Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electric Circuits
Electric Circuits
Uploaded by
Akil Lyons0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3 pagesElectric Circuits
Electric Circuits
Uploaded by
Akil LyonsCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
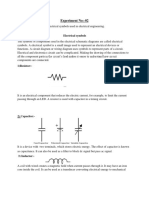
1. An electric circuit is a closed loop through which electric current can flow.
2. The basic components of an electric circuit include a source of electrical
energy (like a battery), conductors (wires), and load (devices such as light
bulbs, motors, etc.).
3. There are two types of electric circuits: series circuits and parallel circuits.
4. In a series circuit, the components are connected end-to-end, forming a
single pathway for current flow.
5. In a parallel circuit, the components are connected across multiple pathways,
allowing current to divide and flow through each path independently.
6. Kirchhoff's laws govern the behavior of electric circuits, including
Kirchhoff's voltage law (KVL) and Kirchhoff's current law (KCL).
7. KVL states that the sum of the voltages around any closed loop in a circuit is
zero.
8. KCL states that the sum of currents entering a junction in a circuit is equal
to the sum of currents leaving that junction.
9. Ohm's law describes the relationship between voltage, current, and
resistance in a circuit, given by V = IR, where V is voltage, I is current, and R
is resistance.
10. Resistance is a measure of how much a material opposes the flow of electric
current.
11. The unit of resistance is the ohm (Ω).
12. Conductors have low resistance, while insulators have high resistance.
13. Resistors are components designed to introduce specific amounts of
resistance into a circuit.
14. Capacitors are components used to store and release electrical energy in a
circuit.
15. Inductors are components that store energy in a magnetic field when
current flows through them.
16. Diodes are components that allow current to flow in one direction only.
17. Transistors are semiconductor devices used for amplification, switching, and
signal modulation.
18. Integrated circuits (ICs) are miniature electronic circuits consisting of many
interconnected components, such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors,
fabricated onto a single chip of semiconductor material.
19. Printed circuit boards (PCBs) are platforms used to mechanically support and
electrically connect electronic components using conductive pathways etched
from copper sheets laminated onto a non-conductive substrate.
20. Switches are components used to open or close circuits, controlling the flow
of current.
21. Relays are electromechanical switches operated by an electric current in one
circuit to control the flow of electricity in another circuit.
22. Fuses and circuit breakers are safety devices designed to protect circuits
from overcurrent conditions that could cause damage or fire.
23. A multimeter is a versatile tool used to measure voltage, current, and
resistance in electric circuits.
24. Oscilloscopes are instruments used to visualize and analyze the waveform of
electrical signals over time.
25. Electric circuits play a fundamental role in electronics, telecommunications,
power distribution, and countless other technological applications.
26. Alternating current (AC) is a type of electrical current that periodically
reverses direction, commonly used in household and industrial power
systems.
27. Direct current (DC) is a type of electrical current that flows consistently in
one direction, commonly used in batteries and electronic devices.
28. Transformers are devices used to change the voltage of an alternating
current, facilitating power transmission and distribution.
29. Superconductors are materials that exhibit zero electrical resistance when
cooled below a critical temperature, enabling extremely efficient electrical
transmission.
30. Electric circuits can be found in everyday objects such as smartphones,
computers, appliances, vehicles, and lighting systems.
31. The study of electric circuits is essential for understanding electronics,
electrical engineering, and related fields.
32. The concept of electric circuits dates back to the late 18th and early 19th
centuries, with the work of scientists like Alessandro Volta, André-Marie
Ampère, and Georg Ohm.
33. The invention of the telegraph in the 19th century spurred advancements in
electric circuit theory and technology.
34. The development of semiconductor devices in the mid-20th century
revolutionized electronics and led to the miniaturization of electronic
components.
35. Modern electric circuits rely heavily on semiconductor technology, enabling
the creation of compact, powerful, and energy-efficient electronic devices.
36. Digital circuits use discrete voltage levels to represent binary information,
forming the basis of digital computers and communication systems.
37. The field of nanoelectronics explores electric circuits and devices on the
nanoscale, promising novel applications and breakthroughs in technology.
38. Electric circuit simulation software allows engineers and hobbyists to design,
analyze, and test circuits virtually before building physical prototypes.
39. Advances in electronic circuit design and technology continue to drive
innovation across various industries, shaping the future of electronics and
electrical engineering.
You might also like
- Bill 06242018Document5 pagesBill 06242018Sukrit Ghorai50% (2)
- Predictive Modeling Business ReportDocument69 pagesPredictive Modeling Business Reportpreeti100% (3)
- Electronics by Sir JoelDocument47 pagesElectronics by Sir JoelDann SarteNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual To Computer Networks, 4th Ed., by Andrew S. TanenbaumDocument3 pagesSolution Manual To Computer Networks, 4th Ed., by Andrew S. Tanenbaumzmtg20150% (11)
- 4 The Formal History of HFE: Page 146Document25 pages4 The Formal History of HFE: Page 146Alex RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Manual Liberty SelectDocument2 pagesManual Liberty SelectMarcos AcioliNo ratings yet
- MontazarmohammedkhalafDocument8 pagesMontazarmohammedkhalafيقين محمد خلفNo ratings yet
- Topic One Introduction To ElectronicsDocument22 pagesTopic One Introduction To ElectronicsBlueprint MihNo ratings yet
- Electronics: Electronics Is The Discipline Dealing With The Development and Application of DevicesDocument3 pagesElectronics: Electronics Is The Discipline Dealing With The Development and Application of DevicesAlbertNo ratings yet
- Principles of Electrical Engineering Lab 2020-21Document68 pagesPrinciples of Electrical Engineering Lab 2020-21riko.mori.toi22No ratings yet
- Electronics - WikipediaDocument5 pagesElectronics - WikipediaAlex ZXNo ratings yet
- Basic ElectronicsDocument10 pagesBasic ElectronicsFrancess Mae AlonzoNo ratings yet
- TransistorsDocument6 pagesTransistorsdeepakvasavaNo ratings yet
- Electronic Materials-G5Document15 pagesElectronic Materials-G5Joana MendoNo ratings yet
- Prepare Electrical Installation and Maintenance TerminologiesDocument7 pagesPrepare Electrical Installation and Maintenance TerminologiesJoevertVillartaBentulanNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electrical EngineeringDocument31 pagesFundamentals of Electrical EngineeringErick BuksonNo ratings yet
- Robotics HW 3-1Document3 pagesRobotics HW 3-1Awesomus BerjaNo ratings yet
- Study of Various Basic Instruments and Components of Electrical EngineeringDocument7 pagesStudy of Various Basic Instruments and Components of Electrical Engineeringnational printersNo ratings yet
- Electro 1 Student FileDocument6 pagesElectro 1 Student FileHarveyBidañaNo ratings yet
- Electronic ComponentDocument1 pageElectronic ComponentJedediah D. MagannonNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Terms and Definitions - E-Green ElectricalDocument5 pagesBasic Electrical Terms and Definitions - E-Green ElectricalJohn Florenz VasquezNo ratings yet
- Tampioc, CM-Utilities Compilation - Sec ADocument45 pagesTampioc, CM-Utilities Compilation - Sec Aneal saladagaNo ratings yet
- EE Ass 1Document3 pagesEE Ass 1Daniela MadelaNo ratings yet
- Circuit NotesDocument1 pageCircuit Notestemp manNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics: Course Instructor: Rida ShifaDocument34 pagesBasic Electronics: Course Instructor: Rida ShifaA S M Younus Bhuiyan SabbirNo ratings yet
- BCM Practical 1 2Document9 pagesBCM Practical 1 2Adi KhardeNo ratings yet
- Key Terms OldDocument4 pagesKey Terms Oldklewis1764No ratings yet
- Science DataDocument1 pageScience DataMaria Hazel Villarosa EndayaNo ratings yet
- Hiostry of Electrical EngineeringDocument41 pagesHiostry of Electrical EngineeringFootkball 1No ratings yet
- MigirubbbbnDocument4 pagesMigirubbbbnehigie300ezekielNo ratings yet
- 14 Basic Electrical ComponentsDocument17 pages14 Basic Electrical ComponentsShimpy MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Electrical Symbols: Splices and JointsDocument6 pagesElectrical Symbols: Splices and JointsBeronica AguilarNo ratings yet
- Light Dependent Resistor-Physics Investigatory Project.Document16 pagesLight Dependent Resistor-Physics Investigatory Project.Saicharan NaiduNo ratings yet
- BASIC ELEX SendDocument28 pagesBASIC ELEX SendALDWIN H. POSTRERONo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics L1Document19 pagesBasic Electronics L1msellereneNo ratings yet
- ElectronicsDocument11 pagesElectronicsyee cNo ratings yet
- Electronics Is A Scientific and Engineering Discipline That Studies and Applies The Principles of Physics To DesignDocument10 pagesElectronics Is A Scientific and Engineering Discipline That Studies and Applies The Principles of Physics To DesignRommel estrelladoNo ratings yet
- Beeie Lecture - NotesDocument210 pagesBeeie Lecture - Notesmuru54321No ratings yet
- Electricity and Electronics BasicsDocument94 pagesElectricity and Electronics BasicsHassan SaidiNo ratings yet
- Tugas 3 Pengukuran ListrikDocument6 pagesTugas 3 Pengukuran ListrikPutraNo ratings yet
- Eeuti130 Lec1Document22 pagesEeuti130 Lec1frankorola0207No ratings yet
- Slides - Topic 2 - Introduction To ElectronicsDocument9 pagesSlides - Topic 2 - Introduction To ElectronicsweretereNo ratings yet
- Technical Language of Electrical EngineeringDocument11 pagesTechnical Language of Electrical EngineeringhadiNo ratings yet
- AIM:-Wireless Power Transmission: Page - 1Document19 pagesAIM:-Wireless Power Transmission: Page - 1prerna ojhaNo ratings yet
- 1 Basic Electronics P1 NotesDocument18 pages1 Basic Electronics P1 NotesEphraem RobinNo ratings yet
- Experiment No:-02: Electrical SymbolsDocument6 pagesExperiment No:-02: Electrical SymbolsAdesh Bhortakke100% (2)
- Electronics: Electronics Comprises The Physics, Engineering, TechnologyDocument10 pagesElectronics: Electronics Comprises The Physics, Engineering, TechnologyirayoNo ratings yet
- Physics Electricity One LinerDocument7 pagesPhysics Electricity One LinerSaranya SNo ratings yet
- CT PeriodicDocument2 pagesCT PeriodicJ.P. SumandoNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Flux: ' Between The Terminals Is A Function of The Amount of Electric Charge Q' That Has PassedDocument27 pagesMagnetic Flux: ' Between The Terminals Is A Function of The Amount of Electric Charge Q' That Has PassedravitejapotuNo ratings yet
- ELECTRICAL INSTALLATION AND MAINTENANCE NC II MODULE New Edited MASTER LEODocument26 pagesELECTRICAL INSTALLATION AND MAINTENANCE NC II MODULE New Edited MASTER LEOOLINSTERG COLLEGENo ratings yet
- Guía 1Document8 pagesGuía 1AlejandroDuranNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument22 pagesPhysics ProjectthaswikaamaraNo ratings yet
- Minor Project Report On Design of A Transmission LineDocument52 pagesMinor Project Report On Design of A Transmission Lineberwalravi88% (8)
- Power Electronics-1st ChapterDocument24 pagesPower Electronics-1st ChapterPasupuleti SivakumarNo ratings yet
- Tif InglesDocument12 pagesTif InglesLord KingNo ratings yet
- Electric Current and CircuitsDocument2 pagesElectric Current and CircuitsshadnawazkhanNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuit Principles Form The Foundation of Modern Electrical Engineering and Are Crucial For Understanding The Behavior of Electrical SystemsDocument1 pageElectrical Circuit Principles Form The Foundation of Modern Electrical Engineering and Are Crucial For Understanding The Behavior of Electrical Systemssuliman bobNo ratings yet
- Electronic Materials and DevicesDocument9 pagesElectronic Materials and DevicesmjjgillbanksNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1-EeeDocument112 pagesUNIT 1-EeeRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics: Semester 7 Electronics Engineering: What Is Power Electronics and Explain Its Block Diagram?Document6 pagesPower Electronics: Semester 7 Electronics Engineering: What Is Power Electronics and Explain Its Block Diagram?Asha DurafeNo ratings yet
- EEC PROJECT FinalDocument21 pagesEEC PROJECT Final221 Siddhant shitoleNo ratings yet
- Series CircuitsDocument3 pagesSeries CircuitsEnglish TeacherNo ratings yet
- Power ElectronicsDocument14 pagesPower Electronicsmichael higginsNo ratings yet
- Deep Vein ThrombosisDocument11 pagesDeep Vein ThrombosisTushar GhuleNo ratings yet
- Lecture Three Actuators ObjectivesDocument5 pagesLecture Three Actuators ObjectivesKenani SaningaNo ratings yet
- Application Binary Interface For The ARM ArchitectureDocument15 pagesApplication Binary Interface For The ARM Architecturejames4registerNo ratings yet
- NHMWriter User ManualDocument7 pagesNHMWriter User Manualvelxerox4123No ratings yet
- Buildings On RailsDocument3 pagesBuildings On RailsZachary RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Municipality of Camalaniugan: Amounting ToDocument3 pagesMunicipality of Camalaniugan: Amounting ToMelody Frac ZapateroNo ratings yet
- Ca360b - Brochure BiotechDocument2 pagesCa360b - Brochure BiotechHawerasNo ratings yet
- Catalogo Baterias Estacionarias HoppeckeDocument2 pagesCatalogo Baterias Estacionarias HoppeckeQuique RuizNo ratings yet
- Checkpoint Science Past Papers 2008Document2 pagesCheckpoint Science Past Papers 2008Zindaba Shoko50% (2)
- WDD Study D-FineDocument12 pagesWDD Study D-FineuiprailNo ratings yet
- Revision Process of MeasurementDocument3 pagesRevision Process of MeasurementAISHAH IWANI BINTI ZULKARNAIN A22DW0732No ratings yet
- 2 - How To Cretae PIRDocument8 pages2 - How To Cretae PIRSambit MohantyNo ratings yet
- Counter AffidavitDocument3 pagesCounter AffidavitArmen MalawaniNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Wal-Mart and Costco in Conte PDFDocument10 pagesAnalysis of Wal-Mart and Costco in Conte PDFShreyash RajNo ratings yet
- Final Paper - Ana Maria PumneaDocument2 pagesFinal Paper - Ana Maria PumneaAnna Pumnea0% (1)
- Occupational Health Hazards Due To Mine Dust: Unit-14Document9 pagesOccupational Health Hazards Due To Mine Dust: Unit-14Dinesh dhakarNo ratings yet
- Design and Simulation of Digital Phase Locked Loop Using MOSFET SPICE Models of 300nmDocument4 pagesDesign and Simulation of Digital Phase Locked Loop Using MOSFET SPICE Models of 300nmIJRT OnlineNo ratings yet
- ChargeTech PLUG Manual - 42K & 54KDocument6 pagesChargeTech PLUG Manual - 42K & 54KKian GonzagaNo ratings yet
- LV059Document136 pagesLV059Boris KoganNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis and Optimization of Active Power and Delay of 1-Bit Full Adder at 45 NM TechnologyDocument3 pagesComparative Analysis and Optimization of Active Power and Delay of 1-Bit Full Adder at 45 NM TechnologyNsrc Nano ScientifcNo ratings yet
- Personnel Management REPORTDocument4 pagesPersonnel Management REPORTAL STAJUANANo ratings yet
- Motor Vehicle InsuranceDocument12 pagesMotor Vehicle InsuranceDhruv SiddarthNo ratings yet
- Mastery 3 (MIL)Document2 pagesMastery 3 (MIL)Jude Mandal MetanteNo ratings yet
- DILG Resources 2013108 9774ac16f4 PDFDocument2 pagesDILG Resources 2013108 9774ac16f4 PDFJhacie OronganNo ratings yet
- What Lies Ahead?: Learning EpisodeDocument8 pagesWhat Lies Ahead?: Learning EpisodeMarvin GeneblazoNo ratings yet