Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pharma
Pharma
Uploaded by
ARVIN ZUBIAGAOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pharma
Pharma
Uploaded by
ARVIN ZUBIAGACopyright:
Available Formats
Plasma Proteins – albumin, lipoproteins, alpha-1-acid-
glycoproteing (AGP)
Basic drugs (morphine, amantadine) binds to AGP.
Highly protein bound drugs >90% bound to proteins
(warfarin, glyburide, sertraline, furosemide, and
diazepam).
Weakly protein-bound drugs - <10% bound to protein
(gentamycin, metformin, metopolol, and lisinopril).
The portion that remains unbound is free, active drug.
Free drugs are able to exit blood vessels and reach their
site of action, causing a pharmacological response.
Low level of plasma protein can cause drug toxicity due
to low available binding sites of the drug thus increasing
the amount of free drug.
Pts with liver or kidney disease and malnourished have
significantly lower serum albumin levels.
Older adults have hypoalbuminemia particularly if they
have multiple chronic illnesses.
NOTES: prior administration of medication it is
important as a nurse to check the protein and albumin
level of the patient to prevent drug toxicity.
Pregnancy: 1st trimester drugs can lead to spontaneous
abortion; 2nd trimester spontaneous abortion,
teratogenesis, or other subtler defects; may alter fetal
growth and development. During breastfeeding, drugs
can pass to breast milk.
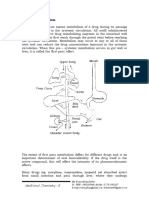
Pharmacokinetics: ADME
Absorption
Distribution
Metabolism
Excretion
Liver is the primary site of metabolism of drugs.
P450 system – cytochrome P 450 system – convert
drugs into metabolites.
Large percentage of drugs are lipid soluble thus the liver
metabolize the lipid-soluble drug substance into a
water-soluble substance for renal excretion.
Liver disease that alter drug metabolism by inhibiting
the drug-metabolizing enzymes in the liver resulting to
decrease drug metabolism increasing the risk of drug
toxicity by increase amount of free drugs.
Half life is the time it takes for a drug to be reduced in
half inside the body.
With liver and kidney disease a half life can be
prolonged.
Half life is used to determine dosing interval.
You might also like
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Proses F.kinetik-F.dinamik Ppds 2017Document33 pagesProses F.kinetik-F.dinamik Ppds 2017intan purnamaNo ratings yet
- Geriatric Pharmacology. Journal of The American Podriatric Medical AssociationDocument8 pagesGeriatric Pharmacology. Journal of The American Podriatric Medical AssociationJose Fernando Díez ConchaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pharmacology 9-16Document31 pagesClinical Pharmacology 9-16mill otoiNo ratings yet
- Drug Interaction Can Be Defined As TheDocument34 pagesDrug Interaction Can Be Defined As TheIstianah Es100% (1)
- Drug InteractionsDocument43 pagesDrug InteractionsNinaNo ratings yet
- PregnancyDocument16 pagesPregnancyMydhilyNo ratings yet
- ParacetamolDocument5 pagesParacetamolunimintt100% (1)
- Firstpass MetabolismDocument5 pagesFirstpass MetabolismAhnaf Muttaqi Spondan 1716No ratings yet
- Liver DiseaseDocument17 pagesLiver DiseaseGANESH KUMAR JELLANo ratings yet
- Food-Drug Interactions 1Document73 pagesFood-Drug Interactions 1salimahNo ratings yet
- Age and Drug Disposition PresentationDocument35 pagesAge and Drug Disposition PresentationMalueth AnguiNo ratings yet
- AntiepilepticsDocument13 pagesAntiepilepticstbuyinza21apNo ratings yet
- Diabetes MedicationDocument17 pagesDiabetes MedicationTaj lamajedNo ratings yet
- TDM of PhenytoinDocument5 pagesTDM of PhenytoinMounika16 PedamalluNo ratings yet
- List The Factors Influencing The Interpretation of TDM ReportDocument3 pagesList The Factors Influencing The Interpretation of TDM ReportOdyNo ratings yet
- Adverse Drug Reactions and Drug InteractionsDocument10 pagesAdverse Drug Reactions and Drug Interactions88AKKNo ratings yet
- Reversibledementias: Milta O. LittleDocument26 pagesReversibledementias: Milta O. LittleLUCAS IGNACIO SANCHEZNo ratings yet
- Biopharm M5-M8Document15 pagesBiopharm M5-M8Peniel ResurreccionNo ratings yet
- Inborn Error of Metabolism and Introduction To Cancer GeneticsDocument9 pagesInborn Error of Metabolism and Introduction To Cancer GeneticsviancaNo ratings yet
- Clinical ChemistryDocument12 pagesClinical ChemistryClark Lopez100% (1)
- A3 Introduction To Drug ActionDocument55 pagesA3 Introduction To Drug ActionSHIELOU LOMODNo ratings yet
- DRUG SODIUM VALPROATE (Depakote, Epilim, Episenta)Document5 pagesDRUG SODIUM VALPROATE (Depakote, Epilim, Episenta)Pearl Princess Guerrero100% (2)
- Areviewofacetaminophen Poisoning: Michael J. Hodgman,, Alexander R. GarrardDocument18 pagesAreviewofacetaminophen Poisoning: Michael J. Hodgman,, Alexander R. Garrardأحمد علي حبيبNo ratings yet
- Metformin For DiabetesDocument9 pagesMetformin For Diabetesubaid khan afridiNo ratings yet
- FemaleDocument5 pagesFemaleospapNo ratings yet
- Stilpane Comb Tab Za Stiltab 1204 03 Epi 2020.03.09-1Document16 pagesStilpane Comb Tab Za Stiltab 1204 03 Epi 2020.03.09-1allan.prathipati07No ratings yet
- Drugs Used During Pregnancy and LactationDocument21 pagesDrugs Used During Pregnancy and LactationHarsheethaNo ratings yet
- Geriatrics Department BookDocument69 pagesGeriatrics Department BookHazemAbu-BakrNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyRai D. MacapantonNo ratings yet
- Assignment On-: "Pharmacokinetics of Drug Molecules in Different Disease Condition"Document19 pagesAssignment On-: "Pharmacokinetics of Drug Molecules in Different Disease Condition"Susmoy SinhaNo ratings yet
- PRIMAQUINE PHOSPHATE-primaquine Phos Phate Tablet Bays Hore Pharmaceuticals, LLCDocument8 pagesPRIMAQUINE PHOSPHATE-primaquine Phos Phate Tablet Bays Hore Pharmaceuticals, LLCKulfi BarfiNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Biotransformation of DrugsDocument20 pagesFactors Affecting Biotransformation of DrugsSohan PrasathNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Management of Hyperprolactinemia: Review SynthèseDocument7 pagesDiagnosis and Management of Hyperprolactinemia: Review SynthèseMónica Carolina Avila CruzNo ratings yet
- 5perinatal Pediatric PharmacologyDocument5 pages5perinatal Pediatric Pharmacologymkpkqc4j4hNo ratings yet
- Drug Eff On Food Intake PDFDocument9 pagesDrug Eff On Food Intake PDFAbdul Azis MauludinNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pharmacy I: Izzatullahkhan Assistant Professor (LCPS) PHARMD (BMU) M.Sc. (Uk)Document20 pagesClinical Pharmacy I: Izzatullahkhan Assistant Professor (LCPS) PHARMD (BMU) M.Sc. (Uk)Noreen ArshadNo ratings yet
- Metformin Hydrochloride PDFDocument4 pagesMetformin Hydrochloride PDFHannaNo ratings yet
- Prescribing in Liver Disease Issue 2 Volume 32 Australian PrescriberDocument6 pagesPrescribing in Liver Disease Issue 2 Volume 32 Australian PrescriberAnonymous 9dVZCnTXSNo ratings yet
- Furosemide Tables:: Pharmacokinetics Bioavailability Peak Plasma Level Plasma Half-Life Active Metabolites EliminationDocument4 pagesFurosemide Tables:: Pharmacokinetics Bioavailability Peak Plasma Level Plasma Half-Life Active Metabolites Eliminationmole_fkNo ratings yet
- MetFormin Generic Health TabDocument9 pagesMetFormin Generic Health TabNur Ekayani SyamNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pharmacokinetics 2013Document68 pagesClinical Pharmacokinetics 2013Law YouNo ratings yet
- Drug-Induced Hepatotoxicity: BackgroundDocument13 pagesDrug-Induced Hepatotoxicity: BackgroundrianiNo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetic in PregnancyDocument7 pagesPharmacokinetic in PregnancyPatrick AnthonyNo ratings yet
- FolartcapsulepdfDocument2 pagesFolartcapsulepdfRoadtoforever123No ratings yet
- Drug - Drug Int2Document35 pagesDrug - Drug Int2alishba100% (2)
- Objectives:: IndicationsDocument5 pagesObjectives:: IndicationsChrisNo ratings yet
- Metformin: Dosing & UsesDocument8 pagesMetformin: Dosing & UsesMaria Alejandra Siachoque JaraNo ratings yet
- Omeprazole PDFDocument8 pagesOmeprazole PDFRafael SyfuNo ratings yet
- Go To Top of The PageDocument9 pagesGo To Top of The PageQaffah Silma AzasNo ratings yet
- Diuretics: Generic Name: FUROSEMIDEDocument12 pagesDiuretics: Generic Name: FUROSEMIDEJR BetonioNo ratings yet
- PharmacogeneticsDocument3 pagesPharmacogeneticsPardeep Sony100% (1)
- Pharmacokinetic Changes in The Elderly: and Implications For Drug TherapyDocument34 pagesPharmacokinetic Changes in The Elderly: and Implications For Drug TherapymerkuriNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Pharmacokinetic Drug Interaction: Teerthanker Mahaveer UniversityDocument8 pagesAssignment On Pharmacokinetic Drug Interaction: Teerthanker Mahaveer Universityt24008882No ratings yet
- MercaptopurineDocument2 pagesMercaptopurineBigBoostingNo ratings yet
- Prenatal PharmacologyDocument23 pagesPrenatal Pharmacology88AKKNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Drug Interaction and the Mechanism of InteractionFrom EverandHandbook of Drug Interaction and the Mechanism of InteractionRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet