Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Adobe Scan 12 Apr 2024
Adobe Scan 12 Apr 2024
Uploaded by
hitukatariya02Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Adobe Scan 12 Apr 2024
Adobe Scan 12 Apr 2024
Uploaded by
hitukatariya02Copyright:
Available Formats
\
I
w 1"c\,1catn tc..t1on and -.Im1 il' pape :;, .,1 cow K 1,h
.i:
broug/lt to rou lly..,. CORE
t ,; iic rtC '
.:. tor b "=
.1S,_ '-
~-
tnternation11t Journal of Food Procoss/ng Tochnology:,_2_0_15_:.,_5;__,9_-1_2_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _9
Mushroom: Cultivation and Processing
Kratika Sharma·
/CAR- Central Arid Zone Research lnstitulo (C/\ZRI), .Jodhpur, Rajas/hen, India
Abstract: This paper presents review of various hteralures concerning the types of edible mushrooms consumed In
India. their cultivation and processing Mushrooms are fungi which arc cherished for their flavor as well for their
nutnllonal value They are low In salt and sugar and arc a rich natural source of Vitamin D. Mushroom farming Is gaining
popularity day by day among new entrepreneurs. They are cultivated with specifically propagated spawns on a well
prepared compost. Being tender in nature they deteriorate rapidly if not refngerated or processed in lime hence
subJected to vanous processing methods such as drying, !reeling, canning, pickling and sterilization. These methods not
only preserves them but also helps In flavor development as in the case of pickllng
Keywords: Mushroom, Moisture, Humidity. Temperature, Growth.
INTRODUCTION of them might cause food poisoning or allergy upon
consumption. Some of the major varieties consumed in
Mushrooms are one of the most loved food not only India are as follows:
for its exotic taste but also for the benefits with which it
comes. It can be consumed 111 various forms like fr~:sh, Button Mushroom
pickled. dned, powdered. canned etc Its farming has
picked up a fast pace among contemporary Button mushroom (Agaricus bisporus) belongs to
entrepreneurs owing to tis nutritional and medicinal Class Basid1omycetes and Family Agaricaceae and is
benefits and low cost input with high output. native to Europe and North America. It is of two types
Mushrooms are a fleshy fungi (Basidiomycotr1, white and brown, out of which white button mushroom
Agaricomycetes) having a stem, cap and gills
underneath the cap (1 ]. They can be edible, wild and
Table 1: Nutritional Value of Agaricus bisporus (White
some of them can be toxic too. It contains more than Button Mushrooms) per 100 g
90% water and less than 1% fat, loaded with Vitamin B,
copper and selenium and low in sodium (1 ]. Usually Nutritional Value per 100 g (3.5 oz.)
vegetables, milk and other food products are fortified
with Vitamin D by irradiation or direct addition but Energy 113 kJ (27 kcal)
mushrooms are unique in this sense because they are Water 92.45 g
naturally a rich source of Vitamin D which otherwise is Carbohydrates 4.1 g
procured from animals or poultry [2]. The reason bcinq rat 0.1 g
that it contains copious amount of plant sterol
Protein 2.5 g
"Ergosterol". It is a precursor of Vitamin D which when
Thiamine (Vil B,) 0.1 mg (9%)
stimulated by sunlight or artificial lightening source
converts to Vitamin D (3). Table 1 presents the details R1bonav1n (Vit B2) 0.5 mg (42%)
of nutritional value of Agaricus bisporus (White Button Niacin (Vil B,) 3.8 mg (25%)
Mushrooms) (1, 4-6]. Pantothenic /\c1d (Bs) 1.5 mg (30%)
TYPES OF MUSHROOMS Vitamin C 0 mg (0%)
Calcium 18 mg (2%)
Mushrooms are easily cultivable in hilly regions due
- -
Phosphorous 120 mg (17%)
to abundant moisture but can also be grown in artificial
Potassium 448 mg (10%)
environment with proper temperature and humidity
Sodium 6 mg (0%)
control. Varieties must be identified thoroughly as some
Zinc 1.1 mg (12%)
Vitamin D (D2 + D3) 0.2 µg
'Address correspondence to this author at the !CAR- Central And Zone
Sugar 1.98 g
Hesoarch ln~t,tute (CAZRI), D1v1s1on of Integrated Farming System, Jodhpur.
Raiasthan, India; Percentages are relative to US recommendations for adults.
Tel 9205758338;
Ema I krah~a494@gmaJI com Source: USDA Nutrient Database
E-ISSN: 2408-9826/18 © 2018 Cosmos Scholarli Publishing House
You might also like
- Barsmarts Workbook PDFDocument214 pagesBarsmarts Workbook PDFIonut BasarabNo ratings yet
- English4 q1 Mod7 EnrichingYourVocabulary v2Document19 pagesEnglish4 q1 Mod7 EnrichingYourVocabulary v2Nikoru100% (1)
- Viktoras KulvinskasDocument6 pagesViktoras KulvinskasKarin RuppNo ratings yet
- Mushroom: Cultivation and Processing: Kratika SharmaDocument4 pagesMushroom: Cultivation and Processing: Kratika SharmaNatalijaNo ratings yet
- Mushroom: Cultivation and Processing: Kratika SharmaDocument4 pagesMushroom: Cultivation and Processing: Kratika SharmaGustavo Prado AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Punjab MilletDocument40 pagesPunjab MilletSHubhamNo ratings yet
- MUSHROOMDocument8 pagesMUSHROOMsaravanan lakshmananNo ratings yet
- Guinea Corn (Sorghum Vulgare) Leaf, A Potential Source of Nutrients and PhytochemicalsDocument3 pagesGuinea Corn (Sorghum Vulgare) Leaf, A Potential Source of Nutrients and PhytochemicalsMercy peterNo ratings yet
- Cauliflower Nutrition Facts and Health BenefitsDocument3 pagesCauliflower Nutrition Facts and Health BenefitsAllan LariosaNo ratings yet
- Tamarind Nutrition Facts, Medicinal Properties and Health BenefitsDocument8 pagesTamarind Nutrition Facts, Medicinal Properties and Health BenefitsayendeisraelNo ratings yet
- Batra 2013Document17 pagesBatra 2013Catalina CastilloNo ratings yet
- Eggplant PDFDocument16 pagesEggplant PDFAj Ceniza Amancio0% (1)
- Cosmetics: Spirulina For Skin Care: A Bright Blue FutureDocument19 pagesCosmetics: Spirulina For Skin Care: A Bright Blue FutureEGA HPNo ratings yet
- Seminar 2019Document11 pagesSeminar 2019mmuruganandamNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Proses Pengolahan Terhadap Kadar Beta Karoten PADA UBI JALAR VARIETAS UNGU (Ipomoea Batatas (L.) Lam) Dengan Metode Spektrofotometri VisibelDocument11 pagesPengaruh Proses Pengolahan Terhadap Kadar Beta Karoten PADA UBI JALAR VARIETAS UNGU (Ipomoea Batatas (L.) Lam) Dengan Metode Spektrofotometri VisibelVivi HikmawatiNo ratings yet
- Scope and Imp. of MushroomDocument10 pagesScope and Imp. of MushroomRasmi RanjanNo ratings yet
- Aonla Assignment (Priyam)Document24 pagesAonla Assignment (Priyam)PRIYAM NANDINI BARUAHNo ratings yet
- Fungi As FoodDocument4 pagesFungi As Fooddd6893452No ratings yet
- Effect of A Probiotic and Herbal Additives On Growth, Survival and Disease Resistance of Striped MurrelDocument4 pagesEffect of A Probiotic and Herbal Additives On Growth, Survival and Disease Resistance of Striped MurrelAlan Daniel EspañaNo ratings yet
- Determination of Total Phenolic, Flavonoid, Carotenoid, and Mineral Contents in Peel, Flesh, and Seeds of Pumpkin (Cucurbita Maxima)Document8 pagesDetermination of Total Phenolic, Flavonoid, Carotenoid, and Mineral Contents in Peel, Flesh, and Seeds of Pumpkin (Cucurbita Maxima)Meliza DwiNo ratings yet
- Effect of Dietary Vitamin C On Growth and Survival of GIFT TilapiaDocument7 pagesEffect of Dietary Vitamin C On Growth and Survival of GIFT TilapiarizazNo ratings yet
- IodineDocument3 pagesIodineAndreas StavrianosNo ratings yet
- Importance of FungiDocument83 pagesImportance of FungiKazi HossainNo ratings yet
- Moringa: The Tree of Life'Document4 pagesMoringa: The Tree of Life'kanagarathinamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 34Document22 pagesChapter 34Konishko DeyNo ratings yet
- Mushroom PaperDocument7 pagesMushroom Paperpennylanecortez12No ratings yet
- ChayoteDocument9 pagesChayoteMichaelNo ratings yet
- Scholars Research Library: J. K. Mensah, B. Ikhajiagbe, N. E. Edema, J. EmokhorDocument6 pagesScholars Research Library: J. K. Mensah, B. Ikhajiagbe, N. E. Edema, J. EmokhorFariha MarirohNo ratings yet
- Vitamins LasDocument18 pagesVitamins Lasmiti.pongos.swuNo ratings yet
- A Review On The Beneficial Effect of Thymol On Health and Production of FishDocument11 pagesA Review On The Beneficial Effect of Thymol On Health and Production of FishEnrique ValleNo ratings yet
- Foodsafety IrradiationDocument4 pagesFoodsafety IrradiationFadhilah QomariyantoNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Composition of Dried Curry Leaf Powder (Murraya Koenigii)Document5 pagesNutritional Composition of Dried Curry Leaf Powder (Murraya Koenigii)anithaNo ratings yet
- Oyster Mushroom (Pleurotus Pulmonarius) Production Using Different Substrates Under 27.30C Average TemperatureDocument9 pagesOyster Mushroom (Pleurotus Pulmonarius) Production Using Different Substrates Under 27.30C Average TemperatureInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Cantharellus AntioxidanteDocument6 pagesCantharellus AntioxidanteWendy BautistaNo ratings yet
- 2021 Article 4987Document11 pages2021 Article 4987Asim DuttaNo ratings yet
- Uses and Health Benefits of JackfruitDocument2 pagesUses and Health Benefits of JackfruitZineil BlackwoodNo ratings yet
- Da 5 Mushroom Production 2017Document12 pagesDa 5 Mushroom Production 2017Chary Johanne MenesesNo ratings yet
- Vitamin ThiamineDocument15 pagesVitamin ThiamineRam MaheshNo ratings yet
- Banana and Plantain As Medicinal FoodDocument5 pagesBanana and Plantain As Medicinal Fooddevanti trisNo ratings yet
- Clemente - Plagas en RosellaDocument8 pagesClemente - Plagas en RosellaKo WyNo ratings yet
- 808 Agriculture Xii Draft PDFDocument209 pages808 Agriculture Xii Draft PDFYashraj Singh BhadoriyaNo ratings yet
- Guide To Eating More Vegetables: CarrotsDocument7 pagesGuide To Eating More Vegetables: CarrotsAli SherNo ratings yet
- The Nutritional Value and Phytochemical Components of Taro Colocasia Esculenta L Schott Powder and Its Selected Processed Foods 2155 9600.1000207Document7 pagesThe Nutritional Value and Phytochemical Components of Taro Colocasia Esculenta L Schott Powder and Its Selected Processed Foods 2155 9600.1000207Crazyyy XhinsyaaNo ratings yet
- Applications of Biotechnology in AgricultureDocument11 pagesApplications of Biotechnology in AgricultureMarkuz SenonNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of in Vivo Probiotic Efficiency of BacillusDocument8 pagesEvaluation of in Vivo Probiotic Efficiency of BacillusANDRADANo ratings yet
- Low Cost Production of Mushroom Using Agricultural Waste in A Controlledenvironment For Economic Advancement 2252 5211 1000329Document5 pagesLow Cost Production of Mushroom Using Agricultural Waste in A Controlledenvironment For Economic Advancement 2252 5211 1000329Excelsis VallejoNo ratings yet
- Creation and implementation of a procedure to assess a sustainable biobased composite materialDocument7 pagesCreation and implementation of a procedure to assess a sustainable biobased composite materialhemant sadafaleNo ratings yet
- Economic Importance of Algae 1Document13 pagesEconomic Importance of Algae 1yamuna veniNo ratings yet
- 53 IFRJ 21 (06) 2014 Gupta 426Document5 pages53 IFRJ 21 (06) 2014 Gupta 426SteryNo ratings yet
- Mahanta 2007Document6 pagesMahanta 2007elias.bio892No ratings yet
- Notes. Principles of Crop ProtectionDocument3 pagesNotes. Principles of Crop ProtectionAliah Alleyne Canals - BSA - 1ANo ratings yet
- 7 3 104 192Document4 pages7 3 104 192Sonia BalintNo ratings yet
- Impact of Soaking Sprouting On Antioxidant and AntDocument5 pagesImpact of Soaking Sprouting On Antioxidant and AntPaviNo ratings yet
- PSB 206 Mushroom Economic ImportanceDocument4 pagesPSB 206 Mushroom Economic Importanceummiy999No ratings yet
- 2 KMANI-NutritionalandMedicinalvaluesofMushroomsDocument5 pages2 KMANI-NutritionalandMedicinalvaluesofMushroomspremkumaru182106No ratings yet
- Medicinal Properties of Oyster MushroomDocument8 pagesMedicinal Properties of Oyster MushroomJOSE ESTRADANo ratings yet
- Impact of abamectin, Bacillus thuriengiensis and Neem oil extract on Aphis gossypii glover and Bemissia tabaci pests of the watermelon (Citrullus lanatus) in DschangDocument9 pagesImpact of abamectin, Bacillus thuriengiensis and Neem oil extract on Aphis gossypii glover and Bemissia tabaci pests of the watermelon (Citrullus lanatus) in DschangOpenaccess Research paperNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of Bitterness in Bamboo ShootsDocument8 pagesBiochemistry of Bitterness in Bamboo ShootsKuo SarongNo ratings yet
- Ijert Ijert: Development of Watermelon Rind Incorporated Fruit ButterDocument6 pagesIjert Ijert: Development of Watermelon Rind Incorporated Fruit ButterdianashanepNo ratings yet
- Investigation of Antimicrobial Activity of Some Currently Available Topical Antimicrobial ProductsDocument2 pagesInvestigation of Antimicrobial Activity of Some Currently Available Topical Antimicrobial ProductsZheefNo ratings yet
- Nutrient Distribution From A Newly Cultivated Edible Mushroom Lentinus Tuberregium FR Tamil Nadu IndiaDocument4 pagesNutrient Distribution From A Newly Cultivated Edible Mushroom Lentinus Tuberregium FR Tamil Nadu Indiasunaina agarwalNo ratings yet
- Simple Present Tense - Present Continuous TenseDocument12 pagesSimple Present Tense - Present Continuous TenseIrfan HasifNo ratings yet
- Burnt CityDocument46 pagesBurnt CityFelixKalmensonNo ratings yet
- Sentence SkillsDocument27 pagesSentence SkillsTamikaNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics: Section: GA4AA Activity 11 (Week 11) Five Manufacturing BusinessDocument2 pagesApplied Economics: Section: GA4AA Activity 11 (Week 11) Five Manufacturing BusinessDanica May CobillaNo ratings yet
- Performance Task in Personal Development (Depression) : Submitted By: Submitted ToDocument6 pagesPerformance Task in Personal Development (Depression) : Submitted By: Submitted ToJanea Arinya100% (1)
- FSSC 22000 Version 6.0 Upgrade ProcessDocument7 pagesFSSC 22000 Version 6.0 Upgrade ProcessKarim HandoyoNo ratings yet
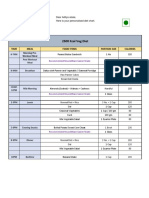
- Simple 30 Day Summer Meal Plan For Weight Loss Printable FinalDocument2 pagesSimple 30 Day Summer Meal Plan For Weight Loss Printable Finaljeffersonkimotho42No ratings yet
- 2500 Kcal Veg Diet: Time Meal Food Items Portion Size CaloriesDocument2 pages2500 Kcal Veg Diet: Time Meal Food Items Portion Size CaloriesVishal 777No ratings yet
- Potassium-metaBisulphite 12 3Document25 pagesPotassium-metaBisulphite 12 3Prakash SwainNo ratings yet
- Metodos Simples de AcuiculturaDocument16 pagesMetodos Simples de AcuiculturaWilfrido Rosado0% (1)
- What Einstein Told His CookDocument3 pagesWhat Einstein Told His CookAnitaNo ratings yet
- 80 A 85 HOWTHEDESERTTORTOISEGOTITSSHELLDocument6 pages80 A 85 HOWTHEDESERTTORTOISEGOTITSSHELLClaudiaLoredoNo ratings yet
- Pedel Opertated Areca Nut Feeling MachineDocument15 pagesPedel Opertated Areca Nut Feeling MachineSammed DarurNo ratings yet
- Public Health 101: Class Assignment Faculty: Dr. MD Abdul Waheed (ABL) Topic: Public Health Nutrition and Importance ForDocument4 pagesPublic Health 101: Class Assignment Faculty: Dr. MD Abdul Waheed (ABL) Topic: Public Health Nutrition and Importance ForShamin Yasar ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Chicken Cordon Bleu RecipeDocument7 pagesChicken Cordon Bleu RecipeRodena DadaleNo ratings yet
- Menu Finch Coffee & Kitchen Latest-1Document8 pagesMenu Finch Coffee & Kitchen Latest-1Deni PrastikoNo ratings yet
- UNIDAD 1 VOCABULARY InglesDocument3 pagesUNIDAD 1 VOCABULARY InglesMaría Vasquez CamposNo ratings yet
- NCERT Book Class 7 Science Chapter 2Document14 pagesNCERT Book Class 7 Science Chapter 2gnv kaliamanNo ratings yet
- Commodity CodesDocument55 pagesCommodity CodesjesuswithusNo ratings yet
- Sindhi Cook BookDocument64 pagesSindhi Cook BookofusandeepNo ratings yet
- English Vocabulary Booster: HealthDocument2 pagesEnglish Vocabulary Booster: HealthPháp Sư Giấu MặtNo ratings yet
- Water CalculationsDocument2 pagesWater CalculationsBhavika Dabhi50% (2)
- Disneyland California Map 2022Document2 pagesDisneyland California Map 2022SomeGayGalNo ratings yet
- Cafe Basque Dinner Menu Template 8.5x14 Shell Layer Red HeadingsDocument2 pagesCafe Basque Dinner Menu Template 8.5x14 Shell Layer Red HeadingsCatherine ChaplinNo ratings yet
- Espada FishDocument23 pagesEspada FishRSNo ratings yet
- Session 1Document20 pagesSession 1ARACELI NOEMI COLUMCHE ESPINOZANo ratings yet
- Fabulous Kahk (Eid Cookies) CleobutteraDocument1 pageFabulous Kahk (Eid Cookies) CleobutteraaydaNo ratings yet