Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tenses Resumen
Tenses Resumen
Uploaded by
Mailen Lo Pilato BloisCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- English File Final Tests, Int End Test BDocument6 pagesEnglish File Final Tests, Int End Test BAriadne_77780% (5)
- Frans Mind Map PDFDocument1 pageFrans Mind Map PDFAnastasya Zalsabilla Hermawan100% (1)
- Revolution in Poetic Language: by Julia KristevaDocument25 pagesRevolution in Poetic Language: by Julia KristevaMalik AtifNo ratings yet
- Tamil Self TaughtDocument102 pagesTamil Self TaughtÁgnesNagy100% (1)
- Gateway-B1 SB Unit7Document28 pagesGateway-B1 SB Unit7anisalera1507No ratings yet
- Tenses ResumenDocument8 pagesTenses ResumenMailen Lo Pilato BloisNo ratings yet
- Verbal Times Review: Structures Example When They Are UsedDocument4 pagesVerbal Times Review: Structures Example When They Are UsedDiego GonzalezNo ratings yet
- English TensesDocument1 pageEnglish TensesCarmen ChowNo ratings yet
- Present and Past TensesDocument3 pagesPresent and Past TensesAia NikolovaNo ratings yet
- All TensesDocument6 pagesAll TensesAndres ValdezNo ratings yet
- Resumen de InglésDocument8 pagesResumen de Inglésmapaus07No ratings yet
- Verb Forms Guide - A4Document1 pageVerb Forms Guide - A4Juan Miguel Ala TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Tenses TheoryDocument6 pagesTenses TheoryMỹ NhaNo ratings yet
- Tiempos VerbalesDocument6 pagesTiempos VerbalesMaria Ines RoqueNo ratings yet
- Verb TensesDocument35 pagesVerb TensesGlaiza VillaverNo ratings yet
- Past Forms TableDocument1 pagePast Forms TableДашаNo ratings yet
- Grammar Tenses Table PDFDocument2 pagesGrammar Tenses Table PDFDaniel MiuNo ratings yet
- 02 Summary of Tenses & Aspects of VerbsDocument10 pages02 Summary of Tenses & Aspects of Verbslasnfbf asigfnNo ratings yet
- Tense Structure Function ExampleDocument2 pagesTense Structure Function Examplenano yyNo ratings yet
- Simple Past Vs Past ContinuousDocument2 pagesSimple Past Vs Past ContinuousIltze RDNo ratings yet
- Tense Signal Words Use Form Ex Affirmative (+) Ex Negative (-) Ex Interrogative (?)Document4 pagesTense Signal Words Use Form Ex Affirmative (+) Ex Negative (-) Ex Interrogative (?)Yen RitaNo ratings yet
- Verb Tenses Present Future PastDocument6 pagesVerb Tenses Present Future PastcharguibachaghaNo ratings yet
- Ingles PAST CONTINUOUSDocument4 pagesIngles PAST CONTINUOUSDavid Robles HerreraNo ratings yet
- Explore The World of English TensesDocument13 pagesExplore The World of English Tensescaroline.helmiNo ratings yet
- The PassiveDocument12 pagesThe PassiveAngelica SantiNo ratings yet
- Grammar Tenses: PresentDocument3 pagesGrammar Tenses: PresentPaola FloresNo ratings yet
- Tenses ReviewDocument2 pagesTenses ReviewLyane FleuriaultNo ratings yet
- Tenses Chart WorkDocument2 pagesTenses Chart WorkvitaNo ratings yet
- Golden TensesDocument1 pageGolden TensesnajjarmohdNo ratings yet
- Verbs, Tense, Aspect, and Mood: By: Acmad Yani, S.SDocument19 pagesVerbs, Tense, Aspect, and Mood: By: Acmad Yani, S.SametgembulNo ratings yet
- Prsent's Página 2.drawioDocument1 pagePrsent's Página 2.drawioBrandon PerezNo ratings yet
- Chart of Verb Tenses PDFDocument3 pagesChart of Verb Tenses PDFTasnim MustafaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Tenses: by Oxtapianus TawarikDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Tenses: by Oxtapianus Tawariko.tawarikNo ratings yet
- Perfect or Compound TensesDocument3 pagesPerfect or Compound TensesZaidy GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Passive ENGDocument10 pagesPassive ENGjawess5666100% (2)
- Past Simple + Present Perfect SummaryDocument1 pagePast Simple + Present Perfect SummaryKagome HigurashiNo ratings yet
- Present Simple: Always, Ussualy.Document11 pagesPresent Simple: Always, Ussualy.epincarrNo ratings yet
- ELEC 100 Tenses of Verbs S V AgreementDocument39 pagesELEC 100 Tenses of Verbs S V AgreementPrincess Darlene GallardoNo ratings yet
- Past Continuous TenseDocument4 pagesPast Continuous TenseThet HtarNo ratings yet
- Grammar Map2Document1 pageGrammar Map2Patrcia CostaNo ratings yet
- PHRASAL VERBS 8oDocument4 pagesPHRASAL VERBS 8oVale OlveraNo ratings yet
- Present Simple Present Continuous Present Perfect: English TensesDocument1 pagePresent Simple Present Continuous Present Perfect: English TensesKhaled AdelNo ratings yet
- Ingles MacheDocument3 pagesIngles Machefeat08ronNo ratings yet
- The Present Perfect Progressive TenseDocument11 pagesThe Present Perfect Progressive Tensecather youngNo ratings yet
- The Verb Tenses and Their UsageDocument1 pageThe Verb Tenses and Their UsageJerick CruzNo ratings yet
- 7.1 (PDF AT Task 1) Tenses PDFDocument4 pages7.1 (PDF AT Task 1) Tenses PDFP A Wan SunarNo ratings yet
- Aptis BookDocument174 pagesAptis Bookdarkpechuga59No ratings yet
- Past Simple Present PerfectDocument1 pagePast Simple Present PerfectDaniela MartinsNo ratings yet
- Checklist Present PerfectDocument1 pageChecklist Present PerfectNurgul LadyNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument3 pagesTensesHihachi SarahNo ratings yet
- Perfect Tenses Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument2 pagesPerfect Tenses Cheat Sheet: by ViaAura SkyNo ratings yet
- (Grammar Booster) Verb Tenses ReviewDocument8 pages(Grammar Booster) Verb Tenses Reviewmarisa hirano taiboNo ratings yet
- Verb Tenses: Star TrekDocument8 pagesVerb Tenses: Star TrekodethNo ratings yet
- Verb Tenses Chart PDFDocument2 pagesVerb Tenses Chart PDFHanie Mesina-EloriagaNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet 2023Document6 pagesActivity Sheet 2023Glädje VRNo ratings yet
- Grammar + Sentence SkillDocument63 pagesGrammar + Sentence SkillKay Chan SothearaNo ratings yet
- Grammar BookletDocument40 pagesGrammar BookletSALDAÑA NAVARRETE ANDREANo ratings yet
- Verb TensesDocument20 pagesVerb Tensesvpetrovaa23No ratings yet
- Esquemas Gramática B2 @opomaestra - Enproceso PDFDocument35 pagesEsquemas Gramática B2 @opomaestra - Enproceso PDFLucia Garcia CoyNo ratings yet
- Ventures3e SB2 U08Document15 pagesVentures3e SB2 U08Doan TonyNo ratings yet
- KulitanDocument30 pagesKulitanJhn CarloNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Unseen Poetry ContinuedDocument37 pagesWeek 2 Unseen Poetry ContinuedHelen WallisNo ratings yet
- English 10 Third QuarterDocument28 pagesEnglish 10 Third QuarterEHdz D. JameraNo ratings yet
- Dual Award Programme Individual/Group Assignment Cover SheetDocument5 pagesDual Award Programme Individual/Group Assignment Cover SheetJuneid ImritNo ratings yet
- Class 6: Possessive Adjectives Review On Personal PronounsDocument46 pagesClass 6: Possessive Adjectives Review On Personal PronounsSmart AcademyNo ratings yet
- Mysticism Examined - Philosophical Inquiries Into Mysticism PDFDocument304 pagesMysticism Examined - Philosophical Inquiries Into Mysticism PDFWilliam Davidans SversuttiNo ratings yet
- Communication Skills Class 10 NotesDocument8 pagesCommunication Skills Class 10 Notesronitkhedekar2008No ratings yet
- GRAMMARDocument32 pagesGRAMMARnarendra mishraNo ratings yet
- GrapeSEED Pratom Unit 29 Test PARKDocument3 pagesGrapeSEED Pratom Unit 29 Test PARKRuthessa LeyrosNo ratings yet
- Bài Tập Thì Hiện Tại ĐơnDocument3 pagesBài Tập Thì Hiện Tại Đơnsylvester.powellNo ratings yet
- Reflections On Native Language Use in Adult ESL Classrooms: ResearchDocument11 pagesReflections On Native Language Use in Adult ESL Classrooms: ResearchJessieRealistaNo ratings yet
- English Tips 1 - Something, Nothing, Anything, Everything (Only English)Document4 pagesEnglish Tips 1 - Something, Nothing, Anything, Everything (Only English)Thainá TakemotoNo ratings yet
- Memo WritingDocument10 pagesMemo WritingMuhammad JunaidNo ratings yet
- An English Accent Free Sample PDFDocument13 pagesAn English Accent Free Sample PDFMarija DanilovicNo ratings yet
- ACR - Filipino Reading InterventionDocument3 pagesACR - Filipino Reading InterventionSamantha Jane AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- English Language Communication Skills Lab Manual: Name Roll No. Branch SectionDocument39 pagesEnglish Language Communication Skills Lab Manual: Name Roll No. Branch SectionSurendrakumar ThotaNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 - Yellowstone National ParkDocument2 pagesUnit 7 - Yellowstone National ParkDaniel ChioseauaNo ratings yet
- 1st Term Syllabus 2024-25Document9 pages1st Term Syllabus 2024-25hamzakhanshamsi100% (1)
- Step6 SummativediagnosticDocument4 pagesStep6 Summativediagnosticapi-329778412100% (2)
- Unit 3pdf 1666860611Document5 pagesUnit 3pdf 1666860611Miku kepoNo ratings yet
- Filipino 10: - Saint Mary's UniversityDocument33 pagesFilipino 10: - Saint Mary's UniversityVince ViayNo ratings yet
- Five Lectures On General Semantics KorzybskiDocument25 pagesFive Lectures On General Semantics KorzybskiLucas67% (3)
- 3 Kinds of Tests and Testing, Hughes 2003, AbridgedDocument12 pages3 Kinds of Tests and Testing, Hughes 2003, AbridgedLydia Siallagan83% (6)
- Journalism Jargon WordsDocument4 pagesJournalism Jargon WordszachyzakizadaNo ratings yet
- Thirty Theses On Interpretation (Richard Palmer)Document12 pagesThirty Theses On Interpretation (Richard Palmer)raccoonie81No ratings yet
Tenses Resumen
Tenses Resumen
Uploaded by
Mailen Lo Pilato BloisOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tenses Resumen
Tenses Resumen
Uploaded by
Mailen Lo Pilato BloisCopyright:
Available Formats
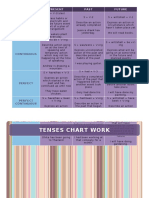
Common
Verb Tense Adverbs
(English) Structure (English) Explanation (English) (English) Explanation (English)
General facts, To describe actions
Subject + Base Form Always, often,
Present Simple routines, habits, and that are regularly true,
of Verb usually
permanent situations. habits, or facts.
Actions happening For actions taking
Present Subject + "to be" + now, near future Now, at the place at the time of
Continuous Present Participle plans, temporary moment speaking or near-future
situations. plans.
To narrate specific
Completed actions or
Subject + Past Yesterday, last past events that
Past Simple events at a specific
Simple Form of Verb year occurred at a definite
time in the past.
time.
Ongoing actions in For describing actions
Subject + "was" or
the past or actions While, when, in progress or actions
Past Continuous "were" + Present
interrupted by another as interrupted by another
Participle
event. event in the past.
Actions that have a To indicate actions that
Subject + "have" or connection to the started in the past and
Present Perfect Already,
"has" + Past present, completed continue into the
Simple recently
Participle actions with present or are relevant
relevance. now.
To emphasize the
Subject + "have" or Actions that started in duration of actions that
Present Perfect
"has" + Been + the past and continue For, since began in the past and
Continuous
Present Participle into the present. are ongoing into the
present.
For actions that
Actions completed occurred and were
Past Perfect Subject + "had" +
before a specific time Before, already completed before
Simple Past Participle
in the past. another event in the
past.
To describe actions
Ongoing actions
that were in progress
Past Perfect Subject + "had been" completed before a
For, since and were completed
Continuous + Present Participle specific time in the
before a specific past
past.
event.
For future actions,
Predictions, promises,
Will (Simple Subject + Will + Base Tomorrow, decisions, promises, or
spontaneous
Future) Form of Verb soon predictions with no
decisions, offers.
prior plan.
For expressing future
Future plans,
Subject + "am/is/are plans, intentions, or
Going to (Future intentions, and Later, in the
going to" + Base predictions when there
Intent) predictions based on future
Form of Verb is evidence or prior
evidence.
planning.
For future events that
Present Simple Subject + Base Form Scheduled future
Next week, on are part of a schedule,
with Future of Verb (for events, timetables,
Friday timetables, or fixed
Meaning scheduled events) and fixed plans.
plans.
Subject + "to be" +
Present Personal future For personal
Present Participle This evening,
Continuous with arrangements and arrangements in the
(for personal next month
Future Meaning intentions. near future.
arrangements)
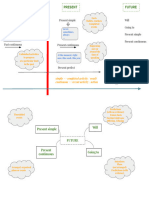
Present Simple (Presente Simple): Se utiliza para expresar hechos generales,
hábitos y rutinas. Por ejemplo, "I speak" se traduce como "Hablo" y describe
una acción habitual.
Present Continuous (Presente Continuo): Este tiempo verbal se usa para
acciones que ocurren en el momento presente o planes cercanos en el futuro.
Por ejemplo, "I am speaking" se traduce como "Estoy hablando" y señala una
acción en curso en el presente.
Past Simple (Pasado Simple): Se emplea para narrar acciones pasadas
completadas en un momento específico en el pasado. Por ejemplo, "I spoke" se
traduce como "Hablé" y indica una acción pasada con un tiempo claro.
Past Continuous (Pasado Continuo): Este tiempo se utiliza para describir
acciones en progreso en el pasado o acciones interrumpidas por otro evento. Por
ejemplo, "I was speaking" se traduce como "Estaba hablando" y muestra una
acción en curso en el pasado.
Present Perfect (Presente Perfecto): Se usa para acciones que tienen relevancia
en el presente o acciones completadas recientemente. Por ejemplo, "I have
spoken" se traduce como "He hablado" y destaca la relevancia actual de la
acción.
Present Perfect Continuous (Presente Perfecto Continuo): Este tiempo verbal
indica acciones que comenzaron en el pasado y continúan en el presente. Por
ejemplo, "I have been speaking" se traduce como "He estado hablando" y
resalta la duración de la acción en curso.
Past Perfect (Pasado Perfecto): Se emplea para describir acciones completadas
antes de un punto específico en el pasado. Por ejemplo, "I had spoken" se
traduce como "Había hablado" y señala una acción anterior a otro evento en el
pasado.
Past Perfect Continuous (Pasado Perfecto Continuo): Este tiempo verbal se usa
para acciones en progreso que se completaron antes de un punto específico en
el pasado. Por ejemplo, "I had been speaking" se traduce como "Había estado
hablando" y describe una acción en curso antes de un evento pasado.
Will (Futuro Simple): Se utiliza para hacer predicciones, tomar decisiones
espontáneas, ofrecer promesas o indicar acciones futuras sin un plan previo. Por
ejemplo, "I will speak" se traduce como "Hablaré" y expresa una acción futura
sin planificación previa.
Going to (Futuro Próximo): Se emplea para expresar planes e intenciones
futuras basados en evidencia o intenciones personales. Por ejemplo, "I am going
to speak" se traduce como "Voy a hablar" y señala un plan futuro personal.
Present Simple with Future Meaning (Presente Simple con Sentido de Futuro):
Este uso del presente simple se refiere a eventos futuros programados, horarios
y planes fijos. Por ejemplo, "I fly tomorrow" se traduce como "Vuelo mañana" y
muestra un evento futuro programado.
Present Continuous with Future Meaning (Presente Continuo con Sentido de
Futuro): Se utiliza para describir arreglos personales o eventos futuros cercanos
planeados personalmente. Por ejemplo, "I am flying to Paris" se traduce como
"Voy a París" y destaca un arreglo personal en el futuro cercano.
Present Simple (Presente Simple):
I speak English fluently. (Hablo inglés con fluidez).
Present Continuous (Presente Continuo):
I am speaking with my friend on the phone. (Estoy hablando con mi amigo por
teléfono).
Past Simple (Pasado Simple):
Yesterday, I spoke to her about the project. (Ayer, le hablé sobre el proyecto).
Past Continuous (Pasado Continuo):
While I was speaking on the phone, the power went out. (Mientras hablaba por
teléfono, se fue la luz).
Present Perfect (Presente Perfecto):
I have spoken to the manager about your request. (He hablado con el gerente
sobre tu solicitud).
Present Perfect Continuous (Presente Perfecto Continuo):
I have been speaking for an hour, and my throat is sore. (He estado hablando
durante una hora, y tengo dolor de garganta).
Past Perfect (Pasado Perfecto):
By the time I arrived, they had spoken to the client. (Cuando llegué, habían
hablado con el cliente).
Past Perfect Continuous (Pasado Perfecto Continuo):
He had been speaking on the phone for hours before it died. (Había estado
hablando por teléfono durante horas antes de que se apagara).
Will (Futuro Simple):
I will speak at the conference next week. (Hablaré en la conferencia la próxima
semana).
Going to (Futuro Próximo):
I am going to speak with the team about the new project. (Voy a hablar con el
equipo sobre el nuevo proyecto).
Present Simple with Future Meaning (Presente Simple con Sentido de Futuro):
The flight departs at 7 AM tomorrow. (El vuelo sale a las 7 de la mañana
mañana).
Present Continuous with Future Meaning (Presente Continuo con Sentido de
Futuro):
I am flying to Paris next month for a business meeting. (Voy a París el próximo
mes para una reunión de negocios).
You might also like
- English File Final Tests, Int End Test BDocument6 pagesEnglish File Final Tests, Int End Test BAriadne_77780% (5)
- Frans Mind Map PDFDocument1 pageFrans Mind Map PDFAnastasya Zalsabilla Hermawan100% (1)
- Revolution in Poetic Language: by Julia KristevaDocument25 pagesRevolution in Poetic Language: by Julia KristevaMalik AtifNo ratings yet
- Tamil Self TaughtDocument102 pagesTamil Self TaughtÁgnesNagy100% (1)
- Gateway-B1 SB Unit7Document28 pagesGateway-B1 SB Unit7anisalera1507No ratings yet
- Tenses ResumenDocument8 pagesTenses ResumenMailen Lo Pilato BloisNo ratings yet
- Verbal Times Review: Structures Example When They Are UsedDocument4 pagesVerbal Times Review: Structures Example When They Are UsedDiego GonzalezNo ratings yet
- English TensesDocument1 pageEnglish TensesCarmen ChowNo ratings yet
- Present and Past TensesDocument3 pagesPresent and Past TensesAia NikolovaNo ratings yet
- All TensesDocument6 pagesAll TensesAndres ValdezNo ratings yet
- Resumen de InglésDocument8 pagesResumen de Inglésmapaus07No ratings yet
- Verb Forms Guide - A4Document1 pageVerb Forms Guide - A4Juan Miguel Ala TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Tenses TheoryDocument6 pagesTenses TheoryMỹ NhaNo ratings yet
- Tiempos VerbalesDocument6 pagesTiempos VerbalesMaria Ines RoqueNo ratings yet
- Verb TensesDocument35 pagesVerb TensesGlaiza VillaverNo ratings yet
- Past Forms TableDocument1 pagePast Forms TableДашаNo ratings yet
- Grammar Tenses Table PDFDocument2 pagesGrammar Tenses Table PDFDaniel MiuNo ratings yet
- 02 Summary of Tenses & Aspects of VerbsDocument10 pages02 Summary of Tenses & Aspects of Verbslasnfbf asigfnNo ratings yet
- Tense Structure Function ExampleDocument2 pagesTense Structure Function Examplenano yyNo ratings yet
- Simple Past Vs Past ContinuousDocument2 pagesSimple Past Vs Past ContinuousIltze RDNo ratings yet
- Tense Signal Words Use Form Ex Affirmative (+) Ex Negative (-) Ex Interrogative (?)Document4 pagesTense Signal Words Use Form Ex Affirmative (+) Ex Negative (-) Ex Interrogative (?)Yen RitaNo ratings yet
- Verb Tenses Present Future PastDocument6 pagesVerb Tenses Present Future PastcharguibachaghaNo ratings yet
- Ingles PAST CONTINUOUSDocument4 pagesIngles PAST CONTINUOUSDavid Robles HerreraNo ratings yet
- Explore The World of English TensesDocument13 pagesExplore The World of English Tensescaroline.helmiNo ratings yet
- The PassiveDocument12 pagesThe PassiveAngelica SantiNo ratings yet
- Grammar Tenses: PresentDocument3 pagesGrammar Tenses: PresentPaola FloresNo ratings yet
- Tenses ReviewDocument2 pagesTenses ReviewLyane FleuriaultNo ratings yet
- Tenses Chart WorkDocument2 pagesTenses Chart WorkvitaNo ratings yet
- Golden TensesDocument1 pageGolden TensesnajjarmohdNo ratings yet
- Verbs, Tense, Aspect, and Mood: By: Acmad Yani, S.SDocument19 pagesVerbs, Tense, Aspect, and Mood: By: Acmad Yani, S.SametgembulNo ratings yet
- Prsent's Página 2.drawioDocument1 pagePrsent's Página 2.drawioBrandon PerezNo ratings yet
- Chart of Verb Tenses PDFDocument3 pagesChart of Verb Tenses PDFTasnim MustafaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Tenses: by Oxtapianus TawarikDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Tenses: by Oxtapianus Tawariko.tawarikNo ratings yet
- Perfect or Compound TensesDocument3 pagesPerfect or Compound TensesZaidy GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Passive ENGDocument10 pagesPassive ENGjawess5666100% (2)
- Past Simple + Present Perfect SummaryDocument1 pagePast Simple + Present Perfect SummaryKagome HigurashiNo ratings yet
- Present Simple: Always, Ussualy.Document11 pagesPresent Simple: Always, Ussualy.epincarrNo ratings yet
- ELEC 100 Tenses of Verbs S V AgreementDocument39 pagesELEC 100 Tenses of Verbs S V AgreementPrincess Darlene GallardoNo ratings yet
- Past Continuous TenseDocument4 pagesPast Continuous TenseThet HtarNo ratings yet
- Grammar Map2Document1 pageGrammar Map2Patrcia CostaNo ratings yet
- PHRASAL VERBS 8oDocument4 pagesPHRASAL VERBS 8oVale OlveraNo ratings yet
- Present Simple Present Continuous Present Perfect: English TensesDocument1 pagePresent Simple Present Continuous Present Perfect: English TensesKhaled AdelNo ratings yet
- Ingles MacheDocument3 pagesIngles Machefeat08ronNo ratings yet
- The Present Perfect Progressive TenseDocument11 pagesThe Present Perfect Progressive Tensecather youngNo ratings yet
- The Verb Tenses and Their UsageDocument1 pageThe Verb Tenses and Their UsageJerick CruzNo ratings yet
- 7.1 (PDF AT Task 1) Tenses PDFDocument4 pages7.1 (PDF AT Task 1) Tenses PDFP A Wan SunarNo ratings yet
- Aptis BookDocument174 pagesAptis Bookdarkpechuga59No ratings yet
- Past Simple Present PerfectDocument1 pagePast Simple Present PerfectDaniela MartinsNo ratings yet
- Checklist Present PerfectDocument1 pageChecklist Present PerfectNurgul LadyNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument3 pagesTensesHihachi SarahNo ratings yet
- Perfect Tenses Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument2 pagesPerfect Tenses Cheat Sheet: by ViaAura SkyNo ratings yet
- (Grammar Booster) Verb Tenses ReviewDocument8 pages(Grammar Booster) Verb Tenses Reviewmarisa hirano taiboNo ratings yet
- Verb Tenses: Star TrekDocument8 pagesVerb Tenses: Star TrekodethNo ratings yet
- Verb Tenses Chart PDFDocument2 pagesVerb Tenses Chart PDFHanie Mesina-EloriagaNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet 2023Document6 pagesActivity Sheet 2023Glädje VRNo ratings yet
- Grammar + Sentence SkillDocument63 pagesGrammar + Sentence SkillKay Chan SothearaNo ratings yet
- Grammar BookletDocument40 pagesGrammar BookletSALDAÑA NAVARRETE ANDREANo ratings yet
- Verb TensesDocument20 pagesVerb Tensesvpetrovaa23No ratings yet
- Esquemas Gramática B2 @opomaestra - Enproceso PDFDocument35 pagesEsquemas Gramática B2 @opomaestra - Enproceso PDFLucia Garcia CoyNo ratings yet
- Ventures3e SB2 U08Document15 pagesVentures3e SB2 U08Doan TonyNo ratings yet
- KulitanDocument30 pagesKulitanJhn CarloNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Unseen Poetry ContinuedDocument37 pagesWeek 2 Unseen Poetry ContinuedHelen WallisNo ratings yet
- English 10 Third QuarterDocument28 pagesEnglish 10 Third QuarterEHdz D. JameraNo ratings yet
- Dual Award Programme Individual/Group Assignment Cover SheetDocument5 pagesDual Award Programme Individual/Group Assignment Cover SheetJuneid ImritNo ratings yet
- Class 6: Possessive Adjectives Review On Personal PronounsDocument46 pagesClass 6: Possessive Adjectives Review On Personal PronounsSmart AcademyNo ratings yet
- Mysticism Examined - Philosophical Inquiries Into Mysticism PDFDocument304 pagesMysticism Examined - Philosophical Inquiries Into Mysticism PDFWilliam Davidans SversuttiNo ratings yet
- Communication Skills Class 10 NotesDocument8 pagesCommunication Skills Class 10 Notesronitkhedekar2008No ratings yet
- GRAMMARDocument32 pagesGRAMMARnarendra mishraNo ratings yet
- GrapeSEED Pratom Unit 29 Test PARKDocument3 pagesGrapeSEED Pratom Unit 29 Test PARKRuthessa LeyrosNo ratings yet
- Bài Tập Thì Hiện Tại ĐơnDocument3 pagesBài Tập Thì Hiện Tại Đơnsylvester.powellNo ratings yet
- Reflections On Native Language Use in Adult ESL Classrooms: ResearchDocument11 pagesReflections On Native Language Use in Adult ESL Classrooms: ResearchJessieRealistaNo ratings yet
- English Tips 1 - Something, Nothing, Anything, Everything (Only English)Document4 pagesEnglish Tips 1 - Something, Nothing, Anything, Everything (Only English)Thainá TakemotoNo ratings yet
- Memo WritingDocument10 pagesMemo WritingMuhammad JunaidNo ratings yet
- An English Accent Free Sample PDFDocument13 pagesAn English Accent Free Sample PDFMarija DanilovicNo ratings yet
- ACR - Filipino Reading InterventionDocument3 pagesACR - Filipino Reading InterventionSamantha Jane AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- English Language Communication Skills Lab Manual: Name Roll No. Branch SectionDocument39 pagesEnglish Language Communication Skills Lab Manual: Name Roll No. Branch SectionSurendrakumar ThotaNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 - Yellowstone National ParkDocument2 pagesUnit 7 - Yellowstone National ParkDaniel ChioseauaNo ratings yet
- 1st Term Syllabus 2024-25Document9 pages1st Term Syllabus 2024-25hamzakhanshamsi100% (1)
- Step6 SummativediagnosticDocument4 pagesStep6 Summativediagnosticapi-329778412100% (2)
- Unit 3pdf 1666860611Document5 pagesUnit 3pdf 1666860611Miku kepoNo ratings yet
- Filipino 10: - Saint Mary's UniversityDocument33 pagesFilipino 10: - Saint Mary's UniversityVince ViayNo ratings yet
- Five Lectures On General Semantics KorzybskiDocument25 pagesFive Lectures On General Semantics KorzybskiLucas67% (3)
- 3 Kinds of Tests and Testing, Hughes 2003, AbridgedDocument12 pages3 Kinds of Tests and Testing, Hughes 2003, AbridgedLydia Siallagan83% (6)
- Journalism Jargon WordsDocument4 pagesJournalism Jargon WordszachyzakizadaNo ratings yet
- Thirty Theses On Interpretation (Richard Palmer)Document12 pagesThirty Theses On Interpretation (Richard Palmer)raccoonie81No ratings yet