Professional Documents
Culture Documents
AO2 Worksheet 3 Chains of Analysis Answers-1
AO2 Worksheet 3 Chains of Analysis Answers-1
Uploaded by
kavyapatel1328Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
AO2 Worksheet 3 Chains of Analysis Answers-1
AO2 Worksheet 3 Chains of Analysis Answers-1
Uploaded by
kavyapatel1328Copyright:
Available Formats
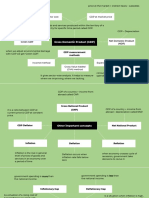
Worksheet 3: Chains of analysis answers
(Change in) Economic … (may) lead(s) to … which may/result(s) Therefore, …
concept in …
Net immigration Increase in population More of the resource The economy’s PPC shifts
labour available to the right
Cut in interest rates Lower cost of Increased access to Investment in capital
borrowing finance for firms goods increases
Increase in demand A short-term state of Creating upward Equilibrium price
shortage pressure on the price increases
to clear the shortage
A surplus Quantity supplied Downward pressure on Price decreases
exceeding quantity the price to clear the
demanded surplus
Increase in price An increase in revenue A greater Total revenue increases
per unit sold but proportionate rise in
decreases quantity total revenue from the
demanded rise in price if PED<1
Information failure Consumers Underconsumption of The market has failed
underestimating the merit goods
private benefits of
merit goods
Deregulation Reduced barriers to Increase in competition The likelihood of abuse
entry in a market of monopoly power
decreases
Division of labour Increase in productivity Higher wages earned, Living standards increase
of workers giving them access
to more goods and
services
Increase in unemployment Weaker power of trade Decreasing their Average wages decrease
unions bargaining power
Increase in the size of the Greater ability to Lower average cost Selling price decreases
firm take advantage of
economies of scale
A change towards The firm investing Higher investment/ Total costs increase
more capital-intensive in more capital fixed costs
production equipment
Existence of monopoly Decrease in/absence of The monopoly Consumers pay higher
competition becoming a price prices
maker/gaining control
over prices
Expansionary fiscal policy Increase in aggregate Firms producing higher Economic growth
demand output if there is spare
capacity
© Cambridge University Press & Assessment 2023 vX 3
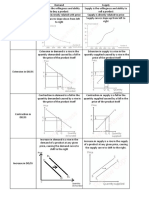
(Change in) Economic … (may) lead(s) to … which may/result(s) Therefore, …
concept in …
Contractionary monetary Decrease in aggregate Decrease in the derived Greater unemployment
policy demand demand for labour
Supply-side policy Provision of more Workers becoming Reduced poverty
training and education more employable/
increase in workers’
earning potential
Decrease in incomes Decrease in the A decrease in net Causing a recession in the
abroad demand for the exports and domestic domestic economy
domestic economy’s output
exports
Frictional unemployment Workers staying in Workers finding a Increasing an individual’s
between jobs better-paid job standard of living
Increase in cost of An increase in import- Imported cost-push Decreasing export
imported raw materials reliant industries’ costs inflation competitiveness
of production
Greater indebtedness of Outflows from the BoP Future generations Lowering living standards
developing countries to repay the loans experiencing a decrease in developing countries
in national income
Lack of access to Learners being absent Decrease in knowledge/ Creating a poverty trap
healthcare from school more often qualifications and
due to sickness earning potential for
future generations
Low living standards Net emigration in A decrease in working Increasing a country’s
search of employment population dependency ratio
abroad
Reduction in quotas Decrease in quantity of Decrease in Growth of infant industries
imports and increase competition for local
in their price industries
Decrease in the exchange Decrease in export Decrease in export Worsening the Balance of
rate prices and increase in revenue (if PED<1) Trade deficit
import prices and increase in import
expenditure (if PED<1)
© Cambridge University Press & Assessment 2023 v1 4
You might also like
- Short-Run Aggregate Supply (SRAS) : Macro Topic 3.3Document2 pagesShort-Run Aggregate Supply (SRAS) : Macro Topic 3.3kawii.fighting10No ratings yet
- A level Economics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA level Economics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- AO2 Worksheet 3 Chains of Analysis-1Document2 pagesAO2 Worksheet 3 Chains of Analysis-1kavyapatel1328No ratings yet
- AO2 Worksheet 1 Cause and Effect AnswersDocument2 pagesAO2 Worksheet 1 Cause and Effect Answerskavyapatel1328No ratings yet
- 2.1.4 Balance of Payments 2Document2 pages2.1.4 Balance of Payments 2fpd06972No ratings yet
- CH 26 - InflationDocument26 pagesCH 26 - InflationNatalie LamNo ratings yet
- AO2 Worksheet 1 Cause and EffectDocument2 pagesAO2 Worksheet 1 Cause and Effectkavyapatel1328No ratings yet
- Macroeconomic Objectives - Low Inflation Rate - HandoutDocument48 pagesMacroeconomic Objectives - Low Inflation Rate - Handoutdenny_sitorusNo ratings yet
- Chains 90Document22 pagesChains 90legendarykamilNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheets - Monetary, Fiscal, Exchange RateDocument10 pagesCheat Sheets - Monetary, Fiscal, Exchange RateShaurya Pratap ShekhawatNo ratings yet
- Economics Cheat SheetsDocument8 pagesEconomics Cheat Sheetspratyushsahu180No ratings yet
- Factors Causing Shifts in Demand CurveDocument2 pagesFactors Causing Shifts in Demand CurveHema NarulaNo ratings yet
- Monetary Policy Effects and Outcomes Grid: ActionDocument1 pageMonetary Policy Effects and Outcomes Grid: ActionXiaolin SuNo ratings yet
- Me Quizzes1Document283 pagesMe Quizzes1Mary Allysa ArroyoNo ratings yet
- Abdul Mussavir Hassan Rind 12718 Macro EconomicsDocument9 pagesAbdul Mussavir Hassan Rind 12718 Macro EconomicsUzair HussainNo ratings yet
- Alawin Activity 3Document3 pagesAlawin Activity 3RheineNo ratings yet
- International Trade - ProtectionismDocument15 pagesInternational Trade - ProtectionismsrishtimantravadiNo ratings yet
- A Presentation On Effect of Recession On AgricultureDocument17 pagesA Presentation On Effect of Recession On Agriculturevandana chandra100% (3)
- Aggregate Demand and Aggregate SupplyDocument33 pagesAggregate Demand and Aggregate Supplyprajjwal khatriNo ratings yet
- Cheat SheetDocument1 pageCheat Sheetimran.alamNo ratings yet
- ++Acc322..Standard Costing Part 2.Document9 pages++Acc322..Standard Costing Part 2.David ONo ratings yet
- Advantages of Supply Side PoliciesDocument1 pageAdvantages of Supply Side PoliciesGupi PalNo ratings yet
- Asleveleconrevisionstudyguide PKDocument5 pagesAsleveleconrevisionstudyguide PKSaqib RehanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document33 pagesChapter 4rhitikaparajuliNo ratings yet
- Reasons For Inflation Explained Cost Push and Demand PullDocument1 pageReasons For Inflation Explained Cost Push and Demand Pullbk3pgxrthpNo ratings yet
- EconomicsDocument1 pageEconomicsmishu singhNo ratings yet
- Review Premidterm Exam EmanDocument20 pagesReview Premidterm Exam EmanIrwanda AnggaraNo ratings yet
- SupplyDocument24 pagesSupplyΙωάννα ΑδαμοπούλουNo ratings yet
- Chains On ADDocument4 pagesChains On ADlegendarykamilNo ratings yet
- Class Lecture - 29Document17 pagesClass Lecture - 29Tanay BansalNo ratings yet
- ch9 Lecture & Textbook NotesDocument10 pagesch9 Lecture & Textbook Notes47fwhvhc6kNo ratings yet
- CMFS Microeconomic Concepts SummaryDocument66 pagesCMFS Microeconomic Concepts SummaryReylend YanataNo ratings yet
- Aggregate Demand Aggregate Supply: VariablesDocument2 pagesAggregate Demand Aggregate Supply: VariablesMohsin Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- Macro Chap 9Document10 pagesMacro Chap 9KunikaNo ratings yet
- 4.1 - 4.2 Price ControlsDocument5 pages4.1 - 4.2 Price ControlsSreeRoopa SankararamanNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Econ Economic RecessionDocument3 pagesIGCSE Econ Economic RecessionmiriamhoooylNo ratings yet
- Unemployment: Causes Effects SolutionsDocument1 pageUnemployment: Causes Effects Solutionsalyssa valdezNo ratings yet
- How The Macroeconomy Works The Circular Flow of Income Aggregate Demandaggregate Supply Analysis and Related ConceptsDocument21 pagesHow The Macroeconomy Works The Circular Flow of Income Aggregate Demandaggregate Supply Analysis and Related Conceptsamjad sittarNo ratings yet
- Taste AND PreferencesDocument5 pagesTaste AND PreferencesPauline BiancaNo ratings yet
- Chap015 TNx2Document52 pagesChap015 TNx2nugroho.aditya12334No ratings yet
- The Business CycleDocument31 pagesThe Business CyclePavithra SalankeNo ratings yet
- Important Basics of EconomyDocument4 pagesImportant Basics of EconomyRamana ReddyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 & 8 NotesDocument3 pagesChapter 7 & 8 NotesShreeyaa MehtaNo ratings yet
- A) Economic GrowthDocument9 pagesA) Economic GrowthChristineNo ratings yet
- Economics 1Document17 pagesEconomics 1ghimire123niteshNo ratings yet
- Economic TermsDocument60 pagesEconomic TermsTsuNo ratings yet
- Ss 1Document2 pagesSs 1Mycka Joy HernandezNo ratings yet
- CH 7 External Economic Influences On Business ActivityDocument49 pagesCH 7 External Economic Influences On Business Activityaliabbasrizvipc2022No ratings yet
- Economics 24Document106 pagesEconomics 24suranains7No ratings yet
- Test 3 ReviewDocument7 pagesTest 3 ReviewJAL4No ratings yet
- Inflation: Measures Types Causes EffectsDocument12 pagesInflation: Measures Types Causes Effectsali.alianwarNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Econ Causes of Economic GrowthDocument3 pagesIGCSE Econ Causes of Economic GrowthmiriamhoooylNo ratings yet
- Set-Bot Q&aDocument5 pagesSet-Bot Q&aBammNo ratings yet
- BHMCT/Managerial Economics: Item Text Option Text 1 Option Text 2 Option Text 3 Option Text 4Document2 pagesBHMCT/Managerial Economics: Item Text Option Text 1 Option Text 2 Option Text 3 Option Text 4Xiaomi TvNo ratings yet
- Simplified Economics WPSDocument33 pagesSimplified Economics WPSlensxellenceNo ratings yet
- Caie Igcse Business Studies 0450 Theory v5 RemovedDocument5 pagesCaie Igcse Business Studies 0450 Theory v5 RemovedSwagata DebnathNo ratings yet
- Aggregate Supply and Aggregate Demand: Session 16Document22 pagesAggregate Supply and Aggregate Demand: Session 16Raj PatelNo ratings yet
- Glossary NewDocument61 pagesGlossary NewStudent Charlotte WONG, CharlotteNo ratings yet
- Mixed Economic SystemDocument35 pagesMixed Economic Systemcheeze473No ratings yet
- Econs NotesDocument2 pagesEcons NotessivanesshniNo ratings yet
- Althea Geronimo Unit I Lesson 1 Statement of Financial PositionDocument6 pagesAlthea Geronimo Unit I Lesson 1 Statement of Financial PositionJoana Jean SuymanNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Financial Management 11th Edition Brigham Solutions ManualDocument26 pagesIntermediate Financial Management 11th Edition Brigham Solutions ManualSabrinaFloresmxzie100% (51)
- Land Documents Submission Letter LDocument2 pagesLand Documents Submission Letter LLegal Al-Mostafa GroupNo ratings yet
- Maita Gomez Value Chain Luzon ConferenceDocument29 pagesMaita Gomez Value Chain Luzon ConferenceBlogWatchNo ratings yet
- CA Foundation - MCQ's - 1Document97 pagesCA Foundation - MCQ's - 1Harshit GulatiNo ratings yet
- 1ccounting VoucherDocument3 pages1ccounting VoucherSuhas TopkarNo ratings yet
- ACECOSTDocument6 pagesACECOSTXyne FernandezNo ratings yet
- FABM - L-10Document16 pagesFABM - L-10Seve HanesNo ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting Decisions: DR R.S. Aurora, Faculty in FinanceDocument31 pagesCapital Budgeting Decisions: DR R.S. Aurora, Faculty in FinanceAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics: 3 Quarterly ExaminationDocument2 pagesApplied Economics: 3 Quarterly ExaminationArcueno Lore-AnnNo ratings yet
- Sample Business Contract: 1. The Contract Is BetweenDocument3 pagesSample Business Contract: 1. The Contract Is BetweenJunaid KhanNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic ModelsDocument31 pagesDiagnostic ModelsValentin Adam100% (2)
- Bmat Quizzes W1 10Document30 pagesBmat Quizzes W1 10Johndonrobert VargasNo ratings yet
- Bosch WKD28352GB Washer-DryerDocument56 pagesBosch WKD28352GB Washer-DryerRenz Aldrin EchaoreNo ratings yet
- Module - 4 PDFDocument15 pagesModule - 4 PDFKeyur PopatNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship: (BCAS401)Document6 pagesEntrepreneurship: (BCAS401)Akash HalsanaNo ratings yet
- Weekly Account Statement - RW9913Document1 pageWeekly Account Statement - RW9913swastik prasadNo ratings yet
- In Tax GBT Alert Depreciation Allowable On Windmills Connected To Grid During The Financial Year NoexpDocument4 pagesIn Tax GBT Alert Depreciation Allowable On Windmills Connected To Grid During The Financial Year NoexpAnanyaNo ratings yet
- BACOLOD NegoSale Batch 59074 093022Document7 pagesBACOLOD NegoSale Batch 59074 093022Leo Laurenzhe CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Final ME-Construction Chemicals MarketDocument11 pagesFinal ME-Construction Chemicals MarketAlaz FofanaNo ratings yet
- MATERIALSDocument2 pagesMATERIALSitsmeyojlynNo ratings yet
- DOCUMENT: Bank Statement Reflecting All FIRS Transfers To President Buhari's FriendDocument1 pageDOCUMENT: Bank Statement Reflecting All FIRS Transfers To President Buhari's FriendSahara ReportersNo ratings yet
- Copa Airlines Story English Part 2Document2 pagesCopa Airlines Story English Part 2emenacho24No ratings yet
- Introduction To Econometrics, 5 Edition: Chapter 3: Multiple Regression AnalysisDocument28 pagesIntroduction To Econometrics, 5 Edition: Chapter 3: Multiple Regression AnalysisRamarcha KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document3 pagesChapter 1Shakib Ahmed Emon 0389No ratings yet
- Paper Mill Asset MaterialDocument141 pagesPaper Mill Asset MaterialMD. MONIRUZZAMANNo ratings yet
- Soal Mid B Inggris MTSDocument3 pagesSoal Mid B Inggris MTSRizki MaulaniNo ratings yet
- Subject:: Payment of Education StipendDocument12 pagesSubject:: Payment of Education StipendShahaan ZulfiqarNo ratings yet
- DPWH Sample CardDocument1 pageDPWH Sample CardRamVin Arano100% (1)
- SAMPLE PDF Macroeconomics XII 2021-22 Edition by Subhash DeyDocument124 pagesSAMPLE PDF Macroeconomics XII 2021-22 Edition by Subhash DeyAbhinav Kalra100% (1)