Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson 1 Quarter 3 - Endocrine
Lesson 1 Quarter 3 - Endocrine
Uploaded by
rafaelesguerra028Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson 1 Quarter 3 - Endocrine
Lesson 1 Quarter 3 - Endocrine
Uploaded by
rafaelesguerra028Copyright:
Available Formats
Lesson 1-Quarter 3: Endocrine System
Biology-originated from the Greek words bios (“life”)
and logos (“study)
Functions of Endocrine System
Controls the body processes that happen slowly such as
cell growth
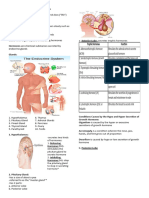
Endocrine System -is composed of glands
a. Anterior Lobe- secretes trophic hormones
Gland-is an organ capable of secreting hormones
Trophic Hormones Function
Hormones-are chemical substances secreted by 1. Adrenocorticotrophic Hormone Stimulates the adrenal cortex to secrete
endocrine glands
(ACTH) glucocorticoid hormone
Glands: 2. Somatotrophic Hormone (Growth Stimulates metabolism and the bones and
Hormone) the muscles to grow
3. Thyrotrophic Stimulating Hormone Stimulates the thyroid to secrete hormones
(TSH)
4. Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) Stimulates the secretion of estrogen in
female and the development of egg cell and
sperm cell
5. Leutinizing Hormone (LH) Stimulates the secretion of progesterone in
female and testosterone in male
6. Luteotrophic Hormone (LtH) or Stimulates the breast to secrete milk
Prolactin
Conditions Causes by the Hypo and Hyper Secretion of
1. Hypothalamus 6. Thymus Growth Hormone:
2. Pituitary Gland 7. Adrenal Glands Gigantism-is caused by the hyper or excessive
3. Pineal Gland 8. Pancreas secretions of growth hormone
4. Thyroid Gland 9. Ovary
5. Parathyroid 10. Testis Acromegaly-is a condition wherein the nose, jaw,
hands, and feet grow out of proportion
1. Hypothalamus:
-secretes two kinds Dwarfism-is caused by hypo or low secretion of growth
of hormones: hormone
1. Releasing
Hormone (RH)- b. Posterior Lobe
stimulates the Hormones Function
pituitary gland to
secrete hormone 1. Anti-diuretic Hormone (ADH) or Promotes the retention of water by the kidneys
2. Inhibiting
Hormone (IH)- stop
Vasopressin
the pituitary gland
to stop in secreting 2. Oxytocin Stimulates the contraction of uterus durong
hormone*
childbirth and the mammary gland to release milk
2. Pituitary Gland:
-has a size of about a pea 3. Pineal Gland:
-referred to as the ”master gland”* -has a size of about a pea located at the base of a
-has 2 parts: human brain
a. Anterior Lobe
b. Posterior Lobe
-secretes melatonin that functions in maintaining out 7. Adrenal Glands-
body’s rhythm and it promotes sleep -are the paired glands
above the kidneys
-consist of 2 parts:
a. adrenal cortex
b. adrenal medulla
a. Adrenal Cortex- is the outer layer and secretes
corticosteroids
4. Thyroid Gland:
Corticosteroids Function
-is an H-shaped gland located in the neck on both sides
of the trachea
1. Glucocorticoids increase blood gluccose and aid the body in
-secretes thyroxin coping with stressful conditions
Conditions Causes by the Hypo and Hyper Secretion of 2. Mineralocorticoids Regulate the absorption of sodium ions and the
Thyroxin
a. Hyperthyroidism- is due to over secretion of thyroxin secretion of potassium ions in the kidneys
-effects: irritability, weight loss, high blood pressure,
and exophthalmic goiter
b. Adrenal Medulla- is the inner layer and is referred to
as the “gland of combat”*
Exophthalmic Goiter
-aka Graves’ disease Hormones Function
characterized by the
enlargement of the thyroid 1. Adrenaline (Epinephrine) The emergency hormone that hastens metabolic
gland and suffering from
exophthalmos activities of the body
b. Hypothyroidism- is due to under secretion of 2. Noradrenaline (Norepinephrine) Similar to adrenaline function and supplements
thyroxin
-effects: endemic goiter and cretinism
the action of the nervous system
8. Pancreas-consists of Islets of Langerhans (tissues of
pancreas) which is made up of 2 kinds of cells:
a. alpha cells b. beta cells
Endemic Goiter-is an iodine-deficiency disease
characterized by thyroid enlargement that occurs in
more than 10% of a population
Cretin- is a severe deficiency of thyroid hormone which
leads to stunted growth and mental retardation
4. Thyroid Gland-also secretes calcitonin causes storage
of calcium in the bones
a. alpha cells -secretes glucagon which increases the
5. Parathyroid Gland-are the four, small, and reddish level of glucose in the blood by changing the glycogen
glands that are found on the posterior lobes of the to glucose
thyroid gland
-secretes parathormone a. beta cells -secretes insulin which lowers blood
glucose by changing it to glycogen
6. Thymus-located at the middle part of the chest
-plays an important role in the immune system by 9. Gonads
secreting thymosin a. Ovaries-female gonads which secrete estrogen
-thymosin aids in the development of T cells and progesterone
estrogen- develops and maintains the
development of the secondary sex characteristics
and the development of the uterine linings
progesterone- doubles the effect of estrogen in
developing the uterine linings during pregnancy
b. Testes-male gonads which secrete testosterone
testosterone- function in sperm production; and in
the development and maintenance of the
secondary sex characteristics
You might also like
- Endocrine Lesson 1 Grade 10Document3 pagesEndocrine Lesson 1 Grade 10Christine omaney MalagambaNo ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument6 pagesEndocrineIdrees Nazim QureshiNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System XVDocument10 pagesEndocrine System XVaraineNo ratings yet
- AnaPhy Lec - Endocrine SystemDocument2 pagesAnaPhy Lec - Endocrine SystemReigh DakotaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System NotesDocument8 pagesEndocrine System NotesShiela Mae SagayoNo ratings yet
- E N D O C R I N E System: Hormonal Control of A. PituitaryDocument3 pagesE N D O C R I N E System: Hormonal Control of A. PituitaryMayet BautistaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Reviewer LecDocument3 pagesEndocrine System Reviewer LecNOELLE LAURAINNE TANZONo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument7 pagesEndocrine SystemClyde CapapasNo ratings yet
- 10 Endocrine SystemDocument3 pages10 Endocrine SystemMardy Martin SorianoNo ratings yet
- Medical Aspects of Endocrine SystemDocument8 pagesMedical Aspects of Endocrine SystemNitya SaxenaNo ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument5 pagesEndocrineShem DelolaNo ratings yet
- Script For Midterm VRDocument5 pagesScript For Midterm VRDanica MerinNo ratings yet
- Hsslive Xi Zoology CH 22Document4 pagesHsslive Xi Zoology CH 22Ashly Santhosh KNo ratings yet
- Quick Study Guide To The Endocrine SystemDocument11 pagesQuick Study Guide To The Endocrine SystemMc Luis Glen AserdanoNo ratings yet
- Notes in Science LT 10 - Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesNotes in Science LT 10 - Endocrine SystemAlven ReyNo ratings yet
- Science - LensDocument8 pagesScience - LensAte DannyNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine SystemDocument7 pagesThe Endocrine SystemRODGIELYN MAE GEJONNo ratings yet
- 10 Endocrine SystemDocument3 pages10 Endocrine SystemGracia Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- ANAPHYDocument7 pagesANAPHYMary Joyce MejiaNo ratings yet
- 6 Hormones Secreted by The AdenohypophysisDocument5 pages6 Hormones Secreted by The Adenohypophysischristine_8995No ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument13 pagesEndocrineElyka Alivan Valdez PolonioNo ratings yet
- 22 Chemical Co-OrdinationDocument47 pages22 Chemical Co-OrdinationRachna JaiswalNo ratings yet
- AP1 Lab16 Endocrine System FA2021Document11 pagesAP1 Lab16 Endocrine System FA2021daleng subNo ratings yet
- Chemical Co Ordination and Integration - 434dea34 f494 4704 A8c9 6876397e324eDocument53 pagesChemical Co Ordination and Integration - 434dea34 f494 4704 A8c9 6876397e324epcgurukotari9No ratings yet
- X CBSE Bio Human Endocrine SystemDocument4 pagesX CBSE Bio Human Endocrine Systemkaustubhchoudhary2005No ratings yet
- Ing - Sistem EndokrinDocument9 pagesIng - Sistem EndokrinWarman PurbaNo ratings yet
- Exercise 13 EditDocument10 pagesExercise 13 EditSamantha De JesusNo ratings yet
- Name of The GlandDocument3 pagesName of The GlandSajeevNo ratings yet
- BSA 1C 10-26-2021 Endocrine SystemDocument38 pagesBSA 1C 10-26-2021 Endocrine SystemAngelika ButaslacNo ratings yet
- Ch45 EndocrineSystemDocument3 pagesCh45 EndocrineSystemCristie SumbillaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Lecture EndocrineDocument16 pagesNursing Lecture EndocrineAedge010100% (3)
- PNKND Les 0 V 9 VWR60 B RCNDocument4 pagesPNKND Les 0 V 9 VWR60 B RCNaadeshthite476No ratings yet
- Midterm - AnaphyDocument6 pagesMidterm - AnaphyJustine Mae OyongNo ratings yet
- Metabolism ConceptDocument76 pagesMetabolism ConceptrlinaoNo ratings yet
- Organ SystemsDocument4 pagesOrgan SystemsDenine Dela Rosa OrdinalNo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument3 pagesChemical Coordination and Integrationakhil01ajNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System: Properties: Mechanisms of Hormone ActionDocument5 pagesThe Endocrine System: Properties: Mechanisms of Hormone ActionaudreyNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Hand OutDocument10 pagesEndocrine Hand OutbetazenNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument21 pagesBiologynitesh.th15005No ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Endocrine Pituitary Gland: A.) Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)Document3 pagesChapter 10 - Endocrine Pituitary Gland: A.) Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)Reen BalbaguioNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesEndocrine SystemDearly Niña OsinsaoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument6 pagesEndocrine SystemynaNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System NotesDocument5 pagesThe Endocrine System NotesasymptomaticcrisisNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledJhannyt Jyn BasaloNo ratings yet
- Endocrinesys TEM: Principles of Chemical CommunicationDocument4 pagesEndocrinesys TEM: Principles of Chemical CommunicationCatherine Joy delos SantosNo ratings yet
- (Transes) Human Histology - 10 Endocrine GlandsDocument10 pages(Transes) Human Histology - 10 Endocrine GlandsReina CastronuevoNo ratings yet
- Abdul MananDocument2 pagesAbdul MananscribdNo ratings yet
- Endrocrine NotesDocument5 pagesEndrocrine NoteskatNo ratings yet
- Endocrine GlandDocument9 pagesEndocrine GlandKUNAL1221No ratings yet
- Unit - Iv Human Anatomy and Physiology: Very Short Answer QuestionsDocument12 pagesUnit - Iv Human Anatomy and Physiology: Very Short Answer QuestionsRK YeleswarapuNo ratings yet
- BasicsDocument120 pagesBasicsbiniam MesfinNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine SystemDocument18 pagesThe Endocrine SystemMON RYAN REYNo ratings yet
- Bio ReportDocument4 pagesBio ReportKate MabanagNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Glands - 1st - ChapterDocument12 pagesEndocrine Glands - 1st - Chaptervarun kumarNo ratings yet
- The Slim Book of Health Pearls: Hormones, Nerves, and StressFrom EverandThe Slim Book of Health Pearls: Hormones, Nerves, and StressNo ratings yet
- Intro To Human Anatomy & Physiology: Quick Review Notes Chapter 1From EverandIntro To Human Anatomy & Physiology: Quick Review Notes Chapter 1No ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Pituitary Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Pituitary Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Equilibrium: Navigating the Hormonal Seas: Navigating the Whispers of Hormones: A Delicate Dance of BalanceFrom EverandEndocrine Equilibrium: Navigating the Hormonal Seas: Navigating the Whispers of Hormones: A Delicate Dance of BalanceNo ratings yet
- Pituitary Gland, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandPituitary Gland, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Thyroid Health: The Thyroid Solution Diet ExposedFrom EverandThyroid Health: The Thyroid Solution Diet ExposedRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Clinical Liver Disease - 2022 - Memel - Intermittent Fasting As A Treatment For Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease What IsDocument5 pagesClinical Liver Disease - 2022 - Memel - Intermittent Fasting As A Treatment For Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease What Isarranguezjr5991No ratings yet
- Popliteal Fossa 1Document21 pagesPopliteal Fossa 1Kesheni LemiNo ratings yet
- Ses 12 Principles of Newborn Adaption To The Extra-Uterine LifeDocument25 pagesSes 12 Principles of Newborn Adaption To The Extra-Uterine Lifelandegre KNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Safety of Long Acting Beta Agonist-Inhaled Corticosteroid Combination Products in Adult Patients With Asthma: A Systematic ReviewDocument8 pagesCardiovascular Safety of Long Acting Beta Agonist-Inhaled Corticosteroid Combination Products in Adult Patients With Asthma: A Systematic ReviewHaniifah Dhiya UlhaqNo ratings yet
- Recent Advances in Cerebral PalsyDocument16 pagesRecent Advances in Cerebral PalsyTasyaNo ratings yet
- Hypertension in Adolescents and Young Adults Referred To A Tertiary Hypertension Clinic in Cape Town, South AfricaDocument5 pagesHypertension in Adolescents and Young Adults Referred To A Tertiary Hypertension Clinic in Cape Town, South AfricahanifahNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Fill in The BlanksDocument30 pagesAnatomy Fill in The BlanksJhanzaib ahmed gujar bajarNo ratings yet
- CardioDocument122 pagesCardioAdrian Rosell Carrillo EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Perioperative Medicines Management V8Document7 pagesPerioperative Medicines Management V8Waleed Ahmad.No ratings yet
- Abdominal Aortic AneurysmDocument44 pagesAbdominal Aortic Aneurysmalebelucci69No ratings yet
- Drug Study orDocument6 pagesDrug Study orAlliah MayoNo ratings yet
- Low Risk Flowchart Anticoagulation WWW - Ruh.nhs - UkDocument1 pageLow Risk Flowchart Anticoagulation WWW - Ruh.nhs - UkborstNo ratings yet
- OmanDocument79 pagesOmanAhmed KassemNo ratings yet
- Modifiable Stroke Risk FactorsDocument2 pagesModifiable Stroke Risk FactorsPricilia GunawanNo ratings yet
- Body Fluids and Blood - HUMAN PHYSIOLOGYDocument29 pagesBody Fluids and Blood - HUMAN PHYSIOLOGYSodeinde SimeonNo ratings yet
- Screening: Muhammad Jawaid KhanzadaDocument12 pagesScreening: Muhammad Jawaid Khanzadashazia_tabassumNo ratings yet
- ARTIKEL9 - Jurnal Elective Birth in Twin PregnancyDocument11 pagesARTIKEL9 - Jurnal Elective Birth in Twin PregnancyFarid NurdiansyahNo ratings yet
- Unique Point Japanese AcupunctureDocument12 pagesUnique Point Japanese Acupuncturepustinikki100% (4)
- High Blood PressureDocument9 pagesHigh Blood PressureshashidharanNo ratings yet
- 5 Amiodarona ArticlesDocument36 pages5 Amiodarona ArticlesSacrificiuPopescuNo ratings yet
- Textbook Pulmonary Hypertension Basic Science To Clinical Medicine 1St Edition Bradley A Maron Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument53 pagesTextbook Pulmonary Hypertension Basic Science To Clinical Medicine 1St Edition Bradley A Maron Ebook All Chapter PDFcarol.greenwell527100% (7)
- Science-9 q1 w2 Mod2 AdmDocument36 pagesScience-9 q1 w2 Mod2 AdmMA MERCEDES POSADAS100% (3)
- ASA 1501-Assignment 1Document8 pagesASA 1501-Assignment 1grimsdellaNo ratings yet
- Clozapine DiazepamDocument2 pagesClozapine Diazepamalteahmichaella.mintuNo ratings yet
- Early Embryology Week OneDocument14 pagesEarly Embryology Week OnelukesqueNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Nur Pediatric Nur Pediatric Nur Pediatric Nur Pediatric Nursing Sing Sing Sing SingDocument10 pagesPediatric Nur Pediatric Nur Pediatric Nur Pediatric Nur Pediatric Nursing Sing Sing Sing Singtheiam772No ratings yet
- PDF Paediatric Symptom and Sign Sorter Second Edition El Radhi Ebook Full ChapterDocument53 pagesPDF Paediatric Symptom and Sign Sorter Second Edition El Radhi Ebook Full Chapteralexander.boyd500100% (2)
- Case Presentation - Visceral LeishmaniaDocument18 pagesCase Presentation - Visceral LeishmaniaAAANo ratings yet
- Preboard B J2021Document15 pagesPreboard B J2021Banana QNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology in Nursing 3Rd Australian New Zealand Edition Bonita E Broyles All ChapterDocument67 pagesPharmacology in Nursing 3Rd Australian New Zealand Edition Bonita E Broyles All Chaptertrevor.morvillo782100% (9)