Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Eons Geological Eras
Eons Geological Eras
Uploaded by
paula zapataOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Eons Geological Eras
Eons Geological Eras
Uploaded by
paula zapataCopyright:
Available Formats
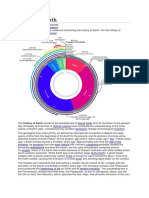
The geological history of Earth is not only divided into eras but also into larger units
called eons, each representing a vast expanse of time and marked by distinctive
geological and biological events. Let's delve into the eons of Earth's history.
Proterozoic Eon: The Proterozoic Eon covers the time-period from around 2.5
billion years ago to 541 million years ago. Notable events during this eon include the
oxygenation of the atmosphere, the formation of more complex multicellular life
forms, and the Snowball Earth episodes, where the planet experienced extreme
glaciations.
Hadean Eon: The Hadean Eon is the earliest and longest eon, spanning from the
formation of the Earth about 4.6 billion years ago to roughly 4 billion years ago. This
eon is named after Hades, the ancient Greek god of the underworld, reflecting the
extreme conditions on early Earth, including intense heat and volcanic activity.
Phanerozoic Eon: The Phanerozoic Eon is the most recent eon, starting around
541 million years ago and continuing to the present day. It is divided into three eras:
the Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic. The Phanerozoic Eon is marked by the
proliferation of complex life forms, including the rise of animals with hard shells, the
evolution of vertebrates, and the dominance of mammals and birds.
Archean Eon: Following the Hadean Eon, the Archean Eon extends from about 4
billion years ago to 2.5 billion years ago. During this time, the Earth's surface
gradually cooled, and the first continents began to form. The emergence of life is
believed to have occurred during the latter part of the Archean, with the development
of simple single-celled organisms.
Understanding the eons provides a broader perspective on the immense timescales
over which Earth has evolved. It's a journey through billions of years, from the fiery
beginnings of the Hadean to the diverse and dynamic ecosystems of the present day
in the Phanerozoic. Each eon has left its imprint on the planet, shaping the geological
and biological landscapes that we observe today.
You might also like
- History of EarthDocument38 pagesHistory of Earthrcu8cdvgfdtujc100% (1)
- Lesson 9 History of The EarthDocument4 pagesLesson 9 History of The EarthRazen SisonNo ratings yet
- Module 12Document19 pagesModule 12jpenagunda23No ratings yet
- History of Earth: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchDocument26 pagesHistory of Earth: Jump To Navigationjump To Searchrafid jafarNo ratings yet
- Earth FormationDocument1 pageEarth FormationAnh ThưNo ratings yet
- Geological-Time-Scale Grade 11 LessonDocument43 pagesGeological-Time-Scale Grade 11 LessonWilson CadienteNo ratings yet
- EarthDocument2 pagesEarthalberneinstein76No ratings yet
- ScienceDocument32 pagesScienceJustin Solis EvangelioNo ratings yet
- All Species of Living OrganismsDocument2 pagesAll Species of Living OrganismsLei JapsayNo ratings yet
- Evolution and Origin of BiodiversityDocument25 pagesEvolution and Origin of Biodiversitykaren milloNo ratings yet
- Proterozoic Eon: ArcheanDocument3 pagesProterozoic Eon: ArcheanDick Jefferson Ocampo PatingNo ratings yet
- Eolo Gic ImeDocument7 pagesEolo Gic ImeNctzen ExolNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science: Geological EventsDocument8 pagesEarth and Life Science: Geological EventsJoseffia MedranoNo ratings yet
- Bienvenidos A Nuestra Clase!: Welcome To Our Class!Document39 pagesBienvenidos A Nuestra Clase!: Welcome To Our Class!naomiNo ratings yet
- Eons - BiologyDocument4 pagesEons - BiologyA - UNO, France Jhondale B.No ratings yet
- History of EarthDocument32 pagesHistory of Earthyanachii22No ratings yet
- The History of The Earth and ManDocument2 pagesThe History of The Earth and Manthe wolf gaming JDBNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1684675219114 7066040010231468268Document21 pagesOrca Share Media1684675219114 7066040010231468268Norsaifah AbduljalalNo ratings yet
- Basics of Archaeological AnthropologyDocument37 pagesBasics of Archaeological AnthropologyUsha HorapetiNo ratings yet
- History of EarthDocument29 pagesHistory of EarthRozalia KobierzyńskaNo ratings yet
- History of The EarthDocument2 pagesHistory of The EarthednakNo ratings yet
- Modern Group Project Presentation 20231128 190057 0000Document34 pagesModern Group Project Presentation 20231128 190057 0000Cariza Nicole LeonorNo ratings yet
- Name: Student Id: Course: Assignment No.: TitleDocument6 pagesName: Student Id: Course: Assignment No.: Titlelife lineNo ratings yet
- ES - Q2 - Week 7Document9 pagesES - Q2 - Week 7Shekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- Lesson No. 16 Earths StoryDocument6 pagesLesson No. 16 Earths StoryLucas KovesworhtNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 5 ReportDocument5 pagesGen Bio 5 ReportCyra BantilloNo ratings yet
- Task On Geologic TimesDocument5 pagesTask On Geologic TimesShark UwUNo ratings yet
- CE 416 GEOLOGIC-WPS OfficeDocument2 pagesCE 416 GEOLOGIC-WPS OfficeTȷ EspalabrʌNo ratings yet
- Era (Geology) : Geological History of EarthDocument10 pagesEra (Geology) : Geological History of EarthYasir ButtNo ratings yet
- History of The EarthDocument2 pagesHistory of The EarthednakNo ratings yet
- Handout For GLY 137 - The DinosaursDocument13 pagesHandout For GLY 137 - The DinosaursAdnen GuedriaNo ratings yet
- Beige Brown Abstract Organic Class Syllabus Blank Presentation 1Document20 pagesBeige Brown Abstract Organic Class Syllabus Blank Presentation 1ITZDUSTY gamerNo ratings yet
- History of EarthDocument2 pagesHistory of Earthshantanudass06No ratings yet
- Beige Brown Abstract Organic Class Syllabus Blank Presentation 2Document35 pagesBeige Brown Abstract Organic Class Syllabus Blank Presentation 2ITZDUSTY gamerNo ratings yet
- Els l10. Earth HistoryDocument34 pagesEls l10. Earth HistoryJhon Kelly SarzonaNo ratings yet
- Proterozoic EraDocument13 pagesProterozoic EraSofia AzoresNo ratings yet
- Factsheets of Earth ScienceDocument7 pagesFactsheets of Earth ScienceBok ManNo ratings yet
- Biosphere Report Earth Science Denzel ArmelonDocument60 pagesBiosphere Report Earth Science Denzel ArmelonQueencess Ara TorresNo ratings yet
- GEN-BIO-2-History of Life On EarthDocument22 pagesGEN-BIO-2-History of Life On EarthGeminiNo ratings yet
- THE Geolocical ERA: Presented by Group 3Document17 pagesTHE Geolocical ERA: Presented by Group 3Sean KelvinNo ratings yet
- Modern ZoologyDocument2 pagesModern ZoologyAnwita JhaNo ratings yet
- History of EarthDocument2 pagesHistory of EarthJosiah ZeusNo ratings yet
- Geologic Time ScaleDocument30 pagesGeologic Time ScaleLoch SolidumNo ratings yet
- History of Life On Earth - 210513 - 212301Document17 pagesHistory of Life On Earth - 210513 - 212301Christine FayeNo ratings yet
- Geologic Time ScaleDocument26 pagesGeologic Time ScaleClarence Nebril100% (1)
- Life During Precambrian and Paleozoic PeriodDocument26 pagesLife During Precambrian and Paleozoic PeriodAlesandra PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Geologic Time ScaleDocument48 pagesGeologic Time ScaleApril TolosaNo ratings yet
- GTS (Final)Document4 pagesGTS (Final)Nctzen ExolNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument2 pagesIntroductioncarmen.blasco.fdezNo ratings yet
- Earth History Shor SummaryDocument4 pagesEarth History Shor Summaryshahana akbarNo ratings yet
- General-Biology-2 Q3 W2 M2 LDS History-Of-Life-On-Earth RTPDocument7 pagesGeneral-Biology-2 Q3 W2 M2 LDS History-Of-Life-On-Earth RTPallenford ordoñezNo ratings yet
- Stromatolites Existed and Other Bacterial CellsDocument3 pagesStromatolites Existed and Other Bacterial CellsRheena FelicianoNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document11 pagesPresentation 1jccultura657No ratings yet
- EONSDocument13 pagesEONSKimberly Ann EismaNo ratings yet
- Geologic Time Scale and PakistanDocument36 pagesGeologic Time Scale and Pakistantalha butt100% (1)
- Scienze ClilDocument1 pageScienze ClilSereNo ratings yet
- Bio 2 Lesson 2Document5 pagesBio 2 Lesson 2rharpienNo ratings yet