submitted By: Ayesha Farooq Roll No: 19010920-104 Course: PSY 101 Section: Bba (B)Document9 pagesAssignment Submitted To: Sir Muneeb Ahmad Submitted By: Ayesha Farooq Roll No: 19010920-104 Course: PSY 101 Section: Bba (B)Ayesha FarooqNo ratings yet
- Human Eye 13Document1 pageHuman Eye 13Dorcas CuevasNo ratings yet
- Lo Week 3 Blok Sss - April 2Document12 pagesLo Week 3 Blok Sss - April 2mellyNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology 1st SessionDocument26 pagesOphthalmology 1st SessionWais samarNo ratings yet
- Creating 3D Eyes: One: The Anatomy of The Human EyeDocument2 pagesCreating 3D Eyes: One: The Anatomy of The Human Eyekora_c995No ratings yet
- Health Assessment Nursing Chapter 11: EyesDocument3 pagesHealth Assessment Nursing Chapter 11: EyesRobin OommenNo ratings yet
- EENT Review ManualDocument19 pagesEENT Review ManualJohn Darvin TanNo ratings yet
- EyeballDocument14 pagesEyeballMirko BelanNo ratings yet
- Special SensesDocument21 pagesSpecial SensesJhemDelfinNo ratings yet
- Human Senses: Monique MavronicolasDocument10 pagesHuman Senses: Monique MavronicolasMonique MavronicolasNo ratings yet
- Low Vision: Assessment and Educational Needs: A Guide to Teachers and ParentsFrom EverandLow Vision: Assessment and Educational Needs: A Guide to Teachers and ParentsNo ratings yet
- Test On Past Tenses and Filming VocabularyDocument2 pagesTest On Past Tenses and Filming VocabularyOsvaldo Ariel TonelloNo ratings yet
- Hello, Hello - SongDocument1 pageHello, Hello - SongOsvaldo Ariel TonelloNo ratings yet
- Differences Between American and British EnglishDocument3 pagesDifferences Between American and British EnglishOsvaldo Ariel TonelloNo ratings yet
- English Test Dietetics - 30-Minute VersionDocument1 pageEnglish Test Dietetics - 30-Minute VersionOsvaldo Ariel TonelloNo ratings yet
- Dictionary of Health Related Terms English SpanishDocument77 pagesDictionary of Health Related Terms English Spanishjosemiguel100% (4)
- Colors DocDocument12 pagesColors DocTeorija PajaclukaNo ratings yet
- TaxanomyDocument32 pagesTaxanomyChucho Reach100% (1)
- ABE 313 Properties of AB Materials Module 6Document21 pagesABE 313 Properties of AB Materials Module 6Eloisa Marie SilausoNo ratings yet
- 691566643060unit-6 - Housing and Interior DesignDocument13 pages691566643060unit-6 - Housing and Interior DesignGaganpreet Kaur Fashion Designing100% (1)
- Vrinda ThesisDocument58 pagesVrinda ThesisArun FizardoNo ratings yet
- Cyborg Parts and Implants - Fallout 2d20Document22 pagesCyborg Parts and Implants - Fallout 2d20PoohatyNo ratings yet
- Eye PhysiologyDocument11 pagesEye PhysiologyAmanuel DinaNo ratings yet
- Vision Development - Childhood - American Academy of OphthalmologyDocument1 pageVision Development - Childhood - American Academy of Ophthalmologysneha duttaNo ratings yet
- Leonardo Da Vinci's Study of Light and Optics: A Synthesis of Fields in The Last Supper by Nicole BitlerDocument9 pagesLeonardo Da Vinci's Study of Light and Optics: A Synthesis of Fields in The Last Supper by Nicole BitlerAllie IelanNo ratings yet
- Places and LandscapeDocument113 pagesPlaces and LandscapeJimson SolisNo ratings yet
- Science of ColorsDocument6 pagesScience of Colorsprateeksaxena88100% (1)
- Material Color Code Identification - BarzanDocument1 pageMaterial Color Code Identification - BarzanMadhavMitruNo ratings yet
- Latihan PTS PEC Pamulang 1,2Document2 pagesLatihan PTS PEC Pamulang 1,2Pec Pamulang 1No ratings yet
- Es2 SC 179 The Sense of Sight Labelling Activity SheetDocument4 pagesEs2 SC 179 The Sense of Sight Labelling Activity Sheethamsat_eshq_51681625No ratings yet
- Humanities 11 - Introduction To Arts Color WheelDocument9 pagesHumanities 11 - Introduction To Arts Color Wheelmarangen125No ratings yet
- PG 03 TextDocument25 pagesPG 03 TextMohammed JammaNo ratings yet
- Is The Visual PoliticalDocument108 pagesIs The Visual PoliticalAbidin ZeinNo ratings yet
- Rethinking Psychological Anthropology - Continuity and Change in The Study of Human Action (2nd Ed)Document317 pagesRethinking Psychological Anthropology - Continuity and Change in The Study of Human Action (2nd Ed)bakbolom100% (3)
- Print-Testing-Tools-Mir - Copy-MergedDocument2 pagesPrint-Testing-Tools-Mir - Copy-Mergedbelive itNo ratings yet
- GE 106 Art Appreciation WK 3Document18 pagesGE 106 Art Appreciation WK 3daryl.pradoNo ratings yet
- Flock Color Scheme Worksheets - 1Document5 pagesFlock Color Scheme Worksheets - 1Olivia GogasNo ratings yet
- Computational Ethics - 1-S2.0-S1364661322000456-MainDocument18 pagesComputational Ethics - 1-S2.0-S1364661322000456-MainIRWA BUCHNo ratings yet
- Ingold SurfaceVisions PDFDocument10 pagesIngold SurfaceVisions PDFDirceu MauésNo ratings yet
- Ecological Approach: James Gibson'SDocument13 pagesEcological Approach: James Gibson'SmmtruffautNo ratings yet
- Sway Trumpet PDFDocument1 pageSway Trumpet PDFOleg Zaiat0% (1)
- Eye Examination: OSCE ChecklistDocument2 pagesEye Examination: OSCE ChecklistMohamed Anas SayedNo ratings yet
- Chart - Stitch FiddleDocument3 pagesChart - Stitch FiddleKnot by AlkiNo ratings yet
- Children and Their Development 6th Edition Kail Test BankDocument33 pagesChildren and Their Development 6th Edition Kail Test Bankdaywoman.frachozbkywc100% (35)