Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Input 1 To 5
Input 1 To 5
Uploaded by
Starskie Monacar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views57 pagesOriginal Title
INPUT-1-TO-5 (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views57 pagesInput 1 To 5
Input 1 To 5
Uploaded by
Starskie MonacarCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 57
Electromagnetic radiation is a special
kind of energy that travels in waves
through space. It is like a wave of
energy that can move without
needing anything else to carry it,
even in empty space.
1. WAVE – a disturbance that travels through space and matter
transferring energy from one place to another.
2. ELECTRICITY - a form of energy resulting from the existence
of charged particles (such as electrons or protons), either
statically as an accumulation of charge or dynamically as a
current.
3. MAGNETISM- a physical phenomenon produced by the
motion of electric charges, resulting in attractive and repulsive
forces between objects.
4.ELECTROMAGNETISM- the combination of alternating electric
and magnetic fields created by accelerated charges that propagate
out from these charges at the speed of light in the form of waves.
5. ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES - are waves created as a result of
vibrations between an electric field and a magnetic field.
6. ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION- the flow of energy at the
universal speed of light through free space or through a material
medium in the form of the electric and magnetic fields that make
up electromagnetic waves.
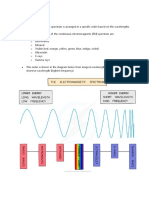
7.ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM- The electromagnetic spectrum
covers electromagnetic waves with frequencies ranging from
below one hertz to above 10 hertz, corresponding to wavelengths
from thousands of kilometers down to a fraction of the size of an
atomic nucleus.
input 2:
development of e.m. theory
input 3:
properties of electromagnetic waves
1. EM waves are all transverse wave that propagates outward from
a source perpendicular to the direction of the wave’s travel.
2. The creation of all EM waves begins with an oscillating charged
particle, which creates oscillating electric field and magnetic
fields.
3. EM waves differ from mechanical waves in that they do not
require a medium to propagate. This means that electromagnetic
waves can travel not only through the air and the solid materials,
but also through the vacuum, a space without matter or air, at the
same, constant speed that is the speed of light (c)
4. EM waves possess different velocity of propagation in different
medium. When travelling between media, the wavelength changes
and therefore the speed of EM wave also changes. Also this change
is different for different frequencies.
5. The electromagnetic spectrum is a sequence of all EM waves
arranged according to frequency and wavelength.
1.39𝑥1027 Hz
1.4𝑥1027 Hz
3.315𝑥10 −7 Hz
Radio waves Microwaves Infrared Visible Light
Visible Light Ultraviolet X-Radiation Gamma Ray
These are the waves that allow us to
listen to the radio. They have long
wavelengths and low frequencies.
Radio waves are used for
broadcasting music, news, and other
information.
Microwaves have shorter wavelengths
and higher frequencies than radio
waves. They are used in microwave
ovens to cook and heat food. They are
also used for communication, such as
cell phones and Wi-Fi.
Infrared radiation is sometimes called
"heat radiation" because we feel it as
warmth. It has longer wavelengths
than visible light. Infrared radiation is
used in devices like TV remote
controls and thermal cameras.
This is the type of electromagnetic
radiation that allows us to see the
world around us. Visible light comes in
different colors, like red, orange,
yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet.
Each color has a different wavelength.
UV radiation has shorter wavelengths
and higher frequencies than visible
light. It comes from the sun and is
responsible for causing sunburns. We
can't see UV radiation, but it can be
harmful to our skin and eyes.
X-rays have even shorter wavelengths
and higher frequencies than UV
radiation. They can pass through our
bodies and are used in medical
imaging, like X-ray machines, to see
our bones and organs.
Gamma rays have the shortest
wavelengths and highest frequencies
of all the radiations. They are
produced during nuclear reactions
and can be very harmful. Scientists
use gamma rays to treat cancer.
Radio waves Microwaves Infrared Visible Light
Electromagnetic waves are all around us! When you watch your favorite
TV shows, listen to the radio, when you use your gadgets such as
cellphone, even when you just go outside for your morning jogging, you
are exposed to electromagnetic waves. One way or another, our lives
depend on the use of electromagnetic waves and therefore it is important
to note which E.M. wave radiation is beneficial, and which might pose
potential hazards to us. E.M. wave radiation possesses energy that is
dependent on the frequency of the wave.
This means that E.M. waves with high frequency (short wavelength)
have great amounts of energy. This is summarized in the equation: E = hf
Where E is the energy of the wave, 𝑓 is the frequency of the wave and ℎ is
the Planck’s constant. We will not focus on the details of this equation,
but it is important to note that E.M. waves with high energy could have
both benefits and hazards for living organisms, especially to human
beings.
E.M. wave radiation can be classified as Ionizing Radiation and Non – Ionizing Radiation.
Non-ionizing E.M. wave Radiation includes Radio wave, Microwave, Infrared and visible light.
These E.M. waves are of low energy level and are not known to cause harmful effects to
living organisms. The E.M. wave radiation from Microwave ovens, global positioning systems
(GPS), Cellphones, TV stations, FM and AM radio, Computers and other gadgets are all
examples of non-ionizing radiation. Low-frequency Ultraviolet radiation can still be
considered as non-ionizing radiation but at certain amounts, could pose hazards to our
health such as causing sunburns and even skin cancer. It is therefore important to practice
caution every time that we are exposed to sunlight that contains Ultraviolet radiation. When
exercising or jogging, it is advisable to do it early in the morning to avoid being exposed to
too much UV rays which can cause harm to our skin. It is also not advisable to directly look at
the sun because too much exposure of the eyes to UV rays can cause cataracts and
permanent blindness.
Ionizing E.M. wave radiation on the other hand includes high frequency UV radiation, X-Ray,
and Gamma Ray. Ionization is process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or
positive charge by gaining or losing electrons, often in conjunction with other chemical changes.
Ionization radiation causes changes in the structure of atoms and molecules by ionization, so
that’s why ionizing radiation can cause damage to living atoms/molecules and have the
tendency to cause changes in the structure of DNA in the living organism. This is the reason why
over exposure to these kinds of E.M. radiation is very harmful for living organisms. Ionizing E.M
Radiation can have benefits in the field of medical imaging and therapy. X-rays which are used
to diagnose problems in our body such as bones and the lungs. Gamma rays are used in
radiation therapy for the treatment of cancer. Whether it is Non-ionizing or ionizing radiation, it
is essential to minimize too much exposure especially from sources of high energy E.M.
Radiation. Though not as harmful as ionizing E.M. wave radiation, Non-ionizing E.M. wave
radiation can still cause heating of surfaces being exposed (remember that microwave is used to
cook food). For you to understand how to protect yourself from E.M. Wave radiation,
accomplish the following activities.
Three factors to consider in minimizing E.M. wave radiation exposure.
1. Distance -As the distance from the source of radiation increases, the risk of exposure
becomes less. This is the reason why it is very important to keep distance from potential sources of
high energy sources of E.M. radiation. People who work very close to a source of radiation are said
to be more prone to the hazards brought about by the high ionizing power of ionizing radiation.
2. Time- As the time of exposure increases, the risk of getting harmful effects also increases.
Being exposed to sources of E.M. Radiation for prolonged periods of time could produce harm to
the human body. This is the reason why even being exposed to low energy radiation such as
radiation from TV could sometimes produce negative effects to human health.
3. Shielding Radiation can be absorbed by materials placed between the source of the radiation
and the user. The type of shielding that is the most appropriate to use depends on the nature of
the penetrating power of the radiation. Materials such as aluminum and lead are better in
shielding against radiation. This is the reason why it is less likely that EM waves from the remote
and cellphone would be transmitted if it is shielded with layers of aluminum foil.
Numerous scientific researches have been conducted to determine the potential benefits
and hazards of E.M. Wave radiation. The table below summarizes these benefits and hazards
from being exposed to E.M. Waves. Write your answers in a separate answer sheet
Justification in radiation exposure means that the benefits gained should outweigh the
potential harm caused by the radiation. If there's no benefit, the exposure is not justified.
Dose limitation involves restricting normal exposure to ensure it doesn't surpass established
limits, except in special cases. Optimization of protection aims to keep exposure as low as
reasonably achievable (ALARA) by minimizing risks, balancing the cost of reducing risks
further against the benefits gained.
Understanding the benefits and risks helps decide how to handle materials emitting
electromagnetic wave radiation. Radiation effects are measured in units like roentgen (R) for
exposure, gray (Gy) for absorbed dose, and sievert (Sv) or rem for effective dose. The annual
acceptable limit for radiation on average should not exceed 5 rems, considering adjustments
for radiation type and its impact on organs.
You might also like
- Electromagnetic Waves ProjectDocument13 pagesElectromagnetic Waves ProjectDiya Kumar81% (58)
- Sci 10 PPT - em WavesDocument27 pagesSci 10 PPT - em WavesDioscora S. GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument25 pagesElectromagnetic Wavesputri_latifah100% (3)
- 06 237046 001 - BDDocument1 page06 237046 001 - BDcarlos yepezNo ratings yet
- Presentation Fabrication of Storage TankDocument43 pagesPresentation Fabrication of Storage TankAbdul Manaf100% (1)
- EM WavesDocument11 pagesEM WavesHomok Noki100% (1)
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument23 pagesElectromagnetic WavesNjike ChigbuNo ratings yet
- Effect of Electromagnetic Radiation On Human BeingsDocument26 pagesEffect of Electromagnetic Radiation On Human Beingsdrmarwayaseen85No ratings yet
- Welcome To My Presentation: Submitted By: Submitted ToDocument14 pagesWelcome To My Presentation: Submitted By: Submitted ToHasibul HossainNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument16 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumTanish100% (1)
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument10 pagesElectromagnetic WavesririkgopeNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument15 pages3.3 Electromagnetic SpectrumMadiha AhmedNo ratings yet
- Module 8 PhysicsDocument7 pagesModule 8 PhysicsLopez AeraNo ratings yet
- 2023-11-10 11 - 13 - 50.563 - 1Document2 pages2023-11-10 11 - 13 - 50.563 - 1pranitjadhav0407No ratings yet
- What Are Electromagnetic Waves?Document8 pagesWhat Are Electromagnetic Waves?Jay Marie OcampoNo ratings yet
- EM SpectrumDocument6 pagesEM SpectrumKaren100% (1)
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument11 pagesElectromagnetic WavesSherazNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjektDocument12 pagesPhysics Projektrupendrajain20No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic PDFDocument13 pagesElectromagnetic PDFkanishksajankar735No ratings yet
- The Electromagnetic WavesDocument45 pagesThe Electromagnetic WavesCeejay BaliwagNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument13 pages3.3 Electromagnetic SpectrumMadiha AhmedNo ratings yet
- Peoplesafe Electromagnetic Radiation TutorialDocument48 pagesPeoplesafe Electromagnetic Radiation TutorialGeoffrey AlleyneNo ratings yet
- The Effects of EM Radiations On Living Things and EnvironmentDocument30 pagesThe Effects of EM Radiations On Living Things and EnvironmentJhunner Buan100% (1)
- Electromagnetic RadiationDocument5 pagesElectromagnetic RadiationAyman BashirNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic RadiationDocument10 pagesElectromagnetic RadiationEldsoky DabaNo ratings yet
- School of Applied Natural Science: Adama Science and Technology UniversityDocument22 pagesSchool of Applied Natural Science: Adama Science and Technology UniversityFayisaa LamessaNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument9 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumAk R71No ratings yet
- Introduction To EM SpectrumDocument8 pagesIntroduction To EM SpectrumKushal BhattNo ratings yet
- Science 10 - Learning ModuleDocument16 pagesScience 10 - Learning Modulemn Kim100% (1)
- Essay 300 Words Orig.Document1 pageEssay 300 Words Orig.Yeddah Marie TanezaNo ratings yet
- Team Leader - Ibasan, Michael Ellise: I. Cover Page II. Members and Assigned TasksDocument12 pagesTeam Leader - Ibasan, Michael Ellise: I. Cover Page II. Members and Assigned TasksJOHN ASHLEY RANIN CARIAGANo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer QuizDocument4 pagesScience Reviewer Quiz28. Pinera, Yna Angela S.No ratings yet
- Science Reviewer 1Document15 pagesScience Reviewer 1Symon MarianoNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 Electromagnetism: Kushal BhattDocument21 pagesUnit-1 Electromagnetism: Kushal BhattKushal BhattNo ratings yet
- Worksheet On Electromagnetic Waves FADRIGONDocument3 pagesWorksheet On Electromagnetic Waves FADRIGONNarahmie RuadoNo ratings yet
- SCH 100 Notes 2013-2014 ALLDocument42 pagesSCH 100 Notes 2013-2014 ALLErick Wangila WanyonyiNo ratings yet
- 005 - ManMadeRadiation (2018)Document7 pages005 - ManMadeRadiation (2018)Bert AndersonNo ratings yet
- What Is Electromagnetc Spectrum?Document11 pagesWhat Is Electromagnetc Spectrum?Rodrigo SeriozaNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves: Vina P. Hipolito Iv-Silvestre Assignment )Document7 pagesElectromagnetic Waves: Vina P. Hipolito Iv-Silvestre Assignment )VhinaP.HipolitoNo ratings yet
- Uses of Electromagnetic WavesDocument4 pagesUses of Electromagnetic WavesMarlou PrincesaNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument8 pagesElectromagnetic WavesHafid ZainulNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument1 pageElectromagnetic SpectrumIAN TAPIANo ratings yet
- Science 10 SECOND QuarterDocument152 pagesScience 10 SECOND QuarterAPPLE GRACE MARIE SEBASTIAN100% (1)
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument7 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrummuddasarhussain739No ratings yet
- Dangers of Invisible EMF & EMR PollutionDocument88 pagesDangers of Invisible EMF & EMR PollutionOne_sofian2715100% (2)
- Science 10 - Q2W3-4Document15 pagesScience 10 - Q2W3-4quackity obamaNo ratings yet
- LESSON 2. Calculating Wavelengtdytrjycghh and FrequencyDocument37 pagesLESSON 2. Calculating Wavelengtdytrjycghh and FrequencyRyan Aint simpNo ratings yet
- 2NDQ Science NotesDocument38 pages2NDQ Science NotesEzekiel BayocotNo ratings yet
- EVS SeminarDocument30 pagesEVS SeminarMonica SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project CbseDocument17 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project CbseKavin PatelNo ratings yet
- THE Electromagnetic Spectrum: Unit 2, Module 2 Kiziah F. GranilDocument10 pagesTHE Electromagnetic Spectrum: Unit 2, Module 2 Kiziah F. GranilHannah Joy DulayNo ratings yet
- Reflection EM WAVESDocument2 pagesReflection EM WAVESPatricia BaezaNo ratings yet
- Properties of Electromagnetic WavesDocument3 pagesProperties of Electromagnetic WavesAayan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 Module 2Document73 pagesQuarter 2 Module 2princesslayshoNo ratings yet
- Engineering Electromagnetism Assignment: Gaurav Kumar, Roll No.-108110029. 10/27/2011Document4 pagesEngineering Electromagnetism Assignment: Gaurav Kumar, Roll No.-108110029. 10/27/2011Gaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- Electro Magnetic Waves M@trix FoundationDocument7 pagesElectro Magnetic Waves M@trix FoundationdjbabuNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Radiation and Human HealthDocument7 pagesElectromagnetic Radiation and Human HealthRabia Mutlu100% (1)
- Thenatureoflight 140212073224 Phpapp01Document32 pagesThenatureoflight 140212073224 Phpapp01Nathaniel De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Spectrum: Juan Carlos Isaza Jacome Byron Cubides Romero Duvan Reyes SaenzDocument20 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrum: Juan Carlos Isaza Jacome Byron Cubides Romero Duvan Reyes SaenzJuan Carlos Isaza JacomeNo ratings yet
- The Electromagnetic Spectrum 3Document7 pagesThe Electromagnetic Spectrum 3Nur-shima SakilinNo ratings yet
- The Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument5 pagesThe Electromagnetic SpectrumTomas Aquino DiquitoNo ratings yet
- Isgot Receive Nitrogen - TO BE POSTED IN CCRDocument1 pageIsgot Receive Nitrogen - TO BE POSTED IN CCRsonerNo ratings yet
- Barreira OMRON MS4800Document36 pagesBarreira OMRON MS4800sandrasandradaxanaNo ratings yet
- JSA HEMP Well Services Pg36-40Document5 pagesJSA HEMP Well Services Pg36-40Ashok Suresh100% (1)
- Uputstvo EDS800 PDFDocument139 pagesUputstvo EDS800 PDFrzrasaNo ratings yet
- 1 PDFDocument103 pages1 PDF123qweNo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of Hybrid VehicleDocument4 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Hybrid VehicleRagbt CNo ratings yet
- TI Furadur Kitt 322 - enDocument3 pagesTI Furadur Kitt 322 - engonzalogvargas01No ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheets English 2, Quarter 3, Week 1Document11 pagesLearning Activity Sheets English 2, Quarter 3, Week 1CHERIE LYN TORRECAMPONo ratings yet
- Contract Labour FORM XIIDocument1 pageContract Labour FORM XIIhdpanchal86100% (1)
- KB 500wlDocument1 pageKB 500wljanaka escoNo ratings yet
- Hang Out 3 Student - S Key PDFDocument19 pagesHang Out 3 Student - S Key PDFyuliNo ratings yet
- The Winners and Losers of GlobalizationDocument7 pagesThe Winners and Losers of GlobalizationRalucutsaNo ratings yet
- Programme Fire Sprinkler International 2023 3Document4 pagesProgramme Fire Sprinkler International 2023 3Carlos_MKTRNo ratings yet
- Conservation of A Neolithic Plaster StatueDocument1 pageConservation of A Neolithic Plaster StatueJC4413No ratings yet
- Autism TherapyDocument2 pagesAutism TherapyVasile PitelNo ratings yet
- Global Vaccine Action Plan: Tetanus & Difteri (TD/DPT)Document6 pagesGlobal Vaccine Action Plan: Tetanus & Difteri (TD/DPT)Gusti IndrakusumaNo ratings yet
- FOMAR-QTN-2019-20-117 Kamat PDFDocument1 pageFOMAR-QTN-2019-20-117 Kamat PDFPriyesh KamatNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument8 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemEfanPutraNo ratings yet
- Coorination Compounds Board Questions 2010: π-complexes are known for the transition metals onlyDocument3 pagesCoorination Compounds Board Questions 2010: π-complexes are known for the transition metals onlyamone nNo ratings yet
- TDS ASP-epoxyCoveDocument2 pagesTDS ASP-epoxyCovetatenda mhuruNo ratings yet
- S Listing Ui Group Eae26ab3f22c4787 2603 125516 DefaultDocument16 pagesS Listing Ui Group Eae26ab3f22c4787 2603 125516 DefaulthcghealthcureNo ratings yet
- Common Proper Noun Worksheet Underlining IntermediateDocument1 pageCommon Proper Noun Worksheet Underlining Intermediaterazeen_93No ratings yet
- Application of Dorothea Orem-PRELIMSDocument6 pagesApplication of Dorothea Orem-PRELIMSJessica Ella Hernandez Agunday0% (1)
- Implementing A Digital Transformation: November 2018Document5 pagesImplementing A Digital Transformation: November 2018Hasti YektaNo ratings yet
- Textile Internship - Usha YarnsDocument49 pagesTextile Internship - Usha YarnsROHAN GIREESHNo ratings yet
- 1150-1155 Haybuster Parts SN0191 and Up Aug-2020Document306 pages1150-1155 Haybuster Parts SN0191 and Up Aug-2020Jason CrowleyNo ratings yet
- Biosci 3Document15 pagesBiosci 3MARJORYNo ratings yet
- Total Parenteral NutritionDocument59 pagesTotal Parenteral NutritionMARIAH ALEXIE GASALNo ratings yet