Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cap HR Checklist
Cap HR Checklist
Uploaded by
Fatima Kasim MacarongonOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cap HR Checklist
Cap HR Checklist
Uploaded by
Fatima Kasim MacarongonCopyright:
Available Formats
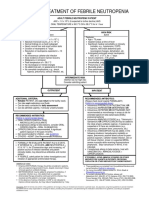
CAP-HIGH RISK: FIRST LINE THERAPY
Non-pseudomonal Beta-lactam
HISTORY antibiotic
HISTORY of COUGH within the past 24 Ampicillin-sulbactam 1.5–3 g
hours or less than 2 weeks IV every 6 h
Unstable decompensated comorbid OR
condition Cefotaxime 1–2 g IV every 8 h
UNCONTROLLED DIABETES OR
MELLITUS Ceftriaxone 1–2 g IV daily
ACTIVE MALIGNANCIES PLUS
Macrolide
NEUROLOGIC DISEASE IN
EVOLUTION Azithromycin 500 mg PO/IV
CONGESTIVE HEART daily
OR
FAILURE (CHF) CLASS II-IV
Erythromycin 500 mg PO
UNSTABLE CORONARY
every 6 hours
ARTERY DISEASE
OR
(+) with suspected aspiration
Clarithromycin 500 mg PO
(+/-) Severe sepsis and Septic shock twice daily
PHYSICAL EXAM ALTERNATIVE THERAPY
Abnormal VITAL SIGNS: Non-pseudomonal Beta-lactam
Tachypnea (RR >30/min) antibiotic
PLUS
Tachycardia (HR>125/min)
Respiratory fluoroquinolone*
Fever (Temp>37.8)
Levofloxacin 750 mg PO/IV daily
SBP <90 mmHg
OR
DBP ≤60 mmHg Moxifloxacin 400 mg PO/IV daily
Temp ≤36 °C or ≥40 °C * given as 1 hour IV infusion
(+) Altered mental state of
acute onset
One ABNORMAL CHEST FINDINGS:
DIMINISHED BREATH
SOUNDS
RHONCHI
CRACKLES
WHEEZES
DIAGNOSTICS:
CXR
BLOOD CULTURE
GS/CS (RESPIRATORY SPECIMEN)
ABG
*NO Improvement after 72 hours of treatment, patient
should be reassessed for possible resistance to the
antibiotics or “for presence of other pathogens such as
M. tuberculosis, viruses, parasites or fungi”
MANAGEMENT:
(-/+) need for mechanical ventilator
LENGTH OF STAY
> 4 days confinement, at least 3 days
IV antibiotics
The following antibiotics should be started for empiric
treatment of patients with high risk CAP without MDRO
infection:
You might also like
- Nursing Care Plan For Risk For Aspiration NCPDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For Risk For Aspiration NCPaudreyNo ratings yet
- CHN Action PlanDocument9 pagesCHN Action PlanseeyarahNo ratings yet
- BTUH Antibiotics Pocket Guidelines For Prescribing in Adults 2017 2018Document2 pagesBTUH Antibiotics Pocket Guidelines For Prescribing in Adults 2017 2018Corry ApriliaNo ratings yet
- 8.11.08 Davis-Hovda. TB PleurisyDocument13 pages8.11.08 Davis-Hovda. TB Pleurisyawaniedream8391No ratings yet
- Hpei PneumgdlnsDocument7 pagesHpei PneumgdlnsNurbayanti HermanNo ratings yet
- Protcolo NacDocument2 pagesProtcolo NacJdmp Lopez MorenoNo ratings yet
- Outpatient Cheat CodeDocument18 pagesOutpatient Cheat CodeElaine IllescasNo ratings yet
- HD ComplicationsDocument1 pageHD ComplicationsTyler VintNo ratings yet
- CNS: Ent:: Review Antibiotic Therapy Daily - Can You: Stop? Switch? Simplify? or State Duration?Document1 pageCNS: Ent:: Review Antibiotic Therapy Daily - Can You: Stop? Switch? Simplify? or State Duration?Fitri RachmadaniNo ratings yet
- Health PEI: Provincial Antibiotic Advisory Team Empiric Antibiotic Treatment Guidelines For Sepsis Syndromes in AdultsDocument10 pagesHealth PEI: Provincial Antibiotic Advisory Team Empiric Antibiotic Treatment Guidelines For Sepsis Syndromes in AdultsFarmasi RSUD Kramat JatiNo ratings yet
- Community Acquired Pneumonia in AdultsDocument5 pagesCommunity Acquired Pneumonia in AdultsEspie FerrerNo ratings yet
- Ckhs Empiric Antibiotic Guidance For Adult Pneumonia.2016Document3 pagesCkhs Empiric Antibiotic Guidance For Adult Pneumonia.2016surenvishvaNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic RegimetotreatpneumoniaDocument1 pageAntibiotic RegimetotreatpneumoniaNousheen ThakurNo ratings yet
- NH Protocol For Covid Management FinalDocument7 pagesNH Protocol For Covid Management FinalhoneyworksNo ratings yet
- SHC ABSSSI ED CDU GuidelineDocument4 pagesSHC ABSSSI ED CDU GuidelineHector Sanchez LacayoNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Classification Mechanism of Action Indication ContraindicationsDocument4 pagesDrug Name Classification Mechanism of Action Indication ContraindicationsAthena SaturdayNo ratings yet
- Wound Infections: Common PathogensDocument1 pageWound Infections: Common PathogensAnonymous KGxzow5zxhNo ratings yet
- PcolDocument17 pagesPcolThea JulianaNo ratings yet
- Students Training Unit College of Pharmacy Taif University Kingdome of Saudi Arabia 2020-2021Document13 pagesStudents Training Unit College of Pharmacy Taif University Kingdome of Saudi Arabia 2020-2021Fahad AlosaimiNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Treatment Guidelines For Common Infections: June 2016Document56 pagesAntimicrobial Treatment Guidelines For Common Infections: June 2016mario x.p.de araujoNo ratings yet
- Anti-Tubercular DrugsDocument11 pagesAnti-Tubercular DrugsAudrey Beatrice ReyesNo ratings yet
- MedimapDocument2 pagesMedimapKristian Dave DivaNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Treatment Guidelines For Common Infections enDocument111 pagesAntimicrobial Treatment Guidelines For Common Infections enRoofia VahedianNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Treatment Algorithm With Addendum For Aspiration 2015-2016.01.19Document2 pagesPneumonia Treatment Algorithm With Addendum For Aspiration 2015-2016.01.19Irsalina TriastutikNo ratings yet
- VTE Prophylaxis PROTOCOL V1.2 Withforms 31 Dec 2023Document19 pagesVTE Prophylaxis PROTOCOL V1.2 Withforms 31 Dec 2023hatem newishyNo ratings yet
- VTE - Prophylaxis - PROTOCOL - V1.1 - With Forms - 07 - Dec - 2023Document20 pagesVTE - Prophylaxis - PROTOCOL - V1.1 - With Forms - 07 - Dec - 2023hatem newishyNo ratings yet
- MAPPING PALEM 1 (TB) - 03 Mei 2021: Prof - Dr.dr.H.Muh - Amin, SP.P (K)Document5 pagesMAPPING PALEM 1 (TB) - 03 Mei 2021: Prof - Dr.dr.H.Muh - Amin, SP.P (K)Yudi ApriyantoNo ratings yet
- Adult Sepsis Order SetDocument3 pagesAdult Sepsis Order SetYoussef MokdadNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug Studyuntoned100% (1)
- Common DrugsDocument15 pagesCommon DrugsKate Penelope DalidNo ratings yet
- Empiric Antibiotic ListDocument2 pagesEmpiric Antibiotic ListpasswordNo ratings yet
- Vancomycin DRUGSTUDYDocument3 pagesVancomycin DRUGSTUDYEmagra AzilNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary SyndromeDocument1 pageAcute Coronary SyndromeMuhammad Ricky Julian AdhetiaNo ratings yet
- ACLS Algorithms Adult 2010Document12 pagesACLS Algorithms Adult 2010anon_336736395No ratings yet
- Diarrhea: Bloody 1-2daysDocument3 pagesDiarrhea: Bloody 1-2daysKassem HijazyNo ratings yet
- OAB113511Document1 pageOAB113511trillion5No ratings yet
- Antibiotic Hospital ManDocument1 pageAntibiotic Hospital Manarshiya.manasekiNo ratings yet
- Acls Algorithms 2012Document12 pagesAcls Algorithms 2012kivuNo ratings yet
- (According To Alphabetical Order) : Community Acquired Meningitis (CAM)Document69 pages(According To Alphabetical Order) : Community Acquired Meningitis (CAM)Nuhiat NahreenNo ratings yet
- Magumun - 3B WARDDocument13 pagesMagumun - 3B WARDFrancesca Aurea MagumunNo ratings yet
- NICU ABX ChartDocument11 pagesNICU ABX ChartdrchiNo ratings yet
- DRUG Study PiyaliDocument10 pagesDRUG Study PiyaliPiyali SahaNo ratings yet
- Course in The Ward Date & Side Notes Doctor's Order Rationale Nursing Responsibility RationaleDocument3 pagesCourse in The Ward Date & Side Notes Doctor's Order Rationale Nursing Responsibility RationaleArmie Joy Embat CariazoNo ratings yet
- Malaria: DR MD Mamunul Abedin ShimulDocument41 pagesMalaria: DR MD Mamunul Abedin ShimulDr. Mamunul AbedinNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic GuidelineDocument60 pagesAntibiotic GuidelineNazmul Alam FarukiNo ratings yet
- VTE-Prophylaxis-Protocol - MOHDocument13 pagesVTE-Prophylaxis-Protocol - MOHreham ONo ratings yet
- BCCA AB in Febrile Neutropenia GuidelinesDocument2 pagesBCCA AB in Febrile Neutropenia GuidelinesAlvy SyukrieNo ratings yet
- Cardiology Doses: WhiteknightloveDocument3 pagesCardiology Doses: WhiteknightloveSelim TarekNo ratings yet
- Empiric Treatment Guidelines Common InfectionsDocument9 pagesEmpiric Treatment Guidelines Common InfectionsShiza Batool100% (1)
- DosesDocument16 pagesDosesAli Adnan AfridiNo ratings yet
- SHC Outpatient Cough GuideDocument2 pagesSHC Outpatient Cough GuideKanaga6432No ratings yet
- Antibiotic Guidelines For SKIN AND SOFT TISSUE INFECTIONSDocument11 pagesAntibiotic Guidelines For SKIN AND SOFT TISSUE INFECTIONSlaptopgreyNo ratings yet
- ConnectorDocument4 pagesConnectoryetaung8No ratings yet
- Acls Algorithms 2012Document12 pagesAcls Algorithms 2012Prashanth KumarNo ratings yet
- Hypertensive State of Pregnancy-Ready ToDocument2 pagesHypertensive State of Pregnancy-Ready ToEdmund Lominoque LamelaNo ratings yet
- Anticoagulant ReversalDocument4 pagesAnticoagulant Reversalapi-647779956No ratings yet
- Ventura County Medical Center: Mi Thrombolysis, Management ofDocument3 pagesVentura County Medical Center: Mi Thrombolysis, Management ofblackcat657No ratings yet
- LevofloxacinDocument3 pagesLevofloxacinLIEZEL GRACE VELAYO100% (1)
- January 14, 2011 Pharmacology 2: Clinical Management TargetsDocument15 pagesJanuary 14, 2011 Pharmacology 2: Clinical Management Targetsrichardmd2No ratings yet
- Drug Study NurseryDocument2 pagesDrug Study Nurseryjulesubayubay54280% (1)
- Antibiotic ProtocolDocument37 pagesAntibiotic ProtocolSrinivas VadtheNo ratings yet
- CDC Malaria Program 2021Document2 pagesCDC Malaria Program 2021Susila100% (1)
- Schizophrenia Unit 4Document9 pagesSchizophrenia Unit 4varadarajanNo ratings yet
- FNCP 3Document11 pagesFNCP 3Lucelle Arellano0% (1)
- A2 - Loi, 2021Document8 pagesA2 - Loi, 2021bayu seno ajiNo ratings yet
- Budget of Work For Personal DevelopmentDocument17 pagesBudget of Work For Personal DevelopmentAngelica Velaque Babsa-ay AsiongNo ratings yet
- Risk Management PlanDocument29 pagesRisk Management Plan01095902062ahmedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Nutrition Weight Control and ExerciseDocument11 pagesChapter 4 Nutrition Weight Control and ExerciseDevanshNo ratings yet
- Kerry J Barrett: Overview of QualificationsDocument2 pagesKerry J Barrett: Overview of QualificationsKerry J. BarrettNo ratings yet
- Pe NotesDocument2 pagesPe NotesNicole Silva100% (1)
- Lecture 3Document6 pagesLecture 3api-707529158No ratings yet
- Fracture Blowout OrbitalDocument6 pagesFracture Blowout OrbitalMasitha RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Respiratory System "COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease) "Document15 pagesNursing Respiratory System "COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease) "ilhamNo ratings yet
- Mechanick 2020 AACE TOS ASMBS GuidelinesDocument73 pagesMechanick 2020 AACE TOS ASMBS GuidelinesCláudia NevesNo ratings yet
- CARE International Brochure 13Document40 pagesCARE International Brochure 13Arun TamilvananNo ratings yet
- PMLS 6 LABORATORY SAFETY Converted 1Document9 pagesPMLS 6 LABORATORY SAFETY Converted 1seaynNo ratings yet
- Assessment 2 CHCAGE001 - Facilitate The Empower Older People - Reaserach Work and Group ProjectsDocument19 pagesAssessment 2 CHCAGE001 - Facilitate The Empower Older People - Reaserach Work and Group ProjectsMary Jane EsparragoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Genetic CounselingDocument23 pagesLecture 3 Genetic Counselingimorkzone100% (1)
- Complications in Children With Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy (PEG) PlacementDocument5 pagesComplications in Children With Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy (PEG) PlacementHenry BarberenaNo ratings yet
- A Report On The Importance of Work-Life BalanceDocument3 pagesA Report On The Importance of Work-Life Balancedeepti_leleNo ratings yet
- Ayush Dubai3Document1 pageAyush Dubai3deepakmukhiNo ratings yet
- Female Genital MutilationDocument21 pagesFemale Genital MutilationAbdirahmaan Abdi0% (1)
- Obstructive Jaundice: DR Anupam Lahiri Central Hospital, South Eastern Railway, Garden ReachDocument19 pagesObstructive Jaundice: DR Anupam Lahiri Central Hospital, South Eastern Railway, Garden Reachahmed arafaNo ratings yet
- Business PlanDocument7 pagesBusiness PlanddddddaaaaeeeeNo ratings yet
- Consowhlp q1 Week2 Grade 10 Quality Sy 2021 22Document22 pagesConsowhlp q1 Week2 Grade 10 Quality Sy 2021 22NURSHAHADAH ISMAELNo ratings yet
- CSHCNExpert MeetingDocument20 pagesCSHCNExpert MeetingcanaborbeNo ratings yet
- Depression Anxiety Stress ScaleDocument2 pagesDepression Anxiety Stress ScaleYanna LozanoNo ratings yet
- Consumer Understanding of Food Quality, Healthiness, and Environmental Impact: A Cross-National PerspectiveDocument20 pagesConsumer Understanding of Food Quality, Healthiness, and Environmental Impact: A Cross-National PerspectiveTeffi Boyer MontoyaNo ratings yet