Professional Documents
Culture Documents
6.1genetics One Pager Eng Memo-1
6.1genetics One Pager Eng Memo-1
Uploaded by
lesedilesedi179Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
6.1genetics One Pager Eng Memo-1
6.1genetics One Pager Eng Memo-1
Uploaded by
lesedilesedi179Copyright:
Available Formats
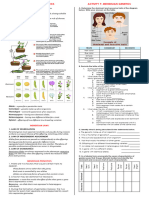
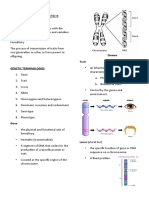
GENETICS AND INHERITANCE 6.
Types of Dominance
1. Define the following terms:
Genetics: The study of heredity / study of inheritance of traits from one generation Distinguish between Complete dominance, co-dominance and incomplete
2. The diagram below shows alleles controlling skin colour dominance and give one example of each.
to another and hair shape. Complete dominance: one allele is dominant and the other is recessive,
Gene: A segment of DNA on a chromosome that contains the code for a certain
such that the effect of the recessive allele is masked by the dominant allele in
characteristic d D KEY the heterozygous condition
Allele: Two or more forms of a gene located at the same position on a chromosome B-- brown eye colour Example: eye-colour, tongue rolling, blood groups IA and IB over i
b-- blue eye colour
Dominant allele: An allele that masks or suppresses the expression of the allele D-- curly hair
Incomplete dominance: neither one of the two alleles of a gene is
partner on the chromosome pair in the phenotype b B dominant over the other, resulting in an intermediate phenotype in the
d – straight hair
Recessive allele: An allele only expressed in the phenotype when a dominant heterozygous condition
2.1 Write the genotype for an individual who is
allele is not present Example: Humans with wavy hair; pink roses bred from red and white roses
heterozygous for hair shape. Dd ✓ (1)
Genotype: The genetic composition of an organism Co- dominance: both alleles of a gene are equally dominant whereby both
2.2 Give the genotype of an individual with blue eye alleles express themselves in the phenotype in the heterozygous condition
Phenotype: The external physical appearance of an organism Colour. bb ✓ (1)
Homozygous: Two alleles for the same trait are the same Example: Roan coat cows; blood groups involving IA and IB
2.3 Explain why an individual with Dd has curly hair. (4)
Heterozygous: Two alleles for the same trait are different Individual is heterozygous ✓having two alleles D and d. D
for curly hair is dominant and masks d which is recessive✓. 6.1 Study the diagram below and answer the questions.
Monohybrid cross: A genetic cross involving one trait only
Curly hair is expressed /visible in the phenotype. ✓ 6.1.1 Identify the type of Dominance
Dihybrid cross: A genetic cross involving two different characteristics shown above. (1)
2.4 Why is an individual with genotype dd said to be White flower (W)
3.Gregor Mendel, an Austrian Monk, is regarded as the father of homozygous? (1) Red flower (R) Incomplete dominance ✓
The two alleles for hair structure are the same✓ 6.1.2 Explain your answer in
genetics for his work on garden pea plants that helped explain how R W
genes are passed from parents to offspring. QUESTION 6.1.1 (2)
Based on his experiments he formulated the following laws:
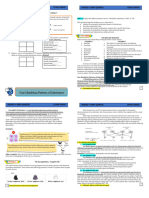
5. In rabbits the dominant allele (B) produces black fur and the A white flower crossed with a red flower
recessive allele (b) produces white fur. Study the table below yields a pink flower/an alternative
1. Mendel’s Law of Segregation states that An organism possesses two
showing the genotypes of four rabbits. phenotyp) . It indicates that neither
‘factors’ which separate or segregate so that each gamete contains only
one of these ‘factors’ Rabbit 1 2 3 4 white nor red is dominant
2. Mendel’s Law of Dominance states: When two homozygous organisms Genotype BB Bb Bb bb 6.1.3 Complete the Punnet square:
with contrasting characteristics are crossed, all the individuals of the F1 5.1 What are the phenotypes for rabbits 2 and 4 respectively. (2) P1 genotype: R and R ✓ x W and W ✓
generation will display the dominant trait. An individual that is Gametes R R
heterozygous for a particular characteristic will have the dominant trait 2- black fur 4 - white fur
W RW RW
as the phenotype. 5.2 State the genotypic ratio shown in the table.
3. Mendel’s principle of independent assortment states 1:2:1 (1) W RW RW
✓✓
The various ‘factors’ controlling the different characteristics are 5.2 Rabbit 2 was allowed to breed with rabbit 3. Use a genetic F1 genotype: RW ✓
separate entities, not influencing each other in any way, and sorting cross to show the possible phenotypes and genotypes of phenotype Pink ✓
themselves out independently during gamete formation. the F1 generation for fur colour. (6) 6.2 In certain marine invertebrates the colour of the shell is under the control of
P1 Phenotype Black fur X Black fur
one gene with three alleles. In different combinations, the three alleles produce
4. A Monohybrid cross is a cross between 2 individuals four phenotypes: orange, yellow, orange-yellow and black.
Genotype Bb X Bb ✓
that looks at ONE TRAIT The table below shows the results of the offspring produced from crosses involving
E.g.: Just looking at the height of a person Meiosis
Gametes B and b X B and b ✓ parents of different phenotypes.
TEMPLATE FOR A GENETIC CROSS – note the mark allocation ✓
Gametes PHENOTYPES OF SHELLS
B b CROSS
PARENTS OFFSPRING
Fertilisation B BB Bb 1 Yellow X Yellow 27 yellow:9 black
b Bb bb 2 Black X Black All Black
3 Orange X Orange 30 orange: 10 black
4 Orange X Yellow All orange-yellow
F1 Phenotype Black Black Black White 6.2.1 Name and describe the type of dominance shown by cross 4. (3)
✓ Incomplete dominance✓. Phenotypes of parents ( orange and yellow) are equally
P1 & F1 ✓ Genotype BB Bb Bb bb dominant ✓and are both expressed in the offspring
✓ 6.2.2 Which shell colour is controlled by the recessive allele? Black (1)
Phenotypic ratio: Black:White = 3:1
6.2.3 Use the information in the table to support your answer to QUESTION 6.2.2. (2)
Genotypic ratio: 1:2:1
This was not asked, but it is
In cross 1 both parents are yellow /none of the parents are black
included in exam guidelines. But black appears in the phenotype of the offspring OR In cross 3 both parents are
orange but black appears in the phenotype of the offspring
MSED GENETICS ONE PAGER 1 OF 4 MEMO
- But black appears in the phenotype of the
You might also like
- Mendelian Genetics of CornDocument21 pagesMendelian Genetics of CornAloysius Raj100% (1)
- This Study Resource Was: H H H H H HDocument2 pagesThis Study Resource Was: H H H H H HcokcreNo ratings yet
- G9 Science Worktext - Attachment For Week 4-5 PRINTEDDocument5 pagesG9 Science Worktext - Attachment For Week 4-5 PRINTEDClarice Jenn MaltoNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences Grade 12 Genetics Concepts Virtual Lesson PowerPoint NotesDocument19 pagesLife Sciences Grade 12 Genetics Concepts Virtual Lesson PowerPoint Notescrisseldah1No ratings yet
- Mendelian GeneticsDocument1 pageMendelian Geneticsninaquizon314No ratings yet
- Key Answer Exercise 7Document6 pagesKey Answer Exercise 7diezelNo ratings yet
- Biology First Term 24Document21 pagesBiology First Term 24Mohamed AliNo ratings yet
- Sec 2a Genetics ReviewerDocument4 pagesSec 2a Genetics ReviewerGeemaica MacaraigNo ratings yet
- Mendelian Genetics HeredityDocument19 pagesMendelian Genetics HeredityRahema VelmiNo ratings yet
- Genetics 2024Document63 pagesGenetics 2024davidmajutla87No ratings yet
- General-Biology-4th-Quarterly-ReviewerDocument3 pagesGeneral-Biology-4th-Quarterly-ReviewerSunoo EnhypenNo ratings yet
- G9 Science - Lesson 3 Non Mendelian InheritanceDocument1 pageG9 Science - Lesson 3 Non Mendelian InheritanceClarice Jenn MaltoNo ratings yet
- Cytogenetics 3Document6 pagesCytogenetics 3Jessamin Velasco Sta RomanaNo ratings yet
- ERI Monohybrid InheritanceDocument35 pagesERI Monohybrid Inheritancenanamd96No ratings yet
- Chapter 27Document58 pagesChapter 27Konishko DeyNo ratings yet
- GENBIO NotesDocument5 pagesGENBIO Notess8704386100% (1)
- INHERITANCEDocument55 pagesINHERITANCEDivine GordonNo ratings yet
- AlleleDocument121 pagesAlleleChristine CayosaNo ratings yet
- 6.4 Interactive Reader Biology 10th GradeDocument2 pages6.4 Interactive Reader Biology 10th GradeMichael TweedNo ratings yet
- General Biology ReviewerDocument8 pagesGeneral Biology Reviewernd555No ratings yet
- 156 DominantDocument3 pages156 Dominantschwarznight100% (1)
- 11.3 Note-Taking PageDocument4 pages11.3 Note-Taking Pageangelina100906No ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Introduction To GeneticsDocument4 pagesChapter 4: Introduction To Geneticsnd555No ratings yet
- 7 Priciple of Genetic 1Document22 pages7 Priciple of Genetic 1beyonduckNo ratings yet
- HEREDITARYDocument8 pagesHEREDITARYSiti Hajar RevillaNo ratings yet
- Review On Genetic TermsDocument7 pagesReview On Genetic TermsRyan HermosoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 BIO 1510Document34 pagesChapter 12 BIO 1510Chachi CNo ratings yet
- Activity in Non - Mendelian GeneticsDocument2 pagesActivity in Non - Mendelian GeneticsKarylle Joy TerezoNo ratings yet
- BIO 2 2nd SemDocument7 pagesBIO 2 2nd SemKelly Misha NoolNo ratings yet
- Bio120 Labex12 Genetics 1Document30 pagesBio120 Labex12 Genetics 1api-525858524No ratings yet
- 4.2 Cell Cycle, Division and Principles of InheritanceDocument36 pages4.2 Cell Cycle, Division and Principles of InheritanceMoza AlaliliNo ratings yet
- Mendelian, Pedigree and Modification NotesDocument7 pagesMendelian, Pedigree and Modification NotesJoyceNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 2 ReportingDocument25 pagesGen Bio 2 ReportingJhonNo ratings yet
- Genetics: General Biology II Jose Amado Ds. TorredaDocument30 pagesGenetics: General Biology II Jose Amado Ds. TorredaDyames TVNo ratings yet
- Cytological Basis of Monohybrid CrossingDocument14 pagesCytological Basis of Monohybrid CrossingShynar BekbolatNo ratings yet
- Dr. Osama Al-Amer: Chapter Iii: Extension To Mendelian GeneticsDocument29 pagesDr. Osama Al-Amer: Chapter Iii: Extension To Mendelian GeneticsBnDeRNo ratings yet
- Genetics MergedDocument385 pagesGenetics MergedYesh kumarNo ratings yet
- Genetics From Genes To Genomes 5th Edition Hartwell Solutions ManualDocument25 pagesGenetics From Genes To Genomes 5th Edition Hartwell Solutions ManualNancyWardDDSrods100% (53)
- Plant Genetics and Molecular BiologyDocument30 pagesPlant Genetics and Molecular BiologyCeazar Ian PesimoNo ratings yet
- Genbio 2 ReviewerDocument8 pagesGenbio 2 ReviewerLarvin Andrei E. BechaydaNo ratings yet
- SLK 9 - WK4 - Non Mendelian 1 1Document7 pagesSLK 9 - WK4 - Non Mendelian 1 1jerylle25No ratings yet
- M.03 Non-Mendelian GeneticsDocument5 pagesM.03 Non-Mendelian Geneticsno veNo ratings yet
- Genetics Patterns of Genetic Inheritance Genetic TerminologyDocument12 pagesGenetics Patterns of Genetic Inheritance Genetic TerminologyJustin CatalanNo ratings yet
- LessonPlan-Science and GeneticsDocument103 pagesLessonPlan-Science and GeneticsFe JanduganNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2Document16 pagesGeneral Biology 2libbyNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences GR 12 Theory Booklet GeneticsDocument9 pagesLife Sciences GR 12 Theory Booklet GeneticschiomsonzahNo ratings yet
- Genetics 1Document24 pagesGenetics 1api-237826806No ratings yet
- 4 - Q - Genetic InheritanceDocument22 pages4 - Q - Genetic InheritanceNOOR JANNAH FIRDOUSE BINTI ISMAIL KM-Pensyarah100% (1)
- Dragon Genomics Questions: AllelesDocument2 pagesDragon Genomics Questions: AllelesCaroline DrenthNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Non-Mendelian Patterns of InheritanceDocument4 pagesModule 3 - Non-Mendelian Patterns of InheritanceAcel PeñalozaNo ratings yet
- S ENG POI COMPLETE 23 Dec GA SirDocument37 pagesS ENG POI COMPLETE 23 Dec GA SirDave JuneNo ratings yet
- Dominance Relationship 11Document11 pagesDominance Relationship 11azailelleonNo ratings yet
- Bio Booklet 3Document24 pagesBio Booklet 3mert.iseri.trNo ratings yet
- GENETICS - 21.05.21 & 22.05.21 - MASE2 MergedDocument310 pagesGENETICS - 21.05.21 & 22.05.21 - MASE2 MergedHarshit VermaNo ratings yet
- Genetics W RK SHTDocument123 pagesGenetics W RK SHTChristine BelaleNo ratings yet
- Genetics Practice Problems - Simple Worksheet Name - Class PeriodDocument5 pagesGenetics Practice Problems - Simple Worksheet Name - Class PeriodGar FieldNo ratings yet
- Non-Mendelian GeneticsDocument11 pagesNon-Mendelian GeneticsalexandriaNo ratings yet
- BIOL 103 - Lab 8 - Genetics - StudentNameDocument11 pagesBIOL 103 - Lab 8 - Genetics - StudentNamegraham jarvis-lingardNo ratings yet
- PP6. Genetics and Inheritance - TerminologyDocument39 pagesPP6. Genetics and Inheritance - Terminologylebohangcandy8No ratings yet
- Unit 2Document25 pagesUnit 2akankshabhardwaj111No ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Mendel and The Gene IdeaDocument9 pagesChapter 14 Mendel and The Gene IdeaJUNG LEENo ratings yet
- 400 Q For G11 1st TermDocument85 pages400 Q For G11 1st Termromaehab201912No ratings yet
- S402F-Lecture 7 2023 - 7 MAR 2023Document92 pagesS402F-Lecture 7 2023 - 7 MAR 2023Cheung Yuk YamNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Sci 8Document45 pagesWeek 3 Sci 8Joseph Gabriel Genuino CruzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4.1 Mendelian Genetics Mono HybridDocument8 pagesChapter 4.1 Mendelian Genetics Mono HybridNizam YaakubNo ratings yet
- AP Bio Report RichieDocument7 pagesAP Bio Report RichieRcvon5No ratings yet
- Lecture Mendelian GeneticsDocument21 pagesLecture Mendelian GeneticsSunil DhatwaliaNo ratings yet
- Heredity (Class 10) NotesDocument4 pagesHeredity (Class 10) NotesAlok NaikNo ratings yet
- Bcsci 10 Unit 1 Topic1 2Document20 pagesBcsci 10 Unit 1 Topic1 2DemisNo ratings yet
- Probability Calculations in Genetics Problem Solving: Genetics Analysis: An Integrated ApproachDocument44 pagesProbability Calculations in Genetics Problem Solving: Genetics Analysis: An Integrated ApproachTimothy WilliamsNo ratings yet
- CHP 5 - Principles of Inheritance and VariationDocument68 pagesCHP 5 - Principles of Inheritance and VariationAbhishek ratnoo100% (1)
- Cot-Biology Science-DlpDocument16 pagesCot-Biology Science-DlpMarisol Ann de Leon100% (1)
- Mendel and The Gene Idea: Powerpoint Lectures ForDocument79 pagesMendel and The Gene Idea: Powerpoint Lectures ForGaurang DaveNo ratings yet
- ANTHE-2020 (X Studying) Code-PDocument14 pagesANTHE-2020 (X Studying) Code-PJiya MerjaNo ratings yet
- SIK2006 Lecture 03 Selected SlidesDocument46 pagesSIK2006 Lecture 03 Selected SlidesIIV190014 STUDENTNo ratings yet
- Set 2Document25 pagesSet 2SriramNo ratings yet
- Notes - Heredity and EvolutionDocument16 pagesNotes - Heredity and EvolutionweirdoNo ratings yet
- 5 Principles of Inheritance and VariationDocument25 pages5 Principles of Inheritance and Variationsamabdelaal2000No ratings yet
- Chapter - BIOLOGY XII PYQDocument20 pagesChapter - BIOLOGY XII PYQjagec31687No ratings yet
- Science SPL Material PDFDocument289 pagesScience SPL Material PDFViji VjNo ratings yet
- Mendelian GeneticsDocument44 pagesMendelian GeneticsEdessa G. FlordelizNo ratings yet
- Principles of Inheritance and Variation Class 12 Notes Biology - myCBSEguideDocument15 pagesPrinciples of Inheritance and Variation Class 12 Notes Biology - myCBSEguideShireen SuhailNo ratings yet
- Punnett Square 1Document16 pagesPunnett Square 1pranalinshahNo ratings yet
- Genetic Problem Monohybrid CrossesDocument4 pagesGenetic Problem Monohybrid Crosseszvbael01No ratings yet
- Ged Flash Card QuestionDocument19 pagesGed Flash Card QuestionWin Pyae Pyae AungNo ratings yet
- Selina Solutions For Class 10 Biology Chapter 3 Genetics Some Basic FundamentalsDocument9 pagesSelina Solutions For Class 10 Biology Chapter 3 Genetics Some Basic FundamentalsMysterious SinghNo ratings yet
- Genetics and Evolution 03 - Theory Notes - PDF Only - NSEJS 2023Document26 pagesGenetics and Evolution 03 - Theory Notes - PDF Only - NSEJS 2023Chinmay GoelNo ratings yet
- Instructional Technology Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesInstructional Technology Lesson Planapi-688178924No ratings yet
- Cell Division and Genetic Inheritance - FormattedDocument24 pagesCell Division and Genetic Inheritance - FormattedAISHA MUHAMMADNo ratings yet