Professional Documents
Culture Documents
(01-29) Hydraulics 6
(01-29) Hydraulics 6
Uploaded by
Ram CaniculaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
(01-29) Hydraulics 6
(01-29) Hydraulics 6
Uploaded by
Ram CaniculaCopyright:
Available Formats
Review Innovations CE Review for April 2024 - Hydraulics 6
HOOP AND CIRCUMFERENTIAL STRESSES Use (+) sign for upward motion and (-) sign for downward
(HOOP TENSION) motion.
1. Walls Carrying Stress in Pipes and Tanks
VERTICAL MOTION
𝑝𝐷
𝑡=
2𝑆! (𝑒𝑓𝑓)
t = thickness of the wall (mm)
D = inside diameter (mm)
p = unit pressure of fluid (MPa)
St = actual or allowable tensile stress in the wall (MPa)
eff = efficiency of the connections
Note: If efficiency of connections is not mentioned in the
problem, assume 100% efficiency
2. Hoops Carrying Stress in Pipes and Cylindrical
Tanks
2𝑇 𝑎
𝑆= 𝑝 = 𝛾ℎ 51 ± 7
𝑝𝐷 𝑔
S = center to center spacing of the hoops (mm) Use (+) sign for upward motion and (-) sign for downward
T = tensile force in one hoop (N) motion. Also note that a is positive for acceleration and
negative for deceleration.
MOVING VESSEL
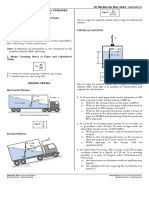
1. A 10 mm thick steel pipe with inside diameter of 600
mm conveys water under a head of 480 m.
Horizontal Motion
a. What is the tensile stress in the pipe in MPa?
b. What is the stress in the pipe wall if the head is
increased to 500 meters of water?
c. What is the required thickness under a head of
500 meters if the allowable tensile stress of the
pipe is 118 MPa and assuming that the joints are
80% efficient?
2. A 1.2-m Ø wood-stave pipe carries 76 m of water. It
is provided with 25-mm Ø steel hoops with an
allowable tensile stress of 104.3 MPa.
𝑎 a. What pressure of water will be resisted by the
tan 𝜃 = hoops?
𝑔 b. What is the actual tensile force in the hoops if
they are spaced at 75 mm center to center?
Inclined Motion
c. What spacing of the hoops will be
implemented?
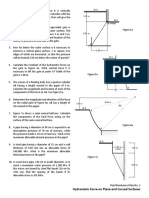
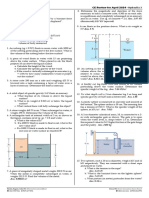
3. An open tank 3 m long, 1.80 m wide, and 1.50 m high
contains water to a depth of 1.20 m. It is moving
parallel to a pair of longest sides. Determine the
following:
a. the maximum acceleration without spilling any
liquid.
b. the unbalanced force causing the acceleration in
part (1)?
c. the volume of water spilled if accelerated at 3
m/s2?
d. the volume of water retained when accelerated
𝑎" at 5.4 m/s2?
tan 𝜃 =
𝑔 ± 𝑎#
Manila FB: @ReviewInnovationsOfficial Davao FB: Review Innovations Davao Branch
( (02) 8735-9161 0919-227-9194 ( (082) 221-1121 0930-256-0998
Review Innovations CE Review for April 2024 - Hydraulics 6
4. A closed tank 2.4 m long, 1.2 m wide and 1.4 m high
contains water 1.1 m deep. A small hole is located
near the center of the cover. It moves in the direction
parallel to the 2.4-m dimension.
a. Determine the acceleration needed so that the
water surface will just touch the bottom of the
front wall.
b. Determine the pressure at the bottom of the rear
wall.
c. Determine the force of water acting on the top
of the tank.
d. Determine the total force acting on the bottom
of the tank.
5. An open circular cylinder with 2 m of water is acted
by an unbalanced upward force of 20 kN. The
volume of water inside the cylinder is 6.28 m3.
a. Compute the acceleration of the tank.
b. Compute the pressure at the bottom of the tank.
c. Calculate the force on the bottom of the tank.
6. A wood-stave pipe carries water under a head of 115
m. It is bound by 20-mm Ø steel hoops having an
allowable tensile stress of 98 MPa. Calculate the
required spacing of the hoops if the pipe’s inside
diameter is 90 cm.
7. A steel pipe having a diameter of 0.90 m carries water
under a head of 230 m of water.
a. Compute the internal pressure on the pipe.
b. Compute the required wall thickness if the
allowable stress for steel pipe is 110 MPa.
c. Compute the tangential force on the steel pipe.
8. A closed cylindrical tank is 2.4 m in diameter and 7.5
m long is completely filled with gasoline (sg = 0.90).
The tank, with its long axis horizontal, is pulled by a
truck along a horizontal surface.
a. Determine the pressure difference between the
ends (along the long axis of the tank) when the
truck undergoes an acceleration of 1.5 m/s2.
b. Determine the force on the front wall.
c. Determine the force on the rear wall.
9. An open vessel of water accelerates up a 25° plane at
2.5 m/s2.
a. What is the horizontal component of the
acceleration?
b. What is the vertical component of the
acceleration?
c. What is the angle that the water surface makes
with the horizontal?
6) 61 mm
7) 2256.3 kPa, 9.2 mm, 1015.3 kN
8) 10.125 kPa, 47.9 kN, 93.7 kN
9) 2.27 m/s2, 1.06 m/s2, 11.8°
Manila FB: @ReviewInnovationsOfficial Davao FB: Review Innovations Davao Branch
( (02) 8735-9161 0919-227-9194 ( (082) 221-1121 0930-256-0998
You might also like
- Mathematics: Wednesday 17 January 2024Document28 pagesMathematics: Wednesday 17 January 2024t.a.qafarovNo ratings yet
- AssigmentsDocument31 pagesAssigmentsKarla Isabel Salgado Sánchez100% (1)
- Assessment Exam 03 1Document7 pagesAssessment Exam 03 1Andrea Magtuto100% (1)
- Strength of Materials: Axial StressesDocument3 pagesStrength of Materials: Axial Stressesmonique dianeNo ratings yet
- Assessment Exam 03: Fluid Mechanics and HydraulicsDocument6 pagesAssessment Exam 03: Fluid Mechanics and HydraulicsAndrea MagtutoNo ratings yet
- Lecture HydraulicsDocument27 pagesLecture HydraulicsHarvey Pagaran0% (2)
- Hyd 6Document2 pagesHyd 6Jocelyn Cabarles100% (1)
- CE Board Nov 2021 - Hydraulics - Set 6Document2 pagesCE Board Nov 2021 - Hydraulics - Set 6Lemuel TeopeNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics Review ProblemsDocument9 pagesHydraulics Review ProblemsrojethtrinidadNo ratings yet
- MIDTERM Lesson 3 Pipe Connections and ReservoirDocument18 pagesMIDTERM Lesson 3 Pipe Connections and Reservoir1900651No ratings yet
- Refresher Module 54 - (GH-7) - Geotechnical and HydraulicsDocument2 pagesRefresher Module 54 - (GH-7) - Geotechnical and HydraulicsJoenem AbenojaNo ratings yet
- Code: 13A01303 B.Tech II Year I Semester (R13) Regular Examinations December 2014 Time: 3 HoursDocument2 pagesCode: 13A01303 B.Tech II Year I Semester (R13) Regular Examinations December 2014 Time: 3 HoursBrahmaiah Vendipalli 184No ratings yet
- Hydraulics Set 2Document3 pagesHydraulics Set 2cielo_cetd3670100% (1)
- CECA 2 Problem Set No. 03Document11 pagesCECA 2 Problem Set No. 03carldomingoNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1Document10 pagesSheet 1lawanNo ratings yet
- FM1 (3rd) May2020Document3 pagesFM1 (3rd) May2020Lakshay KoundalNo ratings yet
- FM Question Bank PDFDocument6 pagesFM Question Bank PDFprabhumaluNo ratings yet
- Model Question (Hydraulic Structures)Document5 pagesModel Question (Hydraulic Structures)Debanjan Banerjee71% (7)
- Sheet 1Document10 pagesSheet 1lawanNo ratings yet
- Fresh Water: Pine LeadDocument3 pagesFresh Water: Pine LeadRobby BajamondeNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1Document10 pagesSheet 1lawanNo ratings yet
- CE-Board-Exam-1997 Hydrau Geo OnlyDocument10 pagesCE-Board-Exam-1997 Hydrau Geo OnlyNekat EvalsNo ratings yet
- Mega Review Assessment Exam (Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulics)Document6 pagesMega Review Assessment Exam (Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulics)maklincarl.diaz.dNo ratings yet
- F.M Qp.Document3 pagesF.M Qp.ankurthakurxNo ratings yet
- AUXILIARY LESSON - Water HammerDocument6 pagesAUXILIARY LESSON - Water HammerFrancis HernandezNo ratings yet
- Hyd - 4Document2 pagesHyd - 4SamNo ratings yet
- Hydau GeoDocument9 pagesHydau GeoAngelica TecsonNo ratings yet
- HydraulicsDocument3 pagesHydraulicsStudent555No ratings yet
- PHY 108 Collaborative Problem Solving Chapter 11 Solution and HintsDocument2 pagesPHY 108 Collaborative Problem Solving Chapter 11 Solution and HintsNey CampoNo ratings yet
- CE EVALUATION EXAM No. 5 - Buoyancy, Equilibrium, Fluid Flows (Answer Key)Document5 pagesCE EVALUATION EXAM No. 5 - Buoyancy, Equilibrium, Fluid Flows (Answer Key)Angelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- Hyd 11Document1 pageHyd 11eufemiorodolfoNo ratings yet
- HydraulicsDocument3 pagesHydraulicsPraveen ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Hyd 13Document2 pagesHyd 13eufemiorodolfoNo ratings yet
- Advance Fluid Mechanics TurorialDocument2 pagesAdvance Fluid Mechanics Turorialpinakramanuj11150% (2)
- Fluid Mechanics Plate No. 2Document1 pageFluid Mechanics Plate No. 2Andrei AlidoNo ratings yet
- Hyd Ref 1Document2 pagesHyd Ref 1rando12345No ratings yet
- Ce 343L - Fluid Mechanics Final ExamDocument3 pagesCe 343L - Fluid Mechanics Final ExamMichelle DaarolNo ratings yet
- Preboard 2 GeoDocument4 pagesPreboard 2 GeoLienardNo ratings yet
- Unit - V Analysis of Pipe Flow and Laminar and Turbulent Flow in PipesDocument6 pagesUnit - V Analysis of Pipe Flow and Laminar and Turbulent Flow in PipesajaythermalNo ratings yet
- Hydrau 1Document3 pagesHydrau 1Mayya BonaNo ratings yet
- Compilation of Solved ProblemsDocument7 pagesCompilation of Solved ProblemsyslovillanuevaNo ratings yet
- B.Tech II Year I Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations November/December 2016 Time: 3 HoursDocument2 pagesB.Tech II Year I Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations November/December 2016 Time: 3 HoursBrahmaiah Vendipalli 184No ratings yet
- Compiled Question Ce 3227Document9 pagesCompiled Question Ce 3227Hamisi MzariNo ratings yet
- Fluids PDFDocument8 pagesFluids PDFSamuel SiyumNo ratings yet
- Lab 16 - Hydrostatic Forces and WorkDocument9 pagesLab 16 - Hydrostatic Forces and WorkMike JawNo ratings yet
- CENG 197 Problem Set 2Document5 pagesCENG 197 Problem Set 2edmar limNo ratings yet
- Hyd 13Document2 pagesHyd 13Luna RonquilloNo ratings yet
- AsdfasdfasdfabDocument4 pagesAsdfasdfasdfabFleight VandollinNo ratings yet
- HGE Refresher QuestionsDocument8 pagesHGE Refresher QuestionsCj SuarezNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document2 pagesAssignment 2mustefa kelil100% (1)
- 2022MAY HPGE UnlockedDocument2 pages2022MAY HPGE UnlockedKristelle V. TorrealbaNo ratings yet
- RM 38 - Hydraulics 4 Weirs-Reservoirs Part 02Document2 pagesRM 38 - Hydraulics 4 Weirs-Reservoirs Part 02theengineerNo ratings yet
- Wren201 Tutorial Questions-2Document12 pagesWren201 Tutorial Questions-2yemivibezNo ratings yet
- Problem Exercise No.5Document4 pagesProblem Exercise No.5Ey KaguriNo ratings yet
- 100 ProblemsFINALDocument6 pages100 ProblemsFINAL852sx4h7cbNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering November 2020 Review Innovations Strength of Materials 2Document2 pagesCivil Engineering November 2020 Review Innovations Strength of Materials 2Kervin Manila100% (1)
- Homework 1 PDFDocument4 pagesHomework 1 PDFعلي علي صالح انقعNo ratings yet
- Ce8302 Iq UqDocument4 pagesCe8302 Iq UqAkxzNo ratings yet
- The Mechanics of Water-Wheels - A Guide to the Physics at Work in Water-Wheels with a Horizontal AxisFrom EverandThe Mechanics of Water-Wheels - A Guide to the Physics at Work in Water-Wheels with a Horizontal AxisNo ratings yet
- Irrigation Works: The Principles on Which Their Design and Working Should Be Based, with Special Details Relating to Indian Canals and Some Proposed ImprovementsFrom EverandIrrigation Works: The Principles on Which Their Design and Working Should Be Based, with Special Details Relating to Indian Canals and Some Proposed ImprovementsNo ratings yet
- Part Ni JanmarDocument31 pagesPart Ni JanmarRam CaniculaNo ratings yet
- Geo Terms (Questions Only)Document22 pagesGeo Terms (Questions Only)Ram CaniculaNo ratings yet
- Assumption LogDocument1 pageAssumption LogRam CaniculaNo ratings yet
- Geo Terms (Answer Key)Document22 pagesGeo Terms (Answer Key)Ram CaniculaNo ratings yet
- (01-22) Geotechnical Engineering - Set 3Document2 pages(01-22) Geotechnical Engineering - Set 3Ram CaniculaNo ratings yet
- (01-25) Hydraulics 3Document2 pages(01-25) Hydraulics 3Ram CaniculaNo ratings yet
- April 2024 Refresher - MSTE 6 - BWDocument2 pagesApril 2024 Refresher - MSTE 6 - BWRam CaniculaNo ratings yet
- ASTM E 139-06 Standard Test Methods For Conducting Creep, Creep-Rupture, and Stress-Rupture Tests of Metallic Materials1Document14 pagesASTM E 139-06 Standard Test Methods For Conducting Creep, Creep-Rupture, and Stress-Rupture Tests of Metallic Materials1Angel RamirezNo ratings yet
- Newtons Laws QPDocument14 pagesNewtons Laws QPNIAZ HUSSAINNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics in SI Units, 12e: Kinematics of A ParticleDocument30 pagesEngineering Mechanics: Dynamics in SI Units, 12e: Kinematics of A ParticleBELAL ALSUBARINo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Moment Distribution: Dr. C. CapraniDocument177 pagesChapter 6 - Moment Distribution: Dr. C. Capranihitendra_gk100% (2)
- Chapter 16 Problems-Applied Thermodynamics and Engineering 5th EditionDocument5 pagesChapter 16 Problems-Applied Thermodynamics and Engineering 5th EditionLudwig van RooyenNo ratings yet
- DeThi Final PHY212 - Jan - 2016Document3 pagesDeThi Final PHY212 - Jan - 2016Kanekii HaiseNo ratings yet
- Assignment Concept of StressDocument3 pagesAssignment Concept of StressYasser ZubaidiNo ratings yet
- Stability of Corrugated Expansion BellowsDocument21 pagesStability of Corrugated Expansion Bellowsnutan zambreNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2Document2 pagesExercise 2Nikhil RanjanNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Metal FatigueDocument32 pagesFundamentals of Metal Fatiguepkpnitian_152297088No ratings yet
- PSC-Superstructure SheetDocument118 pagesPSC-Superstructure SheetVibhasBambrooNo ratings yet
- Egg Drop LabDocument5 pagesEgg Drop LabRobinhood Jevons MartirezNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics: Volumetric Properties of Pure FluidDocument20 pagesChemical Engineering Thermodynamics: Volumetric Properties of Pure FluidThurgah VshinyNo ratings yet
- Lecture7,8 PDFDocument31 pagesLecture7,8 PDFPrabhath Jyøthülâ PJNo ratings yet
- Soil-Foundation-Structure Interaction Analysis: Tahmeed Al-HussainiDocument15 pagesSoil-Foundation-Structure Interaction Analysis: Tahmeed Al-HussainiMila Kusuma WardaniNo ratings yet
- Convection G BiswasDocument331 pagesConvection G Biswaspriyanka0% (1)
- F5C1 (Tutorial1 6)Document3 pagesF5C1 (Tutorial1 6)ChewLee TanNo ratings yet
- Charles Poor, Relativity and The Law of GravitationDocument3 pagesCharles Poor, Relativity and The Law of Gravitationbluefenix11No ratings yet
- Nonlinearity in A Dynamo: Geophysical & Astrophysical Fluid Dynamics May 2010Document14 pagesNonlinearity in A Dynamo: Geophysical & Astrophysical Fluid Dynamics May 2010Milan StepanovNo ratings yet
- Built-Up Compression MembersDocument7 pagesBuilt-Up Compression MembersDaniela DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Physics 406: Winter, 2016Document3 pagesPhysics 406: Winter, 20160pt618No ratings yet
- 2.2 Linear Motion GraphsDocument6 pages2.2 Linear Motion GraphsWan HasliraNo ratings yet
- Symmetry Boundary Condition FEADocument4 pagesSymmetry Boundary Condition FEAShubham SatheNo ratings yet
- MM658 HandoutDocument1 pageMM658 Handoutmanojpatel2410No ratings yet
- Design of A Low Cost Loop Heat PipeDocument12 pagesDesign of A Low Cost Loop Heat PipeSuraj Kuber AbdanNo ratings yet
- Pressure Bulb or Stress Isobar ConceptDocument3 pagesPressure Bulb or Stress Isobar ConceptRajesh KhadkaNo ratings yet
- HardDocument11 pagesHardMengzhe XuNo ratings yet
- Proposal and Analysis of A Novel Single-Drive Bearingless MotorDocument10 pagesProposal and Analysis of A Novel Single-Drive Bearingless MotorMohsenHonarNo ratings yet
- Atomic and Molecular Physics JEST 2012-2017 PDFDocument5 pagesAtomic and Molecular Physics JEST 2012-2017 PDFSADDAM ANSARINo ratings yet