Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Power Factor Correction
Power Factor Correction
Uploaded by
giedrius.s95Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Power Factor Correction
Power Factor Correction
Uploaded by
giedrius.s95Copyright:
Available Formats
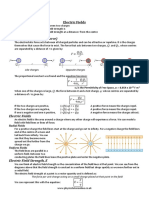
POWER FACTOR CORRECTION
Once you have established the P, S, Q and pf of a load you can then calculate the values of the
components required to correct the power factor (pf).
S
Q
Φ
P
Figure 1 Initial Power Triangle
The purpose of power factor correction is to minimise the Reactive power in the load, with the ideal
power factor being 1 which would mean zero Reactive power. In most cases we are given a specific
power factor to which we should correct. Once we have the required power factor value then there
are a number of steps required to find out the value of the components required to achieve the
required power factor.
1. Establish the New reactive power (Qn) that will be in the system
2. Calculate the reduction required in reactive power to go from the initial Q to the new Qn
• If the initial load is inductive then we need to add capacitive reactive power to
reduce overall reactive power (QC)
• If the initial load is capacitive then we need to add inductive reactive power to
reduce overall reactive power (QL)
• We will assume an inductive load and therefore a QC correction for the rest of this
description
3. The power factor capacitor is placed in parallel with the load therefore the capacitive
𝑉
reactance can be calculated using the formula 𝑄𝐶 = 𝑋
𝐶
1
4. With XC established we can calculate the capacitance required using the formula 𝑋𝐶 = 2𝜋𝑓𝐶
S Q
Φ Sn
Φn Qn
P
Figure 2POwer triangle showing pf correction
You might also like
- Experiment 3 Power FactorDocument8 pagesExperiment 3 Power FactorKyleNo ratings yet
- Calculation of The Power FactorDocument50 pagesCalculation of The Power FactorAurobindo MandalNo ratings yet
- Power FactorDocument21 pagesPower FactorHosam JabrallahNo ratings yet
- Calculate Reactive Power of The Capacitor Bank and Improve Power FactorDocument4 pagesCalculate Reactive Power of The Capacitor Bank and Improve Power Factorfigo lordNo ratings yet
- Calculate Reactive Power of The Capacitor Bank and Improve Power FactorDocument4 pagesCalculate Reactive Power of The Capacitor Bank and Improve Power FactornagarajaNo ratings yet
- 1 BoardCompanion Physics PDFDocument61 pages1 BoardCompanion Physics PDFSrn YuvaneshNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 Sinusoidal Steady State Power Measurements & Power Factor CorrectionDocument4 pagesLab 6 Sinusoidal Steady State Power Measurements & Power Factor CorrectionTayyab AhmedNo ratings yet
- ElecDocument30 pagesEleczakariareal623No ratings yet
- Lecture 6Document18 pagesLecture 6Abdelrahman MuadiNo ratings yet
- CH 7 Power in AC CircuitsDocument14 pagesCH 7 Power in AC Circuitsshresthaamisha489No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 3.0 Power in AC Circuits With SolutionDocument20 pagesCHAPTER 2 3.0 Power in AC Circuits With SolutionMUHAMMAD ALIFF DANIAL RAZMINo ratings yet
- Power in AC Circuits Module 3 CompressedDocument27 pagesPower in AC Circuits Module 3 CompressedTatsumaki TornadoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Electrostatics: Subtopic C1 & C2 C3 & C4Document15 pagesChapter 1: Electrostatics: Subtopic C1 & C2 C3 & C4Suthan MariappenNo ratings yet
- (L4) Electrostatics - 20 April NotesDocument33 pages(L4) Electrostatics - 20 April NotesAyush Kumar MishraNo ratings yet
- Week 4Document5 pagesWeek 4soetunNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of Power SystemDocument30 pagesFundamental of Power SystemGetahun shankoNo ratings yet
- Calculate Reactive Power Rev 1Document3 pagesCalculate Reactive Power Rev 1visanuNo ratings yet
- F Lect 5Document26 pagesF Lect 5Abdelrahman MuadiNo ratings yet
- NCERT Class 12 Physics Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance PDFDocument42 pagesNCERT Class 12 Physics Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance PDFAlice AntilNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics TH XIIDocument28 pagesElectrostatics TH XIIDark gaming liveNo ratings yet
- 2009 Kamaraju - Electrical Power Distribution systems-McGraw Hill-131-154Document24 pages2009 Kamaraju - Electrical Power Distribution systems-McGraw Hill-131-154C071Ridho Setiawan TuitantoNo ratings yet
- Analysis of UPQC With Advanced Control Scheme Under Different SituationsDocument4 pagesAnalysis of UPQC With Advanced Control Scheme Under Different SituationserpublicationNo ratings yet
- PSS LabDocument79 pagesPSS LabLakshmi ZaharaNo ratings yet
- Operation of Two Converter IPFC Considering Complementary VoltageDocument9 pagesOperation of Two Converter IPFC Considering Complementary Voltageht jadhavNo ratings yet
- Power Factor GuidanceDocument3 pagesPower Factor GuidanceAshish KalamkarNo ratings yet
- Lab 6Document8 pagesLab 6hamzaNo ratings yet
- ADE7978/ADE7933/ADE7932/ADE7923 Power Factor Calculation and Total Harmonic Distortion CalculationDocument1 pageADE7978/ADE7933/ADE7932/ADE7923 Power Factor Calculation and Total Harmonic Distortion CalculationDeepak GehlotNo ratings yet
- EE301 Lesson 24 AC Power and PWR TriangleDocument23 pagesEE301 Lesson 24 AC Power and PWR TriangleJidi rector100% (1)
- Power in Ac CircuitDocument18 pagesPower in Ac CircuitSinteyahu YilmaNo ratings yet
- A Novel Time-Domain Perspective of The CPC Power Theory Single-Phase SystemsDocument10 pagesA Novel Time-Domain Perspective of The CPC Power Theory Single-Phase SystemsLuiz_F_A_ViannaNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic Potential and CapacitanceDocument28 pagesElectrostatic Potential and CapacitanceTanya SinghNo ratings yet
- PSF Lecture 2Document26 pagesPSF Lecture 2bhaweshratni08No ratings yet
- Lecture 7Document32 pagesLecture 7NiwekNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Magnetism Lecture 5 Part (1-4)Document5 pagesElectricity and Magnetism Lecture 5 Part (1-4)Hamza IqbalNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic Potential and CapacitanceDocument28 pagesElectrostatic Potential and CapacitanceRupesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document25 pagesLecture 4Rana EL ArabeNo ratings yet
- Journal Papers IeeeDocument10 pagesJournal Papers Ieee21-202 Furqan Saleem MohammedNo ratings yet
- PS5111-Power System Simulation Lab-IDocument97 pagesPS5111-Power System Simulation Lab-ILakshmi Zahara67% (3)
- Electrostatic Potential: DifferenceDocument16 pagesElectrostatic Potential: DifferenceEmmaNo ratings yet
- Exp 11Document7 pagesExp 11abdelmalekhadiakNo ratings yet
- Power Factor Improvement: Unit - IvDocument20 pagesPower Factor Improvement: Unit - IvDIVYA PRASOONA CNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4: Part A: Linearization of Output of A Wheatstone BridgeDocument3 pagesExperiment 4: Part A: Linearization of Output of A Wheatstone BridgeAditya SundarNo ratings yet
- Module3 - Power in AC CircuitsDocument107 pagesModule3 - Power in AC CircuitsTatsumaki TornadoNo ratings yet
- Edj27103 - Lab2 (New) - Power Factor CorrectionDocument10 pagesEdj27103 - Lab2 (New) - Power Factor CorrectionpreethikaNo ratings yet
- Reactive Power Management and CapacitorsDocument5 pagesReactive Power Management and Capacitorsk K MurtyNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - Power Factor Correction Note 1Document18 pagesMicrosoft Word - Power Factor Correction Note 1Swagatam BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- AC Power AnalysisDocument19 pagesAC Power AnalysisMD EM MASUMNo ratings yet
- F Lect 4Document13 pagesF Lect 4Abdelrahman MuadiNo ratings yet
- Automatic Power Factor Correction Using MircrocontrollerDocument13 pagesAutomatic Power Factor Correction Using MircrocontrollermakibenNo ratings yet
- PanPearl2016 Solutions 1Document8 pagesPanPearl2016 Solutions 1tanNo ratings yet
- Be 12Document39 pagesBe 12221618No ratings yet
- Voltage Stability Aspects in Power Transmission System and Its Mitigation Using FACTs Devices.Document43 pagesVoltage Stability Aspects in Power Transmission System and Its Mitigation Using FACTs Devices.chandueeeNo ratings yet
- Engineering Electromagnetics: Energy and PotentialDocument44 pagesEngineering Electromagnetics: Energy and Potentialkallepalli venu ManikantaNo ratings yet
- Power Factor Correction Sizing From Utility Meter DataDocument9 pagesPower Factor Correction Sizing From Utility Meter DataAnonymous C52AEINo ratings yet
- Power Factor Correction in Photovoltaic PlantsDocument9 pagesPower Factor Correction in Photovoltaic PlantsAurobindo MandalNo ratings yet
- Electric Fields NOTESDocument2 pagesElectric Fields NOTESJOHANNESKIFENDINo ratings yet
- Unified Power Quality ConditionerDocument19 pagesUnified Power Quality ConditionerShameer Sr S RNo ratings yet
- Complex Numbers Intro 1 - 20240318120234Document43 pagesComplex Numbers Intro 1 - 20240318120234giedrius.s95No ratings yet
- Electrical Principles Mock PaperDocument4 pagesElectrical Principles Mock Papergiedrius.s95No ratings yet
- Significant FiguresDocument2 pagesSignificant Figuresgiedrius.s95No ratings yet
- Boolean LogicDocument38 pagesBoolean Logicgiedrius.s95No ratings yet
- EP Lab 3bDocument4 pagesEP Lab 3bgiedrius.s95No ratings yet
- EP Lab 5Document3 pagesEP Lab 5giedrius.s95No ratings yet