Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 viewsA1 U1 Grammar Reference
A1 U1 Grammar Reference
Uploaded by
Juan De La Cruz Perez TejedaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- EF4e A1A2 Pocket BookDocument34 pagesEF4e A1A2 Pocket BookTatiana Ermakova75% (24)
- Simple Present of The Verb TO BEDocument5 pagesSimple Present of The Verb TO BEcarlher69No ratings yet
- A1 1 Student's Book 124 125Document5 pagesA1 1 Student's Book 124 125Marika PutkaradzeNo ratings yet
- Resumen de Grammar Book 1Document46 pagesResumen de Grammar Book 1Kathe Segura SánchezNo ratings yet
- The Verb To Be ExplanationsDocument5 pagesThe Verb To Be ExplanationsLuz Maria Batista MendozaNo ratings yet
- Complementar 03Document33 pagesComplementar 03Dilan sosa moraNo ratings yet
- InglesDocument8 pagesInglesKarina InesNo ratings yet
- Course 1Document3 pagesCourse 1Zhanna KhairushevaNo ratings yet
- Wa 01 GFDocument46 pagesWa 01 GFCinthya VillareviaNo ratings yet
- The Verb To Be in Present Simple Tense SextoDocument4 pagesThe Verb To Be in Present Simple Tense SextoMaría Angélica Vargas MNo ratings yet
- Proceso IsobáricoDocument5 pagesProceso IsobáricoalfredoNo ratings yet
- Present Tense Verb Be: Full Form ContractionDocument3 pagesPresent Tense Verb Be: Full Form ContractionRodrigo Quispe FlorezNo ratings yet
- Grammar File 1: Verb Be: Present SimpleDocument0 pagesGrammar File 1: Verb Be: Present SimpleNoeliaa de la CalleNo ratings yet
- To Be - Present TenseDocument5 pagesTo Be - Present Tensemariamunozp0322No ratings yet
- Personal Pronoun & Verb To BeDocument5 pagesPersonal Pronoun & Verb To Bealine.8udgNo ratings yet
- 1B Present Tense Verb Be (-) andDocument2 pages1B Present Tense Verb Be (-) andsinisbafcoNo ratings yet
- Present Tense Verb Be: Full Form ContractionDocument2 pagesPresent Tense Verb Be: Full Form ContractionRodrigo Quispe FlorezNo ratings yet
- Resumen Elemental 1 Units 1 To 6Document39 pagesResumen Elemental 1 Units 1 To 6Aerlins HidalgoNo ratings yet
- 1 - Verb To BeDocument29 pages1 - Verb To BeJosé SantosNo ratings yet
- Student - Simple Present Verb To BeDocument4 pagesStudent - Simple Present Verb To Beluz areli diaz meneses100% (2)
- A Am Not O: Affirmative Negative InterrogativeDocument2 pagesA Am Not O: Affirmative Negative InterrogativeManuel CorreiaNo ratings yet
- To Be LessonDocument4 pagesTo Be LessonkhalidtsouliNo ratings yet
- 1B World MusicDocument7 pages1B World MusicGeorge ZarpateNo ratings yet
- To Be - Present Tense: English Grammar RulesDocument4 pagesTo Be - Present Tense: English Grammar RulesCarlos Alan Luis GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Language Production 1Document8 pagesLanguage Production 1CAROL CASTELLANOSNo ratings yet
- Affirmative Forms of The Verb To BeDocument3 pagesAffirmative Forms of The Verb To BeMisael ReyesNo ratings yet
- Teacher's Grammar Sumary Life 2Document24 pagesTeacher's Grammar Sumary Life 2lynhua inbaobiNo ratings yet
- English Grammar Rules: To Be - AffirmativeDocument5 pagesEnglish Grammar Rules: To Be - AffirmativeElton CohenNo ratings yet
- Complementar 01Document34 pagesComplementar 01Dilan sosa moraNo ratings yet
- Country Verb To BeDocument28 pagesCountry Verb To BeJUDITH LLANOS DURANNo ratings yet
- Unidad L Ingles LDocument20 pagesUnidad L Ingles LOscar MatamorosNo ratings yet
- Data Analysis Journal Power PointDocument31 pagesData Analysis Journal Power PointRobin Stevens EvansNo ratings yet
- First and Second Class Basic 4Document10 pagesFirst and Second Class Basic 4LEONARDO DIEGO ALBINAGORTA PAREDESNo ratings yet
- Grammar Bank: Possessives My, Your, His, Her, EtcDocument0 pagesGrammar Bank: Possessives My, Your, His, Her, EtcLaura NaNo ratings yet
- KEY 02 Personal Pronouns +to BeDocument3 pagesKEY 02 Personal Pronouns +to BeCHRISTOPHER WISFORS SURCO AROTAIPENo ratings yet
- 1B Grammar Bank YMDocument3 pages1B Grammar Bank YMMIRIAM ELIZABETH NANCO VEGANo ratings yet
- English IDocument16 pagesEnglish ILibia Cabana GalindoNo ratings yet
- Verb To Be Allison y SofiaDocument3 pagesVerb To Be Allison y SofiaNicola CuervoNo ratings yet
- Inglés - Séptimo 7º Guide 8: Personal InformationDocument8 pagesInglés - Séptimo 7º Guide 8: Personal InformationTania Daniela LONDONO SIERRANo ratings yet
- Verb To Be - All FormsDocument26 pagesVerb To Be - All FormsMa AvNo ratings yet
- Clase # 1Document2 pagesClase # 1juanpabon14No ratings yet
- Lourdes Desiree Perez Garcia 17-MPSS-6-053: NombreDocument7 pagesLourdes Desiree Perez Garcia 17-MPSS-6-053: NombreJose Nicolás Valdez Burgos100% (1)
- 2e Level 1 Language Focus ReferenceDocument20 pages2e Level 1 Language Focus ReferenceCami Adorno100% (1)
- Ingles Pasado Simple Del Verbo 'To Be': AfirmativoDocument5 pagesIngles Pasado Simple Del Verbo 'To Be': AfirmativoEric ZambranoNo ratings yet
- Tiempo PresenteDocument13 pagesTiempo PresenteJosé Luis MJNo ratings yet
- Ficha de Ingles 1 SecundariaDocument3 pagesFicha de Ingles 1 SecundariaPAMELA MONICA QUISPE VILLARESNo ratings yet
- The To Be Verb in PresentDocument4 pagesThe To Be Verb in PresentYulicita Tkm Llanos LlamoNo ratings yet
- To Be Worksheet 2Document3 pagesTo Be Worksheet 2Yulieth Paola Martines GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Ingles Comercial IDocument6 pagesIngles Comercial IorellanafelmyelizabethNo ratings yet
- The Simple Present of Verb To BeDocument2 pagesThe Simple Present of Verb To BeMed MouminNo ratings yet
- Verb To Be 1BDocument12 pagesVerb To Be 1BPatricia FranciscoNo ratings yet
- First Unit - March 23rd.Document12 pagesFirst Unit - March 23rd.royer208No ratings yet
- 11 Verb To Be - CPDocument7 pages11 Verb To Be - CPTania Zapata VargasNo ratings yet
- El Verbo To BE +and-Sentences+readingDocument3 pagesEl Verbo To BE +and-Sentences+readingEusebio Oscco QuispeNo ratings yet
- Tu, Usted y Ustedes "You"Document12 pagesTu, Usted y Ustedes "You"Jhanet AHNo ratings yet
- 4 - PPT To BeDocument21 pages4 - PPT To BecarlosNo ratings yet
- Free English Grammar Ebook Beginner WDocument45 pagesFree English Grammar Ebook Beginner WgirmachewNo ratings yet
- Qué Debo SaberDocument14 pagesQué Debo SaberMaria Angelica Moreno O.100% (1)
- Learn Spanish For Beginners: 11+ Short Stories& Accelerated Language Learning Lessons- Conversations, Grammar& Vocabulary Mastery+ 1001 Phrases& Words In Context- 21 Day BlueprintFrom EverandLearn Spanish For Beginners: 11+ Short Stories& Accelerated Language Learning Lessons- Conversations, Grammar& Vocabulary Mastery+ 1001 Phrases& Words In Context- 21 Day BlueprintNo ratings yet
- Learn Spanish For Beginners Complete Course (2 in 1): 33+ Language Lessons- 10 Short Stories, 1000+ Phrases& Words, Grammar Mastery, Conversations& Intermediate Vocabulary AcceleratorFrom EverandLearn Spanish For Beginners Complete Course (2 in 1): 33+ Language Lessons- 10 Short Stories, 1000+ Phrases& Words, Grammar Mastery, Conversations& Intermediate Vocabulary AcceleratorNo ratings yet
- A1 U1 Vocabulary - Countries and ContinentsDocument2 pagesA1 U1 Vocabulary - Countries and ContinentsJuan De La Cruz Perez TejedaNo ratings yet
- A1 U1 Video TranscriptDocument1 pageA1 U1 Video TranscriptJuan De La Cruz Perez TejedaNo ratings yet
- A1 U2 Reading TextDocument1 pageA1 U2 Reading TextJuan De La Cruz Perez TejedaNo ratings yet
- A1 U2 Listening TranscriptDocument1 pageA1 U2 Listening TranscriptJuan De La Cruz Perez TejedaNo ratings yet
- A1 U2 Vocabulary - Daily RoutinesDocument1 pageA1 U2 Vocabulary - Daily RoutinesJuan De La Cruz Perez TejedaNo ratings yet
- A1 U2 Grammar ReferenceDocument3 pagesA1 U2 Grammar ReferenceJuan De La Cruz Perez TejedaNo ratings yet
- Tag Questions - CuadernilloDocument7 pagesTag Questions - CuadernilloEric Luz GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Mosaic Trd4 U8 EpDocument4 pagesMosaic Trd4 U8 EpfernandoNo ratings yet
- The Contemporary World Prelim To FinalsDocument264 pagesThe Contemporary World Prelim To FinalsGerille CruzNo ratings yet
- Writing Skills Mechanic of WritingDocument3 pagesWriting Skills Mechanic of WritingPK-0619 Numan Helmi Bin ZulkipliNo ratings yet
- Elements of PoetryDocument13 pagesElements of PoetryMarjorie O. MalinaoNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary Jigsaw Activity InstructionsDocument3 pagesVocabulary Jigsaw Activity InstructionsWork Related100% (1)
- 3161713Document28 pages3161713JohnNo ratings yet
- Genesis: Ferēbātur Is Literally 'Was Being Carried'Document86 pagesGenesis: Ferēbātur Is Literally 'Was Being Carried'John WhelptonNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice HW 27marzo and Personal-ImpersonalDocument4 pagesPassive Voice HW 27marzo and Personal-ImpersonalFacundo LahittetteNo ratings yet
- Minutes Good Practice Guide 0.5Document12 pagesMinutes Good Practice Guide 0.5Jerlyn MalimataNo ratings yet
- D Pronunciation Tongue TanglersDocument54 pagesD Pronunciation Tongue Tanglersashik aem ashilNo ratings yet
- EAPP Transes Quarter 1Document5 pagesEAPP Transes Quarter 1Ma. Rhona Faye MedesNo ratings yet
- Semester-V GrammarDocument12 pagesSemester-V GrammarMohammad ShahbazNo ratings yet
- SPAN103 Course Syllabus - SPRING 2023Document3 pagesSPAN103 Course Syllabus - SPRING 2023Amaris FraserNo ratings yet
- Does Theo Like Playing FootballDocument3 pagesDoes Theo Like Playing FootballnagoreNo ratings yet
- Eng310 Course SyllabusDocument4 pagesEng310 Course SyllabusAsma R. El KawafiNo ratings yet
- ڏاهپ جو جنمDocument96 pagesڏاهپ جو جنمFayaz Ahmed KhattiNo ratings yet
- Adj Vs Adv 1Document2 pagesAdj Vs Adv 1Muhammad Fachru RaziNo ratings yet
- Leyte Agro-Industrial School Learning Competency Directory in English 7 S.Y. 2018-2019Document12 pagesLeyte Agro-Industrial School Learning Competency Directory in English 7 S.Y. 2018-2019Julette MansuetoNo ratings yet
- Lý luậnDocument51 pagesLý luậnMai Phạm ThanhNo ratings yet
- Zondiwe MbanoDocument166 pagesZondiwe Mbanocaphus mazengera100% (2)
- Powerful Vocabulary For Reading Success Students Edition Grade 4Document204 pagesPowerful Vocabulary For Reading Success Students Edition Grade 4iustin stingaNo ratings yet
- Hello !: Tim / Billy / Rosy / Miss JonesDocument4 pagesHello !: Tim / Billy / Rosy / Miss Jonesmaroua chtourouNo ratings yet
- Liddell 1980Document21 pagesLiddell 1980Felipe AleixoNo ratings yet
- Describe A Bedroom British English StudentDocument6 pagesDescribe A Bedroom British English StudentAmanda CamposNo ratings yet
- BI Y6 LP TS25 (Unit 2 - Life in The Past - LP 17-32)Document18 pagesBI Y6 LP TS25 (Unit 2 - Life in The Past - LP 17-32)NOOR SUFANIE BINTI MAT SOKRI MoeNo ratings yet
- Midterm DefinitionsDocument1 pageMidterm DefinitionsHannah YuiNo ratings yet
- Intermediate C21 Skills Projects 1Document5 pagesIntermediate C21 Skills Projects 1billionaireaj569626No ratings yet
- SF1 - 2021 - Grade 7 (Year I) - LAUANDocument8 pagesSF1 - 2021 - Grade 7 (Year I) - LAUANJucel MarcoNo ratings yet
- Table of Irregular Verbs - English Grammar Today - Cambridge DictionaryDocument1 pageTable of Irregular Verbs - English Grammar Today - Cambridge Dictionarysweetrenata_28No ratings yet
A1 U1 Grammar Reference
A1 U1 Grammar Reference
Uploaded by
Juan De La Cruz Perez Tejeda0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views3 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views3 pagesA1 U1 Grammar Reference
A1 U1 Grammar Reference
Uploaded by
Juan De La Cruz Perez TejedaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
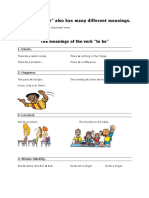
Simple Present of the verb ‘be’ in the affirmative form
Full form Contraction
I am from Spain. I’m from Spain.
You are from Germany. You’re from Germany.
He is in room 18. He’s in room 18.
She is a teacher. She’s a teacher.
It is in Bristol. It’s in Bristol.
We are students. We’re students.
You are my teachers. You’re my teachers.
They are at the airport. They’re at the airport.
Simple Present of the verb ‘be’ in the negative form
Full form Contraction
I am not from Spain. I’m not from Spain.
You are not from Germany. You aren’t from Germany.
He is not in room 18. He isn’t in room 18.
She is not a teacher. She isn’t a teacher.
It is not in Bristol. It isn’t in Bristol.
We are not students. We aren’t students.
You are not my teachers. You aren’t my teachers.
They are not at the airport. They aren’t at the airport.
Question forms and short answers
Question Short answer
Are you Irish? Yes, I am. / No, I’m not.
Is he in room 18? Yes, he is. / No, he isn’t.
Is she a teacher? Yes, she is. / No, she isn’t.
Is it in Bristol? Yes, it is. / No, it isn’t.
Are we in this class? Yes, you are. / No, you aren’t.
Are they at the airport? Yes, they are. / No, they aren’t.
Importante:
• Utilizamos contracciones cuando hablamos.
• Para contestar utilizamos una forma corta (= “short answer”).
e.g., Are you American? Yes,I am (NO Yes, I’m American).
• En inglés siempre tenemos que incluir un sujeto antes de un verbo.
e.g., She is Spanish; Enzo is Italian (NO is Spanish; is Italian).
A1 English Course: Unit 1 Grammar Reference
• Siempre utilizamos mayúscula para “I”.
e.g., I’m from Spain (NO i’m from Spain).
• Utilizamos “you” para tu/vosotros/vosotras/usted/ustedes.
• Se utiliza he para una persona masculina.
e.g., Peter is the teacher. He is from Bristol.
• Se utiliza “she” para una persona femenina.
e.g., Manuela is from Madrid. She is in class 12.
• Se utiliza “it” para una cosa o lugar.
e.g., You are in class 12. It is on the first floor.
• Usamos “they” para personas en plural.
e.g., Their names are Manuela and Andi. They are in my class.
• “They” se utiliza para cosas o lugares también.
e.g., Where are the tickets? They are in my bag.
• En la forma negativa, también se puede contraer de esta manera:
- is not: She’s not Spanish (= She isn’t Spanish).
- are not: They’re not at the airport (= They aren’t at the airport).
• Tenemos un solo verbo “be” para ser/estar.
e.g., ¿Dónde estás? = Where are you?
¿Eres mi profesor? = Are you my teacher?
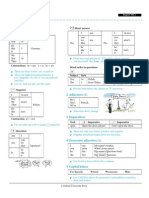
Possessive Adjectives
I’m Spanish. My name’s Sofía.
You’re in class 12. This is your teacher.
He’s the director. His name’s John.
She’s my teacher. Her name’s Clare.
It’s a language school. Its name is International School.
We’re at the airport. Our flight number is EZY1221.
They’re in room 112. Their names are Elena and Pierre.
A1 English Course: Unit 1 Grammar Reference
Importante
• Utilizamos “his” para su de él.
• Utilizamos “her” para su de ella.
• Utilizamos “its” para su de una cosa o lugar.
• Los adjetivos posesivos no cambian en la forma del plural.
e.g., Our names are Sophie and David (NO Ours names are Sophie and David).
• Cuidado con its y it’s:
- its es un adjetivo posesivo.
- it’s es la contracción de it is.
Question words
- What is your name? My name’s Karen.
- How are you? I’m fine!
- Where are you from? I’m from Ireland.
- How old are you? I’m 45 years old.
- Who is your tour guide? Peter.
Importante
En inglés decimos how old are you? (NO how old have you?)
A1 English Course: Unit 1 Grammar Reference
You might also like
- EF4e A1A2 Pocket BookDocument34 pagesEF4e A1A2 Pocket BookTatiana Ermakova75% (24)
- Simple Present of The Verb TO BEDocument5 pagesSimple Present of The Verb TO BEcarlher69No ratings yet
- A1 1 Student's Book 124 125Document5 pagesA1 1 Student's Book 124 125Marika PutkaradzeNo ratings yet
- Resumen de Grammar Book 1Document46 pagesResumen de Grammar Book 1Kathe Segura SánchezNo ratings yet
- The Verb To Be ExplanationsDocument5 pagesThe Verb To Be ExplanationsLuz Maria Batista MendozaNo ratings yet
- Complementar 03Document33 pagesComplementar 03Dilan sosa moraNo ratings yet
- InglesDocument8 pagesInglesKarina InesNo ratings yet
- Course 1Document3 pagesCourse 1Zhanna KhairushevaNo ratings yet
- Wa 01 GFDocument46 pagesWa 01 GFCinthya VillareviaNo ratings yet
- The Verb To Be in Present Simple Tense SextoDocument4 pagesThe Verb To Be in Present Simple Tense SextoMaría Angélica Vargas MNo ratings yet
- Proceso IsobáricoDocument5 pagesProceso IsobáricoalfredoNo ratings yet
- Present Tense Verb Be: Full Form ContractionDocument3 pagesPresent Tense Verb Be: Full Form ContractionRodrigo Quispe FlorezNo ratings yet
- Grammar File 1: Verb Be: Present SimpleDocument0 pagesGrammar File 1: Verb Be: Present SimpleNoeliaa de la CalleNo ratings yet
- To Be - Present TenseDocument5 pagesTo Be - Present Tensemariamunozp0322No ratings yet
- Personal Pronoun & Verb To BeDocument5 pagesPersonal Pronoun & Verb To Bealine.8udgNo ratings yet
- 1B Present Tense Verb Be (-) andDocument2 pages1B Present Tense Verb Be (-) andsinisbafcoNo ratings yet
- Present Tense Verb Be: Full Form ContractionDocument2 pagesPresent Tense Verb Be: Full Form ContractionRodrigo Quispe FlorezNo ratings yet
- Resumen Elemental 1 Units 1 To 6Document39 pagesResumen Elemental 1 Units 1 To 6Aerlins HidalgoNo ratings yet
- 1 - Verb To BeDocument29 pages1 - Verb To BeJosé SantosNo ratings yet
- Student - Simple Present Verb To BeDocument4 pagesStudent - Simple Present Verb To Beluz areli diaz meneses100% (2)
- A Am Not O: Affirmative Negative InterrogativeDocument2 pagesA Am Not O: Affirmative Negative InterrogativeManuel CorreiaNo ratings yet
- To Be LessonDocument4 pagesTo Be LessonkhalidtsouliNo ratings yet
- 1B World MusicDocument7 pages1B World MusicGeorge ZarpateNo ratings yet
- To Be - Present Tense: English Grammar RulesDocument4 pagesTo Be - Present Tense: English Grammar RulesCarlos Alan Luis GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Language Production 1Document8 pagesLanguage Production 1CAROL CASTELLANOSNo ratings yet
- Affirmative Forms of The Verb To BeDocument3 pagesAffirmative Forms of The Verb To BeMisael ReyesNo ratings yet
- Teacher's Grammar Sumary Life 2Document24 pagesTeacher's Grammar Sumary Life 2lynhua inbaobiNo ratings yet
- English Grammar Rules: To Be - AffirmativeDocument5 pagesEnglish Grammar Rules: To Be - AffirmativeElton CohenNo ratings yet
- Complementar 01Document34 pagesComplementar 01Dilan sosa moraNo ratings yet
- Country Verb To BeDocument28 pagesCountry Verb To BeJUDITH LLANOS DURANNo ratings yet
- Unidad L Ingles LDocument20 pagesUnidad L Ingles LOscar MatamorosNo ratings yet
- Data Analysis Journal Power PointDocument31 pagesData Analysis Journal Power PointRobin Stevens EvansNo ratings yet
- First and Second Class Basic 4Document10 pagesFirst and Second Class Basic 4LEONARDO DIEGO ALBINAGORTA PAREDESNo ratings yet
- Grammar Bank: Possessives My, Your, His, Her, EtcDocument0 pagesGrammar Bank: Possessives My, Your, His, Her, EtcLaura NaNo ratings yet
- KEY 02 Personal Pronouns +to BeDocument3 pagesKEY 02 Personal Pronouns +to BeCHRISTOPHER WISFORS SURCO AROTAIPENo ratings yet
- 1B Grammar Bank YMDocument3 pages1B Grammar Bank YMMIRIAM ELIZABETH NANCO VEGANo ratings yet
- English IDocument16 pagesEnglish ILibia Cabana GalindoNo ratings yet
- Verb To Be Allison y SofiaDocument3 pagesVerb To Be Allison y SofiaNicola CuervoNo ratings yet
- Inglés - Séptimo 7º Guide 8: Personal InformationDocument8 pagesInglés - Séptimo 7º Guide 8: Personal InformationTania Daniela LONDONO SIERRANo ratings yet
- Verb To Be - All FormsDocument26 pagesVerb To Be - All FormsMa AvNo ratings yet
- Clase # 1Document2 pagesClase # 1juanpabon14No ratings yet
- Lourdes Desiree Perez Garcia 17-MPSS-6-053: NombreDocument7 pagesLourdes Desiree Perez Garcia 17-MPSS-6-053: NombreJose Nicolás Valdez Burgos100% (1)
- 2e Level 1 Language Focus ReferenceDocument20 pages2e Level 1 Language Focus ReferenceCami Adorno100% (1)
- Ingles Pasado Simple Del Verbo 'To Be': AfirmativoDocument5 pagesIngles Pasado Simple Del Verbo 'To Be': AfirmativoEric ZambranoNo ratings yet
- Tiempo PresenteDocument13 pagesTiempo PresenteJosé Luis MJNo ratings yet
- Ficha de Ingles 1 SecundariaDocument3 pagesFicha de Ingles 1 SecundariaPAMELA MONICA QUISPE VILLARESNo ratings yet
- The To Be Verb in PresentDocument4 pagesThe To Be Verb in PresentYulicita Tkm Llanos LlamoNo ratings yet
- To Be Worksheet 2Document3 pagesTo Be Worksheet 2Yulieth Paola Martines GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Ingles Comercial IDocument6 pagesIngles Comercial IorellanafelmyelizabethNo ratings yet
- The Simple Present of Verb To BeDocument2 pagesThe Simple Present of Verb To BeMed MouminNo ratings yet
- Verb To Be 1BDocument12 pagesVerb To Be 1BPatricia FranciscoNo ratings yet
- First Unit - March 23rd.Document12 pagesFirst Unit - March 23rd.royer208No ratings yet
- 11 Verb To Be - CPDocument7 pages11 Verb To Be - CPTania Zapata VargasNo ratings yet
- El Verbo To BE +and-Sentences+readingDocument3 pagesEl Verbo To BE +and-Sentences+readingEusebio Oscco QuispeNo ratings yet
- Tu, Usted y Ustedes "You"Document12 pagesTu, Usted y Ustedes "You"Jhanet AHNo ratings yet
- 4 - PPT To BeDocument21 pages4 - PPT To BecarlosNo ratings yet
- Free English Grammar Ebook Beginner WDocument45 pagesFree English Grammar Ebook Beginner WgirmachewNo ratings yet
- Qué Debo SaberDocument14 pagesQué Debo SaberMaria Angelica Moreno O.100% (1)
- Learn Spanish For Beginners: 11+ Short Stories& Accelerated Language Learning Lessons- Conversations, Grammar& Vocabulary Mastery+ 1001 Phrases& Words In Context- 21 Day BlueprintFrom EverandLearn Spanish For Beginners: 11+ Short Stories& Accelerated Language Learning Lessons- Conversations, Grammar& Vocabulary Mastery+ 1001 Phrases& Words In Context- 21 Day BlueprintNo ratings yet
- Learn Spanish For Beginners Complete Course (2 in 1): 33+ Language Lessons- 10 Short Stories, 1000+ Phrases& Words, Grammar Mastery, Conversations& Intermediate Vocabulary AcceleratorFrom EverandLearn Spanish For Beginners Complete Course (2 in 1): 33+ Language Lessons- 10 Short Stories, 1000+ Phrases& Words, Grammar Mastery, Conversations& Intermediate Vocabulary AcceleratorNo ratings yet
- A1 U1 Vocabulary - Countries and ContinentsDocument2 pagesA1 U1 Vocabulary - Countries and ContinentsJuan De La Cruz Perez TejedaNo ratings yet
- A1 U1 Video TranscriptDocument1 pageA1 U1 Video TranscriptJuan De La Cruz Perez TejedaNo ratings yet
- A1 U2 Reading TextDocument1 pageA1 U2 Reading TextJuan De La Cruz Perez TejedaNo ratings yet
- A1 U2 Listening TranscriptDocument1 pageA1 U2 Listening TranscriptJuan De La Cruz Perez TejedaNo ratings yet
- A1 U2 Vocabulary - Daily RoutinesDocument1 pageA1 U2 Vocabulary - Daily RoutinesJuan De La Cruz Perez TejedaNo ratings yet
- A1 U2 Grammar ReferenceDocument3 pagesA1 U2 Grammar ReferenceJuan De La Cruz Perez TejedaNo ratings yet
- Tag Questions - CuadernilloDocument7 pagesTag Questions - CuadernilloEric Luz GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Mosaic Trd4 U8 EpDocument4 pagesMosaic Trd4 U8 EpfernandoNo ratings yet
- The Contemporary World Prelim To FinalsDocument264 pagesThe Contemporary World Prelim To FinalsGerille CruzNo ratings yet
- Writing Skills Mechanic of WritingDocument3 pagesWriting Skills Mechanic of WritingPK-0619 Numan Helmi Bin ZulkipliNo ratings yet
- Elements of PoetryDocument13 pagesElements of PoetryMarjorie O. MalinaoNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary Jigsaw Activity InstructionsDocument3 pagesVocabulary Jigsaw Activity InstructionsWork Related100% (1)
- 3161713Document28 pages3161713JohnNo ratings yet
- Genesis: Ferēbātur Is Literally 'Was Being Carried'Document86 pagesGenesis: Ferēbātur Is Literally 'Was Being Carried'John WhelptonNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice HW 27marzo and Personal-ImpersonalDocument4 pagesPassive Voice HW 27marzo and Personal-ImpersonalFacundo LahittetteNo ratings yet
- Minutes Good Practice Guide 0.5Document12 pagesMinutes Good Practice Guide 0.5Jerlyn MalimataNo ratings yet
- D Pronunciation Tongue TanglersDocument54 pagesD Pronunciation Tongue Tanglersashik aem ashilNo ratings yet
- EAPP Transes Quarter 1Document5 pagesEAPP Transes Quarter 1Ma. Rhona Faye MedesNo ratings yet
- Semester-V GrammarDocument12 pagesSemester-V GrammarMohammad ShahbazNo ratings yet
- SPAN103 Course Syllabus - SPRING 2023Document3 pagesSPAN103 Course Syllabus - SPRING 2023Amaris FraserNo ratings yet
- Does Theo Like Playing FootballDocument3 pagesDoes Theo Like Playing FootballnagoreNo ratings yet
- Eng310 Course SyllabusDocument4 pagesEng310 Course SyllabusAsma R. El KawafiNo ratings yet
- ڏاهپ جو جنمDocument96 pagesڏاهپ جو جنمFayaz Ahmed KhattiNo ratings yet
- Adj Vs Adv 1Document2 pagesAdj Vs Adv 1Muhammad Fachru RaziNo ratings yet
- Leyte Agro-Industrial School Learning Competency Directory in English 7 S.Y. 2018-2019Document12 pagesLeyte Agro-Industrial School Learning Competency Directory in English 7 S.Y. 2018-2019Julette MansuetoNo ratings yet
- Lý luậnDocument51 pagesLý luậnMai Phạm ThanhNo ratings yet
- Zondiwe MbanoDocument166 pagesZondiwe Mbanocaphus mazengera100% (2)
- Powerful Vocabulary For Reading Success Students Edition Grade 4Document204 pagesPowerful Vocabulary For Reading Success Students Edition Grade 4iustin stingaNo ratings yet
- Hello !: Tim / Billy / Rosy / Miss JonesDocument4 pagesHello !: Tim / Billy / Rosy / Miss Jonesmaroua chtourouNo ratings yet
- Liddell 1980Document21 pagesLiddell 1980Felipe AleixoNo ratings yet
- Describe A Bedroom British English StudentDocument6 pagesDescribe A Bedroom British English StudentAmanda CamposNo ratings yet
- BI Y6 LP TS25 (Unit 2 - Life in The Past - LP 17-32)Document18 pagesBI Y6 LP TS25 (Unit 2 - Life in The Past - LP 17-32)NOOR SUFANIE BINTI MAT SOKRI MoeNo ratings yet
- Midterm DefinitionsDocument1 pageMidterm DefinitionsHannah YuiNo ratings yet
- Intermediate C21 Skills Projects 1Document5 pagesIntermediate C21 Skills Projects 1billionaireaj569626No ratings yet
- SF1 - 2021 - Grade 7 (Year I) - LAUANDocument8 pagesSF1 - 2021 - Grade 7 (Year I) - LAUANJucel MarcoNo ratings yet
- Table of Irregular Verbs - English Grammar Today - Cambridge DictionaryDocument1 pageTable of Irregular Verbs - English Grammar Today - Cambridge Dictionarysweetrenata_28No ratings yet