Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ICU One Pager Acid Base v11
ICU One Pager Acid Base v11
Uploaded by
PEDRO RODRIGUEZ0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageICU
Original Title
ICU_one_pager_acid_base_v11
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentICU
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageICU One Pager Acid Base v11
ICU One Pager Acid Base v11
Uploaded by
PEDRO RODRIGUEZICU
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
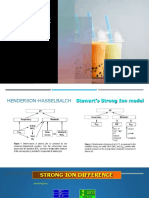
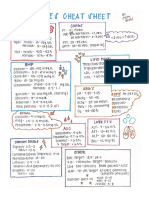
ACID BASE ANALYSIS by Nick Mark MD ONE onepagericu.
com Link to the
most current
@nickmmark version →
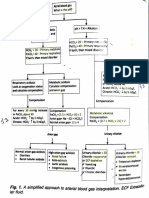
What’s the
primary >7.4
disturbance? alkalemia Airflow obstruction
1. pH • COPD, asthma
Acute or chronic? "Drive
acidemia • Medications
<7.4
What is the chronicity? • Central
What’s the respiratory Look at metabolic compensation !CO2 production
pCO2? ! acidosis Acute: 10 Δ pCO2 # 0.08 Δ pH
! drive
Chronic: 10 Δ pCO2 # 0.03 Δ pH
2. pCO2 • Hypoxemia
" • Pain/anxiety
respiratory • Hepatic enceph
• Pregnancy
alkalosis • Salicylates
“BLVD PLACE”
B - Bartter's
L – Laxative
metabolic V – Vomitting
alkalosis D - Diarrhea/diuretics
P - Post-hypercapnea
! Is the anion gap increased? L - Licorice
What’s the AG = [Na] + ([Cl] + [HCO3]) A - Alkali ingestion
bicarb? Expected AG = 2.5 x Albumin C - Contraction alkalosis
E - Endocrine
3. HCO3- If AG > expected AG, there is an
(Conn’s or Cushing’s)
anion gap present
" non anion gap “RAGES”
R – RTA
metabolic acidosis A – Ammonia
metabolic Acetazolamide
Is there HyperAlimentation
acidosis
compensation? G – GI losses
If there is a metabolic acidosis or alkalosis present E – Endocrine
is there appropriate respiratory compensation? S – Saline
Use one of two rules of find out: “GOLDMARKeT”
1. Expected pCO2 = 1.5 x [HCO3] + 8 ± 2 (Winter’s) anion gap G – Glycols
2. Expected pCO2 = last two digits of pH metabolic acidosis O – Oxoproline
If the measured pCO2 does not match the expected L – Lactic acid
value, there is also a respiratory derangement. D – Lactic acid
M – Methanol
A – Aspirin
Does the change in AG account for the change in HCO3?
R – Renal fail, Rhabdo
Used to determine if there is another derangement. Ke – Ketones
superimposed
T – Toluene
Does ΔHCO3 ≈ ΔAG? !ΔΔ >1.5 metabolic alkalosis
4. ΔAG NO
ΔHCO3
v1.1 (10/2020)
YES "ΔΔ < 0.8 superimposed Salicylate poisoning
NAGMA DKA w/ dehydration
No other derangement
You might also like
- Accu-Measure Body Fat Chart PDFDocument1 pageAccu-Measure Body Fat Chart PDFSinisa HristovNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base WorksheetDocument2 pagesAcid-Base WorksheetMayer Rosenberg100% (18)
- Case Study GerdDocument3 pagesCase Study Gerdapi-287249002No ratings yet
- PH Alkalemia Acidemia Respiratory Acidosis Respiratory AlkalosisDocument1 pagePH Alkalemia Acidemia Respiratory Acidosis Respiratory AlkalosisJuan R Hernandez LozanoNo ratings yet
- ABG InterpretationDocument64 pagesABG InterpretationSiva RamanNo ratings yet
- IM Lecture Acid Base ImbalanceDocument8 pagesIM Lecture Acid Base ImbalanceCHYNNA ALBERTNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pathology: BLUE - Henry'sDocument13 pagesClinical Pathology: BLUE - Henry'sStoloNo ratings yet
- ABG Analysis and Acid Base BalanceDocument16 pagesABG Analysis and Acid Base BalancePrashin RocharamNo ratings yet
- Manajemen Asidosis MetabolikDocument22 pagesManajemen Asidosis MetabolikriyanhstNo ratings yet
- I STAT Alinity V Utilization Guide ABX 00075R1Document8 pagesI STAT Alinity V Utilization Guide ABX 00075R1DrAlaa Zidan100% (1)
- Metabolic Acidosis - Alkalosis Study GuideDocument1 pageMetabolic Acidosis - Alkalosis Study GuideJe KirsteneNo ratings yet
- Blood Gas InterpretationDocument28 pagesBlood Gas InterpretationgjdbfiuvaNo ratings yet
- Basics of Venous Blood Analysis - SLIDESDocument23 pagesBasics of Venous Blood Analysis - SLIDESJenn TNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-10-07 at 7.28.18 PMDocument45 pagesScreenshot 2022-10-07 at 7.28.18 PMMohammed Bin EisaNo ratings yet
- Acid Base DisordersDocument33 pagesAcid Base DisordersShre RanjithamNo ratings yet
- Monitoring+Acid+Base+Fluids+Blood ManagementDocument53 pagesMonitoring+Acid+Base+Fluids+Blood ManagementNikita ShokurNo ratings yet
- i-STAT Alinity V: Utilization GuideDocument8 pagesi-STAT Alinity V: Utilization GuideTony ChenNo ratings yet
- ABG AnalysisDocument1 pageABG AnalysisGulrejNo ratings yet
- ABGs InterpretationDocument33 pagesABGs InterpretationHamza DossaNo ratings yet
- Acid - Base DisturbancesDocument3 pagesAcid - Base DisturbancesMarie Antionette MondragonNo ratings yet
- NCM112 Acid Base DisordersDocument7 pagesNCM112 Acid Base DisordersRalph Elvin MacanlalayNo ratings yet
- Acid Base 1Document20 pagesAcid Base 1Ragul VNo ratings yet
- Analisa Gas Darah - Strong Medicine, IMELS 2021Document5 pagesAnalisa Gas Darah - Strong Medicine, IMELS 2021rifqi hidayatNo ratings yet
- 13 Anion Gap Metabolic AcidosisDocument42 pages13 Anion Gap Metabolic AcidosisJoel Topf100% (3)
- Caveats: Acid Base Disorder Paco2 PH Primary Change Compensatory Change EtiologyDocument6 pagesCaveats: Acid Base Disorder Paco2 PH Primary Change Compensatory Change EtiologyPau SorianoNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Balance: By: Husnil KadriDocument47 pagesAcid-Base Balance: By: Husnil KadriIbnu Firdiansyah ZayyadNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Disorders: Blood PH Acidoses Alkaloses Arterial Blood Gas ABG Metabolic Acidosis Anion GapDocument5 pagesAcid-Base Disorders: Blood PH Acidoses Alkaloses Arterial Blood Gas ABG Metabolic Acidosis Anion GapMaryam RazaNo ratings yet
- Acid Base DisordersDocument66 pagesAcid Base DisordersIvan HensonNo ratings yet
- (Part 3) Acid-Base Balance-1Document7 pages(Part 3) Acid-Base Balance-1lapyem thomasNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Disturbances StudentsDocument44 pagesAcid Base Disturbances StudentsHelene AlawamiNo ratings yet
- ABG Value Urine Electrolytes: HagmaDocument2 pagesABG Value Urine Electrolytes: HagmaPrakash GudsoorkarNo ratings yet
- AcidbaseDocument3 pagesAcidbasepierhot_11No ratings yet
- Insuf Respiratorie 1Document32 pagesInsuf Respiratorie 1Pop AlexNo ratings yet
- K (Anion Gap 12) (Anion Gap 12) Acute Asthma Hypovolemia: - Vomit - Pyloric StenosisDocument4 pagesK (Anion Gap 12) (Anion Gap 12) Acute Asthma Hypovolemia: - Vomit - Pyloric StenosisAhmad Asyraf AzmanNo ratings yet
- La GasometriaDocument17 pagesLa GasometriaMartin GuerraNo ratings yet
- ABG AnalysisDocument26 pagesABG Analysisf5psw2zk6fNo ratings yet
- Funds and Med SurgDocument60 pagesFunds and Med Surgjbaby2993No ratings yet
- Analisis Gas Darah Dan Pem Lab Neonatus PDFDocument64 pagesAnalisis Gas Darah Dan Pem Lab Neonatus PDFvina zulfianiNo ratings yet
- AB ImbalanceDocument32 pagesAB ImbalancePop AlexNo ratings yet
- Acid Base BalanceDocument44 pagesAcid Base BalanceKenny JapNo ratings yet
- Zuku Visual Flashnotes Blood Gas EvalDocument10 pagesZuku Visual Flashnotes Blood Gas EvalvetthamilNo ratings yet
- © Dept. of Medical and Clinical Biochemistry Upjš in Košice, Medical Faculty Eva Ďurovcová, MD, PHDDocument51 pages© Dept. of Medical and Clinical Biochemistry Upjš in Košice, Medical Faculty Eva Ďurovcová, MD, PHDPaulina PaskeviciuteNo ratings yet
- ABG Pocket CardDocument1 pageABG Pocket CardNaheedNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Balance 2 02 AprilDocument62 pagesAcid Base Balance 2 02 AprilSofíaGriggsNo ratings yet
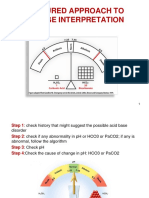
- Structured Approach To Acid Base InterpretationDocument14 pagesStructured Approach To Acid Base InterpretationAnna MNo ratings yet
- Pemeriksaan Laboratorium Pada Gangguan Asam BasaDocument62 pagesPemeriksaan Laboratorium Pada Gangguan Asam BasaOkta Besti ArdikaNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Imbalance (Rubina)Document98 pagesAcid Base Imbalance (Rubina)Parvathy R Nair100% (1)
- Interpretation of ABGsDocument9 pagesInterpretation of ABGsKarl RobleNo ratings yet
- 2016 Acid Base DisordersDocument48 pages2016 Acid Base DisordersbellabelbonNo ratings yet
- Acid Base HerdDocument5 pagesAcid Base Herdramzi MohamedNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry II ELECTROLYTESDocument2 pagesClinical Chemistry II ELECTROLYTESEden MaeNo ratings yet
- Arterial Blood Gas Interpretation: Joseph Brian L. Costiniano, MD, DPCPDocument39 pagesArterial Blood Gas Interpretation: Joseph Brian L. Costiniano, MD, DPCPGio Tamaño BalisiNo ratings yet
- Arterial Blood Gas Interpretation: Joseph Brian L. Costiniano, MD, DPCPDocument39 pagesArterial Blood Gas Interpretation: Joseph Brian L. Costiniano, MD, DPCPevbptrprnrmNo ratings yet
- ABG InterpretationDocument14 pagesABG InterpretationMerganey TebenNo ratings yet
- Med Surg BundleDocument47 pagesMed Surg Bundleezinne obinna-umaNo ratings yet
- 01 - Acid-Base DisturbancesDocument22 pages01 - Acid-Base DisturbancesAyman SaberNo ratings yet
- Cchm2 MidtermsDocument22 pagesCchm2 MidtermsMACOB, ETHELHYN JHANE100% (1)
- Pediatric Emergency ManualDocument272 pagesPediatric Emergency Manualapi-3840428100% (1)
- Insulin Resistance and PrediabetesDocument8 pagesInsulin Resistance and Prediabetesant beeNo ratings yet
- Weight ManagementDocument36 pagesWeight ManagementAbdur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Chloe Ting 2021 2 Weeks Shred ChallengeDocument1 pageChloe Ting 2021 2 Weeks Shred ChallengeTuleen AlkurdiNo ratings yet
- Baseline and Endline ReportDocument7 pagesBaseline and Endline ReportJohn Paul DioneoNo ratings yet
- Physical Activity For HealthDocument7 pagesPhysical Activity For Healthshd9617No ratings yet
- Jurnal PKMDocument12 pagesJurnal PKMfidyaangraeni 61No ratings yet
- Nutrition Lifestyle and Weight ManagementDocument21 pagesNutrition Lifestyle and Weight ManagementKaye Regine Santos100% (1)
- LP 4 - Metabolismul LipidicDocument26 pagesLP 4 - Metabolismul LipidicDaniel LovinNo ratings yet
- Pena Medika: ISSN: 2086-843XDocument19 pagesPena Medika: ISSN: 2086-843XNurul FitriaNo ratings yet
- ArticleDocument9 pagesArticlernvisNo ratings yet
- ApoB 2Document7 pagesApoB 2Alex AlexNo ratings yet
- M4 BIO111 Assignment1Document5 pagesM4 BIO111 Assignment1Kyle DunnNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 Design Personal Training ProgramDocument3 pagesAssignment 3 Design Personal Training ProgramEjhay TenderoNo ratings yet
- Visitacion Act 1 Tdee Stats ReportDocument3 pagesVisitacion Act 1 Tdee Stats ReportHannah VisitacionNo ratings yet
- Faktor Risiko Kejadian Arthritis Gout Pada Pasien Rawat Jalan Di Rumah Sakit Dr. Wahidin Sudirohusodo, MakassarDocument8 pagesFaktor Risiko Kejadian Arthritis Gout Pada Pasien Rawat Jalan Di Rumah Sakit Dr. Wahidin Sudirohusodo, MakassarEster DewNo ratings yet
- 26-36 Pelaksanaan Skrining Kesehatan Sebagai Upaya MencegahDocument10 pages26-36 Pelaksanaan Skrining Kesehatan Sebagai Upaya MencegahMarkus LeonardoNo ratings yet
- 1 PBDocument9 pages1 PBAndre BinsarNo ratings yet
- Aterogeneza ModificatDocument49 pagesAterogeneza ModificatAndreea ŞtefănescuNo ratings yet
- List Pasien USG TerbaruDocument4 pagesList Pasien USG Terbaruzayed norwantoNo ratings yet
- Exercise 5 6 Energy BalanceDocument2 pagesExercise 5 6 Energy BalanceArcee Feb Dela PazNo ratings yet
- Nutrition A Functional Approach Canadian 3rd Edition Thompson Solutions ManualDocument12 pagesNutrition A Functional Approach Canadian 3rd Edition Thompson Solutions Manualhangnhanb7cvf100% (31)
- Lab Report: National Aluminium Company LimitedDocument3 pagesLab Report: National Aluminium Company LimitedSanjay GuptaNo ratings yet
- Special Populations PDFDocument4 pagesSpecial Populations PDFLouis TrầnNo ratings yet
- Philippine National Police Regional Health Service Ncrpo Physical Examination Guide For Annual Physical Examination (APE)Document2 pagesPhilippine National Police Regional Health Service Ncrpo Physical Examination Guide For Annual Physical Examination (APE)james antonioNo ratings yet
- Childhood ObesityDocument13 pagesChildhood Obesityapi-315466994100% (1)
- Medical Nutrition Therapy For DiabetesDocument27 pagesMedical Nutrition Therapy For Diabetesdr.Uci BaharNo ratings yet
- 21-4019 R210463 Add05-22 2023-09Document2 pages21-4019 R210463 Add05-22 2023-09Mima HamiciNo ratings yet
- JURNAL KELOMPOK 3 ABSTRAK SalinanDocument17 pagesJURNAL KELOMPOK 3 ABSTRAK SalinanVikaNo ratings yet