Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biological Molecules AQA AS Biology 5
Biological Molecules AQA AS Biology 5
Uploaded by
RanaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Biological Molecules AQA AS Biology 5
Biological Molecules AQA AS Biology 5
Uploaded by
RanaCopyright:
Available Formats
Biological molecules (AQA AS Biology) PART 5 of 8 TOPICS: Nucleic
TOPI
acids
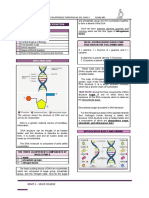
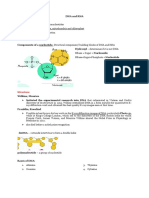
Nucleic acids:
Two types of nucleic acids needs to be known for this module and they are DNA (deoxyribose nucleic
acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid). These are important information carrying molecules where DNA holds
genetic information and RNA transfers the genetic information to the ribosomes. The structures of DNA
To ensure continuity of genetic
and RNA should be known:
1. DNA double helix unwi
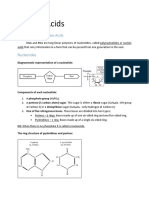
Phosphate group 2. Free nucleotides in the
guanine are compleme
3. DNA polymerase (an en
4. Hydrogen bonds are cr
Nitrogenous base
If the molecule is DNA the four different bases
of which it could be are adenine, thymine,
Pentose sugar (this should be not be
cytosine, and guanine. Adenine and thymine
said on the exam)
are complementary to each other and cytosine
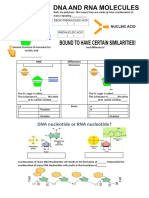
deoxyribose sugar if it is DNA or molecules. This is beca
and guanine are complementary to each other.
ribose sugar if it is RNA
This is why there are two strands of DNA held original strand and one
together (a double helix) because of these
similarities forming hydrogen bonds.
Joining up these individual nucleic acidsIfinvolves
the molecule is RNA the four
a condensation different
reaction tobases
create phosphodiester bonds to create a sugar p
of which it could be are adenine, uracil (instead
of thymine), cytosine and guanine. The same
relationships shown by the complementary
bases in DNA are also shown by RNA however
adenine is complementary to uracil. RNA is
relatively shorter and is single stranded. This
means that the complementary bases shown by
RNA come in handy during protein synthesis
which will be covered later on which is one of
my resources.
You might also like
- Test Bank For Biochemistry 9th Edition Mary K Campbell Shawn o Farrell Shawn o Farrellowen M McdougalDocument8 pagesTest Bank For Biochemistry 9th Edition Mary K Campbell Shawn o Farrell Shawn o Farrellowen M McdougalNathan Cook95% (41)
- Plasmid Mapping Exercises PDFDocument18 pagesPlasmid Mapping Exercises PDFFrancois-YvanNo ratings yet
- Molecular Diagnostics-Fundamentals Methods and Clinical ApplicationsDocument479 pagesMolecular Diagnostics-Fundamentals Methods and Clinical ApplicationsYasen Taha100% (10)
- 1.5 Nucleic AcidsDocument1 page1.5 Nucleic AcidsBlitzSZNNo ratings yet
- Cytogenetics - Lesson 2 - Dna Structure and Dna ExtractionDocument8 pagesCytogenetics - Lesson 2 - Dna Structure and Dna ExtractionAli TaguibaoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Dna Structure and Dna ExtractionDocument8 pagesLesson 2 Dna Structure and Dna ExtractionGreatel Elijah TorregosaNo ratings yet
- 04-Chemical Basis of HeredityDocument10 pages04-Chemical Basis of HeredityBen Abella100% (1)
- Gen Bio 3rd QuarterDocument6 pagesGen Bio 3rd QuarterzafmustaphaNo ratings yet
- Biochem Reviewer FinalsDocument18 pagesBiochem Reviewer Finalscha cuteNo ratings yet
- Simone PostersDocument1 pageSimone PostersMasr RedaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids Fact SheetDocument1 pageNucleic Acids Fact Sheetasieee chimmyNo ratings yet
- Central DogmaDocument4 pagesCentral DogmaalxndrasenalesNo ratings yet
- 1 Nucleic AcidDocument14 pages1 Nucleic AcidYlooner QuitsNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids: DNA Nucleotide or RNA Nucleotide?Document2 pagesNucleic Acids: DNA Nucleotide or RNA Nucleotide?Rachell RequellNo ratings yet
- DNA Kita Iiwan RNA CytoDocument3 pagesDNA Kita Iiwan RNA CytozairahNo ratings yet
- GenBIO REVIEWERDocument39 pagesGenBIO REVIEWERblismae genotivaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry BrochureDocument2 pagesBiochemistry BrochureCaryl Alvarado SilangNo ratings yet
- Biological Significance of DNA and RNA SturucturesDocument2 pagesBiological Significance of DNA and RNA SturucturesDr.Charles BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument23 pagesCell Cyclefrank menshaNo ratings yet
- Self Assessment Answers 6 Asal Biology CBDocument2 pagesSelf Assessment Answers 6 Asal Biology CBsaeed.khedrizaNo ratings yet
- DNA Structure and ReplicationDocument12 pagesDNA Structure and ReplicationJhune Dominique GalangNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid: Genetic CodeDocument2 pagesNucleic Acid: Genetic CodeAngelica AycardoNo ratings yet
- BacterialDocument2 pagesBacterialjulietaira quibilanNo ratings yet
- L11 - How Is DNA Copied To Form 2 Identical MoleculesDocument39 pagesL11 - How Is DNA Copied To Form 2 Identical Moleculesshiyan.konohaNo ratings yet
- DNA Structure and Replication Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument1 pageDNA Structure and Replication Cheat Sheet: by ViaThaboNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids + Protein SynthesisDocument5 pagesNucleic Acids + Protein SynthesisNezza WidarkoNo ratings yet
- DNA Vs RNADocument2 pagesDNA Vs RNAMegat AmirulNo ratings yet
- Mtap I - Molbio - NotesDocument30 pagesMtap I - Molbio - NotesKath CamacamNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 4th QTDocument7 pagesGen Bio 4th QTZuri MaeNo ratings yet
- LeaP Science 10 Q3 Week 4Document6 pagesLeaP Science 10 Q3 Week 4Tzuyu ChouNo ratings yet
- Essential Idea: The Structure of DNA Allows Efficient Storage of Genetic InformationDocument26 pagesEssential Idea: The Structure of DNA Allows Efficient Storage of Genetic InformationReeya WhabiNo ratings yet
- Science 10 NotesDocument1 pageScience 10 Notessarmientoangelica672No ratings yet
- Structure and Functions of DNA and RNADocument3 pagesStructure and Functions of DNA and RNAokonabasimfreke09No ratings yet
- Lesson 5C - Dna Replication and RepairDocument7 pagesLesson 5C - Dna Replication and RepairHelen Gail EmbudoNo ratings yet
- 2.7 DNA Replication, Transcription, and TranslationDocument46 pages2.7 DNA Replication, Transcription, and Translationpapa3rikusNo ratings yet
- GeneticsDocument3 pagesGeneticsbonoo.santuchoNo ratings yet
- Expt. 7 Nucleic Acid WorksheetDocument9 pagesExpt. 7 Nucleic Acid WorksheetMary Ella Mae PilaNo ratings yet
- General Biology - DNA ReplicationDocument3 pagesGeneral Biology - DNA ReplicationChristine Marylou PalomoNo ratings yet
- (SCI) LESSON 5 - DNA, RNA, and PhotosynthesisDocument2 pages(SCI) LESSON 5 - DNA, RNA, and Photosynthesisitz.jdv1694No ratings yet
- 6 Nucleic AcidsDocument3 pages6 Nucleic AcidsTala AlkhawajaNo ratings yet
- WK8-9 - Nucleic Acids 1 - 2Document7 pagesWK8-9 - Nucleic Acids 1 - 2opingaangelamae.opingaNo ratings yet
- 1 Nucleic AcidsDocument11 pages1 Nucleic AcidsSafiya JamesNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids BrochureDocument2 pagesNucleic Acids BrochureCring-cring NavarroNo ratings yet
- PHA6112LAB - Experiment 4 Nucleic Acids ReviewerDocument8 pagesPHA6112LAB - Experiment 4 Nucleic Acids ReviewerMarie Eloise BugayongNo ratings yet
- DNA and RNADocument3 pagesDNA and RNAHans PNo ratings yet
- Rne Dna Nucleotide Structure Worksheet v2Document4 pagesRne Dna Nucleotide Structure Worksheet v2Pham Hoang Nghi LENo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidsDocument23 pagesNucleic AcidsShenne Ann MaghuyopNo ratings yet
- DNA VS RNA - DNA REPLICATIONDocument2 pagesDNA VS RNA - DNA REPLICATIONJuan Carlo SamsonNo ratings yet
- Comparison DNA and RNADocument2 pagesComparison DNA and RNAMani MentalNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3.3 Heredity NotesdocxDocument2 pagesLESSON 3.3 Heredity NotesdocxJedy IvoryNo ratings yet
- BIO-5dll 3rdDocument15 pagesBIO-5dll 3rdarlene dioknoNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid and Protein SynthesisDocument3 pagesNucleic Acid and Protein SynthesisLaurence PriscillaNo ratings yet
- Biology Nucleic A-Level OCR NotesDocument11 pagesBiology Nucleic A-Level OCR Notestbrook2017No ratings yet
- Chromosome, DNA, RNADocument5 pagesChromosome, DNA, RNAShahrat Farsim ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- DNA and RNADocument3 pagesDNA and RNANakajima AtsushiNo ratings yet
- Cell Disease LabDocument1 pageCell Disease Labapi-340815123No ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Glencoe Biology Study GuideDocument11 pagesChapter 12 Glencoe Biology Study GuideabdulazizalobaidiNo ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance - Short NotesDocument3 pagesMolecular Basis of Inheritance - Short Notesp11925885No ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance - Short Notes - Lakshya NEET 2025Document3 pagesMolecular Basis of Inheritance - Short Notes - Lakshya NEET 2025anantpounikar02No ratings yet
- Reviewer Biochem For NucleotidesDocument3 pagesReviewer Biochem For NucleotidesNino D. AtilanoNo ratings yet
- Basis of ComparisonDocument2 pagesBasis of ComparisonJoshua AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic mRNA Transcripts Are Processed: CytoplasmDocument17 pagesEukaryotic mRNA Transcripts Are Processed: CytoplasmanshuNo ratings yet
- August 20-24, 2018Document5 pagesAugust 20-24, 2018Maria Virginia Fernandez100% (1)
- Biosintesa GlukomananDocument12 pagesBiosintesa GlukomananDetya Pitaloka SariNo ratings yet
- Structure: of Bacterial CellDocument25 pagesStructure: of Bacterial CellManila BhatiaNo ratings yet
- WORKSHEET 4.2 The Chemical Compound in The CellDocument4 pagesWORKSHEET 4.2 The Chemical Compound in The Cellmira bonzay100% (1)
- Quote BL19326 - UNDIP - Airin Nur Hidayah - PrimerDocument1 pageQuote BL19326 - UNDIP - Airin Nur Hidayah - Primersri wahyuniNo ratings yet
- LN Molecular Biolog Applied Genetics FINALDocument529 pagesLN Molecular Biolog Applied Genetics FINALarivasudeva100% (1)
- Unit1 - Heaven Gates (Pico Iyer)Document11 pagesUnit1 - Heaven Gates (Pico Iyer)shivay-negi-1484No ratings yet
- Fision KeraVeg18 Brochure FINAL - ReducedDocument12 pagesFision KeraVeg18 Brochure FINAL - ReducedParthMairNo ratings yet
- Indole Signalling Contributes To The Stable Maintenance of Escherichia Coli Multicopy PlasmidsDocument9 pagesIndole Signalling Contributes To The Stable Maintenance of Escherichia Coli Multicopy Plasmidstantry puspitasariNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Labor: Moderator: Dr. Angesom.K, Obs/ Gyn-SpecialistDocument58 pagesPhysiology of Labor: Moderator: Dr. Angesom.K, Obs/ Gyn-SpecialistYobed MengeshaNo ratings yet
- MutationsDocument29 pagesMutationsiariajay100% (1)
- Dr. M. Azhar Chishti Dept. Medical BiochemistryDocument46 pagesDr. M. Azhar Chishti Dept. Medical Biochemistryvarsha CRNo ratings yet
- BIO F4 Chapter 4 Obj QuesttionDocument3 pagesBIO F4 Chapter 4 Obj QuesttionIda KamalNo ratings yet
- KREB's Cycle PDFDocument30 pagesKREB's Cycle PDFRitwik ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Bio Craft CatalogDocument29 pagesBio Craft CatalogHa LeNo ratings yet
- Possible Essay Questions Exam #2Document1 pagePossible Essay Questions Exam #246bwilsonNo ratings yet
- Dikshathakur ResumeDocument2 pagesDikshathakur ResumeDikshaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BiologyDocument4 pagesIntroduction To BiologyEury Marc Suhi-anNo ratings yet
- Protein Denaturation Notes - July 2021Document4 pagesProtein Denaturation Notes - July 2021BOR KIPLANGAT ISAACNo ratings yet
- FISH Word DocumentDocument10 pagesFISH Word DocumentUmmey ShameemNo ratings yet
- Botany AssignmentDocument5 pagesBotany AssignmentHamza MaqboolNo ratings yet
- Mlpa Poster FinalDocument1 pageMlpa Poster Finalapi-448483010No ratings yet
- Classical Vs Reverse Pharmacology in Drug DiscoveryDocument4 pagesClassical Vs Reverse Pharmacology in Drug DiscoveryGourisankar Roul100% (1)
- Intracellular Compartments and Protein SortingDocument9 pagesIntracellular Compartments and Protein SortingJudith UgwujaNo ratings yet
- Mutations PowerpointDocument40 pagesMutations Powerpointkurrupp k.pNo ratings yet
- Hydrophobic Modifications of Cationic Polymers For Gene DeliveryDocument19 pagesHydrophobic Modifications of Cationic Polymers For Gene DeliveryValentina RoznovNo ratings yet