Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Untitled Document
Untitled Document
Uploaded by
ixora.ytqOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Untitled Document
Untitled Document
Uploaded by
ixora.ytqCopyright:
Available Formats
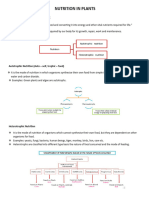
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, some bacteria and some protistans use the
energy from sunlight to produce glucose from carbon dioxide and water. This glucose can be
converted into pyruvate which releases adenosine triphosphate (ATP) by cellular respiration.
Oxygen is also formed. Photosynthesis may be summarised by the word equation: carbon
dioxide + water glucose + oxygen The conversion of usable sunlight energy into chemical
energy is associated with the action of the green pigment chlorophyll. Chlorophyll is a complex
molecule. Several modifications of chlorophyll occur among plants and other photosynthetic
organisms. All photosynthetic organisms have chlorophyll a. Accessory pigments absorb energy
that chlorophyll a does not absorb. Accessory pigments include chlorophyll b (also c, d, and e in
algae and protistans), xanthophylls, and carotenoids (such as beta-carotene). Chlorophyll a
absorbs its energy from the violet-blue and reddish orange-red wavelengths, and little from the
intermediate (green-yellow-orange) wavelengths.Plants are the only photosynthetic organisms
to have leaves (and not all plants have leaves). A leaf may be viewed as a solar collector
crammed full of photosynthetic cells. The raw materials of photosynthesis, water and carbon
dioxide, enter the cells of the leaf, and the products of photosynthesis, sugar and oxygen, leave
the leaf. Water enters the root and is transported up to the leaves through specialized plant cells
known as xylem vessels. Land plants must guard against drying out and so have evolved
specialized structures known as stomata to allow gas to enter and leave the leaf. Carbon
dioxide cannot pass through the protective waxy layer covering the leaf (cuticle), but it can enter
the leaf through the stoma (the singular of stomata), flanked by two guard cells. Likewise,
oxygen produced during photosynthesis can only pass out of the leaf through the opened
stomata. Unfortunately for the plant, while these gases are moving between the inside and
outside of the leaf, a great deal of water is also lost. Cottonwood trees, for example, will lose
100 gallons (about 450 dm3) of water per hour during hot desert days. The structure of the
chloroplast and photosynthetic membranes The thylakoid is the structural unit of
photosynthesis. Both photosynthetic prokaryotes and eukaryotes have these flattened
sacs/vesicles containing photosynthetic chemicals. Only eukaryotes have chloroplasts with a
surrounding membrane. Thylakoids are stacked like pancakes in stacks known collectively as
grana. The areas between grana are referred to as stroma. While the mitochondrion has two
membrane systems, the chloroplast has three, forming three compartments.
You might also like
- OCR As and A Level Biology A SB 1 Answers - Combined - FinalDocument60 pagesOCR As and A Level Biology A SB 1 Answers - Combined - FinalMahdi Hasan Y12E33% (3)
- Cell and Molecular BiologyDocument17 pagesCell and Molecular BiologyHizzei Caballero100% (4)
- CytologyDocument20 pagesCytologykaziba stephen100% (1)
- Bio Module 2 PhotoMasterDocument23 pagesBio Module 2 PhotoMasterh33% (3)
- Unit 7 Notes MetabolismDocument18 pagesUnit 7 Notes MetabolismJody-Ann Mears0% (1)
- Chloroplast GenomeDocument13 pagesChloroplast Genomelordniklaus100% (2)
- Virtual Microscope Lab 1Document6 pagesVirtual Microscope Lab 1Sama WahbaNo ratings yet
- PHOTOSYNTHESISDocument21 pagesPHOTOSYNTHESISEpoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document77 pagesChapter 7Joel CabañasNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and RespirationDocument46 pagesPhotosynthesis and RespirationCarmsNo ratings yet
- Chloroplast and PhotosynthesisDocument19 pagesChloroplast and PhotosynthesisFizul HelmiNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Plants 1 PDFDocument6 pagesNutrition in Plants 1 PDFNakshatra PaliwalNo ratings yet
- Biolab 2Document3 pagesBiolab 2diemtruc414No ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration Cellular Respiration Is The Set of TheDocument2 pagesCellular Respiration Cellular Respiration Is The Set of TheSrinivas LaishettyNo ratings yet
- Labbio Sat DangPhuongQuynh Prelab3Document3 pagesLabbio Sat DangPhuongQuynh Prelab3Quynh Dang PhuongNo ratings yet
- Pre-Labs 3: 1. What Are Autotrophs and Heterotrophs? Give Each One ExampleDocument4 pagesPre-Labs 3: 1. What Are Autotrophs and Heterotrophs? Give Each One ExampleGiao TranNo ratings yet
- Photosyntheis and RespirationDocument37 pagesPhotosyntheis and Respirationfelisilda.136571140273No ratings yet
- Lecture 6 PhotosynthesisDocument12 pagesLecture 6 Photosynthesismichael328wanjiruNo ratings yet
- What Is PhotosynthesisDocument10 pagesWhat Is PhotosynthesisGenie SorianoNo ratings yet
- What Is PhotosynthesisDocument4 pagesWhat Is PhotosynthesisJohn Dulay MendozaNo ratings yet
- Kreb's Cycle 2Document7 pagesKreb's Cycle 2Edelaine V. SayconNo ratings yet
- All About PhotossynthesisDocument7 pagesAll About Photossynthesisapi-341032878No ratings yet
- Nutrition in PlantsDocument6 pagesNutrition in PlantsSarada KasyapNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis PDFDocument30 pagesPhotosynthesis PDFbobbyhaha05No ratings yet
- The Process of PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesThe Process of Photosynthesisnelia mae laroyaNo ratings yet
- Write Ups Chapter 7Document12 pagesWrite Ups Chapter 7Joel CabañasNo ratings yet
- Practical 3: Photosynthesis & Transpiration: Student Name: Lê Hà Phương Ly ID: BTBTIU21220Document2 pagesPractical 3: Photosynthesis & Transpiration: Student Name: Lê Hà Phương Ly ID: BTBTIU21220Le Phuong LyNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis in PlantasDocument4 pagesPhotosynthesis in PlantasAedeni MirandaNo ratings yet
- Differences Between Mitochondria and ChloroplastDocument10 pagesDifferences Between Mitochondria and ChloroplastAsma Adawiyah Idris100% (1)
- Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration (Module 5)Document51 pagesPhotosynthesis Cellular Respiration (Module 5)Trisha DeniseNo ratings yet
- CPTIIDocument23 pagesCPTIIkenfack sergeNo ratings yet
- Formation of Pharmacologically - Active Compounds in Plants - BiosynthesisDocument68 pagesFormation of Pharmacologically - Active Compounds in Plants - BiosynthesisMichi OnozaNo ratings yet
- Plant Growth and DevelopmentDocument9 pagesPlant Growth and Developmentgenettilahun222No ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument15 pagesPhotosynthesishurainsahar21No ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument7 pagesPhotosynthesisShushoku RaikagamiNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis #2Document1 pagePhotosynthesis #2Wally WestNo ratings yet
- What Is Photosynthesis in BiologyDocument3 pagesWhat Is Photosynthesis in BiologyAmna GhafoorNo ratings yet
- ZCR DXF MHAkc KG 6 C ZK GC 1Document39 pagesZCR DXF MHAkc KG 6 C ZK GC 1Venu GopalNo ratings yet
- Exchange Gases, Cellular RespirationDocument4 pagesExchange Gases, Cellular RespirationGISRemoteSensingNo ratings yet
- Chloroplast AssignmentDocument12 pagesChloroplast AssignmentUsama RahimNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis NotesDocument3 pagesPhotosynthesis Notesapi-265547348No ratings yet
- Q2 L3 Science 9Document31 pagesQ2 L3 Science 9Raph tsuNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 L-1.1 1.2 1.3 Science Grade 8Document24 pagesUnit 1 L-1.1 1.2 1.3 Science Grade 8andeepthiNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Hard Copy - Iza JayDocument11 pagesBiochemistry Hard Copy - Iza JayIza Jay Trapa DonatoNo ratings yet
- Concept Notes Concept Notes Concept NotesDocument2 pagesConcept Notes Concept Notes Concept NotesIsmaelAlongNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesPhotosynthesisAlxxd DomingoNo ratings yet
- ECOSYSTEMDocument10 pagesECOSYSTEMRyanKingjimDiezUyNo ratings yet
- Biology Project KBDocument35 pagesBiology Project KBHarshita ThakkarNo ratings yet
- Process of Plants/Crops Making Their Food and The Importance To Study The Mechanism For Plant PhysiologistsDocument17 pagesProcess of Plants/Crops Making Their Food and The Importance To Study The Mechanism For Plant PhysiologistsJos siNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in PlantsDocument2 pagesNutrition in PlantsAhmed OmarNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis?Document2 pagesPhotosynthesis?PrageethNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis #1Document1 pagePhotosynthesis #1Wally WestNo ratings yet
- The PhotosynthesisDocument5 pagesThe Photosynthesisamity nocedaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis (Carbon Assimilation) Explained: 6H2O + 6CO2 C6H12O6 + 6O2Document14 pagesPhotosynthesis (Carbon Assimilation) Explained: 6H2O + 6CO2 C6H12O6 + 6O2bhupatiNo ratings yet
- Chloroplast NotesDocument4 pagesChloroplast NotesAnanda100% (1)
- Photosynthesis NotesDocument3 pagesPhotosynthesis NotesormattNo ratings yet
- 8 PhotosynthesisDocument8 pages8 PhotosynthesisRAVINDRA PRASADNo ratings yet
- PHOTOSYNTHESISDocument4 pagesPHOTOSYNTHESISsuwethajNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Notes and LectureDocument18 pagesPhotosynthesis Notes and LectureDexter JamesNo ratings yet
- CAPE PhotosynthesisDocument20 pagesCAPE PhotosynthesisIsheba Warren100% (24)
- PhotosynthesisDocument13 pagesPhotosynthesisMina IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Plants Food Chemical Carbon Dioxide Algae Protists Bacteria Earth ChemoautotrophsDocument1 pagePlants Food Chemical Carbon Dioxide Algae Protists Bacteria Earth Chemoautotrophsdarenven 1996No ratings yet
- Bioenergetics Photosynthesis and Energy FlowDocument4 pagesBioenergetics Photosynthesis and Energy Flowvin ocangNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Notes - BiologyDocument8 pagesPhotosynthesis Notes - Biologythe lillyNo ratings yet
- Understanding Photosynthesis with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandUnderstanding Photosynthesis with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- Earh and Life Exam 2nd QuarterDocument3 pagesEarh and Life Exam 2nd QuarterAnjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Cell StructureDocument37 pagesChapter 1 Cell StructureNawafNo ratings yet
- D Biology PDFDocument212 pagesD Biology PDFSridhar RaparthiNo ratings yet
- 1 Cellular Processes TestDocument9 pages1 Cellular Processes TestLeo LouisNo ratings yet
- DSE Bio Notes CH 1 2 3Document30 pagesDSE Bio Notes CH 1 2 3chingNo ratings yet
- Cell - The Unit of LIfe - DPPsDocument23 pagesCell - The Unit of LIfe - DPPsMd Faijal100% (1)
- Chapter 10 PhotosynthesisDocument10 pagesChapter 10 PhotosynthesisMicky BanderaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Grading Earth and Life Science 2016-2017Document3 pages2nd Grading Earth and Life Science 2016-2017Mariel VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Isolation of Chloroplast and Its ActivityDocument6 pagesIsolation of Chloroplast and Its ActivityEsen Nur ÖzlükNo ratings yet
- Class 9 BiologyDocument32 pagesClass 9 BiologyAbinaya ParthasarathyNo ratings yet
- Mitochondria and ChloroplastsDocument19 pagesMitochondria and ChloroplastsNadane Aldover100% (1)
- Class 11th UNIT 3 Cell UnitDocument16 pagesClass 11th UNIT 3 Cell UnitSneha AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Cell - Structure and Functions PDFDocument3 pagesCell - Structure and Functions PDFmaya__scribd100% (1)
- Chlorophyta Dichotomous KeyDocument4 pagesChlorophyta Dichotomous KeyFlorence PalomarNo ratings yet
- Functions of Organelles in CellDocument23 pagesFunctions of Organelles in CellZahid ShehzarNo ratings yet
- ELS ReviewerDocument9 pagesELS ReviewerMia TorettoNo ratings yet
- Botany ReviewerDocument14 pagesBotany ReviewerTherese EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of CellDocument11 pagesStructure and Function of CellWoobin RealNo ratings yet
- Toxic Effect of Copper On Ten Rice CultivarsDocument7 pagesToxic Effect of Copper On Ten Rice CultivarsresearchplantscienceNo ratings yet
- 2020 VCE Biology Examination ReportDocument15 pages2020 VCE Biology Examination ReportBikram SainiNo ratings yet
- General Biology-Q2-Week 2Document15 pagesGeneral Biology-Q2-Week 2ALFREDO CALEDANo ratings yet
- Syllabus Mdcat (Nums) 20231688379524 1Document16 pagesSyllabus Mdcat (Nums) 20231688379524 1Ubaid Ul haqNo ratings yet
- Photosynthetic Processes: Chlorophyll and PigmentsDocument5 pagesPhotosynthetic Processes: Chlorophyll and PigmentsLyka LigsonNo ratings yet