Professional Documents
Culture Documents
RefM 08 - Basic Structural Engineering (Part 02)
RefM 08 - Basic Structural Engineering (Part 02)
Uploaded by
usueCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- November 2022 Civil Engineering Board Exam: Review InnovationsDocument4 pagesNovember 2022 Civil Engineering Board Exam: Review Innovationsggomo15100% (2)
- Official Preboard Structural Engineering and ConstructionDocument7 pagesOfficial Preboard Structural Engineering and ConstructionDexter Dote0% (2)
- Ce 603 Set DDocument12 pagesCe 603 Set DJade Paul D. BesanaNo ratings yet
- (Preboard Exam) : Multiple ChoiceDocument12 pages(Preboard Exam) : Multiple ChoiceNicole Rodil100% (1)
- Struc Const 1 1Document23 pagesStruc Const 1 1Marichu Davillo Garbiles100% (2)
- PRE - Board Examination in Structural Engineering and ConstructionDocument11 pagesPRE - Board Examination in Structural Engineering and ConstructiongemNo ratings yet
- SolveDocument2 pagesSolveJea Clarie Mendioro Espinas67% (3)
- CJ20N Change Create Additional WBS-Hierarchy GraphicsDocument9 pagesCJ20N Change Create Additional WBS-Hierarchy Graphicssatheesh408No ratings yet
- HY-eVision2 7.0 User ManualDocument50 pagesHY-eVision2 7.0 User ManualEmerson GomesNo ratings yet
- Frank Gambale - Guitar Sweep PickingDocument4 pagesFrank Gambale - Guitar Sweep Pickingbrightthings100% (17)
- 1st Preboard Design PDocument13 pages1st Preboard Design PHarf MirandaNo ratings yet
- STDocument1 pageSTJea Clarie Mendioro EspinasNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgC6RSwXitvNxv5doXAP4XkxEcDPev5JBWgWWpjIm48Kf0i - FaBwWf5y5kx8AAr2V HM5a9QynzxGonhZ - 17VAFd4bS5yAMOvRzRG5YDbIPKku0 YMNrF340S3 D7Kt3Xg8BwvwMGVVSFmnnDocument2 pagesACFrOgC6RSwXitvNxv5doXAP4XkxEcDPev5JBWgWWpjIm48Kf0i - FaBwWf5y5kx8AAr2V HM5a9QynzxGonhZ - 17VAFd4bS5yAMOvRzRG5YDbIPKku0 YMNrF340S3 D7Kt3Xg8BwvwMGVVSFmnnMark Christian HerreraNo ratings yet
- Final Preboard Design 2021Document2 pagesFinal Preboard Design 2021Vic NairaNo ratings yet
- Refresher Set Sec-6: Review InnovationsDocument4 pagesRefresher Set Sec-6: Review InnovationsJerome YangaNo ratings yet
- Design Nov 2013Document12 pagesDesign Nov 2013Cath100% (1)
- MathalinoDocument2 pagesMathalinoDianna DayawonNo ratings yet
- At 14 2Document7 pagesAt 14 2Icz Fuentes100% (1)
- Pretest in DesignDocument4 pagesPretest in DesignfrancessichNo ratings yet
- Preboard 2 SECDocument14 pagesPreboard 2 SECJae Han100% (1)
- Refresher Psad Preboard Exam 2Document14 pagesRefresher Psad Preboard Exam 2Steven Valerio100% (1)
- PSAD Refresher October 9 2023Document4 pagesPSAD Refresher October 9 2023Joshua CopianNo ratings yet
- Slu Ce Structural June 2020 Problem SetDocument9 pagesSlu Ce Structural June 2020 Problem SetJonathan Basilio100% (1)
- V0L2 PDFDocument4 pagesV0L2 PDFJohannie Nina ClaridadNo ratings yet
- Conc 1 - Nov 2020Document2 pagesConc 1 - Nov 2020Glenn CalingasanNo ratings yet
- Ce 603 Set CDocument12 pagesCe 603 Set CJade Paul D. BesanaNo ratings yet
- Foundationxpart 1Document3 pagesFoundationxpart 1Haydeesheen SisonNo ratings yet
- Excellence in Professional Engineering Review and Training SolutionsDocument3 pagesExcellence in Professional Engineering Review and Training SolutionsGlaiza Marie100% (1)
- Structural Engineering & ConstructionDocument13 pagesStructural Engineering & ConstructionREX AMPONGANNo ratings yet
- Psad - 15Document2 pagesPsad - 15SamNo ratings yet
- Refresher Module 27 - S5 - Basic Structural Engineering 4Document1 pageRefresher Module 27 - S5 - Basic Structural Engineering 4Haoh JamjamNo ratings yet
- Refresher Module 13 Nov 2021Document1 pageRefresher Module 13 Nov 2021JaydeeLove AlconeraNo ratings yet
- Tsu m23 Practice Problems Reinforced Concrete DesignDocument2 pagesTsu m23 Practice Problems Reinforced Concrete DesignMark Lester ValdozNo ratings yet
- Psad November 2022Document33 pagesPsad November 2022paisa baba100% (1)
- Seac 2 - Strength of Materials (No Answers)Document6 pagesSeac 2 - Strength of Materials (No Answers)Joshua John JulioNo ratings yet
- Seac 2 - Strength of Materials (No Answers)Document6 pagesSeac 2 - Strength of Materials (No Answers)Joshua John Julio100% (1)
- Midterm Exam (Sec)Document11 pagesMidterm Exam (Sec)Sherwin ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Module 3 (Reinforced Concrete Design)Document4 pagesModule 3 (Reinforced Concrete Design)Glaiza MarieNo ratings yet
- CS Apr22Document8 pagesCS Apr22John Taylor BernasNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Assessment B3 (SEC) - November 2022Document4 pagesDiagnostic Assessment B3 (SEC) - November 2022Yoshjordan LambNo ratings yet
- Ce Board May 2011Document3 pagesCe Board May 2011DHANYL KHRISSNA MIJARESNo ratings yet
- April 2024 - Psad 20Document2 pagesApril 2024 - Psad 20ralph laurenzNo ratings yet
- Esplana RCDDocument4 pagesEsplana RCDNaigell Solomon100% (1)
- VOL1Document3 pagesVOL1Ho BiNo ratings yet
- Policarpio 5 - Refresher SECDocument2 pagesPolicarpio 5 - Refresher SECMigaea100% (1)
- Refresher - Structural Design Ang ConstructionDocument3 pagesRefresher - Structural Design Ang Constructionmichael SonuganNo ratings yet
- May 2022 Refresher - Dela Cruz 1: Review InnovationsDocument3 pagesMay 2022 Refresher - Dela Cruz 1: Review InnovationsDan Edison RamosNo ratings yet
- Set BDocument12 pagesSet BDan Casurao100% (1)
- Set BDocument12 pagesSet BDan CasuraoNo ratings yet
- Structural AnalysisDocument14 pagesStructural AnalysisPrincess Gupo Tañas100% (1)
- Instruction: Write The Letter of The Correct Answer On The Answer Sheet Box Provided in A Separate FileDocument2 pagesInstruction: Write The Letter of The Correct Answer On The Answer Sheet Box Provided in A Separate FileFernan FalogmeNo ratings yet
- Review - Structural Engineering and Construction: C 3 S 3 A C yDocument2 pagesReview - Structural Engineering and Construction: C 3 S 3 A C ymichael SonuganNo ratings yet
- 5 Design Nov 2013 KeyDocument6 pages5 Design Nov 2013 KeyKenneth PadunanNo ratings yet
- Ce November 2021 Refresher Pantino 4 Sec PDFDocument4 pagesCe November 2021 Refresher Pantino 4 Sec PDFYoshjordan LambNo ratings yet
- 94 - Strength of Materials Refrehser SetDocument4 pages94 - Strength of Materials Refrehser SetJ O M A RNo ratings yet
- Review Problems in Strength of MaterialsDocument10 pagesReview Problems in Strength of MaterialsJenesis de Guzman50% (2)
- Refresher - Structural Design and Construction: Inhinyero Review CenterDocument4 pagesRefresher - Structural Design and Construction: Inhinyero Review Centermichael SonuganNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials With AnswersDocument2 pagesStrength of Materials With AnswersNathaniel Pascua100% (1)
- Tsu m19 Practice Problems Smat2Document1 pageTsu m19 Practice Problems Smat2Mark Lester ValdozNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited: Tvenkat@bheltry - Co.inDocument5 pagesBharat Heavy Electricals Limited: Tvenkat@bheltry - Co.inRukma Goud Shakkari100% (1)
- Emergency Braking SystemDocument4 pagesEmergency Braking Systemieee4mybusinessonlyNo ratings yet
- Os NotesDocument17 pagesOs NotesAshish KadamNo ratings yet
- Easa Part66 Module 01 New Part 2Document11 pagesEasa Part66 Module 01 New Part 2el farissi farisNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra and Random Processes (CS6015)Document5 pagesLinear Algebra and Random Processes (CS6015)CHAKRADHAR PALAVALASANo ratings yet
- 313-317 DEPTO One KDocument5 pages313-317 DEPTO One KPriyadarshini KrishnaswamyNo ratings yet
- Opposite Hypotenuse Adjacent Hypotenuse Sin ! Cos ! Opposite AdjacentDocument43 pagesOpposite Hypotenuse Adjacent Hypotenuse Sin ! Cos ! Opposite AdjacentFerry YutamaNo ratings yet
- Goldengate Installtion 12cDocument6 pagesGoldengate Installtion 12chariprasathdbaNo ratings yet
- A Chapter 1 Textbook SolutionDocument16 pagesA Chapter 1 Textbook SolutionjimNo ratings yet
- Domestic Company Notams 16 Jan 18Document41 pagesDomestic Company Notams 16 Jan 18Swastika MishraNo ratings yet
- 2017 Catalog 99812723Document508 pages2017 Catalog 99812723Valco0% (1)
- Omni Catolog 2005Document116 pagesOmni Catolog 2005Tuan SsvcNo ratings yet
- GitHub - Haibuihoang - Higrads - A Grads Script Library For Managing Subplots & and Other Plotting Functions PDFDocument9 pagesGitHub - Haibuihoang - Higrads - A Grads Script Library For Managing Subplots & and Other Plotting Functions PDFSetyperNo ratings yet
- Lecture 15. SamplingDocument16 pagesLecture 15. Samplingsincere guyNo ratings yet
- Overview:: Book Title:-Engineering Physics, 2E Author:-B. K. Pandey - SDocument2 pagesOverview:: Book Title:-Engineering Physics, 2E Author:-B. K. Pandey - Sdamini chandi priyaNo ratings yet
- Personalized Movie Hybrid Recommendation Model Based On GRUDocument4 pagesPersonalized Movie Hybrid Recommendation Model Based On GRUMritunjay JhaNo ratings yet
- Textbook Inventory: Room 9 Grade Title Qty. Delivered On Hand IssuedDocument4 pagesTextbook Inventory: Room 9 Grade Title Qty. Delivered On Hand IssuedMj TizonNo ratings yet
- Catalogo de RodamientosDocument399 pagesCatalogo de RodamientosmarragezNo ratings yet
- From SQL To Pandas 35Document38 pagesFrom SQL To Pandas 35M. Aji PriyatnaNo ratings yet
- PG2794 00 - en GBDocument4 pagesPG2794 00 - en GBphalkejituNo ratings yet
- A Novel Hybrid Data Balancing and Fraud Detection Approach For Automobile Insurance ClaimsDocument30 pagesA Novel Hybrid Data Balancing and Fraud Detection Approach For Automobile Insurance ClaimsAtul Kumar AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Force and Motion: ESCI 101 (Physics For Engineers)Document16 pagesForce and Motion: ESCI 101 (Physics For Engineers)Irine ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- Soal UTS Bahasa Inggris SD Semester Genap Kelas 5Document5 pagesSoal UTS Bahasa Inggris SD Semester Genap Kelas 5Yusuf HamdaniNo ratings yet
- 111 RX Final Final ManuscriptDocument27 pages111 RX Final Final ManuscriptAdrian Paul A GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Technical Specs PDFDocument12 pagesTechnical Specs PDFcsolanki6586100% (1)
- PROCEDURE For Color Coding R01 (28.06.2014)Document9 pagesPROCEDURE For Color Coding R01 (28.06.2014)punitg_2No ratings yet
- Canon GP405 Part CatalogDocument277 pagesCanon GP405 Part Catalognazmi100% (2)
RefM 08 - Basic Structural Engineering (Part 02)
RefM 08 - Basic Structural Engineering (Part 02)
Uploaded by
usueOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
RefM 08 - Basic Structural Engineering (Part 02)
RefM 08 - Basic Structural Engineering (Part 02)
Uploaded by
usueCopyright:
Available Formats
MANILA: Room 206, JPD Building, CM Recto Avenue, Manila
CEBU: 4/F J. Martinez Bldg., Osmeña Blvd., Cebu City
BAGUIO: Upper Ground Floor, Pilando Center, Baguio City
Contact Number: (+63) 956 2569509 (Manila), (032) 254-9967 (Cebu), (+63) 939 5746940 (Baguio)
E-Mail: buksmarquez1 @yahoo.com
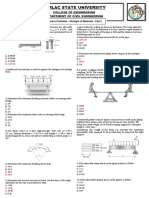
Refresher MODULE – Basic Structural Engineering
SITUATION. A simply supported steel beam spans 9 m. It carries a uniformly SITUATION. A simply supported beam 10 m long has an overhang of 2 m at the
distributed load of 10 kN/m, beam weight already included. left support. If a highway uniform load of 9.35 kN/m and a concentrated load of
Beam Properties: 116 kN passes through the beam.
Area = 8530 mm^2 16. Determine the length (m) of the beam where the uniform load could produce
Depth = 306 mm maximum positive shear at the midspan
Flange width = 204 mm A. 7 B. 5 C. 6 D. 8
Flange thickness = 14.6 mm 17. Determine the length (m) of the beam where the uniform load could produce
Web thickness = 8.5 mm
maximum negative moment at the midspan
Moment of Inertia, Ix = 145 x 10^6 mm^4
Modulus of Elasticity = 200 GPa A. 10 B. 5 C. 2 D. 4
18. If the concentrated load alone is placed at the end of the overhang, compute
1. What is the maximum flexural stress (MPa) in the beam? the maximum shear (kN) at the midspan.
A. 107 B. 54 C. 142 D. 71
2. To prevent excessive deflection, the beam is propped at midspan using a A. 32.2 B. 23.2 C. 20.5 D. 21.0
pipe column. Find the resulting axial stress (MPa) in the column.
Column Properties: SITUATION. A parabolic cable carries a horizontally distributed load of 20 kN/m.
Outside diameter = 200 mm The horizontal span between the supports A and C is 60 m. The lowest point B
Thickness = 10 mm has a vertical distance of 6 m below the support at A and 12 m below the support
Height = 4000 mm at C.
19. Determine the horizontal distance (m) between the lowest point and the
A. 4.7 B. 9.4 C. 18.8 D. 2.8 support at A.
3. How much is the maximum bending stress (MPa) in the propped beam? A. 21.67 B. 24.85 C. 25.35 D. 26.45
A. 26.7 B. 17.8 C. 15.0 D. 35.6 20. What is the tension (kN) at cable A?
A. 1029 B. 1143 C. 1247 D. 703
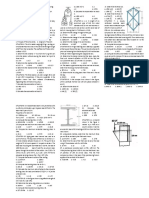
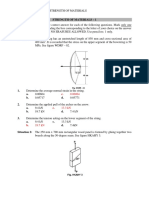
SITUATION. An 8 m high retaining wall is subjected to lateral earth pressure
21. What is the tension (kN) at cable C?
increasing from 34 kPa at the top to 136 kPa at the base. Flexural rigidity EI =
4.5 x1014 N-mm2. Analyze per meter length of the wall. A. 1029 B. 1143 C. 1247 D. 703
4. What is the moment (kN-m) at the base of the cantilever retaining wall?
SITUATION (Practice Problems). A series of uniformly spaced hangers along
A. 2716 B. 2176 C. 2671 D. 2761
a parabolic cable supports a 60 m pipeline weighing 2.8 kN/m. The allowable
5. What is the force to be applied at the proposed end to limit the deflection to tensile load of the cable is 1100 kN.
35 mm? 22. Calculate the maximum tension (kN) in the cable when the sag is 2 m.
A. 163.8 B. 183.6 C. 91.3 D. 92.5 A. 1100 B. 636 C. 630 D. 1096
6. What is the moment at the base when the wall is propped at the top? 23. Calculate the minimum sag of the cable in meters.
A. 707.2 B. 772.0 C. 277.0 D. 270.7 A. 1.15 m B. 1.50 m C. 2 m D. 2.20 m
24. Calculate the tension (kN) at the lowest point of the cable if the cable is
stressed to its allowable tensile load.
SITUATION. A 4-m long beam is fixed at the left end and is supported by a spring A. 1100 B. 636 C. 630 D. 1096
at the right end. The spring stiffness is 60 kN/m. The length of the beam is
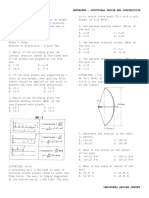
subjected to a uniform load of 800 N/m. SITUATION (Practice Problems).
Given: E = 10 x 109 N/m2 and I = 80 x 106 mm4. Beam Properties: I = 198 x 106 mm4 E = 200 x 103 MPa
7. Determine the deflection (mm) at the right end of the beam when the spring Rod Properties: Diameter = 12 mm E = 200 x 103 MPa
is removed.
A. 22 B. 27 C. 32 D. 37
8. Determine the deflection of the spring (mm).
A. 10.3 B. 11.3 C. 12.3 D. 14.3
9. Determine the moment at the fixed end (kN-m).
A. 1.23 B. 2.34 C. 3.45 D. 6.40
SITUATION. A 12 mm thick steel tire has a width of 110 mm and has an internal
diameter of 800 mm. The tire is heated and shrunk to a steel wheel 800.5 mm
diameter. Take the modulus of Elasticity, E = 200 GPa.
10. Determine the compressive pressure (MPa) between the tire and the wheel. 25. Due to the load, W, rod BC elongates by 1 mm. Find the force (kN) in the rod
A. 7.50 B. 5.25 C. 10.50 D. 3.75 BC which caused the elongation.
11. Determine the tensile stress (MPa) in the tire. A. 9.4 B. 4.9 C. 8.3 D. 3.8
A. 175 B. 125 C. 250 D. 350 26. Due to the load, W, the force developed in rod BC is 12 kN, what is the value
12. Determine the thickness (mm) of the tire to resist pressure of 1.5 MPa if it
has an allowable stress of 124 MPa. of W (kN)?
A. 4.84 B. 8.44 C. 2.12 D. 6.32 A. 12.73 B. 27.31 C. 43.65 D. 56.32
27. Due to the load, W = 40 kN, the force developed in rod BC = 10 kN. The
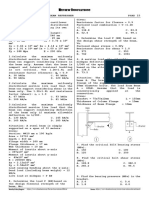
SITUATION. A steel cable is used to lift a load W: diameter of rod BC = 16 mm. Find the moment (kN-m) at the fixed end.
Given: W (total load including of cable) = 175 kN A. 10 B. 20 C. 30 D. 40
Properties of steel cable:
Diameter = 30 mm Length = 12 m SITUATION (Practice Problems). A cantilever beam, 3.5 m long, carries a
Modulus of Elasticity = 200 GPa concentrated load P, at mid-length. Given: P = 200 kN, E = 200 GPa, I = 60.8 x
10^6 MPa
13. Find the elongation (mm) of the cable as it lifts the load W.
28. How much is the beam deflection (mm) at mid-length?
A. 13.45 B. 14.85 C. 16.25 D. 17.50
A. 1.84 B. 23.50 C. 29.40 D. 14.70
14. What is the resulting strain (mm/mm) in the cable as it lifts the load w?
29. What force (kN) should be applied at the free end to prevent deflection?
A. 0.00124 B. 0.00112 C. 0.00146 D. 0.00135 A. 7.8 B. 62.5 C. 41.7 D. 100.0
15. Due to heavy load, the steel cable breaks. The recorded diameter of failure 30. To limit the deflection at mid-length to 9.5 mm, how much force (kN) should
is 27.5 mm. Calculate the ductility of the material. be applied at the free end?
A. 8.33% B. 19.0% C. 15.97 % D. 9.09 % A. 54.1 B. 76.8 C. 129.3 D. 64.7
You might also like
- November 2022 Civil Engineering Board Exam: Review InnovationsDocument4 pagesNovember 2022 Civil Engineering Board Exam: Review Innovationsggomo15100% (2)
- Official Preboard Structural Engineering and ConstructionDocument7 pagesOfficial Preboard Structural Engineering and ConstructionDexter Dote0% (2)
- Ce 603 Set DDocument12 pagesCe 603 Set DJade Paul D. BesanaNo ratings yet
- (Preboard Exam) : Multiple ChoiceDocument12 pages(Preboard Exam) : Multiple ChoiceNicole Rodil100% (1)
- Struc Const 1 1Document23 pagesStruc Const 1 1Marichu Davillo Garbiles100% (2)
- PRE - Board Examination in Structural Engineering and ConstructionDocument11 pagesPRE - Board Examination in Structural Engineering and ConstructiongemNo ratings yet
- SolveDocument2 pagesSolveJea Clarie Mendioro Espinas67% (3)
- CJ20N Change Create Additional WBS-Hierarchy GraphicsDocument9 pagesCJ20N Change Create Additional WBS-Hierarchy Graphicssatheesh408No ratings yet
- HY-eVision2 7.0 User ManualDocument50 pagesHY-eVision2 7.0 User ManualEmerson GomesNo ratings yet
- Frank Gambale - Guitar Sweep PickingDocument4 pagesFrank Gambale - Guitar Sweep Pickingbrightthings100% (17)
- 1st Preboard Design PDocument13 pages1st Preboard Design PHarf MirandaNo ratings yet
- STDocument1 pageSTJea Clarie Mendioro EspinasNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgC6RSwXitvNxv5doXAP4XkxEcDPev5JBWgWWpjIm48Kf0i - FaBwWf5y5kx8AAr2V HM5a9QynzxGonhZ - 17VAFd4bS5yAMOvRzRG5YDbIPKku0 YMNrF340S3 D7Kt3Xg8BwvwMGVVSFmnnDocument2 pagesACFrOgC6RSwXitvNxv5doXAP4XkxEcDPev5JBWgWWpjIm48Kf0i - FaBwWf5y5kx8AAr2V HM5a9QynzxGonhZ - 17VAFd4bS5yAMOvRzRG5YDbIPKku0 YMNrF340S3 D7Kt3Xg8BwvwMGVVSFmnnMark Christian HerreraNo ratings yet
- Final Preboard Design 2021Document2 pagesFinal Preboard Design 2021Vic NairaNo ratings yet
- Refresher Set Sec-6: Review InnovationsDocument4 pagesRefresher Set Sec-6: Review InnovationsJerome YangaNo ratings yet
- Design Nov 2013Document12 pagesDesign Nov 2013Cath100% (1)
- MathalinoDocument2 pagesMathalinoDianna DayawonNo ratings yet
- At 14 2Document7 pagesAt 14 2Icz Fuentes100% (1)
- Pretest in DesignDocument4 pagesPretest in DesignfrancessichNo ratings yet
- Preboard 2 SECDocument14 pagesPreboard 2 SECJae Han100% (1)
- Refresher Psad Preboard Exam 2Document14 pagesRefresher Psad Preboard Exam 2Steven Valerio100% (1)
- PSAD Refresher October 9 2023Document4 pagesPSAD Refresher October 9 2023Joshua CopianNo ratings yet
- Slu Ce Structural June 2020 Problem SetDocument9 pagesSlu Ce Structural June 2020 Problem SetJonathan Basilio100% (1)
- V0L2 PDFDocument4 pagesV0L2 PDFJohannie Nina ClaridadNo ratings yet
- Conc 1 - Nov 2020Document2 pagesConc 1 - Nov 2020Glenn CalingasanNo ratings yet
- Ce 603 Set CDocument12 pagesCe 603 Set CJade Paul D. BesanaNo ratings yet
- Foundationxpart 1Document3 pagesFoundationxpart 1Haydeesheen SisonNo ratings yet
- Excellence in Professional Engineering Review and Training SolutionsDocument3 pagesExcellence in Professional Engineering Review and Training SolutionsGlaiza Marie100% (1)
- Structural Engineering & ConstructionDocument13 pagesStructural Engineering & ConstructionREX AMPONGANNo ratings yet
- Psad - 15Document2 pagesPsad - 15SamNo ratings yet
- Refresher Module 27 - S5 - Basic Structural Engineering 4Document1 pageRefresher Module 27 - S5 - Basic Structural Engineering 4Haoh JamjamNo ratings yet
- Refresher Module 13 Nov 2021Document1 pageRefresher Module 13 Nov 2021JaydeeLove AlconeraNo ratings yet
- Tsu m23 Practice Problems Reinforced Concrete DesignDocument2 pagesTsu m23 Practice Problems Reinforced Concrete DesignMark Lester ValdozNo ratings yet
- Psad November 2022Document33 pagesPsad November 2022paisa baba100% (1)
- Seac 2 - Strength of Materials (No Answers)Document6 pagesSeac 2 - Strength of Materials (No Answers)Joshua John JulioNo ratings yet
- Seac 2 - Strength of Materials (No Answers)Document6 pagesSeac 2 - Strength of Materials (No Answers)Joshua John Julio100% (1)
- Midterm Exam (Sec)Document11 pagesMidterm Exam (Sec)Sherwin ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Module 3 (Reinforced Concrete Design)Document4 pagesModule 3 (Reinforced Concrete Design)Glaiza MarieNo ratings yet
- CS Apr22Document8 pagesCS Apr22John Taylor BernasNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Assessment B3 (SEC) - November 2022Document4 pagesDiagnostic Assessment B3 (SEC) - November 2022Yoshjordan LambNo ratings yet
- Ce Board May 2011Document3 pagesCe Board May 2011DHANYL KHRISSNA MIJARESNo ratings yet
- April 2024 - Psad 20Document2 pagesApril 2024 - Psad 20ralph laurenzNo ratings yet
- Esplana RCDDocument4 pagesEsplana RCDNaigell Solomon100% (1)
- VOL1Document3 pagesVOL1Ho BiNo ratings yet
- Policarpio 5 - Refresher SECDocument2 pagesPolicarpio 5 - Refresher SECMigaea100% (1)
- Refresher - Structural Design Ang ConstructionDocument3 pagesRefresher - Structural Design Ang Constructionmichael SonuganNo ratings yet
- May 2022 Refresher - Dela Cruz 1: Review InnovationsDocument3 pagesMay 2022 Refresher - Dela Cruz 1: Review InnovationsDan Edison RamosNo ratings yet
- Set BDocument12 pagesSet BDan Casurao100% (1)
- Set BDocument12 pagesSet BDan CasuraoNo ratings yet
- Structural AnalysisDocument14 pagesStructural AnalysisPrincess Gupo Tañas100% (1)
- Instruction: Write The Letter of The Correct Answer On The Answer Sheet Box Provided in A Separate FileDocument2 pagesInstruction: Write The Letter of The Correct Answer On The Answer Sheet Box Provided in A Separate FileFernan FalogmeNo ratings yet
- Review - Structural Engineering and Construction: C 3 S 3 A C yDocument2 pagesReview - Structural Engineering and Construction: C 3 S 3 A C ymichael SonuganNo ratings yet
- 5 Design Nov 2013 KeyDocument6 pages5 Design Nov 2013 KeyKenneth PadunanNo ratings yet
- Ce November 2021 Refresher Pantino 4 Sec PDFDocument4 pagesCe November 2021 Refresher Pantino 4 Sec PDFYoshjordan LambNo ratings yet
- 94 - Strength of Materials Refrehser SetDocument4 pages94 - Strength of Materials Refrehser SetJ O M A RNo ratings yet
- Review Problems in Strength of MaterialsDocument10 pagesReview Problems in Strength of MaterialsJenesis de Guzman50% (2)
- Refresher - Structural Design and Construction: Inhinyero Review CenterDocument4 pagesRefresher - Structural Design and Construction: Inhinyero Review Centermichael SonuganNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials With AnswersDocument2 pagesStrength of Materials With AnswersNathaniel Pascua100% (1)
- Tsu m19 Practice Problems Smat2Document1 pageTsu m19 Practice Problems Smat2Mark Lester ValdozNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited: Tvenkat@bheltry - Co.inDocument5 pagesBharat Heavy Electricals Limited: Tvenkat@bheltry - Co.inRukma Goud Shakkari100% (1)
- Emergency Braking SystemDocument4 pagesEmergency Braking Systemieee4mybusinessonlyNo ratings yet
- Os NotesDocument17 pagesOs NotesAshish KadamNo ratings yet
- Easa Part66 Module 01 New Part 2Document11 pagesEasa Part66 Module 01 New Part 2el farissi farisNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra and Random Processes (CS6015)Document5 pagesLinear Algebra and Random Processes (CS6015)CHAKRADHAR PALAVALASANo ratings yet
- 313-317 DEPTO One KDocument5 pages313-317 DEPTO One KPriyadarshini KrishnaswamyNo ratings yet
- Opposite Hypotenuse Adjacent Hypotenuse Sin ! Cos ! Opposite AdjacentDocument43 pagesOpposite Hypotenuse Adjacent Hypotenuse Sin ! Cos ! Opposite AdjacentFerry YutamaNo ratings yet
- Goldengate Installtion 12cDocument6 pagesGoldengate Installtion 12chariprasathdbaNo ratings yet
- A Chapter 1 Textbook SolutionDocument16 pagesA Chapter 1 Textbook SolutionjimNo ratings yet
- Domestic Company Notams 16 Jan 18Document41 pagesDomestic Company Notams 16 Jan 18Swastika MishraNo ratings yet
- 2017 Catalog 99812723Document508 pages2017 Catalog 99812723Valco0% (1)
- Omni Catolog 2005Document116 pagesOmni Catolog 2005Tuan SsvcNo ratings yet
- GitHub - Haibuihoang - Higrads - A Grads Script Library For Managing Subplots & and Other Plotting Functions PDFDocument9 pagesGitHub - Haibuihoang - Higrads - A Grads Script Library For Managing Subplots & and Other Plotting Functions PDFSetyperNo ratings yet
- Lecture 15. SamplingDocument16 pagesLecture 15. Samplingsincere guyNo ratings yet
- Overview:: Book Title:-Engineering Physics, 2E Author:-B. K. Pandey - SDocument2 pagesOverview:: Book Title:-Engineering Physics, 2E Author:-B. K. Pandey - Sdamini chandi priyaNo ratings yet
- Personalized Movie Hybrid Recommendation Model Based On GRUDocument4 pagesPersonalized Movie Hybrid Recommendation Model Based On GRUMritunjay JhaNo ratings yet
- Textbook Inventory: Room 9 Grade Title Qty. Delivered On Hand IssuedDocument4 pagesTextbook Inventory: Room 9 Grade Title Qty. Delivered On Hand IssuedMj TizonNo ratings yet
- Catalogo de RodamientosDocument399 pagesCatalogo de RodamientosmarragezNo ratings yet
- From SQL To Pandas 35Document38 pagesFrom SQL To Pandas 35M. Aji PriyatnaNo ratings yet
- PG2794 00 - en GBDocument4 pagesPG2794 00 - en GBphalkejituNo ratings yet
- A Novel Hybrid Data Balancing and Fraud Detection Approach For Automobile Insurance ClaimsDocument30 pagesA Novel Hybrid Data Balancing and Fraud Detection Approach For Automobile Insurance ClaimsAtul Kumar AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Force and Motion: ESCI 101 (Physics For Engineers)Document16 pagesForce and Motion: ESCI 101 (Physics For Engineers)Irine ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- Soal UTS Bahasa Inggris SD Semester Genap Kelas 5Document5 pagesSoal UTS Bahasa Inggris SD Semester Genap Kelas 5Yusuf HamdaniNo ratings yet
- 111 RX Final Final ManuscriptDocument27 pages111 RX Final Final ManuscriptAdrian Paul A GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Technical Specs PDFDocument12 pagesTechnical Specs PDFcsolanki6586100% (1)
- PROCEDURE For Color Coding R01 (28.06.2014)Document9 pagesPROCEDURE For Color Coding R01 (28.06.2014)punitg_2No ratings yet
- Canon GP405 Part CatalogDocument277 pagesCanon GP405 Part Catalognazmi100% (2)