Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Eosinophilic Granuloma Complex
Eosinophilic Granuloma Complex
Uploaded by
Andreea MayaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Eosinophilic Granuloma Complex
Eosinophilic Granuloma Complex
Uploaded by
Andreea MayaCopyright:
Available Formats
p: 07 3359 0777
p: 1300 A SKIN VET
e: dfa@live.com.au
w: www.skinvet.com.au
Eosinophilic granuloma complex KEY POINTS
(EGC)
EGC is a REACTION pattern NOT a specific
disease and may be triggered by a variety of
causes.
Eosinophilic plaques are caused by allergies
and are very itchy once present.
Eosinophilic granulomas and indolent ulcers
can be triggered by allergies but many are
NOT and the trigger remains unidentified
despite investigation.
Treating the initiating cause is the best
option. If it cannot be identified the
prognosis is guarded and a lifetime of
control may be required
Eosinophilic granuloma Three different patterns are
complex (EGC) is a reaction recognised: the indolent
pattern rather than a specific ulcer that affects the upper A number of different treatment options are
disease. This means that lip; the eosinophilic plaque available to settle the inflammatory pattern.
different primary diseases that is more common on the
may cause the same looking body and is extremely itchy,
lesions to develop. and the eosinophilic
granuloma.
Pathogenesis – What causes it?
The three entities have very different clinical signs, The eosinophilic granuloma (EG) and indolent ulcers
medical course and histological appearance. (IU) may be caused by allergies but many are not and
The eosinophilic plaque is a hypersensitivity reaction have no identifiable trigger despite extensive
(to flea, food or atopy), but the severity of lesion may investigation. EGs cause well-demarcated lesions on
not correlate between time of allergen stimulus and the caudal thigh or lateral truck. IU cause deep ulcers
presentation to clinic. It is generally seen in young on the upper lip that can become very large.
adults and develops that are VERY itchy once Commonly the cat is indifferent to the lesion despite
present. its size.
Clinical signs – What does it look like?
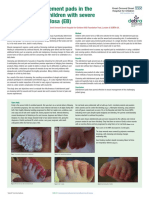
Eosinophilic plaques are hairless,
red lesions ranging from poorly
demarcated erosive lesions to
large well-demarcated glistening
plaques. A hallmark sign is that
they are very itchy and the cat will
lick at them constantly once
formed.
EGs are seen as pink, raised, non-
glistening lumps that may contain
white-yellow foci. They classically
have a linear orientation on the
Eosinophilic plaque Eosinophilic granuloma
caudal thighs, but may affect the
chin causing it to become
thickened. They may also affect
the oral cavity or hard palate,
which can lead to erosion of the
palatine artery and blood loss.
IUs cause erosion on the upper lip
that may affect one or both sides.
They can become very large and
destructive and are commonly
infected. Oral granuloma Indolent ulcer
Treatment
The lesions are commonly infected with bacteria,
which contributes to the severity of the signs. The
Before first step is often to treat with antibiotics to
eliminate this secondary complication. After that a
range of different anti-inflammatory medications
may be used to try and control the inflammatory
response.
Critically important however, is the identification of
the initial trigger and treatment of it. If the
underlying cause cannot be identified and
successfully treated, the long-term prognosis is
guarded and multiple treatment options may need
to used.
After
www.skinvet.com.au
You might also like
- Cathy O'Brien & Mark Philips - Trance Formation of America2Document224 pagesCathy O'Brien & Mark Philips - Trance Formation of America2bld200797% (35)
- Antonia LoLordo Pierre Gassendi and The Birth of Early Modern PhilosophyDocument295 pagesAntonia LoLordo Pierre Gassendi and The Birth of Early Modern PhilosophyAllison Kasandra100% (3)
- Discoid Lupus Erythematosus (DLE) : Key PointsDocument3 pagesDiscoid Lupus Erythematosus (DLE) : Key PointsamvprivateNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Management of Filler AdverDocument9 pagesDiagnosis and Management of Filler AdverTHIEN NGUYENNo ratings yet
- Lupus ErythematosusDocument3 pagesLupus ErythematosusNoviantiNo ratings yet
- Red Eye CheckDocument3 pagesRed Eye CheckkrishnaNo ratings yet
- Itchy Eyes Case Study: Eye Series - 17Document2 pagesItchy Eyes Case Study: Eye Series - 17nicoNo ratings yet
- OnlineMedEd Notes Dermatology 2021Document8 pagesOnlineMedEd Notes Dermatology 2021kirannhyd100% (1)
- Ulceras PrimariasDocument8 pagesUlceras PrimariaspeitoNo ratings yet
- Vitiligo: Clinical PracticeDocument10 pagesVitiligo: Clinical PracticeDORIS Z.No ratings yet
- Buckley Nuttall 2012 Feline Eosinophilic Granuloma Complex (Ities) Some Clinical ClarificationDocument11 pagesBuckley Nuttall 2012 Feline Eosinophilic Granuloma Complex (Ities) Some Clinical ClarificationHeppy FaniNo ratings yet
- NullDocument10 pagesNullapi-25914483No ratings yet
- Recognition and Interpretation of Skin 1Document6 pagesRecognition and Interpretation of Skin 1Veterinarios de ArgentinaNo ratings yet
- Autoeczematization A Strange Id Reaction of The SkinDocument4 pagesAutoeczematization A Strange Id Reaction of The Skincgs08No ratings yet
- 248-Article Text-614-1-10-20210714Document7 pages248-Article Text-614-1-10-20210714Abl ApriliaaNo ratings yet
- Sympathetic Uveitis/ Ophthalmia: PG CornerDocument4 pagesSympathetic Uveitis/ Ophthalmia: PG CornerVincent LivandyNo ratings yet
- Ncma 219 Finals Notes Gang Week 16 RawrDocument34 pagesNcma 219 Finals Notes Gang Week 16 RawrDILG IV-A RIZAL SBDPNo ratings yet
- By: Amit Chandanshive F.Y.M.PHARM.: Guide: Mrs. Vijaya BhogaleDocument39 pagesBy: Amit Chandanshive F.Y.M.PHARM.: Guide: Mrs. Vijaya Bhogaleirfan fadilahNo ratings yet
- Folleto Vitiligo InmunoDocument2 pagesFolleto Vitiligo InmunoGabriela UlloaNo ratings yet
- Pemphigus Vulgaris 1Document3 pagesPemphigus Vulgaris 1Yeni PuspitasariNo ratings yet
- Dentino Jurnal Kedokteran Gigi: Vol IV. No 1. Maret 2019Document4 pagesDentino Jurnal Kedokteran Gigi: Vol IV. No 1. Maret 2019Lidya DiandraNo ratings yet
- Background: Group A StreptococcusDocument4 pagesBackground: Group A StreptococcusCoral Srinivasa RamaluNo ratings yet
- NIH Public Access: Atopic Dermatitis in Children: Clinical Features, Pathophysiology and TreatmentDocument28 pagesNIH Public Access: Atopic Dermatitis in Children: Clinical Features, Pathophysiology and TreatmentzuliaahmadNo ratings yet
- De Bride MentDocument1 pageDe Bride Mentazhar naufaldiNo ratings yet
- Top 5 Causes of Nonblanching Skin LesionsDocument5 pagesTop 5 Causes of Nonblanching Skin LesionsCabinet VeterinarNo ratings yet
- Atopic DermatitisDocument14 pagesAtopic DermatitisityNo ratings yet
- Fauquert 2019@Document10 pagesFauquert 2019@Angel LimNo ratings yet
- Skin Manifestations of Systemic Disease: Key PointsDocument7 pagesSkin Manifestations of Systemic Disease: Key PointsJUAN DAVID RESTREPO MARINNo ratings yet
- FactSheetAD 101 Adults FINAL EditedDocument1 pageFactSheetAD 101 Adults FINAL EditedAidana AidarbekNo ratings yet
- Tutor 7 Blok 9 Skenario 3Document18 pagesTutor 7 Blok 9 Skenario 3Alifa AnatayaNo ratings yet
- ACT1FINALDUODocument6 pagesACT1FINALDUOhalisonhanzurezNo ratings yet
- NIH Public Access: Author ManuscriptDocument23 pagesNIH Public Access: Author ManuscriptNabila ApriyanNo ratings yet
- Blistering Skin ConditionsDocument6 pagesBlistering Skin ConditionsMoet Moet KhineNo ratings yet
- Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis - ClinicalKeyDocument21 pagesStevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis - ClinicalKeyMasithaNo ratings yet
- Preventive OphthalmologyDocument2 pagesPreventive Ophthalmologysarguss14100% (1)
- Actinic Chelitisa Case Report With Literature ReviewDocument2 pagesActinic Chelitisa Case Report With Literature ReviewkholisNo ratings yet
- Allergology International: Hironobu IhnDocument3 pagesAllergology International: Hironobu Ihncreyesdear3978No ratings yet
- Eyenet 10 2016 Corneal PerforationsDocument6 pagesEyenet 10 2016 Corneal Perforationsholly theressaNo ratings yet
- Leaflet Endoftalmitis - RS Mata SMECDocument2 pagesLeaflet Endoftalmitis - RS Mata SMECRS Mata SMEC GroupNo ratings yet
- Assessing Skin Disease in Children: TimingDocument5 pagesAssessing Skin Disease in Children: TimingdongNo ratings yet
- Autoimmune Mucocutaneous Blistering Diseases: Devaraju D. Vijeev Vasudevan Yashoda Devi B.K. Manjunath VDocument7 pagesAutoimmune Mucocutaneous Blistering Diseases: Devaraju D. Vijeev Vasudevan Yashoda Devi B.K. Manjunath VgadispinanditaNo ratings yet
- Targeting Ig EDocument15 pagesTargeting Ig ESisilia ZulkarnainNo ratings yet
- javma-javma.23.01.0002Document13 pagesjavma-javma.23.01.0002SabrinaNo ratings yet
- Epidermolysis AcquisitaDocument3 pagesEpidermolysis Acquisitaabdul.shakoor67No ratings yet
- Como Realizar Una Biopsia en Penfigoide OcularDocument5 pagesComo Realizar Una Biopsia en Penfigoide OcularMiguel HernandezNo ratings yet
- Sle and PerioDocument25 pagesSle and Perioapi-512415352No ratings yet
- Celulitis Odontogenica en Niños Caso Clinico 2Document6 pagesCelulitis Odontogenica en Niños Caso Clinico 2ana mariaNo ratings yet
- Allergic Rhinitis: Practical Management StrategiesDocument6 pagesAllergic Rhinitis: Practical Management StrategiesSravan KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Erythema Multiforme-Oral Variant: Case Report and Review of LiteratureDocument4 pagesErythema Multiforme-Oral Variant: Case Report and Review of LiteratureMarniati JohanNo ratings yet
- A Case of Lichen Amyloidosis With Complete Response To MesalamineDocument3 pagesA Case of Lichen Amyloidosis With Complete Response To MesalamineInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology100% (1)
- Thesis Statement On EczemaDocument7 pagesThesis Statement On Eczemafjgqdmne100% (2)
- JACOBDocument5 pagesJACOBFranzen PalermoNo ratings yet
- Prelims Topic 3 - Causes of DiseaseDocument5 pagesPrelims Topic 3 - Causes of DiseasepanizalesmariajoseNo ratings yet
- Atopic DermatitisDocument4 pagesAtopic DermatitisAditya MalikNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Management of Allergic Conjunctivitis 2018Document10 pagesDiagnosis and Management of Allergic Conjunctivitis 2018Ricardo Robles AlfaroNo ratings yet
- Jurnal AcneDocument10 pagesJurnal Acneasep budiyantoNo ratings yet
- CELLULITISSSDocument5 pagesCELLULITISSSLet BorlagdanNo ratings yet
- Corneal UlcersDocument9 pagesCorneal UlcersAlifa FaradillaNo ratings yet
- Hon 2005Document5 pagesHon 2005lenirizkiNo ratings yet
- Johnson2009Document13 pagesJohnson2009Anggia BungaNo ratings yet
- 5: Allergy and The Skin: Eczema and Chronic Urticaria: Mja Practice Essentials - AllergyDocument6 pages5: Allergy and The Skin: Eczema and Chronic Urticaria: Mja Practice Essentials - AllergyDavid PattersonNo ratings yet
- Eczema Remedies | How to Relieve Eczema With Diet & Natural RemediesFrom EverandEczema Remedies | How to Relieve Eczema With Diet & Natural RemediesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Cardiopet Interpretive Criteria CanineDocument1 pageCardiopet Interpretive Criteria CanineAndreea MayaNo ratings yet
- Bortolami Et Al 2012 Comparison of Two Formulations of Buprenorphine in Cats Administered by The Oral Transmucosal RouteDocument6 pagesBortolami Et Al 2012 Comparison of Two Formulations of Buprenorphine in Cats Administered by The Oral Transmucosal RouteAndreea MayaNo ratings yet
- Total t4 Testing Guide Cat UnifiedDocument2 pagesTotal t4 Testing Guide Cat UnifiedAndreea MayaNo ratings yet
- SodaPDF-converted-PANA LA PAGINA 436 High-Quality, High-Volume Spay and NeuterDocument860 pagesSodaPDF-converted-PANA LA PAGINA 436 High-Quality, High-Volume Spay and NeuterAndreea MayaNo ratings yet
- Smart Technology in Smart CityDocument37 pagesSmart Technology in Smart CityAnaTasya Dian Jr.100% (1)
- Presented By:-Shruti Agrawal (046) Ridhima Kapoor (040) Saloni Monga (043) Kunal Pokarna (024) Priyanka Ghosh Ashish JainDocument22 pagesPresented By:-Shruti Agrawal (046) Ridhima Kapoor (040) Saloni Monga (043) Kunal Pokarna (024) Priyanka Ghosh Ashish JainShruti AgrawalNo ratings yet
- SIR Rahat FinalDocument80 pagesSIR Rahat FinalZuhaib rauf khanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document2 pagesAssignment 2Nzan NkapNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Elementary Geometry For College Students 7th Edition Daniel C Alexander Geralyn M KoeberleinDocument35 pagesSolution Manual For Elementary Geometry For College Students 7th Edition Daniel C Alexander Geralyn M Koeberleinwoolfellinde4jive1100% (29)
- Function GeneratorDocument5 pagesFunction GeneratorvenkumaniNo ratings yet
- ZnetworkDocument368 pagesZnetworkSaurabh SinghNo ratings yet
- 2020 Can Pelvic Floor Muscle TrainingDocument2 pages2020 Can Pelvic Floor Muscle Trainingjuan pabloNo ratings yet
- KPK fsc2 ch02 - NotesDocument33 pagesKPK fsc2 ch02 - NotesShujahatNo ratings yet
- Flame ArresterDocument2 pagesFlame ArresterNicholas RiveraNo ratings yet
- Climatic-Chambers DS FDMDocument3 pagesClimatic-Chambers DS FDMconkhimocNo ratings yet
- Perdev PTDocument3 pagesPerdev PTCamylia CocjinNo ratings yet
- Iot Security FrameworkDocument14 pagesIot Security Frameworkboka987No ratings yet
- Syllabus: M. Tech. Energy Management (Regular)Document28 pagesSyllabus: M. Tech. Energy Management (Regular)Digvijay SinghNo ratings yet
- A Robust Framework For Malicious PDF Detection LeveragingDocument20 pagesA Robust Framework For Malicious PDF Detection LeveragingIdontspeakeNo ratings yet
- MCQ Question Answers Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 Motion in A PlaneDocument8 pagesMCQ Question Answers Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 Motion in A PlaneDisha Tripathi - 10-ENo ratings yet
- Management Information System: Bba LLB by The - Lawgical - WorldDocument15 pagesManagement Information System: Bba LLB by The - Lawgical - WorldK venkataiahNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2095263519300275 MainDocument13 pages1 s2.0 S2095263519300275 MainsafiradhaNo ratings yet
- MOEP - Public-Private Partnership Development in Thermal Power Generation, Thermal Power Department, Myanmar Electric Power EnterpriseDocument15 pagesMOEP - Public-Private Partnership Development in Thermal Power Generation, Thermal Power Department, Myanmar Electric Power EnterpriseTim DingNo ratings yet
- Online EarningDocument3 pagesOnline Earningwordwork373No ratings yet
- Thespaceofk Ahler Metrics: Brief Introduction To The Classical Problems in K Ahler GeometryDocument46 pagesThespaceofk Ahler Metrics: Brief Introduction To The Classical Problems in K Ahler GeometryEliacim VelezNo ratings yet
- Srinivasa RamanujanDocument17 pagesSrinivasa RamanujanNeelkamal RongaliNo ratings yet
- A Study On Students Buying Behavior Towards LaptopsDocument43 pagesA Study On Students Buying Behavior Towards LaptopsShashank Tripathi100% (3)
- Kilimo Cha MbogambogaDocument107 pagesKilimo Cha Mbogambogaazizin1994No ratings yet
- CP E80.50 EPSWindowsClient UserGuide enDocument36 pagesCP E80.50 EPSWindowsClient UserGuide enmbaezasotoNo ratings yet
- Contribution of Visionary Leadership, Lecturer Performance, and Academic CultureDocument17 pagesContribution of Visionary Leadership, Lecturer Performance, and Academic CulturedelaNo ratings yet
- Ibr CalculationsDocument9 pagesIbr CalculationsoperationmanagerNo ratings yet
- LinkedIn Powerpoint AnswersDocument2 pagesLinkedIn Powerpoint AnswersMarcel MatuschekNo ratings yet