Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Benzene 2
Benzene 2
Uploaded by
ST12A3- Pulvera, James McleanCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Experiment 4 CHM207Document7 pagesExperiment 4 CHM207Nur Syakirah Abd NasirNo ratings yet
- Lab Rep 5Document8 pagesLab Rep 5Eugene CodisNo ratings yet
- An Experiment To Prepare Ethene Gas From Ethanol and Examine Its PropertiesDocument6 pagesAn Experiment To Prepare Ethene Gas From Ethanol and Examine Its PropertiesanockNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument3 pagesLab ReportJorita Wjj0% (1)
- Lab Report HydrocarbonsDocument7 pagesLab Report HydrocarbonsAnnrisa Layong Abain25% (4)
- BenzeneDocument14 pagesBenzeneJueeli More100% (1)
- Chirality and Aldehyde HomeworkDocument3 pagesChirality and Aldehyde HomeworkQuang Huy PhạmNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 8 HydrocarbonsDocument7 pagesExperiment No. 8 HydrocarbonsMa Jessa DuntingNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons: The First Family: Exercise 6Document8 pagesHydrocarbons: The First Family: Exercise 6Gagay Villamor CañeteNo ratings yet
- Sion Orgchemlab4 PDFDocument6 pagesSion Orgchemlab4 PDFshellNo ratings yet
- EXPE222Document6 pagesEXPE222K-yanVehraaYomomaNo ratings yet
- Activity No.4: InstructionsDocument7 pagesActivity No.4: Instructionsdenshang 10100% (1)
- Experiment 6 PostlabDocument11 pagesExperiment 6 Postlabaubrey yangzonNo ratings yet
- Labs For WedDocument14 pagesLabs For WedArya SinghNo ratings yet
- ARENES AND PHENOLS (Autosaved)Document85 pagesARENES AND PHENOLS (Autosaved)dodoNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry-Reaction To HydrocarbonsDocument6 pagesOrganic Chemistry-Reaction To HydrocarbonsbdidolNo ratings yet
- 120lab Report 8aDocument4 pages120lab Report 8aValerie Mae Librero AreñoNo ratings yet
- AreneDocument37 pagesArene'Aqilah ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- Properties and Reaction of Methyl BenzeneDocument21 pagesProperties and Reaction of Methyl Benzeneoasis_dessert100% (2)
- 5.4 - Organic Independat OtesDocument5 pages5.4 - Organic Independat Otesvarda9877No ratings yet
- Activity 7 - HydrocarbonsDocument6 pagesActivity 7 - HydrocarbonsDara Ellaine RicafortNo ratings yet
- Title: Chemical Properties of AlkenesDocument8 pagesTitle: Chemical Properties of AlkenesLeeshaaLenee Paramanantha KumarNo ratings yet
- Properties of HydrocarbonDocument9 pagesProperties of Hydrocarbon刘象100% (1)
- 3 Organic Chemistry - BenzeneDocument39 pages3 Organic Chemistry - BenzeneIsuriy AdasuriyaNo ratings yet
- BenzeneDocument21 pagesBenzeneosamakhan8967No ratings yet
- A2 Level Unit V ORGANIC CHEMISTRYDocument19 pagesA2 Level Unit V ORGANIC CHEMISTRYbillaljavedNo ratings yet
- Uace Chem (Benzene NotesDocument15 pagesUace Chem (Benzene NotesmasemvirginNo ratings yet
- (DORDADO) 1 Experiment No. 1 HydrocarbonsDocument8 pages(DORDADO) 1 Experiment No. 1 HydrocarbonsBitterground Corp.No ratings yet
- Analysis of HydrocarbonsDocument4 pagesAnalysis of Hydrocarbonsback upNo ratings yet
- H 0 CCL Naoh H So Cyclohexane (Clear Liquid)Document5 pagesH 0 CCL Naoh H So Cyclohexane (Clear Liquid)Mark GirasolNo ratings yet
- Angelica C. Anabe Bs Psy 2-1: AlkenesDocument12 pagesAngelica C. Anabe Bs Psy 2-1: Alkenesniela cruzNo ratings yet
- Nitration of Benzene: Adia, Sophia Cassandra, ADocument3 pagesNitration of Benzene: Adia, Sophia Cassandra, AS AdiaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Experiment 2Document7 pagesChemistry Experiment 2Alexa Ysabel LiwagNo ratings yet
- Reaction of Alkenes and Alkynes For StudentsDocument53 pagesReaction of Alkenes and Alkynes For StudentsGlen MangaliNo ratings yet
- Experiment 6 - Aromatic HydrocarbonsDocument5 pagesExperiment 6 - Aromatic HydrocarbonsKaye SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Amali 1 LaporanDocument3 pagesAmali 1 LaporanFauzan AzizNo ratings yet
- Data Analysis HydrocarbonDocument7 pagesData Analysis HydrocarbonTHASVIN OFFICIAL NETWORKNo ratings yet
- Organic HydrocarbonsDocument20 pagesOrganic HydrocarbonsOmar Samir0% (1)
- Title: Chemical Properties of AlkanesDocument9 pagesTitle: Chemical Properties of AlkanesLeeshaaLenee Paramanantha KumarNo ratings yet
- HydrocarbonDocument11 pagesHydrocarbonAida IshNo ratings yet
- Chem Lab (Ii) 3Document11 pagesChem Lab (Ii) 3Nurul Hasanah88% (75)
- Hydrocarbons Revision Test SolutionsDocument2 pagesHydrocarbons Revision Test SolutionsShelby Maria AbyNo ratings yet
- Group 5 CHEM111 Properties of Some Aromatic HydrocarbonsDocument6 pagesGroup 5 CHEM111 Properties of Some Aromatic HydrocarbonsmarmitochristineysabelllNo ratings yet
- Classification Tests For HydrocarbonsDocument5 pagesClassification Tests For HydrocarbonsEric AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- Experimental 1 ReportDocument7 pagesExperimental 1 Reportjeremy jasonNo ratings yet
- Aromatic CompoundsDocument36 pagesAromatic CompoundsMaria Ruela Agodera SumogNo ratings yet
- Aliphatic Hydrocarbons: LAB #1 Reactions of HydrocarbonsDocument7 pagesAliphatic Hydrocarbons: LAB #1 Reactions of HydrocarbonsJoshuaArryNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5: Characteristic Reactions of HydrocarbonsDocument7 pagesExperiment 5: Characteristic Reactions of HydrocarbonsJorelle NogoyNo ratings yet
- SC22b Reactions of Alkanes and AlkenesDocument14 pagesSC22b Reactions of Alkanes and AlkenesEmaadB EmaadBNo ratings yet
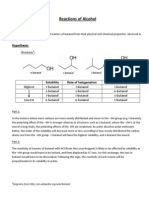
- Reactions of AlcoholDocument5 pagesReactions of AlcoholSourabh Das100% (1)
- CONSCHEMDocument3 pagesCONSCHEM-09876543123456789No ratings yet
- Classification Test For HydrocarbonsDocument3 pagesClassification Test For Hydrocarbonscyberlog21267% (3)
- R315 AbenojaJL HYDROCARBONSDocument8 pagesR315 AbenojaJL HYDROCARBONSJL AbenojaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Notes - Topic 18 Organic Chemistry III - Edexcel Chemistry A LevelDocument23 pagesDetailed Notes - Topic 18 Organic Chemistry III - Edexcel Chemistry A LevelLulwa KhaskiehNo ratings yet
- Anic Ep 3.Document8 pagesAnic Ep 3.Ummu Umar Wa AisyahNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - Arenes AnswersDocument6 pagesWorksheet - Arenes AnswersAbdul AhadhNo ratings yet
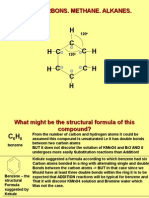
- C H H H H H: Hydrocarbons. Methane. AlkanesDocument14 pagesC H H H H H: Hydrocarbons. Methane. AlkanesDavidDavidovNo ratings yet
- Aromatic Compounds and Uses of BenzeneDocument44 pagesAromatic Compounds and Uses of BenzenePaarijat DubeyNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Organic Chemistry with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Organic Chemistry with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Patent 5Document8 pagesPatent 5ALEXANDER FRANCO CASTRILLONNo ratings yet
- Banana Peel ShampooDocument14 pagesBanana Peel ShampooMhay DingleNo ratings yet
- Exam SolutDocument12 pagesExam Solutnunulovin911No ratings yet
- CARAWAYDocument1 pageCARAWAYBalaji Pharmacy - GMNo ratings yet
- Origin, Generation & Migration of PetroleumDocument26 pagesOrigin, Generation & Migration of PetroleumBharat KumarNo ratings yet
- SC 2024 SP-6Document16 pagesSC 2024 SP-6Swostik RoutNo ratings yet
- Plants: Bioactivity of Common Pesticidal Plants On Fall Armyworm Larvae (Spodoptera Frugiperda)Document10 pagesPlants: Bioactivity of Common Pesticidal Plants On Fall Armyworm Larvae (Spodoptera Frugiperda)salif ouedraogoNo ratings yet
- Waste To Energypptx - 220913 - 151038Document117 pagesWaste To Energypptx - 220913 - 151038Aswini NRNo ratings yet
- Asparagus Benefits 2beingfitDocument7 pagesAsparagus Benefits 2beingfitK AnjaliNo ratings yet
- Enantioselective Total Synthesis of (+) - Wortmannin: Yinliang Guo, Tianfei Quan, Yandong Lu, and Tuoping LuoDocument4 pagesEnantioselective Total Synthesis of (+) - Wortmannin: Yinliang Guo, Tianfei Quan, Yandong Lu, and Tuoping LuoLê MinhNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis ClozeDocument3 pagesProtein Synthesis Clozeapi-309893409No ratings yet
- Free Radical InjuryDocument87 pagesFree Radical InjuryPooja BappannaNo ratings yet
- Kaleab BizunehDocument89 pagesKaleab BizunehTeklit GebrerufaelNo ratings yet
- Reduction, Oxidation - Hydrolysis Exercise PDFDocument24 pagesReduction, Oxidation - Hydrolysis Exercise PDFGOURISH AGRAWAL100% (3)
- Matriculation Chemistry Carbonyl CompoundDocument50 pagesMatriculation Chemistry Carbonyl Compoundiki292100% (1)
- Structures of Organic CompoundsDocument11 pagesStructures of Organic CompoundsJheian Christian TubleNo ratings yet
- Common Polyatomic IonsDocument1 pageCommon Polyatomic Ionsmudasser_rafiq3271No ratings yet
- Analytical Methods For The Determination of Emerging Contaminants in Sewage Sludge Samples. A ReviewDocument26 pagesAnalytical Methods For The Determination of Emerging Contaminants in Sewage Sludge Samples. A ReviewMaria AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Gomes Basso BeansDocument9 pagesGomes Basso Beansjuan diegoNo ratings yet
- Exp. 7 Analysis of Milk For The Lipids Carbohydrates and ProteinsDocument6 pagesExp. 7 Analysis of Milk For The Lipids Carbohydrates and ProteinsEdchelNo ratings yet
- Ammonium Peroxydisulfate MSDSDocument8 pagesAmmonium Peroxydisulfate MSDSFitriani TanraNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Compounds: Chemical Name Chemical FormulaDocument6 pagesInorganic Compounds: Chemical Name Chemical FormulaFrendick LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Sensors & Actuators B. Chemical 304 (2020) 127396Document15 pagesSensors & Actuators B. Chemical 304 (2020) 127396ashwanirubalNo ratings yet
- Fire Prevention & Fire FightingDocument24 pagesFire Prevention & Fire FightingAku RajNo ratings yet
- Balauro Worksheet Protein SynthesisDocument4 pagesBalauro Worksheet Protein SynthesisHami BalauroNo ratings yet
- Primer DesignDocument37 pagesPrimer DesignRyu- MikaNo ratings yet
- Index: Sr. No. Topic NoDocument53 pagesIndex: Sr. No. Topic NoChetana JadhavNo ratings yet
- Sam White 4bk (TDS)Document4 pagesSam White 4bk (TDS)Md.Ifrith RahmanNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution in Petroleum IndustryDocument46 pagesAir Pollution in Petroleum IndustryAtul SharanNo ratings yet
Benzene 2
Benzene 2
Uploaded by
ST12A3- Pulvera, James McleanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Benzene 2
Benzene 2
Uploaded by
ST12A3- Pulvera, James McleanCopyright:
Available Formats
BENZENE (C6H6)
COMBUSTION REACTION - Benzene can burn in the presence of oxygen to produce carbon
dioxide and water. The combustion of benzene is exothermic and can release a large amount of
energy. Sulfonation: Benzene can react with sulfuric acid to form benzenesulfonic acid.
Do the following:
a. 3 Drops of benzene in evaporating dish and ignited using a lighted match stick
Color: leaning more to orange upon combustion
Presence of soot: Yes
Equation: (PA COPY NALNG SA BOOK PLS. PAGE 51)
VON BAEYER’S TEST/ UNSATURATION] - Von Baeyer's Test, also known as the Unsaturation Test,
is a chemical test used to detect the presence of unsaturation in organic compounds, particularly
in aromatic compounds like benzene. This test relies on the reaction of the compound with
bromine (Br2) or potassium permanganate (KMnO4) in the presence of a suitable catalyst.
Mix the following:
a. 5 drops of Benzene
b. 5 drops of dilute KMnO4
Color (deposited at the bottom of the test tube): Dominant purple
Observation: KMnO4 is a strong oxidizing agent and benzene couldn’t react with KMn04
Equation: (Page 51)
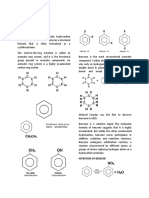
HALOGENATION – SUBSTITUTION TEST - Halogenation, specifically in the context of benzene,
refers to a substitution reaction where one or more hydrogen atoms on the benzene ring are
replaced by halogen atoms such as chlorine (Cl2) or bromine (Br2). This reaction is a
characteristic feature of aromatic compounds due to the high stability of the benzene ring,
which allows it to undergo substitution reactions rather than addition reactions typical of
alkenes.
Use the following:
a. 2 clean dry test tube
b. 10 drops of benzene and 2 drops of bromine water to each tube and mix
c. Cover both tubes with a cork
d. Expose the first tube to sunlight or ultraviolet rays. (Use flashlight)
e. Put inside your locker the second tube
f. Observe and compare their appearances after 10 minutes
Test 1 (exposed): Turned cloudy/ blurry substance and formed bubbles
Test 2 (in locker) light yellowish color
Equation (exposed): (page 52)
Equation 2 (inside the locker): (page 52)
MISCIBILITY AND DENSITY - Benzene, a colorless and flammable liquid aromatic hydrocarbon,
exhibits excellent miscibility with nonpolar solvents due to its nonpolar nature and the presence
of a delocalized electron cloud in its aromatic ring, making it a valuable solvent in various
industries. With a relatively low density of about 0.879 grams per cubic centimeter at room
temperature, benzene floats on water and vaporizes readily. However, its toxicity and
carcinogenicity have led to strict regulations regarding its industrial use and handling.
Use the following:
a. 5 drops of benzene and add 20 drops of water. Shake
Observation: Benzene floats on top while the water would sink to the bottom. Benzene is soluble to
water.
Which is heavier, benzene or water?
*Water is denser than benzene, thus water is heavier.
You might also like
- Experiment 4 CHM207Document7 pagesExperiment 4 CHM207Nur Syakirah Abd NasirNo ratings yet
- Lab Rep 5Document8 pagesLab Rep 5Eugene CodisNo ratings yet
- An Experiment To Prepare Ethene Gas From Ethanol and Examine Its PropertiesDocument6 pagesAn Experiment To Prepare Ethene Gas From Ethanol and Examine Its PropertiesanockNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument3 pagesLab ReportJorita Wjj0% (1)
- Lab Report HydrocarbonsDocument7 pagesLab Report HydrocarbonsAnnrisa Layong Abain25% (4)
- BenzeneDocument14 pagesBenzeneJueeli More100% (1)
- Chirality and Aldehyde HomeworkDocument3 pagesChirality and Aldehyde HomeworkQuang Huy PhạmNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 8 HydrocarbonsDocument7 pagesExperiment No. 8 HydrocarbonsMa Jessa DuntingNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons: The First Family: Exercise 6Document8 pagesHydrocarbons: The First Family: Exercise 6Gagay Villamor CañeteNo ratings yet
- Sion Orgchemlab4 PDFDocument6 pagesSion Orgchemlab4 PDFshellNo ratings yet
- EXPE222Document6 pagesEXPE222K-yanVehraaYomomaNo ratings yet
- Activity No.4: InstructionsDocument7 pagesActivity No.4: Instructionsdenshang 10100% (1)
- Experiment 6 PostlabDocument11 pagesExperiment 6 Postlabaubrey yangzonNo ratings yet
- Labs For WedDocument14 pagesLabs For WedArya SinghNo ratings yet
- ARENES AND PHENOLS (Autosaved)Document85 pagesARENES AND PHENOLS (Autosaved)dodoNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry-Reaction To HydrocarbonsDocument6 pagesOrganic Chemistry-Reaction To HydrocarbonsbdidolNo ratings yet
- 120lab Report 8aDocument4 pages120lab Report 8aValerie Mae Librero AreñoNo ratings yet
- AreneDocument37 pagesArene'Aqilah ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- Properties and Reaction of Methyl BenzeneDocument21 pagesProperties and Reaction of Methyl Benzeneoasis_dessert100% (2)
- 5.4 - Organic Independat OtesDocument5 pages5.4 - Organic Independat Otesvarda9877No ratings yet
- Activity 7 - HydrocarbonsDocument6 pagesActivity 7 - HydrocarbonsDara Ellaine RicafortNo ratings yet
- Title: Chemical Properties of AlkenesDocument8 pagesTitle: Chemical Properties of AlkenesLeeshaaLenee Paramanantha KumarNo ratings yet
- Properties of HydrocarbonDocument9 pagesProperties of Hydrocarbon刘象100% (1)
- 3 Organic Chemistry - BenzeneDocument39 pages3 Organic Chemistry - BenzeneIsuriy AdasuriyaNo ratings yet
- BenzeneDocument21 pagesBenzeneosamakhan8967No ratings yet
- A2 Level Unit V ORGANIC CHEMISTRYDocument19 pagesA2 Level Unit V ORGANIC CHEMISTRYbillaljavedNo ratings yet
- Uace Chem (Benzene NotesDocument15 pagesUace Chem (Benzene NotesmasemvirginNo ratings yet
- (DORDADO) 1 Experiment No. 1 HydrocarbonsDocument8 pages(DORDADO) 1 Experiment No. 1 HydrocarbonsBitterground Corp.No ratings yet
- Analysis of HydrocarbonsDocument4 pagesAnalysis of Hydrocarbonsback upNo ratings yet
- H 0 CCL Naoh H So Cyclohexane (Clear Liquid)Document5 pagesH 0 CCL Naoh H So Cyclohexane (Clear Liquid)Mark GirasolNo ratings yet
- Angelica C. Anabe Bs Psy 2-1: AlkenesDocument12 pagesAngelica C. Anabe Bs Psy 2-1: Alkenesniela cruzNo ratings yet
- Nitration of Benzene: Adia, Sophia Cassandra, ADocument3 pagesNitration of Benzene: Adia, Sophia Cassandra, AS AdiaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Experiment 2Document7 pagesChemistry Experiment 2Alexa Ysabel LiwagNo ratings yet
- Reaction of Alkenes and Alkynes For StudentsDocument53 pagesReaction of Alkenes and Alkynes For StudentsGlen MangaliNo ratings yet
- Experiment 6 - Aromatic HydrocarbonsDocument5 pagesExperiment 6 - Aromatic HydrocarbonsKaye SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Amali 1 LaporanDocument3 pagesAmali 1 LaporanFauzan AzizNo ratings yet
- Data Analysis HydrocarbonDocument7 pagesData Analysis HydrocarbonTHASVIN OFFICIAL NETWORKNo ratings yet
- Organic HydrocarbonsDocument20 pagesOrganic HydrocarbonsOmar Samir0% (1)
- Title: Chemical Properties of AlkanesDocument9 pagesTitle: Chemical Properties of AlkanesLeeshaaLenee Paramanantha KumarNo ratings yet
- HydrocarbonDocument11 pagesHydrocarbonAida IshNo ratings yet
- Chem Lab (Ii) 3Document11 pagesChem Lab (Ii) 3Nurul Hasanah88% (75)
- Hydrocarbons Revision Test SolutionsDocument2 pagesHydrocarbons Revision Test SolutionsShelby Maria AbyNo ratings yet
- Group 5 CHEM111 Properties of Some Aromatic HydrocarbonsDocument6 pagesGroup 5 CHEM111 Properties of Some Aromatic HydrocarbonsmarmitochristineysabelllNo ratings yet
- Classification Tests For HydrocarbonsDocument5 pagesClassification Tests For HydrocarbonsEric AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- Experimental 1 ReportDocument7 pagesExperimental 1 Reportjeremy jasonNo ratings yet
- Aromatic CompoundsDocument36 pagesAromatic CompoundsMaria Ruela Agodera SumogNo ratings yet
- Aliphatic Hydrocarbons: LAB #1 Reactions of HydrocarbonsDocument7 pagesAliphatic Hydrocarbons: LAB #1 Reactions of HydrocarbonsJoshuaArryNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5: Characteristic Reactions of HydrocarbonsDocument7 pagesExperiment 5: Characteristic Reactions of HydrocarbonsJorelle NogoyNo ratings yet
- SC22b Reactions of Alkanes and AlkenesDocument14 pagesSC22b Reactions of Alkanes and AlkenesEmaadB EmaadBNo ratings yet
- Reactions of AlcoholDocument5 pagesReactions of AlcoholSourabh Das100% (1)
- CONSCHEMDocument3 pagesCONSCHEM-09876543123456789No ratings yet
- Classification Test For HydrocarbonsDocument3 pagesClassification Test For Hydrocarbonscyberlog21267% (3)
- R315 AbenojaJL HYDROCARBONSDocument8 pagesR315 AbenojaJL HYDROCARBONSJL AbenojaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Notes - Topic 18 Organic Chemistry III - Edexcel Chemistry A LevelDocument23 pagesDetailed Notes - Topic 18 Organic Chemistry III - Edexcel Chemistry A LevelLulwa KhaskiehNo ratings yet
- Anic Ep 3.Document8 pagesAnic Ep 3.Ummu Umar Wa AisyahNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - Arenes AnswersDocument6 pagesWorksheet - Arenes AnswersAbdul AhadhNo ratings yet
- C H H H H H: Hydrocarbons. Methane. AlkanesDocument14 pagesC H H H H H: Hydrocarbons. Methane. AlkanesDavidDavidovNo ratings yet
- Aromatic Compounds and Uses of BenzeneDocument44 pagesAromatic Compounds and Uses of BenzenePaarijat DubeyNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Organic Chemistry with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Organic Chemistry with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Patent 5Document8 pagesPatent 5ALEXANDER FRANCO CASTRILLONNo ratings yet
- Banana Peel ShampooDocument14 pagesBanana Peel ShampooMhay DingleNo ratings yet
- Exam SolutDocument12 pagesExam Solutnunulovin911No ratings yet
- CARAWAYDocument1 pageCARAWAYBalaji Pharmacy - GMNo ratings yet
- Origin, Generation & Migration of PetroleumDocument26 pagesOrigin, Generation & Migration of PetroleumBharat KumarNo ratings yet
- SC 2024 SP-6Document16 pagesSC 2024 SP-6Swostik RoutNo ratings yet
- Plants: Bioactivity of Common Pesticidal Plants On Fall Armyworm Larvae (Spodoptera Frugiperda)Document10 pagesPlants: Bioactivity of Common Pesticidal Plants On Fall Armyworm Larvae (Spodoptera Frugiperda)salif ouedraogoNo ratings yet
- Waste To Energypptx - 220913 - 151038Document117 pagesWaste To Energypptx - 220913 - 151038Aswini NRNo ratings yet
- Asparagus Benefits 2beingfitDocument7 pagesAsparagus Benefits 2beingfitK AnjaliNo ratings yet
- Enantioselective Total Synthesis of (+) - Wortmannin: Yinliang Guo, Tianfei Quan, Yandong Lu, and Tuoping LuoDocument4 pagesEnantioselective Total Synthesis of (+) - Wortmannin: Yinliang Guo, Tianfei Quan, Yandong Lu, and Tuoping LuoLê MinhNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis ClozeDocument3 pagesProtein Synthesis Clozeapi-309893409No ratings yet
- Free Radical InjuryDocument87 pagesFree Radical InjuryPooja BappannaNo ratings yet
- Kaleab BizunehDocument89 pagesKaleab BizunehTeklit GebrerufaelNo ratings yet
- Reduction, Oxidation - Hydrolysis Exercise PDFDocument24 pagesReduction, Oxidation - Hydrolysis Exercise PDFGOURISH AGRAWAL100% (3)
- Matriculation Chemistry Carbonyl CompoundDocument50 pagesMatriculation Chemistry Carbonyl Compoundiki292100% (1)
- Structures of Organic CompoundsDocument11 pagesStructures of Organic CompoundsJheian Christian TubleNo ratings yet
- Common Polyatomic IonsDocument1 pageCommon Polyatomic Ionsmudasser_rafiq3271No ratings yet
- Analytical Methods For The Determination of Emerging Contaminants in Sewage Sludge Samples. A ReviewDocument26 pagesAnalytical Methods For The Determination of Emerging Contaminants in Sewage Sludge Samples. A ReviewMaria AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Gomes Basso BeansDocument9 pagesGomes Basso Beansjuan diegoNo ratings yet
- Exp. 7 Analysis of Milk For The Lipids Carbohydrates and ProteinsDocument6 pagesExp. 7 Analysis of Milk For The Lipids Carbohydrates and ProteinsEdchelNo ratings yet
- Ammonium Peroxydisulfate MSDSDocument8 pagesAmmonium Peroxydisulfate MSDSFitriani TanraNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Compounds: Chemical Name Chemical FormulaDocument6 pagesInorganic Compounds: Chemical Name Chemical FormulaFrendick LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Sensors & Actuators B. Chemical 304 (2020) 127396Document15 pagesSensors & Actuators B. Chemical 304 (2020) 127396ashwanirubalNo ratings yet
- Fire Prevention & Fire FightingDocument24 pagesFire Prevention & Fire FightingAku RajNo ratings yet
- Balauro Worksheet Protein SynthesisDocument4 pagesBalauro Worksheet Protein SynthesisHami BalauroNo ratings yet
- Primer DesignDocument37 pagesPrimer DesignRyu- MikaNo ratings yet
- Index: Sr. No. Topic NoDocument53 pagesIndex: Sr. No. Topic NoChetana JadhavNo ratings yet
- Sam White 4bk (TDS)Document4 pagesSam White 4bk (TDS)Md.Ifrith RahmanNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution in Petroleum IndustryDocument46 pagesAir Pollution in Petroleum IndustryAtul SharanNo ratings yet