Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BRIDGE FWR Class Notes
BRIDGE FWR Class Notes
Uploaded by
RAJASHEKHARCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Full Wave Rectification Lab ReportDocument2 pagesFull Wave Rectification Lab ReportAbu100% (1)
- Electronics - Diode Applications & TransistorsDocument24 pagesElectronics - Diode Applications & TransistorsA B ShindeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-RectifiersDocument5 pagesChapter 2-RectifiersMehedi hasanNo ratings yet
- Electronics Devices Lab - Exp 2 - Mid Term - Fall 22-23 - ACSDocument19 pagesElectronics Devices Lab - Exp 2 - Mid Term - Fall 22-23 - ACSdark lionNo ratings yet
- Basic Rectifier CircuitsDocument8 pagesBasic Rectifier CircuitssensitivesensesNo ratings yet
- Half Wave Rectifier Circuits Part (1-A) : Experiment: DiodeDocument13 pagesHalf Wave Rectifier Circuits Part (1-A) : Experiment: DiodeCatalina ZelayaNo ratings yet
- RECTIFIERDocument6 pagesRECTIFIEREasy EducationNo ratings yet
- Practical 12thDocument7 pagesPractical 12thkumarnareshNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5Document6 pagesExperiment 5Mashrur Alam KabyaNo ratings yet
- Bridge Rectifier: What Is A Rectifier?Document3 pagesBridge Rectifier: What Is A Rectifier?Jacob GoonaNo ratings yet
- Full Wave Bridge RectifierDocument5 pagesFull Wave Bridge RectifierChennaiSuperkingsNo ratings yet
- Electronics and Electrical PrincipleDocument10 pagesElectronics and Electrical Principlechox69No ratings yet
- Bridge Rectifier Circuit ANSH SHARMADocument13 pagesBridge Rectifier Circuit ANSH SHARMAarush00524No ratings yet
- P-N Junction As A RectifierDocument3 pagesP-N Junction As A RectifierNouman RiazNo ratings yet
- MtE-205 EPD LAB 09Document6 pagesMtE-205 EPD LAB 09Syed Suleman Ayub - Section-BNo ratings yet
- SsssssDocument7 pagesSssssssamveer1234567890No ratings yet
- RECTIFIERSDocument3 pagesRECTIFIERSmehakNo ratings yet
- Rectifier and Power SupplyDocument10 pagesRectifier and Power SupplyNani NaniNo ratings yet
- BEC Microproject IF2IDocument11 pagesBEC Microproject IF2Iif21adityapawarNo ratings yet
- Apl Lab 12aDocument8 pagesApl Lab 12amanavlund5No ratings yet
- Applications of PN Junction Diode PDFDocument8 pagesApplications of PN Junction Diode PDFZain Ul AbedinNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument8 pagesPhysics ProjectXigfon SqitroNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project Work: Jawahar Navodaya Vidyalaya, VATTEM - 509203Document19 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project Work: Jawahar Navodaya Vidyalaya, VATTEM - 509203Md SohelNo ratings yet
- FULL WaveDocument7 pagesFULL WaveManish BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Diode Rectifier Then Provides A Full-WaveDocument4 pagesDiode Rectifier Then Provides A Full-Waveprem035No ratings yet
- Half Wave & Full WaveDocument16 pagesHalf Wave & Full WaveZalakNo ratings yet
- DC Power Supply-An IntroductionDocument9 pagesDC Power Supply-An Introductionchanchal2No ratings yet
- (Final)Document16 pages(Final)saurabhNo ratings yet
- Unit - V InvertersDocument11 pagesUnit - V InvertersSukhpal SinghNo ratings yet
- Module-1 RectifiersDocument5 pagesModule-1 RectifiersSwarup Kumar PadhyNo ratings yet
- 13 PracDocument1 page13 Pracmiss awakeNo ratings yet
- Rectifying CircuitsDocument13 pagesRectifying Circuitssina981No ratings yet
- Rohini 56862343385Document3 pagesRohini 56862343385royrashmi274No ratings yet
- Connection DetailsDocument9 pagesConnection Detailskarthik 'No ratings yet
- Full Wave Bridge RectifierDocument8 pagesFull Wave Bridge RectifierAnonimen AnonimenNo ratings yet
- FULL WAVE RECTIFIERDocument8 pagesFULL WAVE RECTIFIERsakthivel222sanjayNo ratings yet
- Full Wave Bridge RectifierDocument4 pagesFull Wave Bridge RectifierSachit KumarNo ratings yet
- Bridge Rectifier: Bridge Rectifiers Are Circuits That ConvertDocument4 pagesBridge Rectifier: Bridge Rectifiers Are Circuits That ConvertabdulNo ratings yet
- Electronic Circuits Power Supply Electronic Basic Components AC Power Devices Like Home AppliancesDocument21 pagesElectronic Circuits Power Supply Electronic Basic Components AC Power Devices Like Home AppliancesTushar GoelNo ratings yet
- Originalproectphysicsmsword Converted 191225064922Document12 pagesOriginalproectphysicsmsword Converted 191225064922GOKULNo ratings yet
- Exp2Document13 pagesExp2Karim 325No ratings yet
- EPD Lab#9Document8 pagesEPD Lab#9Muhammad ShaheerNo ratings yet
- FULL WAVE RECTIFIER Class NotesDocument2 pagesFULL WAVE RECTIFIER Class NotesRAJASHEKHARNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 (Analogue Electronics I)Document7 pagesLecture 3 (Analogue Electronics I)amash.emillyNo ratings yet
- Assignment MEDocument3 pagesAssignment MESaad AliKhanNo ratings yet
- Physics Project01Document12 pagesPhysics Project01nilu royNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Application CircuitsDocument8 pages1.3 Application Circuitslizhi0007No ratings yet
- Project Report RectifierDocument9 pagesProject Report RectifierMuhammad RashidNo ratings yet
- Bel102-Fundamental of Electrical and Electronics Laboratory Name: Krrish Roll No:12111081Document6 pagesBel102-Fundamental of Electrical and Electronics Laboratory Name: Krrish Roll No:12111081KrrishNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document26 pagesChapter 1nida2505No ratings yet
- EDL Ex No. 2Document2 pagesEDL Ex No. 2Shilpi YadavNo ratings yet
- BESCK104C 204C IEC Module1 NotesDocument24 pagesBESCK104C 204C IEC Module1 Notesblehbo100% (1)
- Bridge Rectifier: Circuit Diagram & Its WorkingDocument12 pagesBridge Rectifier: Circuit Diagram & Its WorkingChandra Sekhar CNo ratings yet
- يجوملا موقملا RectifierDocument18 pagesيجوملا موقملا RectifierYacine KhalidNo ratings yet
- Module 4 (Electronic Fundamentals) B1Document49 pagesModule 4 (Electronic Fundamentals) B1AmirAli MohebbiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Single Phase Full Bridge VSCDocument12 pagesLecture 5 - Single Phase Full Bridge VSCAfsal Abdul KarimNo ratings yet
- Lecture 03 - Diode Applications (Rectification)Document16 pagesLecture 03 - Diode Applications (Rectification)Joseph NgowiNo ratings yet
- Voltagemultiplier AMOSDocument3 pagesVoltagemultiplier AMOSAbhilash OSNo ratings yet
- A Project On Full Wave RectifierDocument10 pagesA Project On Full Wave Rectifiershivansh100% (1)
- Micrwave Effecton Human BodyDocument11 pagesMicrwave Effecton Human BodyRAJASHEKHARNo ratings yet
- New Doc 2017-08-21 - 1Document8 pagesNew Doc 2017-08-21 - 1RAJASHEKHARNo ratings yet
- Beee Unit I-1-8Document8 pagesBeee Unit I-1-8RAJASHEKHARNo ratings yet
- FULL WAVE RECTIFIER Class NotesDocument2 pagesFULL WAVE RECTIFIER Class NotesRAJASHEKHARNo ratings yet
- HALF WAVE RECTIFIER Class NotesDocument2 pagesHALF WAVE RECTIFIER Class NotesRAJASHEKHARNo ratings yet
- Iot Test 2Document2 pagesIot Test 2RAJASHEKHARNo ratings yet
- Unit VDocument46 pagesUnit VRAJASHEKHARNo ratings yet
- Iot Test 1Document7 pagesIot Test 1RAJASHEKHARNo ratings yet
- Unit Iii Micro W A VE Solid State DevicesDocument7 pagesUnit Iii Micro W A VE Solid State DevicesRAJASHEKHARNo ratings yet
- Mwe Unit 3part 3Document24 pagesMwe Unit 3part 3RAJASHEKHARNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Pre PHDDocument16 pagesMathematics Pre PHDRAJASHEKHARNo ratings yet
- Avalanche Breakdown Zener BreakdownDocument2 pagesAvalanche Breakdown Zener BreakdownRAJASHEKHARNo ratings yet
BRIDGE FWR Class Notes
BRIDGE FWR Class Notes
Uploaded by
RAJASHEKHAROriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BRIDGE FWR Class Notes
BRIDGE FWR Class Notes
Uploaded by
RAJASHEKHARCopyright:
Available Formats
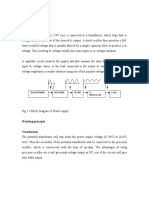
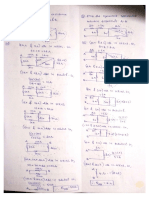
BRIDGE FULL WAVE RECTIFIER:
The basic bridge rectifier circuit is shown in fig. the bridge rectifier circuit is essentially a full-wave rectifier
circuit, using four diodes, forming the four arms of an electrical bridge. To one diagonal of the bridge, the
a.c. voltage is applied through a transformer if necessary and the rectified d.c. voltage is taken from the
other diagonal of the bridge. The main advantage of this circuit is that it does not require a center tap on
the secondary winding of the transformer.
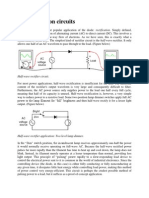
OPERATIO OF THE CIRCUIT:
Consider the positive half of ac input voltage. The point A of secondary becomes positive. The
diodes D1 and D2 will be forward biased, while D3 and D4 reverse biased. The two diodes D1 and D2
conducts in series with the load and the current flows as shown in fig. In the next half cycle, when the
polarity of ac voltage reverses hence point B becomes positive diodes D3 and D4 are forward biased,
while D1 and D2 reverse biased. The two diodes D3 and D4 conducts in series with the load and the
current flows as shown in fig. It is seen that in both cycles of ac, the load current is flowing in the same
direction hence, we get a full-wave rectified output.
You might also like
- Full Wave Rectification Lab ReportDocument2 pagesFull Wave Rectification Lab ReportAbu100% (1)
- Electronics - Diode Applications & TransistorsDocument24 pagesElectronics - Diode Applications & TransistorsA B ShindeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-RectifiersDocument5 pagesChapter 2-RectifiersMehedi hasanNo ratings yet
- Electronics Devices Lab - Exp 2 - Mid Term - Fall 22-23 - ACSDocument19 pagesElectronics Devices Lab - Exp 2 - Mid Term - Fall 22-23 - ACSdark lionNo ratings yet
- Basic Rectifier CircuitsDocument8 pagesBasic Rectifier CircuitssensitivesensesNo ratings yet
- Half Wave Rectifier Circuits Part (1-A) : Experiment: DiodeDocument13 pagesHalf Wave Rectifier Circuits Part (1-A) : Experiment: DiodeCatalina ZelayaNo ratings yet
- RECTIFIERDocument6 pagesRECTIFIEREasy EducationNo ratings yet
- Practical 12thDocument7 pagesPractical 12thkumarnareshNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5Document6 pagesExperiment 5Mashrur Alam KabyaNo ratings yet
- Bridge Rectifier: What Is A Rectifier?Document3 pagesBridge Rectifier: What Is A Rectifier?Jacob GoonaNo ratings yet
- Full Wave Bridge RectifierDocument5 pagesFull Wave Bridge RectifierChennaiSuperkingsNo ratings yet
- Electronics and Electrical PrincipleDocument10 pagesElectronics and Electrical Principlechox69No ratings yet
- Bridge Rectifier Circuit ANSH SHARMADocument13 pagesBridge Rectifier Circuit ANSH SHARMAarush00524No ratings yet
- P-N Junction As A RectifierDocument3 pagesP-N Junction As A RectifierNouman RiazNo ratings yet
- MtE-205 EPD LAB 09Document6 pagesMtE-205 EPD LAB 09Syed Suleman Ayub - Section-BNo ratings yet
- SsssssDocument7 pagesSssssssamveer1234567890No ratings yet
- RECTIFIERSDocument3 pagesRECTIFIERSmehakNo ratings yet
- Rectifier and Power SupplyDocument10 pagesRectifier and Power SupplyNani NaniNo ratings yet
- BEC Microproject IF2IDocument11 pagesBEC Microproject IF2Iif21adityapawarNo ratings yet
- Apl Lab 12aDocument8 pagesApl Lab 12amanavlund5No ratings yet
- Applications of PN Junction Diode PDFDocument8 pagesApplications of PN Junction Diode PDFZain Ul AbedinNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument8 pagesPhysics ProjectXigfon SqitroNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project Work: Jawahar Navodaya Vidyalaya, VATTEM - 509203Document19 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project Work: Jawahar Navodaya Vidyalaya, VATTEM - 509203Md SohelNo ratings yet
- FULL WaveDocument7 pagesFULL WaveManish BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Diode Rectifier Then Provides A Full-WaveDocument4 pagesDiode Rectifier Then Provides A Full-Waveprem035No ratings yet
- Half Wave & Full WaveDocument16 pagesHalf Wave & Full WaveZalakNo ratings yet
- DC Power Supply-An IntroductionDocument9 pagesDC Power Supply-An Introductionchanchal2No ratings yet
- (Final)Document16 pages(Final)saurabhNo ratings yet
- Unit - V InvertersDocument11 pagesUnit - V InvertersSukhpal SinghNo ratings yet
- Module-1 RectifiersDocument5 pagesModule-1 RectifiersSwarup Kumar PadhyNo ratings yet
- 13 PracDocument1 page13 Pracmiss awakeNo ratings yet
- Rectifying CircuitsDocument13 pagesRectifying Circuitssina981No ratings yet
- Rohini 56862343385Document3 pagesRohini 56862343385royrashmi274No ratings yet
- Connection DetailsDocument9 pagesConnection Detailskarthik 'No ratings yet
- Full Wave Bridge RectifierDocument8 pagesFull Wave Bridge RectifierAnonimen AnonimenNo ratings yet
- FULL WAVE RECTIFIERDocument8 pagesFULL WAVE RECTIFIERsakthivel222sanjayNo ratings yet
- Full Wave Bridge RectifierDocument4 pagesFull Wave Bridge RectifierSachit KumarNo ratings yet
- Bridge Rectifier: Bridge Rectifiers Are Circuits That ConvertDocument4 pagesBridge Rectifier: Bridge Rectifiers Are Circuits That ConvertabdulNo ratings yet
- Electronic Circuits Power Supply Electronic Basic Components AC Power Devices Like Home AppliancesDocument21 pagesElectronic Circuits Power Supply Electronic Basic Components AC Power Devices Like Home AppliancesTushar GoelNo ratings yet
- Originalproectphysicsmsword Converted 191225064922Document12 pagesOriginalproectphysicsmsword Converted 191225064922GOKULNo ratings yet
- Exp2Document13 pagesExp2Karim 325No ratings yet
- EPD Lab#9Document8 pagesEPD Lab#9Muhammad ShaheerNo ratings yet
- FULL WAVE RECTIFIER Class NotesDocument2 pagesFULL WAVE RECTIFIER Class NotesRAJASHEKHARNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 (Analogue Electronics I)Document7 pagesLecture 3 (Analogue Electronics I)amash.emillyNo ratings yet
- Assignment MEDocument3 pagesAssignment MESaad AliKhanNo ratings yet
- Physics Project01Document12 pagesPhysics Project01nilu royNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Application CircuitsDocument8 pages1.3 Application Circuitslizhi0007No ratings yet
- Project Report RectifierDocument9 pagesProject Report RectifierMuhammad RashidNo ratings yet
- Bel102-Fundamental of Electrical and Electronics Laboratory Name: Krrish Roll No:12111081Document6 pagesBel102-Fundamental of Electrical and Electronics Laboratory Name: Krrish Roll No:12111081KrrishNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document26 pagesChapter 1nida2505No ratings yet
- EDL Ex No. 2Document2 pagesEDL Ex No. 2Shilpi YadavNo ratings yet
- BESCK104C 204C IEC Module1 NotesDocument24 pagesBESCK104C 204C IEC Module1 Notesblehbo100% (1)
- Bridge Rectifier: Circuit Diagram & Its WorkingDocument12 pagesBridge Rectifier: Circuit Diagram & Its WorkingChandra Sekhar CNo ratings yet
- يجوملا موقملا RectifierDocument18 pagesيجوملا موقملا RectifierYacine KhalidNo ratings yet
- Module 4 (Electronic Fundamentals) B1Document49 pagesModule 4 (Electronic Fundamentals) B1AmirAli MohebbiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Single Phase Full Bridge VSCDocument12 pagesLecture 5 - Single Phase Full Bridge VSCAfsal Abdul KarimNo ratings yet
- Lecture 03 - Diode Applications (Rectification)Document16 pagesLecture 03 - Diode Applications (Rectification)Joseph NgowiNo ratings yet
- Voltagemultiplier AMOSDocument3 pagesVoltagemultiplier AMOSAbhilash OSNo ratings yet
- A Project On Full Wave RectifierDocument10 pagesA Project On Full Wave Rectifiershivansh100% (1)
- Micrwave Effecton Human BodyDocument11 pagesMicrwave Effecton Human BodyRAJASHEKHARNo ratings yet
- New Doc 2017-08-21 - 1Document8 pagesNew Doc 2017-08-21 - 1RAJASHEKHARNo ratings yet
- Beee Unit I-1-8Document8 pagesBeee Unit I-1-8RAJASHEKHARNo ratings yet
- FULL WAVE RECTIFIER Class NotesDocument2 pagesFULL WAVE RECTIFIER Class NotesRAJASHEKHARNo ratings yet
- HALF WAVE RECTIFIER Class NotesDocument2 pagesHALF WAVE RECTIFIER Class NotesRAJASHEKHARNo ratings yet
- Iot Test 2Document2 pagesIot Test 2RAJASHEKHARNo ratings yet
- Unit VDocument46 pagesUnit VRAJASHEKHARNo ratings yet
- Iot Test 1Document7 pagesIot Test 1RAJASHEKHARNo ratings yet
- Unit Iii Micro W A VE Solid State DevicesDocument7 pagesUnit Iii Micro W A VE Solid State DevicesRAJASHEKHARNo ratings yet
- Mwe Unit 3part 3Document24 pagesMwe Unit 3part 3RAJASHEKHARNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Pre PHDDocument16 pagesMathematics Pre PHDRAJASHEKHARNo ratings yet
- Avalanche Breakdown Zener BreakdownDocument2 pagesAvalanche Breakdown Zener BreakdownRAJASHEKHARNo ratings yet