Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Design Conveyor Calculation
Design Conveyor Calculation
Uploaded by
Thành ChíCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
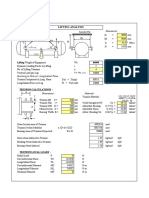
- Lifting Trunnion Calculations - 1Document1 pageLifting Trunnion Calculations - 1shaishav100% (2)
- Lifting Trunnion Calculations On Horizontal Vessel - 1Document1 pageLifting Trunnion Calculations On Horizontal Vessel - 1miteshpatel191No ratings yet
- Cosmology and Gravitation: Spin, Torsion, Rotation, and SupergravityDocument507 pagesCosmology and Gravitation: Spin, Torsion, Rotation, and SupergravityGerové InvestmentsNo ratings yet
- Spreader Beam: ASME BTH-1: InputsDocument17 pagesSpreader Beam: ASME BTH-1: InputsGokul AmarnathNo ratings yet
- Manual Detail Calculation of Conveyor KCDocument32 pagesManual Detail Calculation of Conveyor KCSergio Diaz100% (1)
- Travelling Tripper CalculationDocument5 pagesTravelling Tripper CalculationHarshGupta100% (1)
- Bending Moment Calculation - Anticreep Center, One Cantilever, Tangent TrackDocument7 pagesBending Moment Calculation - Anticreep Center, One Cantilever, Tangent TrackAnkit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Models MultimineralDocument49 pagesModels Multimineralahmed_497959294No ratings yet
- Calculations Summary Sheet: Belt Conveyor Drive Sizing CalculationsDocument5 pagesCalculations Summary Sheet: Belt Conveyor Drive Sizing CalculationsymsyaseenNo ratings yet
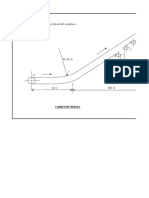
- The Values Are Not Linked With Anywhere ..: Conveyor ProfileDocument33 pagesThe Values Are Not Linked With Anywhere ..: Conveyor ProfileMustafa Akbar100% (1)
- Jis G-3444Document10 pagesJis G-3444Maulana YusufNo ratings yet
- Analisis Drag Scrapper Chain Feeder (FB01 & FB02) EPIDocument10 pagesAnalisis Drag Scrapper Chain Feeder (FB01 & FB02) EPIWaris La Joi WakatobiNo ratings yet
- BC DesignDocument33 pagesBC DesignrohithNo ratings yet
- GDC Steel Pole Self Supporting 410 SQ MM TACSR AS Rev0Document1 pageGDC Steel Pole Self Supporting 410 SQ MM TACSR AS Rev0Victor DoyoganNo ratings yet
- Conveyor Design DraftDocument25 pagesConveyor Design DraftDxFxNo ratings yet
- Winch Hoist Motor Selection For RabutecDocument2 pagesWinch Hoist Motor Selection For RabutecKarikalan JayNo ratings yet
- WINCH and DRUM WINDER Design and AnalysiDocument2 pagesWINCH and DRUM WINDER Design and Analysipetrone.andrea20No ratings yet
- Slab Bridge Design To AASHTO LRFDDocument13 pagesSlab Bridge Design To AASHTO LRFDYOYONo ratings yet
- Manual Detail Calculation KC 1cDocument30 pagesManual Detail Calculation KC 1cfrantor100% (1)
- Lashing Lug Round Bar Design: 1. GeneralDocument3 pagesLashing Lug Round Bar Design: 1. GeneralinnovativekarthiNo ratings yet
- 35m DesignDocument160 pages35m DesignPhanindra NathNo ratings yet
- Project DescritionDocument7 pagesProject DescritionWatcharapol SukhaboteNo ratings yet
- 19m Super Structure Design Report R1Document79 pages19m Super Structure Design Report R1A MNo ratings yet
- General Cargo: Type of VesselDocument3 pagesGeneral Cargo: Type of Vesselphan phucNo ratings yet
- Gantry CraneDocument31 pagesGantry Cranekushaljp8989No ratings yet
- System Information Idler Set DataDocument98 pagesSystem Information Idler Set DataHasan arif KısaalioğluNo ratings yet
- Beam Load Calculator BasicDocument2 pagesBeam Load Calculator Basichary9100No ratings yet
- Power Calculations PPDocument3 pagesPower Calculations PPbashok20No ratings yet
- Gantry CraneDocument20 pagesGantry Cranekushaljp8989No ratings yet
- Steel Beam SpreadsheetDocument27 pagesSteel Beam SpreadsheetHugh McGilveray100% (1)
- Calculation Methods - Conveyor BeltsDocument20 pagesCalculation Methods - Conveyor BeltsPickMe AltheaNo ratings yet
- Design of Square Footing For A Recta Sloped Footing: Check For Development LengthDocument44 pagesDesign of Square Footing For A Recta Sloped Footing: Check For Development LengthSwarna LathaNo ratings yet
- Cor-695 450tph - A AtolloDocument10 pagesCor-695 450tph - A AtolloCristobal JimenezNo ratings yet
- Steel Truss Bridge 85 MT Bowarch Pedestrian BridgeDocument19 pagesSteel Truss Bridge 85 MT Bowarch Pedestrian Bridgeakshay kothiyalNo ratings yet
- Verotop P, 34mm, Galv, 1960, LHLL - 240501 - 123228Document2 pagesVerotop P, 34mm, Galv, 1960, LHLL - 240501 - 123228Juan JoseNo ratings yet
- PV-0013-MEC-MC-0021-B Correa CC-101Document14 pagesPV-0013-MEC-MC-0021-B Correa CC-101Mario Leonel Guerra Box100% (1)
- Watermist SystemDocument21 pagesWatermist SysteminnovativekarthiNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Subject Information: Statical Calculation For Masonry Abutment DesignDocument10 pages1.1 Subject Information: Statical Calculation For Masonry Abutment DesignabadittadesseNo ratings yet
- 2 Ruller BaandtransportoerDocument23 pages2 Ruller BaandtransportoerErich ThomasNo ratings yet
- Appm AndreDocument56 pagesAppm AndreAuliansyahNo ratings yet
- Deck SlabDocument7 pagesDeck Slabedc1312No ratings yet
- CF-PSC-R-02A, 02B, 02C & 02D (Crushed Revert)Document33 pagesCF-PSC-R-02A, 02B, 02C & 02D (Crushed Revert)Harish KumarNo ratings yet
- Rubber Belt Conveyor Calculations (ISO 5048: 1989 E) : BC 2304 NDDocument8 pagesRubber Belt Conveyor Calculations (ISO 5048: 1989 E) : BC 2304 NDmah moud100% (1)
- Thyssenkrupp Fördertechnik GMBH: Organic Growth Project 1 (Ogp1) Execution PhaseDocument11 pagesThyssenkrupp Fördertechnik GMBH: Organic Growth Project 1 (Ogp1) Execution PhasedavidusachNo ratings yet
- Lift Calculation DemoDocument4 pagesLift Calculation Demoa_toups0% (1)
- Isoloated Footing DesignDocument7 pagesIsoloated Footing DesignHayder HasanNo ratings yet
- m-1 ReportDocument58 pagesm-1 ReportHasan arif KısaalioğluNo ratings yet
- Balbhadra FinalDocument2 pagesBalbhadra FinalPRASHANT GIRINo ratings yet
- General Material: CommentsDocument10 pagesGeneral Material: CommentsRafael FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Calculation Cpi Tank: I. Design Parameters I.1 Design DataDocument5 pagesCalculation Cpi Tank: I. Design Parameters I.1 Design DataikramNo ratings yet
- Excel Sheet 2007Document20 pagesExcel Sheet 2007Muhammad ImranNo ratings yet
- RC Footing Design FinalDocument37 pagesRC Footing Design FinalTarunNo ratings yet
- Baja 1Document25 pagesBaja 1Ruddy ChoiruddynNo ratings yet
- Transportador B01 R2 OADocument19 pagesTransportador B01 R2 OAmacbolNo ratings yet
- Saudi Designers: Design of Pad & Chimney FoundationDocument31 pagesSaudi Designers: Design of Pad & Chimney FoundationFayyaz Ali ShahNo ratings yet
- SI Footing Rec BDocument6 pagesSI Footing Rec BRenvil PedernalNo ratings yet
- BK 4 (CC 51400)Document9 pagesBK 4 (CC 51400)hasan arifNo ratings yet
- Cylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsFrom EverandCylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsNo ratings yet
- Handout Powerpoint Chem 301 PharChm1Document101 pagesHandout Powerpoint Chem 301 PharChm1Mikee MeladNo ratings yet
- 01-11-Physics IDocument270 pages01-11-Physics Ikalley minogNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - MATERIAL TESTINGDocument48 pagesChapter 4 - MATERIAL TESTINGتاج نيسهاNo ratings yet
- Soliton Propagation in Optical Fibers: Russell Herman UNC Wilmington March 21, 2003Document34 pagesSoliton Propagation in Optical Fibers: Russell Herman UNC Wilmington March 21, 2003Edina MehicNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Al 6360 Alloy Reinforced With Sic ParticulatesDocument13 pagesEvaluation of Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Al 6360 Alloy Reinforced With Sic ParticulatesSripad ANo ratings yet
- Superstring Theory: Past, Present, and Future: John H. SchwarzDocument30 pagesSuperstring Theory: Past, Present, and Future: John H. SchwarzEvelinaNo ratings yet
- Day Length: DescriptionDocument2 pagesDay Length: DescriptionDianaNo ratings yet
- KooferDocument2 pagesKooferGary JamesNo ratings yet
- Bellofram T2000 IP Transducer Im PDFDocument6 pagesBellofram T2000 IP Transducer Im PDFelyuyaNo ratings yet
- Chinmaya Vidyalaya, Kannamaly: Sample Paper - 1Document19 pagesChinmaya Vidyalaya, Kannamaly: Sample Paper - 1Deanne Joe JohnsonNo ratings yet
- More Uniformly Accelerated MotionDocument2 pagesMore Uniformly Accelerated MotionNguyễn LinhNo ratings yet
- TRANSFORMATIONDocument58 pagesTRANSFORMATIONJavariaNo ratings yet
- ECE330 Fall 16 Lecture3 PDFDocument10 pagesECE330 Fall 16 Lecture3 PDFPhùng Đức AnhNo ratings yet
- Supplementary Assignment For Chem 103Document1 pageSupplementary Assignment For Chem 103madhur sharmaNo ratings yet
- 4WE10 Series - Tech SpecificationsDocument6 pages4WE10 Series - Tech Specificationsargo_arjieantoNo ratings yet
- Math 7 (Week 3)Document16 pagesMath 7 (Week 3)John Raygie Ordoñez CinetaNo ratings yet
- MSC PSPH101 MathmethodsDocument6 pagesMSC PSPH101 MathmethodsashwiniNo ratings yet
- BP701TPDocument1 pageBP701TPsaransh misraNo ratings yet
- Chap 3 - 3.1 - Partial Derivatives - LatestDocument12 pagesChap 3 - 3.1 - Partial Derivatives - LatestsyafiqNo ratings yet
- Ec73 - RF and Microwave Engineering Unit: 1 Two Port RF Networks-Circuit Representation 2 Marks Questions and AnswersDocument27 pagesEc73 - RF and Microwave Engineering Unit: 1 Two Port RF Networks-Circuit Representation 2 Marks Questions and AnswersSanthosh PounrajNo ratings yet
- Derivation of Plancks Formula Radiation Chapter10Document14 pagesDerivation of Plancks Formula Radiation Chapter10TewodrosNo ratings yet
- Phys102 Magnetic FieldDocument34 pagesPhys102 Magnetic FieldMayson UdarbeNo ratings yet
- Design For Simple StressesDocument131 pagesDesign For Simple Stresseskhudhayer1970No ratings yet
- Hindware TILES Multi Charge Catologue HSILDocument4 pagesHindware TILES Multi Charge Catologue HSILKunNous DesignsNo ratings yet
- Yunshu InformationGeometryDocument79 pagesYunshu InformationGeometrysemiringNo ratings yet
- SSPC PA2 Measurement of Dry Coating Thickness With Magnetic GagesDocument11 pagesSSPC PA2 Measurement of Dry Coating Thickness With Magnetic Gageslonglong3003No ratings yet
Design Conveyor Calculation
Design Conveyor Calculation
Uploaded by
Thành ChíCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Design Conveyor Calculation
Design Conveyor Calculation
Uploaded by
Thành ChíCopyright:
Available Formats
REFERENCE STANDARDS AND DOCUMENTS
1. AS4324.1-1995 – Calculation of Machine loads
4. ISO5048 – Continuous mechanical handling equipment – Belt conveyors with carrying idlers - Calculation of operation power and tensile forces
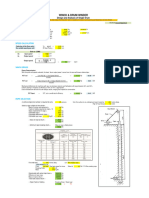
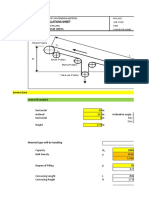
1 PARAMETERS
Symbols Values Units References
Material parameters
Maximum material density; rmax 2500 kg/m3 soil, rock
Minimum material density; rmin 850 kg/m 3
bulk coal
Maximum throughput; Qmax 200 tph assumed
Gravity; g 9.81 m/s2
Conveyor parameters
Troughing angle; l 35 °
Surcharge angle; r 20 °
Angle of repose of material; y 37 °
Total width of belt; B 1200 mm
Effective roller lenth; lm 460 mm
Dyameter of Idler di 152.4 mm 6ins
Maximum belt speed; Vc 4.5 m/s
Conveyor parameters for belt force
Conveyor length (between pulleys); Lc 12 m
Clear width between chute walls; b1 1 m (Assumption)
Average weight of all idlers; qR 20 kg/m (Assumption)
Average weight of belt; qB 16 kg/m
Mass of drive pulley mp 100 kg assumed
Maximum height of raised material; Hc 3.11 m (Calculated 15deg)
Diameter of pulley; Dp 800 mm
Idler spacing on the carrying side of the conveyor; ao 1 m
Idler spacing on the reverse side of the conveyor; au 3 m
Efficiency of belt drive; hc 0.92 (Assumption)
Gear ratio; icb 14
o
Wrapping angle of belt around drive pulley (deg.); fd 187
Coupling factor; fcin 1.6 Assumed Calculation regarding with AS4324.1
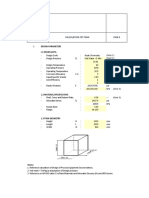
2 Material load calculation regarding with ISO5048
a. Cross section area of conveyor. b. Maximum cross section area
Description Symbols Formulas Value Units References Description Formulas Value units
2.1 Cross-section area of material: 2.1.1. Cross-section area of material (AS 4324.1, App. I2):
Usable width of belt; bc 0.9B – 50mm 1030 mm Useable width of belt; bu = (0.9´B – 50mm) 1030 mm
Length of the centre idler l3 460 mm Horizontal width; c = lm + (bu – lm)´cos(l) 926.9 mm
Troughing angle lc 35 ° Upper area; S1 = c2´(2´r/57.3-sin(2´r))/(8´(sin(r))2) 0.051 m2
Surcharge angle qc 20 ° Lower area; S2 = 0.25´(c2 - (lm)2)´tan(l) 0.113 m2
Upper cross-section area S1 [l3+(bc-l3)cos(lc)]2tan(qc)/6 0.052 m2 Total cross-section area; Sx = S1 + S2 0.164 m2
Lower cross-section area S2 [l3+0.5(bc-l3)cos(lc)](bc-l3)sin(lc)/2 0.113 m2 2.1.2. Maximum cross-section area of material (AS 4324.1, App. I3):
Total cross-section area Sc S1+S2 0.165 m2 Maximum horizontal width; cB = lm + (B – lm)´cos(l) 1066.2 mm
2.2 Maximum cross-section area of material: Upper area (use max. surcharge ) S1m = (cB)2´(2´y/57.3-sin(2´ y))/(8´(sin(y))2) = 0.176 m2 0.130 m2
Max. upper cross-section area S1m [l3+(B-l3)cos(lc)]2tan(qc)/6 0.069 m2 Lower area; S2m = 0.25´((cB)2 - (lm)2)´tan(l) 0.162 m2
Max. lower cross-section area S2m [l3+0.5(B-l3)cos(lc)](B-l3)sin(lc)/2 0.162 m2 Total cross-section area; Sm = S1m + S2m 0.291
Total max. cross-section area Scm S1m+S2m 0.231 m2 2.1.3. Live load on the conveyor (Ref. 7, Cl. 4.3.10):
2.3 Live material on the conveyor Live load on conveyor belt F =rmax´g´Sx 4.025 kN/m
Material load (using area, incl. dyn. Factor of 1.1) Fc1 1.1g Sc rmax 4.464 kN/m Live load on conveyor belt (using throughput) 1.1g Qmax/Vc 0.133 kN/m
Material load (using throughput + dyn. Factor 1.1) Fmq 1.1g Qmax/Vc 0.133 kN/m Flooded belt load; FF = rmax´g´Sm 7.149 kN/m
Nominal material load F (Select minimum value) 0.133 kN/m FEM 1997
Max. material load (using area + dyn. Factor 1.1) Fm 1.1g Scm rmax 6.229 kN/m
3 Conveyor Power & Belt Force
Throughput (tph) Power (kW)
3.1 Drive Power: 2000 41.6
Rolling Friction, Fh: 1000 23.6
Weight of max. load (inc. dyn. factor of 1.1); qG 1.1´Qmax/Vc 13.58 kg/m 200 9.4
Average rolling friction coefficient (fr. 0.016 - 0.03); m 0.023 50 6.7
Main friction; Fh m´(qG+qR+2´qB)´g´Lc 0.2 kN 20 6.2
Additional resistance, Fn: 10 6
Inertial resistance; FbA (qG+qR+2´qB)´(Vc) 2 1.33 kN (Ref. ISO 5048)
Friction between material and belt ( 0.5-0.7); m1 0.50 (Ref. ISO 5048, cl. 5.1.4)
Minimum acceleration length lb_min; lbmin (Vc)2/(2´g´m1) 2.06 m (Ref. ISO 5048) Power vs. throughput
Friction bet. material and skirt plates (0.5-0.7); m2 0.50 (Ref. ISO 5048, cl. 5.1.4)
25
Frictional resistance bw material & skirt plates; Ffc (m2´qG2´g´ lbmin)/(rmax´B2) 0.00 kN (Ref. ISO 5048)
Additional resistance of the individual parts; Fn FbA + Ffc 1.33 kN
Inclination resistance of conveyed load, Fst: 20
Inclination resistance of conveyed load; Fst qG´g´Hc 0.41 kN
Total resistance force; Fu Fst + Fn +Fh 1.92 kN
15
Power (kW)
Drive power:
Required torque on drive pulley; Tu 0.5´Dp´Fu 0.77 kNm
Angular speed of pulley; Vc/(0.5´Dp) 11.25 s-1 10
wp
Required drive power; Pcre (Tu´wp)/hc 9.4 kW
5
Check power when flooded belt:
Minimum tension force for flooded belt; FFu 1.1´FF´Lcm ´ sin(qLmax) 21.28 kN
Required minimum torque on drive pulley; TTu 0.5´Dp´FFu 8.51 kNm 0
Required torque on drive pulley; Tur TTu/fcin 5.32 kNm 0 200 400 600 800 1000 1200
Required drive power; Pcff (Tur´wp)/hc 65.06 kW Throughput (tph)
Require Gear ratio i 6.98
New idlers in new conveyor
You might also like
- Lifting Trunnion Calculations - 1Document1 pageLifting Trunnion Calculations - 1shaishav100% (2)
- Lifting Trunnion Calculations On Horizontal Vessel - 1Document1 pageLifting Trunnion Calculations On Horizontal Vessel - 1miteshpatel191No ratings yet
- Cosmology and Gravitation: Spin, Torsion, Rotation, and SupergravityDocument507 pagesCosmology and Gravitation: Spin, Torsion, Rotation, and SupergravityGerové InvestmentsNo ratings yet
- Spreader Beam: ASME BTH-1: InputsDocument17 pagesSpreader Beam: ASME BTH-1: InputsGokul AmarnathNo ratings yet
- Manual Detail Calculation of Conveyor KCDocument32 pagesManual Detail Calculation of Conveyor KCSergio Diaz100% (1)
- Travelling Tripper CalculationDocument5 pagesTravelling Tripper CalculationHarshGupta100% (1)
- Bending Moment Calculation - Anticreep Center, One Cantilever, Tangent TrackDocument7 pagesBending Moment Calculation - Anticreep Center, One Cantilever, Tangent TrackAnkit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Models MultimineralDocument49 pagesModels Multimineralahmed_497959294No ratings yet
- Calculations Summary Sheet: Belt Conveyor Drive Sizing CalculationsDocument5 pagesCalculations Summary Sheet: Belt Conveyor Drive Sizing CalculationsymsyaseenNo ratings yet
- The Values Are Not Linked With Anywhere ..: Conveyor ProfileDocument33 pagesThe Values Are Not Linked With Anywhere ..: Conveyor ProfileMustafa Akbar100% (1)
- Jis G-3444Document10 pagesJis G-3444Maulana YusufNo ratings yet
- Analisis Drag Scrapper Chain Feeder (FB01 & FB02) EPIDocument10 pagesAnalisis Drag Scrapper Chain Feeder (FB01 & FB02) EPIWaris La Joi WakatobiNo ratings yet
- BC DesignDocument33 pagesBC DesignrohithNo ratings yet
- GDC Steel Pole Self Supporting 410 SQ MM TACSR AS Rev0Document1 pageGDC Steel Pole Self Supporting 410 SQ MM TACSR AS Rev0Victor DoyoganNo ratings yet
- Conveyor Design DraftDocument25 pagesConveyor Design DraftDxFxNo ratings yet
- Winch Hoist Motor Selection For RabutecDocument2 pagesWinch Hoist Motor Selection For RabutecKarikalan JayNo ratings yet
- WINCH and DRUM WINDER Design and AnalysiDocument2 pagesWINCH and DRUM WINDER Design and Analysipetrone.andrea20No ratings yet
- Slab Bridge Design To AASHTO LRFDDocument13 pagesSlab Bridge Design To AASHTO LRFDYOYONo ratings yet
- Manual Detail Calculation KC 1cDocument30 pagesManual Detail Calculation KC 1cfrantor100% (1)
- Lashing Lug Round Bar Design: 1. GeneralDocument3 pagesLashing Lug Round Bar Design: 1. GeneralinnovativekarthiNo ratings yet
- 35m DesignDocument160 pages35m DesignPhanindra NathNo ratings yet
- Project DescritionDocument7 pagesProject DescritionWatcharapol SukhaboteNo ratings yet
- 19m Super Structure Design Report R1Document79 pages19m Super Structure Design Report R1A MNo ratings yet
- General Cargo: Type of VesselDocument3 pagesGeneral Cargo: Type of Vesselphan phucNo ratings yet
- Gantry CraneDocument31 pagesGantry Cranekushaljp8989No ratings yet
- System Information Idler Set DataDocument98 pagesSystem Information Idler Set DataHasan arif KısaalioğluNo ratings yet
- Beam Load Calculator BasicDocument2 pagesBeam Load Calculator Basichary9100No ratings yet
- Power Calculations PPDocument3 pagesPower Calculations PPbashok20No ratings yet
- Gantry CraneDocument20 pagesGantry Cranekushaljp8989No ratings yet
- Steel Beam SpreadsheetDocument27 pagesSteel Beam SpreadsheetHugh McGilveray100% (1)
- Calculation Methods - Conveyor BeltsDocument20 pagesCalculation Methods - Conveyor BeltsPickMe AltheaNo ratings yet
- Design of Square Footing For A Recta Sloped Footing: Check For Development LengthDocument44 pagesDesign of Square Footing For A Recta Sloped Footing: Check For Development LengthSwarna LathaNo ratings yet
- Cor-695 450tph - A AtolloDocument10 pagesCor-695 450tph - A AtolloCristobal JimenezNo ratings yet
- Steel Truss Bridge 85 MT Bowarch Pedestrian BridgeDocument19 pagesSteel Truss Bridge 85 MT Bowarch Pedestrian Bridgeakshay kothiyalNo ratings yet
- Verotop P, 34mm, Galv, 1960, LHLL - 240501 - 123228Document2 pagesVerotop P, 34mm, Galv, 1960, LHLL - 240501 - 123228Juan JoseNo ratings yet
- PV-0013-MEC-MC-0021-B Correa CC-101Document14 pagesPV-0013-MEC-MC-0021-B Correa CC-101Mario Leonel Guerra Box100% (1)
- Watermist SystemDocument21 pagesWatermist SysteminnovativekarthiNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Subject Information: Statical Calculation For Masonry Abutment DesignDocument10 pages1.1 Subject Information: Statical Calculation For Masonry Abutment DesignabadittadesseNo ratings yet
- 2 Ruller BaandtransportoerDocument23 pages2 Ruller BaandtransportoerErich ThomasNo ratings yet
- Appm AndreDocument56 pagesAppm AndreAuliansyahNo ratings yet
- Deck SlabDocument7 pagesDeck Slabedc1312No ratings yet
- CF-PSC-R-02A, 02B, 02C & 02D (Crushed Revert)Document33 pagesCF-PSC-R-02A, 02B, 02C & 02D (Crushed Revert)Harish KumarNo ratings yet
- Rubber Belt Conveyor Calculations (ISO 5048: 1989 E) : BC 2304 NDDocument8 pagesRubber Belt Conveyor Calculations (ISO 5048: 1989 E) : BC 2304 NDmah moud100% (1)
- Thyssenkrupp Fördertechnik GMBH: Organic Growth Project 1 (Ogp1) Execution PhaseDocument11 pagesThyssenkrupp Fördertechnik GMBH: Organic Growth Project 1 (Ogp1) Execution PhasedavidusachNo ratings yet
- Lift Calculation DemoDocument4 pagesLift Calculation Demoa_toups0% (1)
- Isoloated Footing DesignDocument7 pagesIsoloated Footing DesignHayder HasanNo ratings yet
- m-1 ReportDocument58 pagesm-1 ReportHasan arif KısaalioğluNo ratings yet
- Balbhadra FinalDocument2 pagesBalbhadra FinalPRASHANT GIRINo ratings yet
- General Material: CommentsDocument10 pagesGeneral Material: CommentsRafael FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Calculation Cpi Tank: I. Design Parameters I.1 Design DataDocument5 pagesCalculation Cpi Tank: I. Design Parameters I.1 Design DataikramNo ratings yet
- Excel Sheet 2007Document20 pagesExcel Sheet 2007Muhammad ImranNo ratings yet
- RC Footing Design FinalDocument37 pagesRC Footing Design FinalTarunNo ratings yet
- Baja 1Document25 pagesBaja 1Ruddy ChoiruddynNo ratings yet
- Transportador B01 R2 OADocument19 pagesTransportador B01 R2 OAmacbolNo ratings yet
- Saudi Designers: Design of Pad & Chimney FoundationDocument31 pagesSaudi Designers: Design of Pad & Chimney FoundationFayyaz Ali ShahNo ratings yet
- SI Footing Rec BDocument6 pagesSI Footing Rec BRenvil PedernalNo ratings yet
- BK 4 (CC 51400)Document9 pagesBK 4 (CC 51400)hasan arifNo ratings yet
- Cylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsFrom EverandCylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsNo ratings yet
- Handout Powerpoint Chem 301 PharChm1Document101 pagesHandout Powerpoint Chem 301 PharChm1Mikee MeladNo ratings yet
- 01-11-Physics IDocument270 pages01-11-Physics Ikalley minogNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - MATERIAL TESTINGDocument48 pagesChapter 4 - MATERIAL TESTINGتاج نيسهاNo ratings yet
- Soliton Propagation in Optical Fibers: Russell Herman UNC Wilmington March 21, 2003Document34 pagesSoliton Propagation in Optical Fibers: Russell Herman UNC Wilmington March 21, 2003Edina MehicNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Al 6360 Alloy Reinforced With Sic ParticulatesDocument13 pagesEvaluation of Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Al 6360 Alloy Reinforced With Sic ParticulatesSripad ANo ratings yet
- Superstring Theory: Past, Present, and Future: John H. SchwarzDocument30 pagesSuperstring Theory: Past, Present, and Future: John H. SchwarzEvelinaNo ratings yet
- Day Length: DescriptionDocument2 pagesDay Length: DescriptionDianaNo ratings yet
- KooferDocument2 pagesKooferGary JamesNo ratings yet
- Bellofram T2000 IP Transducer Im PDFDocument6 pagesBellofram T2000 IP Transducer Im PDFelyuyaNo ratings yet
- Chinmaya Vidyalaya, Kannamaly: Sample Paper - 1Document19 pagesChinmaya Vidyalaya, Kannamaly: Sample Paper - 1Deanne Joe JohnsonNo ratings yet
- More Uniformly Accelerated MotionDocument2 pagesMore Uniformly Accelerated MotionNguyễn LinhNo ratings yet
- TRANSFORMATIONDocument58 pagesTRANSFORMATIONJavariaNo ratings yet
- ECE330 Fall 16 Lecture3 PDFDocument10 pagesECE330 Fall 16 Lecture3 PDFPhùng Đức AnhNo ratings yet
- Supplementary Assignment For Chem 103Document1 pageSupplementary Assignment For Chem 103madhur sharmaNo ratings yet
- 4WE10 Series - Tech SpecificationsDocument6 pages4WE10 Series - Tech Specificationsargo_arjieantoNo ratings yet
- Math 7 (Week 3)Document16 pagesMath 7 (Week 3)John Raygie Ordoñez CinetaNo ratings yet
- MSC PSPH101 MathmethodsDocument6 pagesMSC PSPH101 MathmethodsashwiniNo ratings yet
- BP701TPDocument1 pageBP701TPsaransh misraNo ratings yet
- Chap 3 - 3.1 - Partial Derivatives - LatestDocument12 pagesChap 3 - 3.1 - Partial Derivatives - LatestsyafiqNo ratings yet
- Ec73 - RF and Microwave Engineering Unit: 1 Two Port RF Networks-Circuit Representation 2 Marks Questions and AnswersDocument27 pagesEc73 - RF and Microwave Engineering Unit: 1 Two Port RF Networks-Circuit Representation 2 Marks Questions and AnswersSanthosh PounrajNo ratings yet
- Derivation of Plancks Formula Radiation Chapter10Document14 pagesDerivation of Plancks Formula Radiation Chapter10TewodrosNo ratings yet
- Phys102 Magnetic FieldDocument34 pagesPhys102 Magnetic FieldMayson UdarbeNo ratings yet
- Design For Simple StressesDocument131 pagesDesign For Simple Stresseskhudhayer1970No ratings yet
- Hindware TILES Multi Charge Catologue HSILDocument4 pagesHindware TILES Multi Charge Catologue HSILKunNous DesignsNo ratings yet
- Yunshu InformationGeometryDocument79 pagesYunshu InformationGeometrysemiringNo ratings yet
- SSPC PA2 Measurement of Dry Coating Thickness With Magnetic GagesDocument11 pagesSSPC PA2 Measurement of Dry Coating Thickness With Magnetic Gageslonglong3003No ratings yet