Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DTASK2
DTASK2
Uploaded by
luciuszogratis561Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Differentiated WorksheetDocument3 pagesDifferentiated Worksheetsfake8693No ratings yet
- Module 2 - Gausss Law Guide QuestionsDocument4 pagesModule 2 - Gausss Law Guide QuestionsEdrielleNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Gausss Law Guide QuestionsDocument4 pagesModule 2 - Gausss Law Guide QuestionsEdrielleNo ratings yet
- Spher Cap ExampleDocument5 pagesSpher Cap ExampleFernanda Victoria Padró QueirugaNo ratings yet
- 2022sem II - PHSH - CC3Document2 pages2022sem II - PHSH - CC3Řůpäm ŔøýNo ratings yet
- Problems 2Document8 pagesProblems 2Jaider MárquezNo ratings yet
- WorkSheet 1 - Chapter1 - Elecrtic Charge & FieldDocument3 pagesWorkSheet 1 - Chapter1 - Elecrtic Charge & FieldseakanugaNo ratings yet
- Em WavesDocument9 pagesEm WavesAyush shuklaNo ratings yet
- SA - ElectrostaticsDocument10 pagesSA - Electrostaticsdheeraj831No ratings yet
- G12 Phy CAT 3 2023-24Document1 pageG12 Phy CAT 3 2023-24Vishwa BaskarNo ratings yet
- 8.application of Gauss TheoremDocument5 pages8.application of Gauss TheoremShubhamNo ratings yet
- Test - 2Document2 pagesTest - 2HhhhNo ratings yet
- GP2 PerformanceTasks1Document5 pagesGP2 PerformanceTasks1mar liaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Worksheet - ElectrostatisticsDocument3 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics Worksheet - ElectrostatisticsSanjukthNo ratings yet
- Mid Exam OnlineDocument2 pagesMid Exam OnlineShakeel Ahmad KasuriNo ratings yet
- Derivations To Discuss in Today's ClassDocument1 pageDerivations To Discuss in Today's ClassKashvi BhatiaNo ratings yet
- ELETROSTATICS - Advanced Level Problems (ALP) - 2Document4 pagesELETROSTATICS - Advanced Level Problems (ALP) - 2Phantom GamingNo ratings yet
- NCERT Exemplar Physics Grade 12 Chapter-2Document20 pagesNCERT Exemplar Physics Grade 12 Chapter-2Sri MeenakshiNo ratings yet
- Maineult Et Al-2012-Geophysical ProspectingDocument8 pagesMaineult Et Al-2012-Geophysical Prospectingjesadu100% (1)
- Electric Charges and FieldDocument3 pagesElectric Charges and FieldgreenalcoveindiaNo ratings yet
- PHY 103 Practice Problem Set - 6 IITK /ynm April 22, 2021Document2 pagesPHY 103 Practice Problem Set - 6 IITK /ynm April 22, 2021RAJ MEENANo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Electric Charges and FieldsDocument6 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics Electric Charges and FieldsSayantan YadavNo ratings yet
- Holidays Homework 2017 PhysicsDocument25 pagesHolidays Homework 2017 PhysicsGunveer SinghNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - Week 3 - GaussDocument3 pagesTutorial - Week 3 - GaussbilalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-Gauss's LawDocument31 pagesChapter 2-Gauss's LawThông LêNo ratings yet
- 12 - Phy - Electric Chargest Field - Question With SolutionDocument7 pages12 - Phy - Electric Chargest Field - Question With Solutionjayamadhavan2007No ratings yet
- Electric Charges and Fields WorksheetDocument1 pageElectric Charges and Fields WorksheetFHD911No ratings yet
- Physics Paper Class 12Document6 pagesPhysics Paper Class 12animeshkumar.cityparkNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document1 pageTutorial 2Alahari sai naga manuNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges and Fields 01Document1 pageElectric Charges and Fields 01sureshNo ratings yet
- Allsaints' School Gandhi Nagar, Bhopal Test - 01 Subject - Physics Class - XIIDocument2 pagesAllsaints' School Gandhi Nagar, Bhopal Test - 01 Subject - Physics Class - XIIEX DEPTT ASCTNo ratings yet
- Ermino G.zara Performance-Tasks-3 q3Document4 pagesErmino G.zara Performance-Tasks-3 q3Andre Jose ErminoNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Electric Charges and Fields PDFDocument6 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics Electric Charges and Fields PDFRanjith M100% (1)
- Assignment#1 PHY108 18 PDFDocument2 pagesAssignment#1 PHY108 18 PDFMahir AbirNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Electric Charges and FieldsDocument6 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics Electric Charges and Fieldsshikha sharma100% (1)
- Second Year Higher Secondary First Terminal EvaluationDocument7 pagesSecond Year Higher Secondary First Terminal EvaluationHarikrishnan NamboothiriNo ratings yet
- 12 Physics Electricchargesfield Tp01Document7 pages12 Physics Electricchargesfield Tp01Aryan KulratanNo ratings yet
- Possible Questions EMFDocument4 pagesPossible Questions EMFSundarNo ratings yet
- CT 1 Model PaperDocument3 pagesCT 1 Model PaperPranavNo ratings yet
- Impt 2 and 3 Marks Qs and Ans (II PU) - 2Document23 pagesImpt 2 and 3 Marks Qs and Ans (II PU) - 2Vishwaradhya KarastalmathNo ratings yet
- Questions: Cbse-English-Class 12-Physics-Chapter 2Document17 pagesQuestions: Cbse-English-Class 12-Physics-Chapter 2kushNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 3 CH: 1 Electric Flux & Gauss's LawDocument2 pagesWorksheet 3 CH: 1 Electric Flux & Gauss's LawJiya JithinNo ratings yet
- KKKC 6014 - 3 Gunn DiodeDocument20 pagesKKKC 6014 - 3 Gunn Diodeiskandar.yahyaNo ratings yet
- ISC Class 12 Physics Syllabus 2023 24Document14 pagesISC Class 12 Physics Syllabus 2023 24Vihan ShuklaNo ratings yet
- PHY 103 Problem Set - 5 IITK /ynm 21 August 2013: DIPA: Discussion of Illustrative Problems and AssignmentsDocument1 pagePHY 103 Problem Set - 5 IITK /ynm 21 August 2013: DIPA: Discussion of Illustrative Problems and AssignmentsPiyush PatelNo ratings yet
- Self AssessmentDocument21 pagesSelf AssessmentPankaj SharmaNo ratings yet
- Emf CH3Document6 pagesEmf CH3Ayhan AbdulAzizNo ratings yet
- Important Questions For Physics Class 12Document15 pagesImportant Questions For Physics Class 12Umar Abdullah100% (1)
- Isc Physics XiiDocument14 pagesIsc Physics XiiStarter gamingNo ratings yet
- ISC PhysicsDocument15 pagesISC PhysicsAparna NagarajNo ratings yet
- Gauss Theorem - WORKSHEET - 17869718 - 2024 - 03 - 03 - 15 - 46Document7 pagesGauss Theorem - WORKSHEET - 17869718 - 2024 - 03 - 03 - 15 - 46parasbhardwaj52159No ratings yet
- 12 Physics Revision Questions Chapter 2Document4 pages12 Physics Revision Questions Chapter 2abhiNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics Test 05 QPDocument3 pagesElectrostatics Test 05 QPrajkaran1991No ratings yet
- ElectrostaticsDocument3 pagesElectrostatics12A07 Nikitha SNo ratings yet
- 24-4 Gauss' LawDocument5 pages24-4 Gauss' LawBárbara MourãoNo ratings yet
- XII UT 2 PhysicsDocument4 pagesXII UT 2 Physicsharsh JoshiNo ratings yet
- Exam 2 8.022Document2 pagesExam 2 8.022Abhik SarkarNo ratings yet
- Physics 2415 Lecture 5: Using Gauss' Theorem: Spheres, Lines, PlanesDocument7 pagesPhysics 2415 Lecture 5: Using Gauss' Theorem: Spheres, Lines, PlanescuntNo ratings yet
- Gauss' Law For ElectricityDocument35 pagesGauss' Law For Electricityhiscasio100% (1)
DTASK2
DTASK2
Uploaded by
luciuszogratis561Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DTASK2
DTASK2
Uploaded by
luciuszogratis561Copyright:
Available Formats
OUR OWN HIGH SCHOOL, DUBAI
GRADE : 12 PHYSICS – ELECTRIC CHARGES AND FIELDS
2
TOPIC : Application of Gauss theorem
1
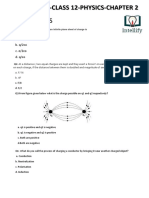
1. Two infinitely large plane thin parallel sheets having surface charge densities σ1 and σ2 are as
shown in the figure. Write the magnitudes and direction of the net fields in the regions marked II
and III. [CBSE 2014]
2. A spherical conducting shell of inner radius r1 and outer radius r2 has a charge Q.
(a) A charge q is placed at the centre of the shell. Find out the surface charge density on
the inner and outer surfaces of the shell.
(b) Is the electric field inside a cavity (with no charge) zero, independent of the fact
whether the shell is spherical or not? Explain.
3. A long charged cylinder of linear charge density +λ1 is surrounded by a hollow coaxial
conducting cylinder of linear charge density –λ2. Use Gauss’s law to obtain expressions
for the electric field at a point
(i) in the space between the cylinders, and (ii) outside the larger cylinder.
Success criteria
I can …… EE ME WT
Understand that electric flux through a Gaussian surface
is independent of the shape and the size of the surface.
Apply Gauss theorem to find the electric field intensity
due to uniform distribution of charges.
You might also like
- Differentiated WorksheetDocument3 pagesDifferentiated Worksheetsfake8693No ratings yet
- Module 2 - Gausss Law Guide QuestionsDocument4 pagesModule 2 - Gausss Law Guide QuestionsEdrielleNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Gausss Law Guide QuestionsDocument4 pagesModule 2 - Gausss Law Guide QuestionsEdrielleNo ratings yet
- Spher Cap ExampleDocument5 pagesSpher Cap ExampleFernanda Victoria Padró QueirugaNo ratings yet
- 2022sem II - PHSH - CC3Document2 pages2022sem II - PHSH - CC3Řůpäm ŔøýNo ratings yet
- Problems 2Document8 pagesProblems 2Jaider MárquezNo ratings yet
- WorkSheet 1 - Chapter1 - Elecrtic Charge & FieldDocument3 pagesWorkSheet 1 - Chapter1 - Elecrtic Charge & FieldseakanugaNo ratings yet
- Em WavesDocument9 pagesEm WavesAyush shuklaNo ratings yet
- SA - ElectrostaticsDocument10 pagesSA - Electrostaticsdheeraj831No ratings yet
- G12 Phy CAT 3 2023-24Document1 pageG12 Phy CAT 3 2023-24Vishwa BaskarNo ratings yet
- 8.application of Gauss TheoremDocument5 pages8.application of Gauss TheoremShubhamNo ratings yet
- Test - 2Document2 pagesTest - 2HhhhNo ratings yet
- GP2 PerformanceTasks1Document5 pagesGP2 PerformanceTasks1mar liaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Worksheet - ElectrostatisticsDocument3 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics Worksheet - ElectrostatisticsSanjukthNo ratings yet
- Mid Exam OnlineDocument2 pagesMid Exam OnlineShakeel Ahmad KasuriNo ratings yet
- Derivations To Discuss in Today's ClassDocument1 pageDerivations To Discuss in Today's ClassKashvi BhatiaNo ratings yet
- ELETROSTATICS - Advanced Level Problems (ALP) - 2Document4 pagesELETROSTATICS - Advanced Level Problems (ALP) - 2Phantom GamingNo ratings yet
- NCERT Exemplar Physics Grade 12 Chapter-2Document20 pagesNCERT Exemplar Physics Grade 12 Chapter-2Sri MeenakshiNo ratings yet
- Maineult Et Al-2012-Geophysical ProspectingDocument8 pagesMaineult Et Al-2012-Geophysical Prospectingjesadu100% (1)
- Electric Charges and FieldDocument3 pagesElectric Charges and FieldgreenalcoveindiaNo ratings yet
- PHY 103 Practice Problem Set - 6 IITK /ynm April 22, 2021Document2 pagesPHY 103 Practice Problem Set - 6 IITK /ynm April 22, 2021RAJ MEENANo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Electric Charges and FieldsDocument6 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics Electric Charges and FieldsSayantan YadavNo ratings yet
- Holidays Homework 2017 PhysicsDocument25 pagesHolidays Homework 2017 PhysicsGunveer SinghNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - Week 3 - GaussDocument3 pagesTutorial - Week 3 - GaussbilalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-Gauss's LawDocument31 pagesChapter 2-Gauss's LawThông LêNo ratings yet
- 12 - Phy - Electric Chargest Field - Question With SolutionDocument7 pages12 - Phy - Electric Chargest Field - Question With Solutionjayamadhavan2007No ratings yet
- Electric Charges and Fields WorksheetDocument1 pageElectric Charges and Fields WorksheetFHD911No ratings yet
- Physics Paper Class 12Document6 pagesPhysics Paper Class 12animeshkumar.cityparkNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document1 pageTutorial 2Alahari sai naga manuNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges and Fields 01Document1 pageElectric Charges and Fields 01sureshNo ratings yet
- Allsaints' School Gandhi Nagar, Bhopal Test - 01 Subject - Physics Class - XIIDocument2 pagesAllsaints' School Gandhi Nagar, Bhopal Test - 01 Subject - Physics Class - XIIEX DEPTT ASCTNo ratings yet
- Ermino G.zara Performance-Tasks-3 q3Document4 pagesErmino G.zara Performance-Tasks-3 q3Andre Jose ErminoNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Electric Charges and Fields PDFDocument6 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics Electric Charges and Fields PDFRanjith M100% (1)
- Assignment#1 PHY108 18 PDFDocument2 pagesAssignment#1 PHY108 18 PDFMahir AbirNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Electric Charges and FieldsDocument6 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics Electric Charges and Fieldsshikha sharma100% (1)
- Second Year Higher Secondary First Terminal EvaluationDocument7 pagesSecond Year Higher Secondary First Terminal EvaluationHarikrishnan NamboothiriNo ratings yet
- 12 Physics Electricchargesfield Tp01Document7 pages12 Physics Electricchargesfield Tp01Aryan KulratanNo ratings yet
- Possible Questions EMFDocument4 pagesPossible Questions EMFSundarNo ratings yet
- CT 1 Model PaperDocument3 pagesCT 1 Model PaperPranavNo ratings yet
- Impt 2 and 3 Marks Qs and Ans (II PU) - 2Document23 pagesImpt 2 and 3 Marks Qs and Ans (II PU) - 2Vishwaradhya KarastalmathNo ratings yet
- Questions: Cbse-English-Class 12-Physics-Chapter 2Document17 pagesQuestions: Cbse-English-Class 12-Physics-Chapter 2kushNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 3 CH: 1 Electric Flux & Gauss's LawDocument2 pagesWorksheet 3 CH: 1 Electric Flux & Gauss's LawJiya JithinNo ratings yet
- KKKC 6014 - 3 Gunn DiodeDocument20 pagesKKKC 6014 - 3 Gunn Diodeiskandar.yahyaNo ratings yet
- ISC Class 12 Physics Syllabus 2023 24Document14 pagesISC Class 12 Physics Syllabus 2023 24Vihan ShuklaNo ratings yet
- PHY 103 Problem Set - 5 IITK /ynm 21 August 2013: DIPA: Discussion of Illustrative Problems and AssignmentsDocument1 pagePHY 103 Problem Set - 5 IITK /ynm 21 August 2013: DIPA: Discussion of Illustrative Problems and AssignmentsPiyush PatelNo ratings yet
- Self AssessmentDocument21 pagesSelf AssessmentPankaj SharmaNo ratings yet
- Emf CH3Document6 pagesEmf CH3Ayhan AbdulAzizNo ratings yet
- Important Questions For Physics Class 12Document15 pagesImportant Questions For Physics Class 12Umar Abdullah100% (1)
- Isc Physics XiiDocument14 pagesIsc Physics XiiStarter gamingNo ratings yet
- ISC PhysicsDocument15 pagesISC PhysicsAparna NagarajNo ratings yet
- Gauss Theorem - WORKSHEET - 17869718 - 2024 - 03 - 03 - 15 - 46Document7 pagesGauss Theorem - WORKSHEET - 17869718 - 2024 - 03 - 03 - 15 - 46parasbhardwaj52159No ratings yet
- 12 Physics Revision Questions Chapter 2Document4 pages12 Physics Revision Questions Chapter 2abhiNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics Test 05 QPDocument3 pagesElectrostatics Test 05 QPrajkaran1991No ratings yet
- ElectrostaticsDocument3 pagesElectrostatics12A07 Nikitha SNo ratings yet
- 24-4 Gauss' LawDocument5 pages24-4 Gauss' LawBárbara MourãoNo ratings yet
- XII UT 2 PhysicsDocument4 pagesXII UT 2 Physicsharsh JoshiNo ratings yet
- Exam 2 8.022Document2 pagesExam 2 8.022Abhik SarkarNo ratings yet
- Physics 2415 Lecture 5: Using Gauss' Theorem: Spheres, Lines, PlanesDocument7 pagesPhysics 2415 Lecture 5: Using Gauss' Theorem: Spheres, Lines, PlanescuntNo ratings yet
- Gauss' Law For ElectricityDocument35 pagesGauss' Law For Electricityhiscasio100% (1)