Professional Documents
Culture Documents
01 What Managers Do and Leadership Styles
01 What Managers Do and Leadership Styles
Uploaded by
ronaldthemusictechfrogCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Sample PHD - DBA Research - ProposalDocument11 pagesSample PHD - DBA Research - ProposalKent Chee Yew MengNo ratings yet
- DocxDocument14 pagesDocxJh Junior100% (1)
- Pedals ParkDocument6 pagesPedals ParkVARUN SINGLA100% (1)
- Decision Without Bias ExplanDocument19 pagesDecision Without Bias ExplanSidiqa KamranNo ratings yet
- REVIEWER Engineering ManagementDocument4 pagesREVIEWER Engineering ManagementJohn Raphael JavierNo ratings yet
- Decision MakingDocument45 pagesDecision MakingNathalie Jewel MarcialNo ratings yet
- UCI 410 Topic 1 IntroductionDocument29 pagesUCI 410 Topic 1 IntroductionmutaniabridgitNo ratings yet
- Decision MakingDocument16 pagesDecision MakingManmeet SardaliaNo ratings yet
- Script For ManagementDocument62 pagesScript For ManagementLara Monique MateoNo ratings yet
- AgripreneursDocument112 pagesAgripreneurssameertupeNo ratings yet
- Applying Scientific Thinking To Management ProblemsDocument42 pagesApplying Scientific Thinking To Management ProblemsusmanivNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3: Managerial Decision Support KnowledgeDocument53 pagesChapter-3: Managerial Decision Support KnowledgeZelalem GashawNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Decision-MakingDocument28 pagesChapter 5 Decision-MakingRaj DudhatraNo ratings yet
- Decision MakingDocument18 pagesDecision MakingManmeet SardaliaNo ratings yet
- Management Skills in The Food IndustryDocument37 pagesManagement Skills in The Food IndustryRACHEL NAKALEMBENo ratings yet
- TKI153102 Teknik Pengambilan KeputusanDocument27 pagesTKI153102 Teknik Pengambilan Keputusandian fajrianaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Managers and You in The WorkplaceDocument239 pagesChapter 1: Managers and You in The Workplacehono.stepstudyNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 NotesDocument12 pagesUnit 2 NotesNitesh NemaNo ratings yet
- Managerial Decision Making - MBA-2017Document46 pagesManagerial Decision Making - MBA-2017Isuru KasthurirathneNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - ES 313Document8 pagesModule 2 - ES 313Cedric EnticoNo ratings yet
- Es5 Engg Management Chapter 2september 102021 Topics AssignmentsDocument3 pagesEs5 Engg Management Chapter 2september 102021 Topics AssignmentsJericko Allen ResusNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1.4 DecisionmakingDocument28 pagesChapter 1.4 DecisionmakingNikshith HegdeNo ratings yet
- The Manager Role in Decision MakingDocument2 pagesThe Manager Role in Decision MakingPriyanjali SainiNo ratings yet
- 0625 Kurtuhuz PDFDocument2 pages0625 Kurtuhuz PDFNimzo scene'sNo ratings yet
- ES 521 Engineering ManagementDocument48 pagesES 521 Engineering ManagementJoshua Pañares MalinaoNo ratings yet
- Module 1 NotesDocument3 pagesModule 1 Notesvhielgdrive1No ratings yet
- MGT230 Chapter 7 Decision Making - UpdatedDocument62 pagesMGT230 Chapter 7 Decision Making - UpdatedMaz MoozaNo ratings yet
- Empirical or Case Approach: Christian Lloyd BadilloDocument106 pagesEmpirical or Case Approach: Christian Lloyd BadilloPoppy MooreNo ratings yet
- Chapter-01 (Decision Macking)Document12 pagesChapter-01 (Decision Macking)devilbondhonNo ratings yet
- Engineering Management Decision MakingDocument15 pagesEngineering Management Decision MakingCassiel Cruz100% (1)
- Principles of Management: Management: Definitions, Roles & SkillsDocument61 pagesPrinciples of Management: Management: Definitions, Roles & SkillszahidmatloobNo ratings yet
- Decision Making and Management of ChangeDocument22 pagesDecision Making and Management of ChangeJayRavasaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Revision Notes On Management Decision MakingDocument11 pagesChapter 2 Revision Notes On Management Decision MakingdaramolamekaiahNo ratings yet
- Sy3 - 1 GU Practicing LeadershipDocument57 pagesSy3 - 1 GU Practicing LeadershipAmira NabilNo ratings yet
- MIdterm Business Logic 2Document12 pagesMIdterm Business Logic 2potatochps563No ratings yet
- Management: Management Is A Process That Unifies - 1-Manpower 2 - Money 3 - Materials 4 - Methods 5 - Machinery 6 - MarketDocument19 pagesManagement: Management Is A Process That Unifies - 1-Manpower 2 - Money 3 - Materials 4 - Methods 5 - Machinery 6 - Marketdharm veerNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - MGT400Document28 pagesTopic 1 - MGT400ifatie hahaNo ratings yet
- 1-Mgeffectiveness (Compatibility Mode)Document12 pages1-Mgeffectiveness (Compatibility Mode)emmy.anitagilbertNo ratings yet
- Industrial Organization and Management: REVIEWERDocument8 pagesIndustrial Organization and Management: REVIEWERGuian RomasantaNo ratings yet
- Mis and Decision Making ConceptsDocument2 pagesMis and Decision Making ConceptsArathy LalNo ratings yet
- Decision Making in Engineering ManagemenDocument10 pagesDecision Making in Engineering ManagemenVJ CarbonellNo ratings yet
- DAB - Lesson 01 (SE) - Part 1Document14 pagesDAB - Lesson 01 (SE) - Part 1thanh vu ducNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 RevisionDocument7 pagesUnit 2 RevisionphippsharmonyNo ratings yet
- Liberty Newspaper - Case Study Explained: ST NDDocument2 pagesLiberty Newspaper - Case Study Explained: ST NDAdrian BenczeNo ratings yet
- Developing Policy and Strategy: There Are Also Some Downfalls To The Top-Down ApproachDocument2 pagesDeveloping Policy and Strategy: There Are Also Some Downfalls To The Top-Down ApproachJerico ManaloNo ratings yet
- Chap 3 PP handoutsDocument10 pagesChap 3 PP handoutshmtrd95No ratings yet
- Engineering Process Education PresentationDocument29 pagesEngineering Process Education PresentationFall KeiNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 mgt162Document20 pagesCHAPTER 1 mgt162Wani HaziqahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document31 pagesChapter 1Anh Thư NgôNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 UiTM MGTDocument37 pagesChapter 3 UiTM MGTclepetproNo ratings yet
- 3106 1638170348452 CC6052 Lecture wk04 DecisionsDocument56 pages3106 1638170348452 CC6052 Lecture wk04 DecisionsMr GamerNo ratings yet
- Decision-Making Eric B BernardoDocument35 pagesDecision-Making Eric B BernardoangeloNo ratings yet
- Ricky PolicyDocument11 pagesRicky Policyrickyedi26No ratings yet
- Managerial Decision MakingDocument4 pagesManagerial Decision MakingNishat NabilaNo ratings yet
- Decision Making ProcessDocument18 pagesDecision Making ProcessKafonyi JohnNo ratings yet
- Managerial Decision Making Report XXXDocument79 pagesManagerial Decision Making Report XXXNichole John ErnietaNo ratings yet
- Effective Decision Making in ManagementDocument2 pagesEffective Decision Making in ManagementInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Decision Making Concepts TodayDocument3 pagesDecision Making Concepts TodayJai GaneshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Introduction MGTDocument18 pagesChapter 1-Introduction MGTIra LyanaNo ratings yet
- Decision Making in An International ContextDocument21 pagesDecision Making in An International ContextDanielaZapataRendonNo ratings yet
- Module 1 INTRODUCTION TO PRINCIPLES OF MGTDocument27 pagesModule 1 INTRODUCTION TO PRINCIPLES OF MGTjuneid al jarwanNo ratings yet
- 1 Intro To MTDocument24 pages1 Intro To MTlanar78505No ratings yet
- 6 - Political & Legal EnvironmentDocument3 pages6 - Political & Legal EnvironmentronaldthemusictechfrogNo ratings yet
- RESEARCH TASK Laws Affecting BusinessDocument2 pagesRESEARCH TASK Laws Affecting BusinessronaldthemusictechfrogNo ratings yet
- 07 Analysing HR PerformanceDocument4 pages07 Analysing HR PerformanceronaldthemusictechfrogNo ratings yet
- 05 Managing The Human Resource FlowDocument4 pages05 Managing The Human Resource FlowronaldthemusictechfrogNo ratings yet
- 06 Improving Employer-Employee RelationsDocument3 pages06 Improving Employer-Employee RelationsronaldthemusictechfrogNo ratings yet
- 02 Decision TreesDocument4 pages02 Decision TreesronaldthemusictechfrogNo ratings yet
- 03 Motivation and Engagement in PracticeDocument5 pages03 Motivation and Engagement in PracticeronaldthemusictechfrogNo ratings yet
- 01 The Nature and Purpose of BusinessesDocument1 page01 The Nature and Purpose of BusinessesronaldthemusictechfrogNo ratings yet
- 02 Business FormsDocument2 pages02 Business FormsronaldthemusictechfrogNo ratings yet
- Diluted Earnings Per ShareDocument2 pagesDiluted Earnings Per ShareGletzmar IgcasamaNo ratings yet
- Progress Test 1Document12 pagesProgress Test 1Alaa eldeepNo ratings yet
- Zto F1 PDFDocument960 pagesZto F1 PDFIshaan MittalNo ratings yet
- Real Options TheoryDocument19 pagesReal Options TheorySaurabh Audichya100% (1)
- Financial Statement AnalysisDocument26 pagesFinancial Statement AnalysisTawsiq Asef MahiNo ratings yet
- Segmentation & Positioning Analysis (Frooti)Document11 pagesSegmentation & Positioning Analysis (Frooti)debrizz50% (2)
- M&R Roadmap Practice Questions Pillar 1Document5 pagesM&R Roadmap Practice Questions Pillar 1Ahmed elsayed ussNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 SI WorksheetDocument5 pagesChapter 4 SI WorksheetFoster PerryNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document50 pagesLecture 3Mehak SinghNo ratings yet
- 2023 Guide To Startup FundingDocument47 pages2023 Guide To Startup FundingssdipaNo ratings yet
- Performance Analysis of Hul - v1 27112020Document56 pagesPerformance Analysis of Hul - v1 27112020ippiligourisankar5442No ratings yet
- 5 Marketing MixDocument58 pages5 Marketing MixFranze CastilloNo ratings yet
- Delivering and Performing Services Through Employees and CustomersDocument35 pagesDelivering and Performing Services Through Employees and Customersneha ugyal100% (1)
- FM 402 - ReportDocument5 pagesFM 402 - Reportdebaleena.chatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Xii - 2022-23 - Acc - RaipurDocument148 pagesXii - 2022-23 - Acc - RaipurNavya100% (1)
- Sap Fico Mock Test IDocument4 pagesSap Fico Mock Test ISyed Sagheer AbbasNo ratings yet
- Pricing StrategyDocument13 pagesPricing Strategyiqra javedNo ratings yet
- Afs FinalDocument21 pagesAfs FinalAjit ShindeNo ratings yet
- Gaither Capitulo 14Document48 pagesGaither Capitulo 14leandrop7No ratings yet
- 026.provision For Bad Debts PDFDocument5 pages026.provision For Bad Debts PDFAbdo AbdalatifNo ratings yet
- PPT On NpaDocument20 pagesPPT On NpaNoor Preet KaurNo ratings yet
- Eco401 Total QuizDocument127 pagesEco401 Total QuizSyed Faisal Bukhari67% (3)
- Business Model Canvas: Customer SegmentsDocument6 pagesBusiness Model Canvas: Customer SegmentsValentino LunardiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02 - Corporate EntrepreneurshipDocument11 pagesChapter 02 - Corporate EntrepreneurshipFadli RushNo ratings yet
- Nas 2 PDFDocument10 pagesNas 2 PDFsandeep gyawaliNo ratings yet
- MIS10E Testbank CH09Document19 pagesMIS10E Testbank CH09Bilal Shakil Qureshi50% (2)
- PHPR 7 CP TPDocument16 pagesPHPR 7 CP TPShivansh JaiswalNo ratings yet
01 What Managers Do and Leadership Styles
01 What Managers Do and Leadership Styles
Uploaded by
ronaldthemusictechfrogOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
01 What Managers Do and Leadership Styles
01 What Managers Do and Leadership Styles
Uploaded by
ronaldthemusictechfrogCopyright:
Available Formats
A-level Business notes
Unit 2: Management, leadership and decision making
What managers do
MAIN ROLE OF A MANAGER:
Set aims and objectives
ADDITIONAL ROLES OF A MANAGER:
Analyse data
Lead
Make decisions
Review business performance
Organisation and planning
Delegation
LEADERSHIP STYLES:
Autocratic:
Strict, direct everything, assertive, strongheaded
Authoritarian, do not consider subordinate viewpoints.
Democratic:
Considers worker’s views
Make decision based on those views
Paternalistic:
Like a father figure
Explains decision / persuade you into it
Still make the decisions
Laissez-faire:
Laid back, let workers get on with their job.
FACTORS THAT AFFECT MANAGEMENT:
INTERNAL EXTERNAL (PESTEL)
Urgency of task Political
Skill and motivation Economic
Size of workforce Social
Type of task Technological
Environmental
Legal
KEY TERMINOLOGY:
Subordinate – worker
Opportunity cost – The next forgone alternative
LEADERSHIP MODELS:
TANNENBAUM SCHMIDT CONTINUUM:
100% FROM 0 – 100:
Tells – All authority by manager (Autocratic)
Authority by
manager Sells – Manager makes decisions then sells it to staff
Suggest – Manager makes suggestions and
subordinates respond to them
Consult – Manager consults subordinates before
Team implementing a decision
participation Joins – Allows for more involvement from staff
Delegates – Passes on roles and responsibilities
0% Abdicates – The ultimate Laissez-faire
BLAKE MOUTON GRID:
Team style – Has high concern for workers and production.
(Best style of management)
Country club – More concerned about the people than the task
(can be motivational but can also lead to workforce being less
productive)
Produce or perish – High concern for the task but no concern for
the people. This can be good in times of crisis but can be
demotivational and cause a lower quality “rushed” product.
Impoverished – Low concern for people and the task. This is the
worst type of management.
Middle of the road – In the middle- has elements of each.
_______________________________________________________________________________________________
*Always refer to corporate objectives
STRENGTHS OF BLAKE’S GRID: STRENGTHS OF SCHMIDT’S CONTINUUM:
Measures two factors: Concern for people and Gives detail about the range of approaches between
performance. the two extremes (autocratic vs. laissez-faire).
Schmidt’s continuum only measures the people aspect.
Blake’s grid is more widely known than the continuum The continuum gives a basis for action as well as
as it shows some leader’s sole drive for results. analysis (i.e. how to become more democratic).
The labels (such as ‘country club’) make it easy to Helps leaders measure their own approach and shows
visualise and remember the type of person. that ‘tell’ is an extreme approach to management.
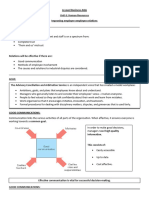
HOW DECISIONS ARE MADE:
There are two types of decision makers:
Scientific
Intuitive Business
objectives
*Scientific decision making is more popular among leaders where it is possible.
SCIENTIFIC:
Strategic
Economic Finance
Scientific decision makers follow a process to make a decision:
conditions Decision- and HR
making
Set objectives Expected
competitor
actions
Review decision Collect data
Scientific
Decision-
making
Implement
Cycle Analyse data
decision
Make decision
INTUITIVE:
Other managers do not follow this process and make decisions based on:
Gut instinct
The situation in front of them (EG: crisis)
A decision involves an opportunity cost. The official definition is: “The next forgone alternative”.
This actually means that in a choice, you choose one route and sacrifice the other in order to achieve your task.
IMPLICATIONS OF MAKING A DECISION: Mission Objectives
Influences on decisions Resources Ethics
Every decision has the following three elements:
External environment
Risk Reward Uncertainty
RISK – Financial loss, lack of security, business failure REWARD – Profit, success, independence
You might also like
- Sample PHD - DBA Research - ProposalDocument11 pagesSample PHD - DBA Research - ProposalKent Chee Yew MengNo ratings yet
- DocxDocument14 pagesDocxJh Junior100% (1)
- Pedals ParkDocument6 pagesPedals ParkVARUN SINGLA100% (1)
- Decision Without Bias ExplanDocument19 pagesDecision Without Bias ExplanSidiqa KamranNo ratings yet
- REVIEWER Engineering ManagementDocument4 pagesREVIEWER Engineering ManagementJohn Raphael JavierNo ratings yet
- Decision MakingDocument45 pagesDecision MakingNathalie Jewel MarcialNo ratings yet
- UCI 410 Topic 1 IntroductionDocument29 pagesUCI 410 Topic 1 IntroductionmutaniabridgitNo ratings yet
- Decision MakingDocument16 pagesDecision MakingManmeet SardaliaNo ratings yet
- Script For ManagementDocument62 pagesScript For ManagementLara Monique MateoNo ratings yet
- AgripreneursDocument112 pagesAgripreneurssameertupeNo ratings yet
- Applying Scientific Thinking To Management ProblemsDocument42 pagesApplying Scientific Thinking To Management ProblemsusmanivNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3: Managerial Decision Support KnowledgeDocument53 pagesChapter-3: Managerial Decision Support KnowledgeZelalem GashawNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Decision-MakingDocument28 pagesChapter 5 Decision-MakingRaj DudhatraNo ratings yet
- Decision MakingDocument18 pagesDecision MakingManmeet SardaliaNo ratings yet
- Management Skills in The Food IndustryDocument37 pagesManagement Skills in The Food IndustryRACHEL NAKALEMBENo ratings yet
- TKI153102 Teknik Pengambilan KeputusanDocument27 pagesTKI153102 Teknik Pengambilan Keputusandian fajrianaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Managers and You in The WorkplaceDocument239 pagesChapter 1: Managers and You in The Workplacehono.stepstudyNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 NotesDocument12 pagesUnit 2 NotesNitesh NemaNo ratings yet
- Managerial Decision Making - MBA-2017Document46 pagesManagerial Decision Making - MBA-2017Isuru KasthurirathneNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - ES 313Document8 pagesModule 2 - ES 313Cedric EnticoNo ratings yet
- Es5 Engg Management Chapter 2september 102021 Topics AssignmentsDocument3 pagesEs5 Engg Management Chapter 2september 102021 Topics AssignmentsJericko Allen ResusNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1.4 DecisionmakingDocument28 pagesChapter 1.4 DecisionmakingNikshith HegdeNo ratings yet
- The Manager Role in Decision MakingDocument2 pagesThe Manager Role in Decision MakingPriyanjali SainiNo ratings yet
- 0625 Kurtuhuz PDFDocument2 pages0625 Kurtuhuz PDFNimzo scene'sNo ratings yet
- ES 521 Engineering ManagementDocument48 pagesES 521 Engineering ManagementJoshua Pañares MalinaoNo ratings yet
- Module 1 NotesDocument3 pagesModule 1 Notesvhielgdrive1No ratings yet
- MGT230 Chapter 7 Decision Making - UpdatedDocument62 pagesMGT230 Chapter 7 Decision Making - UpdatedMaz MoozaNo ratings yet
- Empirical or Case Approach: Christian Lloyd BadilloDocument106 pagesEmpirical or Case Approach: Christian Lloyd BadilloPoppy MooreNo ratings yet
- Chapter-01 (Decision Macking)Document12 pagesChapter-01 (Decision Macking)devilbondhonNo ratings yet
- Engineering Management Decision MakingDocument15 pagesEngineering Management Decision MakingCassiel Cruz100% (1)
- Principles of Management: Management: Definitions, Roles & SkillsDocument61 pagesPrinciples of Management: Management: Definitions, Roles & SkillszahidmatloobNo ratings yet
- Decision Making and Management of ChangeDocument22 pagesDecision Making and Management of ChangeJayRavasaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Revision Notes On Management Decision MakingDocument11 pagesChapter 2 Revision Notes On Management Decision MakingdaramolamekaiahNo ratings yet
- Sy3 - 1 GU Practicing LeadershipDocument57 pagesSy3 - 1 GU Practicing LeadershipAmira NabilNo ratings yet
- MIdterm Business Logic 2Document12 pagesMIdterm Business Logic 2potatochps563No ratings yet
- Management: Management Is A Process That Unifies - 1-Manpower 2 - Money 3 - Materials 4 - Methods 5 - Machinery 6 - MarketDocument19 pagesManagement: Management Is A Process That Unifies - 1-Manpower 2 - Money 3 - Materials 4 - Methods 5 - Machinery 6 - Marketdharm veerNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - MGT400Document28 pagesTopic 1 - MGT400ifatie hahaNo ratings yet
- 1-Mgeffectiveness (Compatibility Mode)Document12 pages1-Mgeffectiveness (Compatibility Mode)emmy.anitagilbertNo ratings yet
- Industrial Organization and Management: REVIEWERDocument8 pagesIndustrial Organization and Management: REVIEWERGuian RomasantaNo ratings yet
- Mis and Decision Making ConceptsDocument2 pagesMis and Decision Making ConceptsArathy LalNo ratings yet
- Decision Making in Engineering ManagemenDocument10 pagesDecision Making in Engineering ManagemenVJ CarbonellNo ratings yet
- DAB - Lesson 01 (SE) - Part 1Document14 pagesDAB - Lesson 01 (SE) - Part 1thanh vu ducNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 RevisionDocument7 pagesUnit 2 RevisionphippsharmonyNo ratings yet
- Liberty Newspaper - Case Study Explained: ST NDDocument2 pagesLiberty Newspaper - Case Study Explained: ST NDAdrian BenczeNo ratings yet
- Developing Policy and Strategy: There Are Also Some Downfalls To The Top-Down ApproachDocument2 pagesDeveloping Policy and Strategy: There Are Also Some Downfalls To The Top-Down ApproachJerico ManaloNo ratings yet
- Chap 3 PP handoutsDocument10 pagesChap 3 PP handoutshmtrd95No ratings yet
- Engineering Process Education PresentationDocument29 pagesEngineering Process Education PresentationFall KeiNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 mgt162Document20 pagesCHAPTER 1 mgt162Wani HaziqahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document31 pagesChapter 1Anh Thư NgôNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 UiTM MGTDocument37 pagesChapter 3 UiTM MGTclepetproNo ratings yet
- 3106 1638170348452 CC6052 Lecture wk04 DecisionsDocument56 pages3106 1638170348452 CC6052 Lecture wk04 DecisionsMr GamerNo ratings yet
- Decision-Making Eric B BernardoDocument35 pagesDecision-Making Eric B BernardoangeloNo ratings yet
- Ricky PolicyDocument11 pagesRicky Policyrickyedi26No ratings yet
- Managerial Decision MakingDocument4 pagesManagerial Decision MakingNishat NabilaNo ratings yet
- Decision Making ProcessDocument18 pagesDecision Making ProcessKafonyi JohnNo ratings yet
- Managerial Decision Making Report XXXDocument79 pagesManagerial Decision Making Report XXXNichole John ErnietaNo ratings yet
- Effective Decision Making in ManagementDocument2 pagesEffective Decision Making in ManagementInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Decision Making Concepts TodayDocument3 pagesDecision Making Concepts TodayJai GaneshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Introduction MGTDocument18 pagesChapter 1-Introduction MGTIra LyanaNo ratings yet
- Decision Making in An International ContextDocument21 pagesDecision Making in An International ContextDanielaZapataRendonNo ratings yet
- Module 1 INTRODUCTION TO PRINCIPLES OF MGTDocument27 pagesModule 1 INTRODUCTION TO PRINCIPLES OF MGTjuneid al jarwanNo ratings yet
- 1 Intro To MTDocument24 pages1 Intro To MTlanar78505No ratings yet
- 6 - Political & Legal EnvironmentDocument3 pages6 - Political & Legal EnvironmentronaldthemusictechfrogNo ratings yet
- RESEARCH TASK Laws Affecting BusinessDocument2 pagesRESEARCH TASK Laws Affecting BusinessronaldthemusictechfrogNo ratings yet
- 07 Analysing HR PerformanceDocument4 pages07 Analysing HR PerformanceronaldthemusictechfrogNo ratings yet
- 05 Managing The Human Resource FlowDocument4 pages05 Managing The Human Resource FlowronaldthemusictechfrogNo ratings yet
- 06 Improving Employer-Employee RelationsDocument3 pages06 Improving Employer-Employee RelationsronaldthemusictechfrogNo ratings yet
- 02 Decision TreesDocument4 pages02 Decision TreesronaldthemusictechfrogNo ratings yet
- 03 Motivation and Engagement in PracticeDocument5 pages03 Motivation and Engagement in PracticeronaldthemusictechfrogNo ratings yet
- 01 The Nature and Purpose of BusinessesDocument1 page01 The Nature and Purpose of BusinessesronaldthemusictechfrogNo ratings yet
- 02 Business FormsDocument2 pages02 Business FormsronaldthemusictechfrogNo ratings yet
- Diluted Earnings Per ShareDocument2 pagesDiluted Earnings Per ShareGletzmar IgcasamaNo ratings yet
- Progress Test 1Document12 pagesProgress Test 1Alaa eldeepNo ratings yet
- Zto F1 PDFDocument960 pagesZto F1 PDFIshaan MittalNo ratings yet
- Real Options TheoryDocument19 pagesReal Options TheorySaurabh Audichya100% (1)
- Financial Statement AnalysisDocument26 pagesFinancial Statement AnalysisTawsiq Asef MahiNo ratings yet
- Segmentation & Positioning Analysis (Frooti)Document11 pagesSegmentation & Positioning Analysis (Frooti)debrizz50% (2)
- M&R Roadmap Practice Questions Pillar 1Document5 pagesM&R Roadmap Practice Questions Pillar 1Ahmed elsayed ussNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 SI WorksheetDocument5 pagesChapter 4 SI WorksheetFoster PerryNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document50 pagesLecture 3Mehak SinghNo ratings yet
- 2023 Guide To Startup FundingDocument47 pages2023 Guide To Startup FundingssdipaNo ratings yet
- Performance Analysis of Hul - v1 27112020Document56 pagesPerformance Analysis of Hul - v1 27112020ippiligourisankar5442No ratings yet
- 5 Marketing MixDocument58 pages5 Marketing MixFranze CastilloNo ratings yet
- Delivering and Performing Services Through Employees and CustomersDocument35 pagesDelivering and Performing Services Through Employees and Customersneha ugyal100% (1)
- FM 402 - ReportDocument5 pagesFM 402 - Reportdebaleena.chatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Xii - 2022-23 - Acc - RaipurDocument148 pagesXii - 2022-23 - Acc - RaipurNavya100% (1)
- Sap Fico Mock Test IDocument4 pagesSap Fico Mock Test ISyed Sagheer AbbasNo ratings yet
- Pricing StrategyDocument13 pagesPricing Strategyiqra javedNo ratings yet
- Afs FinalDocument21 pagesAfs FinalAjit ShindeNo ratings yet
- Gaither Capitulo 14Document48 pagesGaither Capitulo 14leandrop7No ratings yet
- 026.provision For Bad Debts PDFDocument5 pages026.provision For Bad Debts PDFAbdo AbdalatifNo ratings yet
- PPT On NpaDocument20 pagesPPT On NpaNoor Preet KaurNo ratings yet
- Eco401 Total QuizDocument127 pagesEco401 Total QuizSyed Faisal Bukhari67% (3)
- Business Model Canvas: Customer SegmentsDocument6 pagesBusiness Model Canvas: Customer SegmentsValentino LunardiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02 - Corporate EntrepreneurshipDocument11 pagesChapter 02 - Corporate EntrepreneurshipFadli RushNo ratings yet
- Nas 2 PDFDocument10 pagesNas 2 PDFsandeep gyawaliNo ratings yet
- MIS10E Testbank CH09Document19 pagesMIS10E Testbank CH09Bilal Shakil Qureshi50% (2)
- PHPR 7 CP TPDocument16 pagesPHPR 7 CP TPShivansh JaiswalNo ratings yet