Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Envisci PT2
Envisci PT2
Uploaded by
jairahmillanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Envisci PT2
Envisci PT2
Uploaded by
jairahmillanCopyright:
Available Formats
NAME:___________________________________ SECTION:______________
PERFORMANCE TASK 2
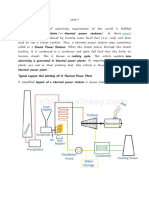
Directions: Read the text and label the diagram of the electricity generation
process below. Write NO MORE THAN TWO WORDS from the passage for each answer. Use
a separate sheet of paper.
How do coal-fired power plants work?
Modern life is unimaginable without electricity, and coal plays a vital role in
electricity generation worldwide. Coal-fired power plants currently fuel 41% of global
electricity and, in some countries, coal fuels a higher percentage of electricity. But how
is coal converted to electricity?
Steam coal, also known as thermal coal, is used in power stations to generate
electricity. After the coal supply is extracted from the carrier, coal is milled to a fine
powder, which increases the surface area and allows it to burn more quickly. In such
pulverized coal combustion systems, the powdered coal is transported from the coal supply
station into a boiler by a conveyor belt. In the boiler, the coal is burnt at high
temperatures. The hot gases arise from the burning coal and the produced heat energy converts
water - in tubes lining the boiler - into steam. Meanwhile, the gases released during the
burning process exit the coal combustion system by a stack - a long tube attached to the
boiler.
Next, the high-pressure steam is passed by the steam line into a turbine. The turbine
contains thousands of propeller-like blades, which are pushed by steam. This causes the
turbine shaft to rotate at high speed. A generator is mounted at one end of the turbine
shaft and consists of carefully wound wire coils. Electricity is generated when these are
rapidly rotated in a strong magnetic field. After passing through the turbine, the steam is
condensed in a special room under the turbine called a condenser. The condenser is connected
to a reservoir of cooling water so that the condensed steam cools quickly and returns to
the boiler to be heated once again.
The electricity is transported from the generator by connector cables to a switchyard,
where it is transformed into the higher voltages (up to 400,000 volts) used for economic,
efficient transmission via power line grids. When it nears the point of consumption, such
as our homes, the electricity is transformed down to the safer 100-250 voltage systems used
in the domestic market.
You might also like
- Lakvijaya Field VisitDocument5 pagesLakvijaya Field VisitIsuru Kodikara100% (2)
- Summer Training Report On NTPC Tanda, Ambedkar NagarDocument9 pagesSummer Training Report On NTPC Tanda, Ambedkar NagarAliraza7660% (5)
- Report Chhabra Thermal Power PlantDocument40 pagesReport Chhabra Thermal Power PlantMangilal LovevanshiNo ratings yet
- PPTDocument29 pagesPPTAnaytullah AnsariNo ratings yet
- Coal To ElectricityDocument5 pagesCoal To ElectricityPravin KumarNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power PlantsDocument24 pagesThermal Power Plantslakshmigsr6610100% (1)
- Power Plant Layout and Essential Feature of RankineDocument7 pagesPower Plant Layout and Essential Feature of RankineMonglafru MogNo ratings yet
- Power Generation ProcessDocument8 pagesPower Generation ProcessIndra PanchalNo ratings yet
- Power Plant Layout and Essential Feature of RankineDocument7 pagesPower Plant Layout and Essential Feature of RankineMonglafru MogNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power PlantDocument35 pagesThermal Power PlantAngelaa DassNo ratings yet
- Power Plant Training ReportDocument26 pagesPower Plant Training ReportAnil YadavNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Internship ReportDocument5 pagesChapter 1 - Internship ReportperminderlbwNo ratings yet
- Distributed Digital Control and Monitoring and Information System" by Designing andDocument29 pagesDistributed Digital Control and Monitoring and Information System" by Designing andjhonnyjungleNo ratings yet
- Summer Training in Badarpur NTPCDocument54 pagesSummer Training in Badarpur NTPCRohit VermaNo ratings yet
- Power PlantsDocument6 pagesPower PlantsyogusmiluNo ratings yet
- Thermal Plant Ropar 1260MWDocument89 pagesThermal Plant Ropar 1260MWRahul Pandey71% (7)
- EPG Micro ProjectDocument11 pagesEPG Micro ProjectTushar MoreNo ratings yet
- NTPCDocument33 pagesNTPCSubodh DuhanNo ratings yet
- Industrial Training Report ON C & I Maintenance Division Unit-8 AT Panipat Thermal Power StationDocument27 pagesIndustrial Training Report ON C & I Maintenance Division Unit-8 AT Panipat Thermal Power StationAbhishek AroraNo ratings yet
- SIREreport 118ee0297Document13 pagesSIREreport 118ee0297Bhabani sankar KishanNo ratings yet
- Cstps Modofied-131230103858Document66 pagesCstps Modofied-131230103858Santoshkumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Ppe NotesDocument51 pagesPpe NotesCharan PrasadNo ratings yet
- Coal Fired Thermal Power Plant What Is A Thermal Power Plant?Document6 pagesCoal Fired Thermal Power Plant What Is A Thermal Power Plant?carlo manabatNo ratings yet
- Types of Power Plant and Their Working PrinciplesDocument11 pagesTypes of Power Plant and Their Working PrinciplesRamzi JamalNo ratings yet
- Amulya Gaikwada ProjectDocument34 pagesAmulya Gaikwada ProjectHarikrishna NethaNo ratings yet
- Power Plants Part-1Document9 pagesPower Plants Part-1Mukesh ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Steam Power PlantDocument20 pagesSteam Power PlantSiddi Sampath Kumar Reddy100% (1)
- General Layout of A Thermal Power PlantDocument87 pagesGeneral Layout of A Thermal Power PlantHarjith Vaibav100% (1)
- Water HarvestingDocument44 pagesWater HarvestingTanmay KhuranaNo ratings yet
- TRNG Proj Rep.Document39 pagesTRNG Proj Rep.sahapinkNo ratings yet
- National Capital Power Station N.T.P.C: Presented by KshitijDocument25 pagesNational Capital Power Station N.T.P.C: Presented by KshitijHarshit MittalNo ratings yet
- Industrial Training PresentationDocument25 pagesIndustrial Training PresentationHarshit MittalNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power Plant - EeDocument20 pagesThermal Power Plant - EePrabhat Chandra100% (1)
- DVC Mejhia Thermal Power Station ReportDocument52 pagesDVC Mejhia Thermal Power Station ReportRahul RoyNo ratings yet
- Power Plant Engineering MTPP-1Document13 pagesPower Plant Engineering MTPP-1devendra pratapNo ratings yet
- Harduaganj Thermal Power Plant by Geetesh SharmaDocument66 pagesHarduaganj Thermal Power Plant by Geetesh Sharmageeteshaccurate100% (1)
- A Report On PHDocument21 pagesA Report On PHకార్తీక్ ఆచార్య మేడిపెల్లిNo ratings yet
- Power Plant EngineeringDocument25 pagesPower Plant EngineeringlitonNo ratings yet
- "Thermal Power Generation": Seminar Report OnDocument10 pages"Thermal Power Generation": Seminar Report OnAram Nasih MuhammadNo ratings yet
- 250MW Thermal Power PlantDocument70 pages250MW Thermal Power Plantdileepjana100% (2)
- Me Lab 3Document27 pagesMe Lab 3Jerome Vega AndesNo ratings yet
- UNIT - 3 BCME FinalDocument26 pagesUNIT - 3 BCME FinalAnith Kumar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Brief Description of Tanda Thermal Project: 1.1 Geographical LocationDocument22 pagesBrief Description of Tanda Thermal Project: 1.1 Geographical Locationcoolvipin1988No ratings yet
- Project ReportDocument103 pagesProject ReportSeth CamachoNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power Plant Layout and OperationDocument8 pagesThermal Power Plant Layout and OperationRAJENDRA TELVEKARNo ratings yet
- DVC Mejia ReportDocument37 pagesDVC Mejia ReportRahul RoyNo ratings yet
- Physics 4.Document5 pagesPhysics 4.SOLAIMANNo ratings yet
- Abhishek Kumar Asif Ahmad Niket Rakeshan Zeeshan AliDocument21 pagesAbhishek Kumar Asif Ahmad Niket Rakeshan Zeeshan AliSuphi YükselNo ratings yet
- Table of Content: Page Number 1 3 2 Parts 6 3 Function Diagram 8 4 Function 9 5 Advantages 18 6 Disadvantages 20Document20 pagesTable of Content: Page Number 1 3 2 Parts 6 3 Function Diagram 8 4 Function 9 5 Advantages 18 6 Disadvantages 20Utsav ShuklaNo ratings yet
- PP 9th Meeting GENERATING STATIONS Thermal Power PlantDocument5 pagesPP 9th Meeting GENERATING STATIONS Thermal Power PlantJohn Kenneth LoricoNo ratings yet
- Avanthi Institute of Engineering & TechnologyDocument20 pagesAvanthi Institute of Engineering & TechnologyBharath AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Sushil LambaDocument32 pagesSushil LambaSushil LambaNo ratings yet
- Power Plant FamiliarisationDocument110 pagesPower Plant FamiliarisationmrdipakwaghNo ratings yet
- Layout of Thermal Power PlantDocument21 pagesLayout of Thermal Power PlantRaj_Jai03100% (1)
- General Layout of The Plant: Power PlantsDocument15 pagesGeneral Layout of The Plant: Power Plantsamitandy134No ratings yet
- Power System by PawanDocument20 pagesPower System by PawanPäwän Kümär MäüryäNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Thermal Power PlantDocument27 pagesIntroduction and Thermal Power PlantKshitij AggarwalNo ratings yet
- The Shocking World of Electricity with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Shocking World of Electricity with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- How it Works: Dealing in simple language with steam, electricity, light, heat, sound, hydraulics, optics, etc., and with their applications to apparatus in common useFrom EverandHow it Works: Dealing in simple language with steam, electricity, light, heat, sound, hydraulics, optics, etc., and with their applications to apparatus in common useNo ratings yet